Electrospun Multiple-Chamber Nanostructure and Its Potential Self-Healing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
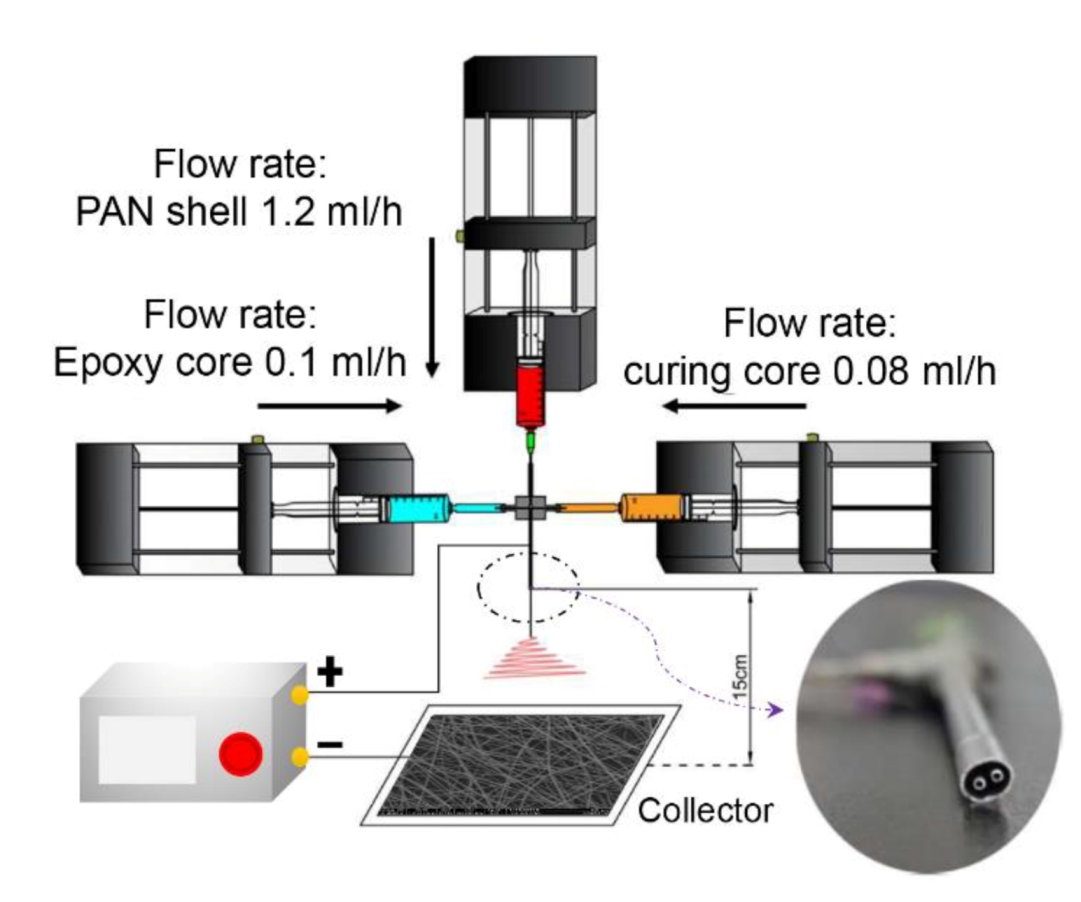
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Morphology
2.3.2. Chemical and Thermodynamic Analyses of the Nanofibers
2.3.3. Thermal Analysis
2.3.4. Electrochemical Corrosion
3. Results and Discussion
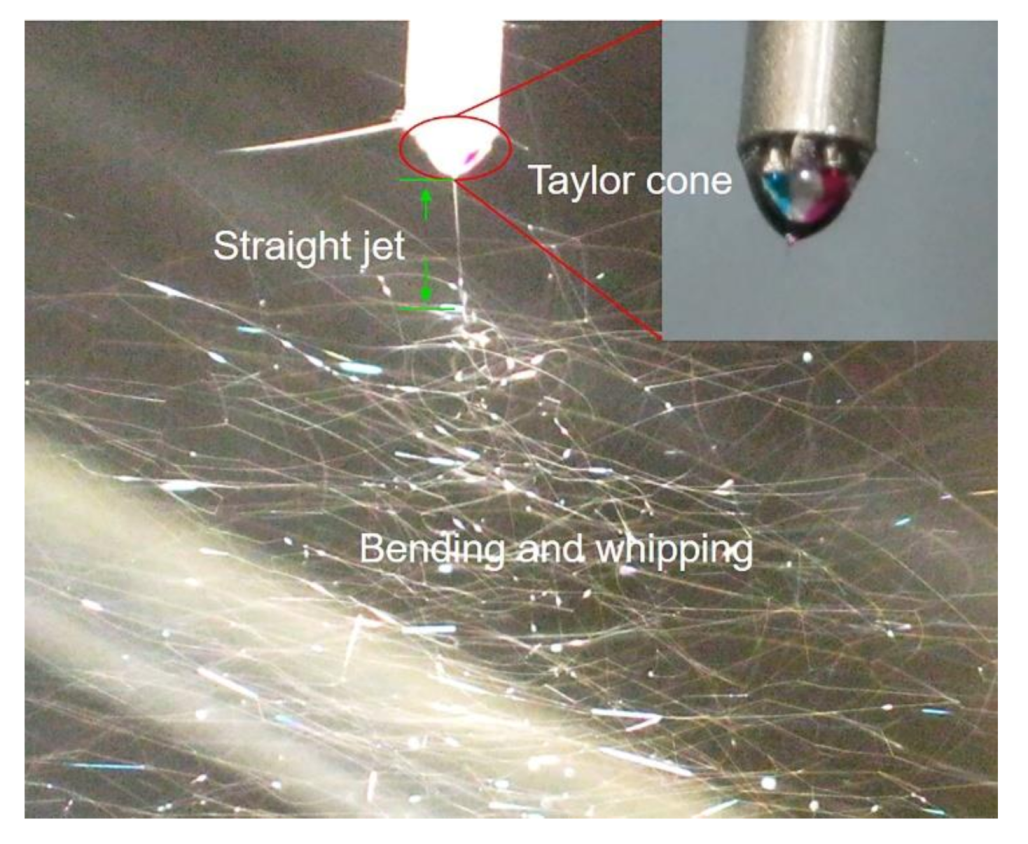
3.1. Electrospinning
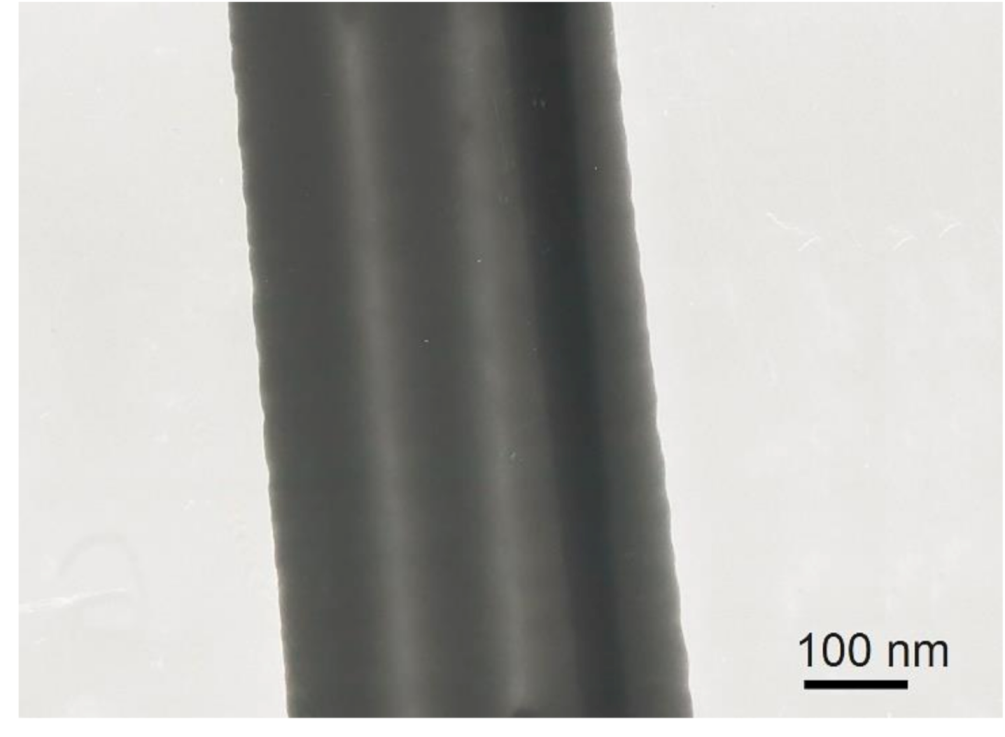
3.2. Morphological Characterization
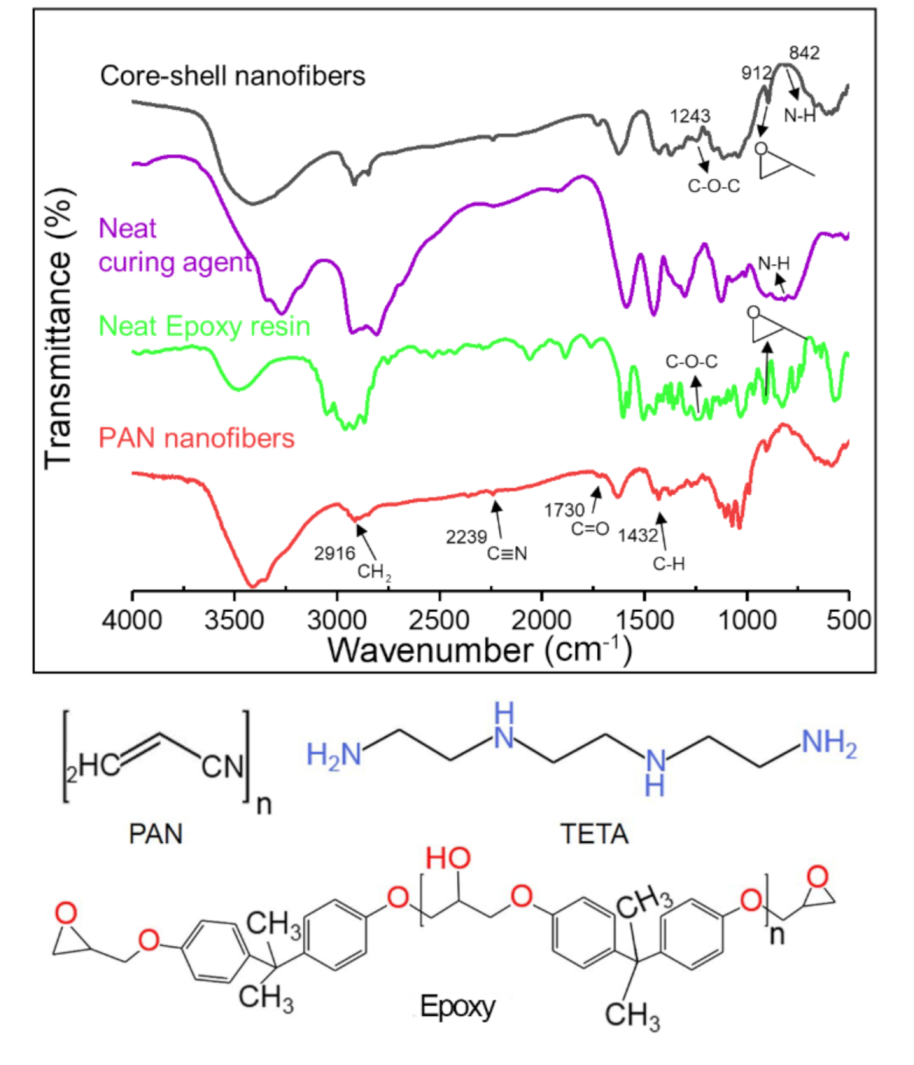
3.3. Chemical Structure of Core-Shell Nanofibers
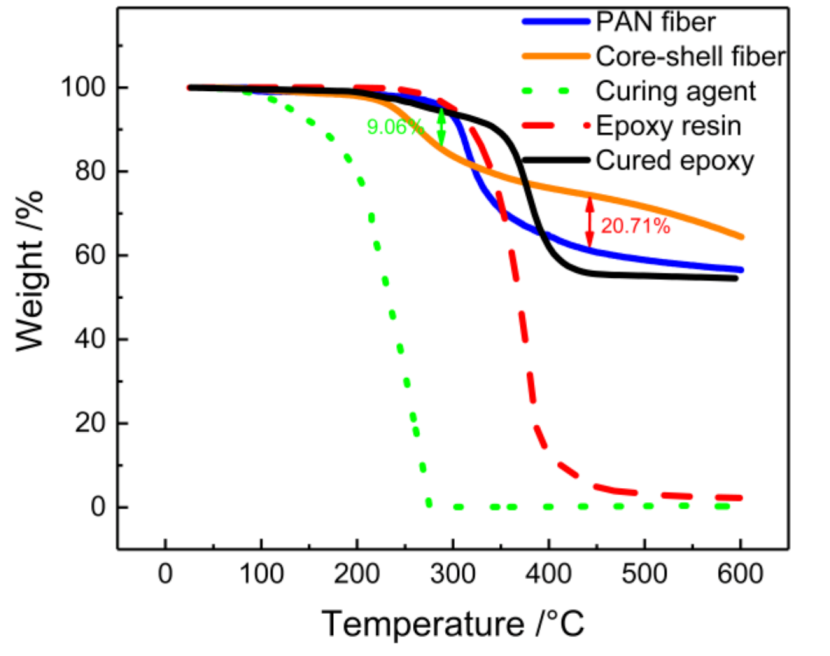
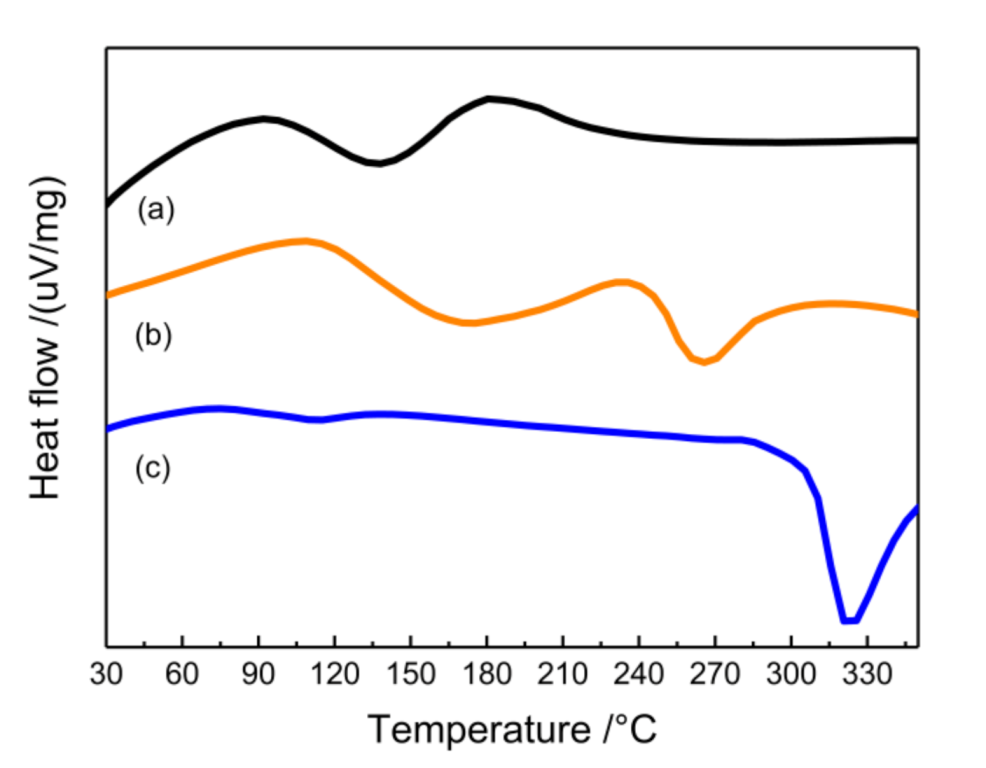
3.4. Thermal Analysis
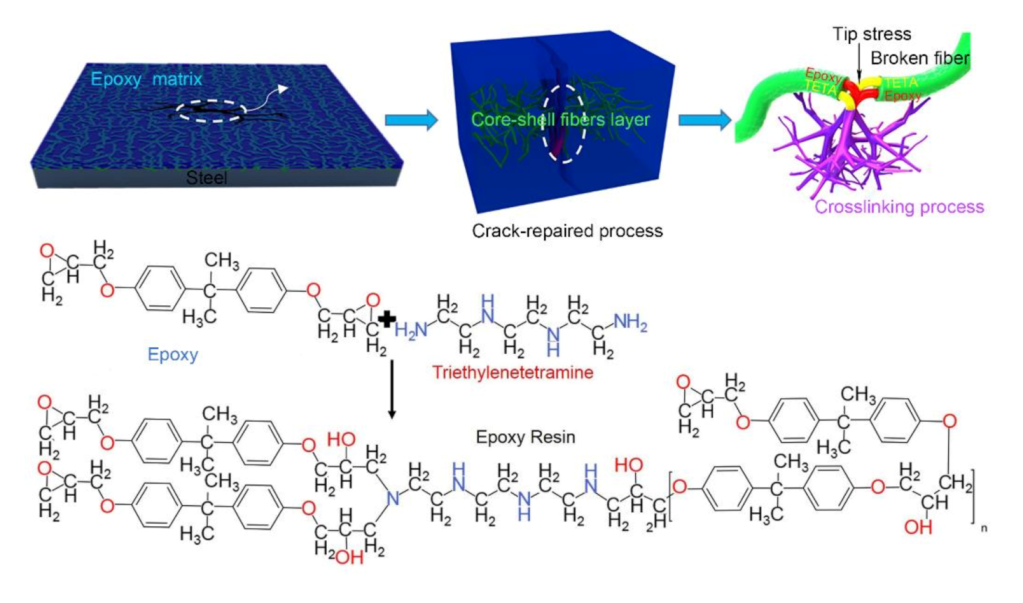
3.5. Self-Healing Mechanism
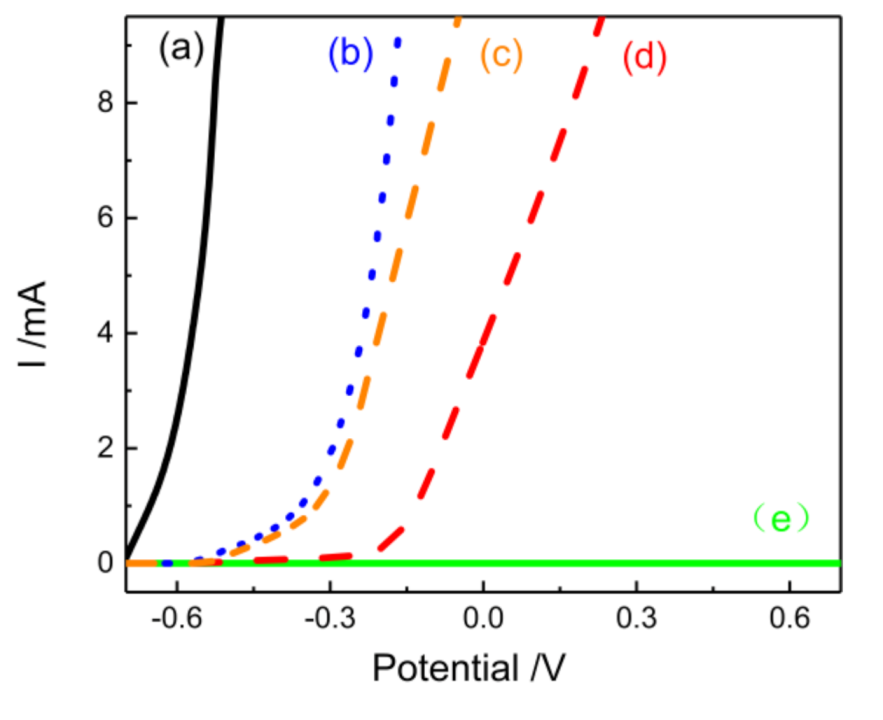
3.6. Corrosion Resistance of Self-Healing Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidi, F.; Jouyandeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Habibzadeh, S.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS)/Epoxy Coatings: A Review. Surf. Innov. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hao, C.; Verdi, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Glycerol Induced Catalyst-Free Curing of Epoxy and Vitrimer Preparation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, e1800889. [Google Scholar]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Ali, J.A.; Aghazadeh, M.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R.; Ranjbar, Z.; Ganjali, M.R. Curing epoxy with electrochemically synthesized ZnxFe3-xO4 magnetic nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekas, D.G.; Tsirka, K.; Baltzis, D.; Paipetis, A.S. Self-healing materials: A review of advances in materials, evaluation, characterization and monitoring techniques. Compos. Pt. B Eng. 2016, 87, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Xu, X.; Yue, Y.; Mei, C.; Huang, C.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Q.; Han, J. Nanocellulose-mediated electroconductive self-healing hydrogels with high strength, plasticity, viscoelasticity, stretchability, and biocompatibility toward multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27987–28002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T. Self-healing anion exchange membrane for ph 7 redox flow batteries. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 201, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, S.K.; Mani, M.P. Electrospun polyurethane nanofibrous composite impregnated with metallic copper for wound-healing application. 3 Biotech. 2018, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R.; Geubelle, P.H.; Moore, J.S.; Kessler, M.R.; Sriram, S.R.; Brown, E.N.; Viswanathan, S. Autonomic healing of polymer composites. Nature 2001, 409, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, K.S.; Sottos, N.R.; Lewis, J.A.; Moore, J.S.; White, S.R. Self-healing materials with microvascular networks. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, K.S.; Hansen, C.J.; Lewis, J.A.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R. Delivery of two-part self-healing chemistry via microvascular networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Lee, M.W.; Yarin, A.L.; Yoon, S.S. A review on corrosion-protective extrinsic self-healing: Comparison of microcapsule-based systems and those based on core-shell vascular networks. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hia, I.L.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Chan, E.S.; Chai, S.P. Electrosprayed multi-core alginate microcapsules as novel self-healing containers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaei, F.; Khorasani, S.N.; Rahnama, H.; Neisiany, R.E.; Koochaki, M.S. Single microcapsules containing epoxy healing agent used for development in the fabrication of cost efficient self-healing epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 114, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Mo, Q.; Li, W.; Gu, F. Preparation and properties of self-healing and self-lubricating epoxy coatings with polyurethane microcapsules containing bifunctional linseed oil. Polymers 2019, 11, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minnebo, P.; Thierens, G.; De Valck, G.; Van Tittelboom, K.; De Belie, N.; Van Hemelrijck, D.; Tsangouri, E. A novel design of autonomously healed concrete: Towards a vascular healing network. Materials 2017, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, L.M.; Singh, S.P.; Henderson, P.W.; Porri, T.J.; Craighead, H.G.; Spector, J.A. Fabrication of an artificial 3-dimensional vascular network using sacrificial sugar structures. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvellier, A.; Torre-Muruzabal, A.; Van Assche, G.; De Clerck, K.; Rahier, H. Selection of healing agents for a vascular self-healing application. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neisiany, R.E.; Khorasani, S.N.; Kong Yoong Lee, J.K.Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Encapsulation of epoxy and amine curing agent in PAN nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning for self-healing purposes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70056–70063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hia, I.L.; Vahedi, V.; Pasbakhsh, P. Self-healing polymer composites: Prospects, challenges, and applications. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 225–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Braun, P.V. Coaxial electrospinning of self-healing coatings. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W. Prospects and future directions of self-healing fiber-reinforced composite materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.Q.; Leslie, L.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Bhargava, R.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R. Characterization of core-shell microstructure and self-healing performance of electrospun fiber coatings. Polymer 2016, 107, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.W.; Yoon, S.S.; Yarin, A.L. Solution-blown core-shell self-healing nano- and microfibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4955–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Sett, S.; Yoon, S.S.; Yarin, A.L. Self-healing of nanofiber-based composites in the course of stretching. Polymer 2016, 103, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Liou, M.; Song, K.Y.; Jo, H.S.; Lee, M.W.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yarin, A.L.; Yoon, S.S. Highly flexible transparent self-healing composite based on electrospun core-shell nanofibers produced by coaxial electrospinning for anti-corrosion and electrical insulation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17778–17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanjani, J.S.M.; Okan, B.S.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Yildiz, M. Repeated self-healing of nano and micro scale cracks in epoxy based composites by tri-axial electrospun fibers including different healing agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 73133–73145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. A nanofiber-based drug depot with high drug loading for sustained release. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun janus nanofibers loaded with a drug and inorganic nanoparticles as an effective antibacterial wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.-G.; Wan, F.; Bligh, S.W.A. Comparative study of electrospun crystal-based and composite-based drug nano depots. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Rath, G.; Singh, R.; Goyal, A.K. Nanofibers: An effective tool for controlled and sustained drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Dou, C.; Chang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J. Core-shell Eudragit S100 nanofibers prepared via triaxial electrospinning to provide a colon-targeted extended drug release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.-M.; Annie Bligh, S.W. Multifluid electrospinning for the generation of complex nanostructures. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.D.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.-L.; Huang, J.X.; Zuo, X.-H.; Lu, X.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Yu, D.G. Electrosprayed ultra-thin coating of ethyl cellulose on drug nanoparticles for improved sustained release. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.Z. Electrospun Janus zein–PVP nanofibers provide a two-stage controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.-G.; Shen, H. Sheath-separate-core nanocomposites fabricated using a trifluid electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2020, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, S.; Bai, Y.; Du, Y.; Yu, D.G. Discrete drug distributions within electrospun tri-layer core-shell nanofibers for accurate dual-stage release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, B.; Zarrintaj, P.; Samadi, A.; Zarrintaj, R.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M.; Park, O.O.; Kim, Y.C. Tissue engineering with electrospun electro-responsive chitosan-aniline oligomer/polyvinyl alcohol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Cao, L.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. Ultrafine hollow TiO2 nanofibers from core-shell composite fibers and their photocatalytic properties. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Wood-inspired anisotropic cellulose nanofibril composite sponges for multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Badiei, A.; Mouradzadegun, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Rezania, H.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Shamiry, F.; Munir, M.T.; Habibzadeh, S.; Saeb, M.R. Nanostructured polyethersulfone membranes for dye and protein separation: Exploring antifouling role of holmium (III) molybdate nanosheets. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Wolcott, M.P.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Propionylation-modified chitin with improved solubility in green ethanol/water binary solvents for sustainable film and coating applications. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 250, 119458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, Z.; Wan, X.; Fang, H.; Yu, D.G.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. The relationships between process parameters and polymeric nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Yu, D.G.; Li, X.; Williams, G.R. The development and bio-applications of multifluid electrospinning. Mater. Highlights 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, D.-G. Preparing composite nanoparticles for immediate drug release by modifying electrohydrodynamic interfaces during electrospraying. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.-F.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.-F. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colon-specific delayed drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Zhang, K.; Gong, Q.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Quan, H. Ethylcellulose-based drug nano depots fabricated using a modified triaxial electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; An, S.; Lee, C.; Liou, M.; Yarin, A.L.; Yoon, S.S. Self-healing transparent core–shell nanofiber coatings for anti-corrosive protection. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P. ‘Containers’ for self-healing epoxy composites and coating: Trends and advances. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 506–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; An, S.; Kim, Y.-I.; Yoon, S.S.; Yarin, A.L. Self-healing three-dimensional bulk materials based on core-shell nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Zheng, Z.; Michailidis, M.; Fleck, N.; Bilton, M.; Song, Y.; Li, G.L.; Shchukin, D.G.; Michailids, M. Mussel-Inspired Self-Healing Coatings Based on Polydopamine-Coated Nanocontainers for Corrosion Protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10283–10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.; Dai, C.; Jiang, S. Thioetherimide-modified cyanate ester resin with better molding performance for glass fiber reinforced composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Li, W.; Han, N.; Li, W.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Li, W. Novel Dual-Component Microencapsulated Hydrophobic Amine and Microencapsulated Isocyanate Used for Self-Healing Anti-Corrosion Coating. Polymers 2018, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rastin, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Nonahal, M.; Shabanian, M.; Vahabi, H.; Formela, K.; Gabrion, X.; Seidi, F.; Zarrintaj, P.; Sari, M.G.; et al. Transparent nanocomposite coatings based on epoxy and layered double hydroxide: Nonisothermal cure kinetics and viscoelastic behavior assessments. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 113, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neisiany, R.E.; Lee, J.K.Y.; Khorasani, S.N.; Ramakrishna, S. Self-healing and interfacially toughened carbon fibre-epoxy composites based on electrospun core-shell nanofibres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Process | FCE a | FCT b | FS c | Morphology d | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mL/h) | (mL/h) | (mL/h) | (nm) | |||
| F1 | Single | -- | -- | 1 | Linear | 230 ± 100 |
| F2 | Tri-axial | 0.1 | 0.08 | 1.2 | Linear | 300 ± 140 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun Multiple-Chamber Nanostructure and Its Potential Self-Healing Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102413
Liu Y, Liu X, Liu P, Chen X, Yu D-G. Electrospun Multiple-Chamber Nanostructure and Its Potential Self-Healing Applications. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102413
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yubo, Xinkuan Liu, Ping Liu, Xiaohong Chen, and Deng-Guang Yu. 2020. "Electrospun Multiple-Chamber Nanostructure and Its Potential Self-Healing Applications" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102413
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, X., Liu, P., Chen, X., & Yu, D.-G. (2020). Electrospun Multiple-Chamber Nanostructure and Its Potential Self-Healing Applications. Polymers, 12(10), 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102413







