Enhanced Bioactivity of Micropatterned Hydroxyapatite Embedded Poly(L-lactic) Acid for a Load-Bearing Implant
Abstract
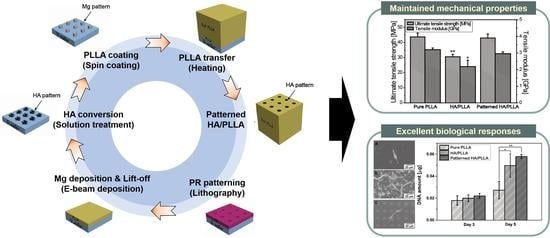
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Pure PLLA and PLLA/HA Composite
2.2. Preparation of Patterned HA/PLLA
2.3. Microstructure and Surface Chemical Behaviors
2.4. Mechanical Behaviors
2.5. In Vitro Biological Behaviors
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Surface Chemical Properties
3.2. Wettability and Mechanical Properties
3.3. In Vitro Cell Responses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, S.; Heath, D.; Coombes, A.; Bock, N.; Textor, M.; Downes, S. Biodegradable polymer/hydroxyapatite composites: Surface analysis and initial attachment of human osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chow, L.C.; Frukhtbeyn, S.A.; Ting, A.H.; Dong, Q.; Yang, M.; Mitchell, J.W. Improve the Strength of PLA/HA Composite Through the Use of Surface Initiated Polymerization and Phosphonic Acid Coupling Agent. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2011, 116, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, A.G.; Thorsen, A.J.; Czerwonka, L.A.; Bao, Y.; Langer, R.; Winslow, D.N.; Vacanti, J.P. Preparation and characterization of poly (l-lactic acid) foams. Polymer 1994, 35, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Cheon, K.-H.; Park, C.; Jang, T.-S.; Kim, H.-E.; Jung, H.-D.J.A.M. Fabrication of poly (lactic acid)/ti composite scaffolds with enhanced mechanical properties and biocompatibility via fused filament fabrication (fff)–based 3d printing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, J.; Alexander, H. Biological response of intramedullary bone to poly-L-lactic acid. J. Appl. Biomater. 1993, 4, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.S.; Daniels, A.U.; Andriano, K.P.; Heller, J. Six bioabsorbable polymers:In vitro acute toxicity of accumulated degradation products. J. Appl. Biomater. 1994, 5, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Seong, Y.-J.; Kang, I.-G.; Song, E.-H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.-D.; Kim, H.-E.; Jang, T.-S. Enhanced Osseointegration Ability of Poly(lactic acid) via Tantalum Sputtering-Based Plasma Immersion Ion Implantation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10492–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, M.; Turner, M.; Duguet, E.; Fontanille, M. PMMA-based composite materials with reactive ceramic fillers. Part 1—Chemical modification and characterisation of ceramic particles. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; De Groot, K. Development of biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(hexamethylene adipamide) composites. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4787–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandrowski, K.-U.; Gresser, J.D.; Wise, D.L.; White, R.L.; Trantolo, D.J. Osteoconductivity of an injectable and bioresorbable poly(propylene glycol-co-fumaric acid) bone cement. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, W. Composites for bone replacement. J. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 10, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.E. Effect of biphasic calcium phosphates on drug release and bioloigical and mechanical properties of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) composite membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 70, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Calcium orthophosphates. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 1061–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Chang, J. Ph-compensation effect of bioactive inorganic fillers on the degradation of plga. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J. Toughening and reinforcing in rigid inorganic particulate filled poly(propylene): A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, H.; Ma, C.; Kimura, Y. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Poly(L-lactide) Incorporating Various Inorganic Fillers with Particle and Whisker Shapes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mak, A.F.T.; Wang, M.; Li, J.S.; Wong, M.-S. In vitro behavior of osteoblast-like cells on PLLA films with a biomimetic apatite or apatite/collagen composite coating. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 19, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-H.; Hutchinson, J.W. Influence of substrate compliance on buckling delamination of thin films. Int. J. Fract. 2002, 113, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Jo, J.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, H.-E.; Estrin, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-W.; Koh, Y.-H. Hydroxyapatite-coated magnesium implants with improvedin vitroandin vivobiocorrosion, biocompatibility, and bone response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 102, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-D.; Park, H.-S.; Kang, M.-H.; Li, Y.; Kim, H.-E.; Koh, Y.-H.; Estrin, Y. Reinforcement of polyetheretherketone polymer with titanium for improved mechanical properties and in vitro biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 104, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.-D.; Jang, T.-S.; Lee, J.E.; Park, S.J.; Son, Y.; Park, S.-H. Enhanced bioactivity of titanium-coated polyetheretherketone implants created by a high-temperature 3D printing process. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 045014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrilmis, N. Effect of layer thickness on surface properties of 3D printed materials produced from wood flour/PLA filament. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Veiga, D.D.; Custódio, C.A.; Mano, J.F. Bioinspired degradable substrates with extreme wettability properties. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Liu, F.; Gao, A.; Lin, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Investigation of the heat resistance, wettability and hemocompatibility of a polylactide membrane via surface crosslinking induced crystallization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20492–20499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindoyo, J.O.; Beg, M.D.; Ghazali, S.; Heim, H.P.; Feldmann, M. Effects of surface modification on dispersion, mechanical, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of injection molded PLA-hydroxyapatite composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 103, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, X.L.; Zheng, Y. Effect of surface modified hydroxyapatite on the tensile property improvement of HA/PLA composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-H.; Lee, H.; Jang, T.-S.; Seong, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-E.; Koh, Y.-H.; Song, J.; Jung, H.-D. Biomimetic porous Mg with tunable mechanical properties and biodegradation rates for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.-Y.; Won, J.-E.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Improvement of surface bioactivity of poly(lactic acid) biopolymer by sandblasting with hydroxyapatite bioceramic. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2951–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Yang, X.; Mei, F.; Hu, X.; Chen, G.; Deng, X.; Ryu, S. Poly-L-lactic acid/hydroxyapatite hybrid membrane for bone tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 82, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pure PLLA | HA/PLLA | Patterned HA/PLLA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength [MPa] | 43.7 ± 2.5 | 30.5 ± 1.6 | 42.9 ± 2.7 |
| Elastic modulus [GPa] | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-M.; Kang, I.-G.; Cheon, K.-H.; Jang, T.-S.; Kim, H.-E.; Jung, H.-D.; Kang, M.-H. Enhanced Bioactivity of Micropatterned Hydroxyapatite Embedded Poly(L-lactic) Acid for a Load-Bearing Implant. Polymers 2020, 12, 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102390
Kim S-M, Kang I-G, Cheon K-H, Jang T-S, Kim H-E, Jung H-D, Kang M-H. Enhanced Bioactivity of Micropatterned Hydroxyapatite Embedded Poly(L-lactic) Acid for a Load-Bearing Implant. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102390
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sae-Mi, In-Gu Kang, Kwang-Hee Cheon, Tae-Sik Jang, Hyoun-Ee Kim, Hyun-Do Jung, and Min-Ho Kang. 2020. "Enhanced Bioactivity of Micropatterned Hydroxyapatite Embedded Poly(L-lactic) Acid for a Load-Bearing Implant" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102390
APA StyleKim, S.-M., Kang, I.-G., Cheon, K.-H., Jang, T.-S., Kim, H.-E., Jung, H.-D., & Kang, M.-H. (2020). Enhanced Bioactivity of Micropatterned Hydroxyapatite Embedded Poly(L-lactic) Acid for a Load-Bearing Implant. Polymers, 12(10), 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102390