Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Citric Acid Hydrogel for Sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CMSS
2.3. Synthesis of CMSS/CA Hydrogel
2.4. Characterization of CMSS/CA Hydrogel
2.5. Sorption Procedure
2.6. Selectivity Study
2.7. Desorption Study
3. Results and Discussion
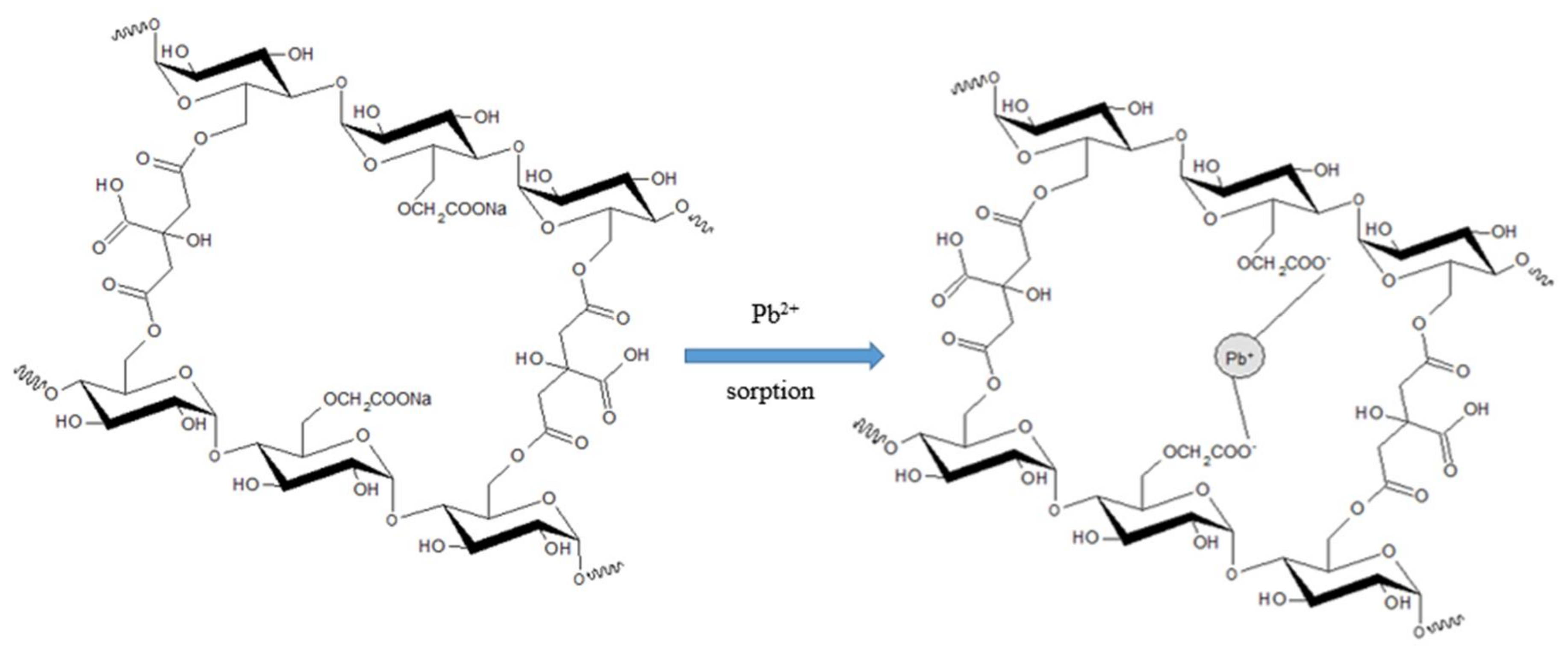
3.1. Characterization of CMSS/CA Hydrogel
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
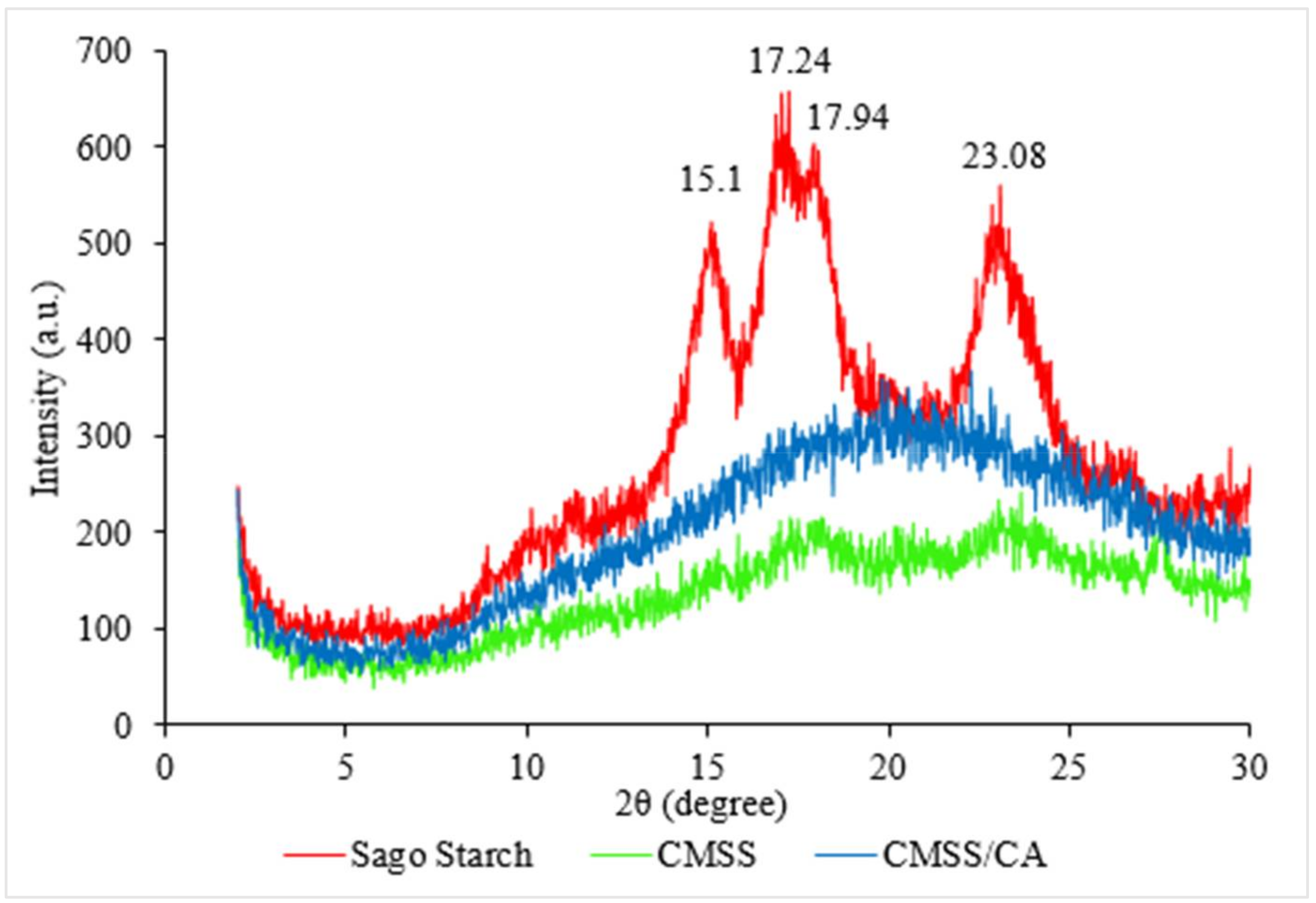
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
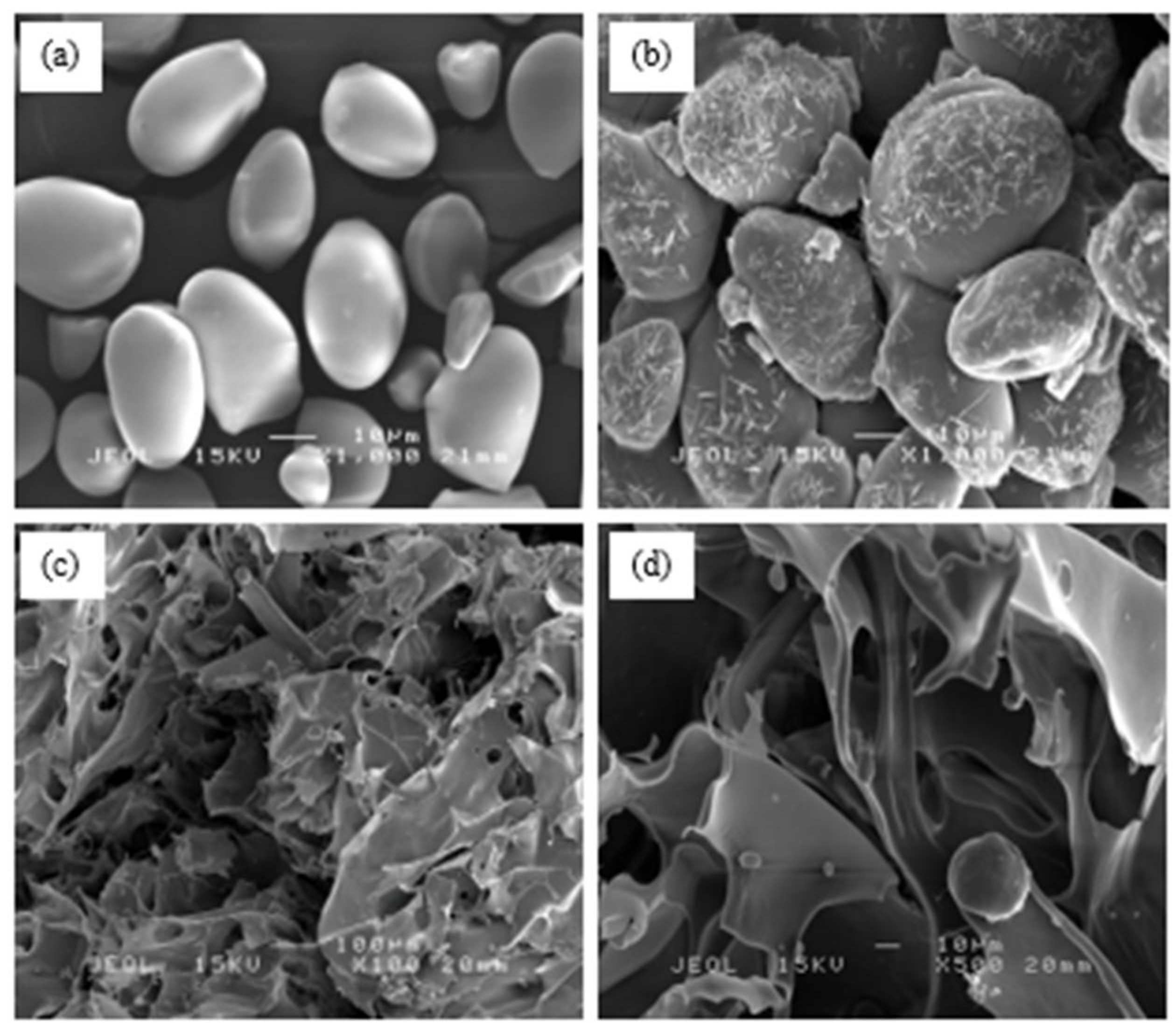
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
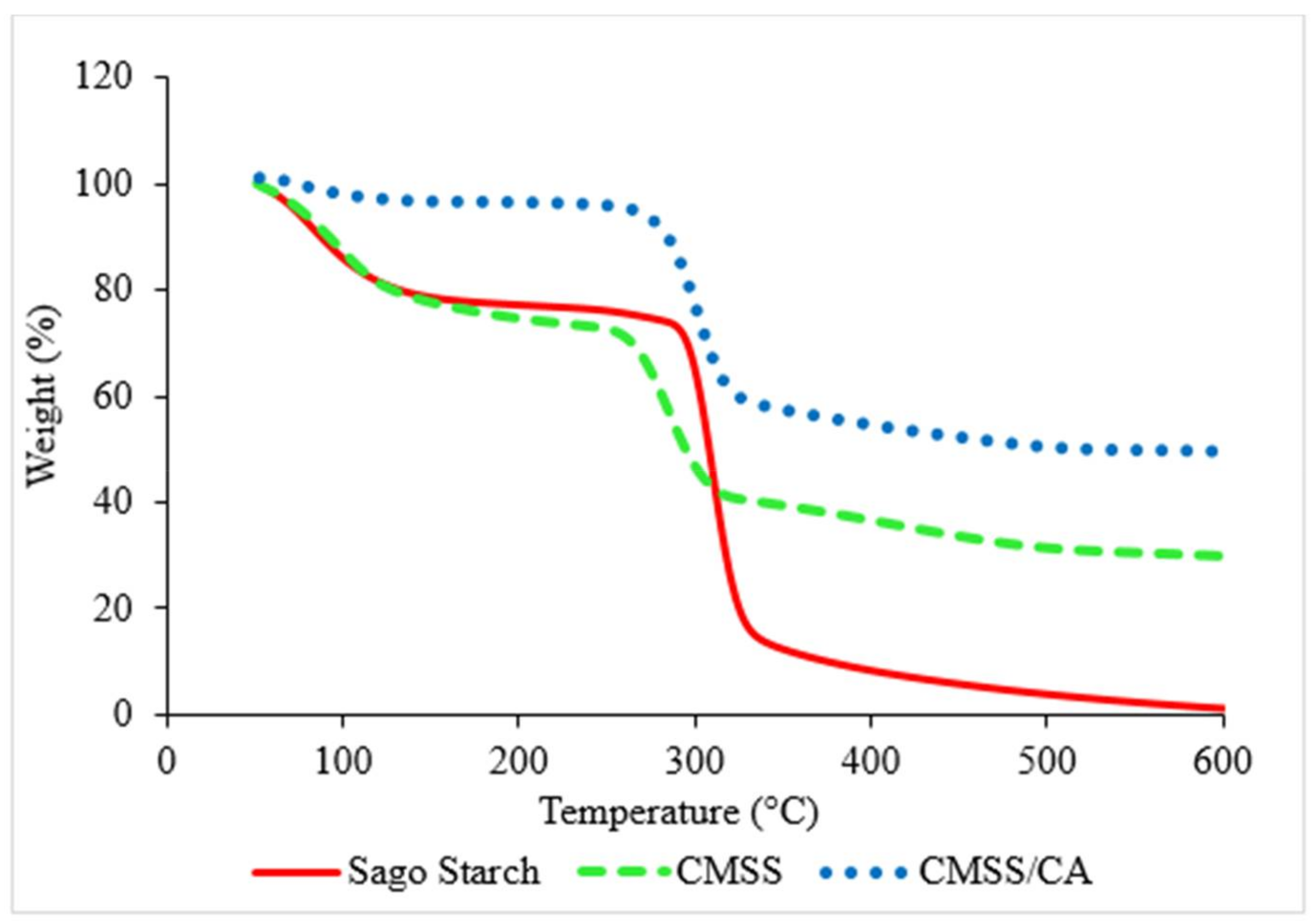
3.1.4. TGA Analysis
3.2. Metal Ions Sorption by CMSS/CA Hydrogel
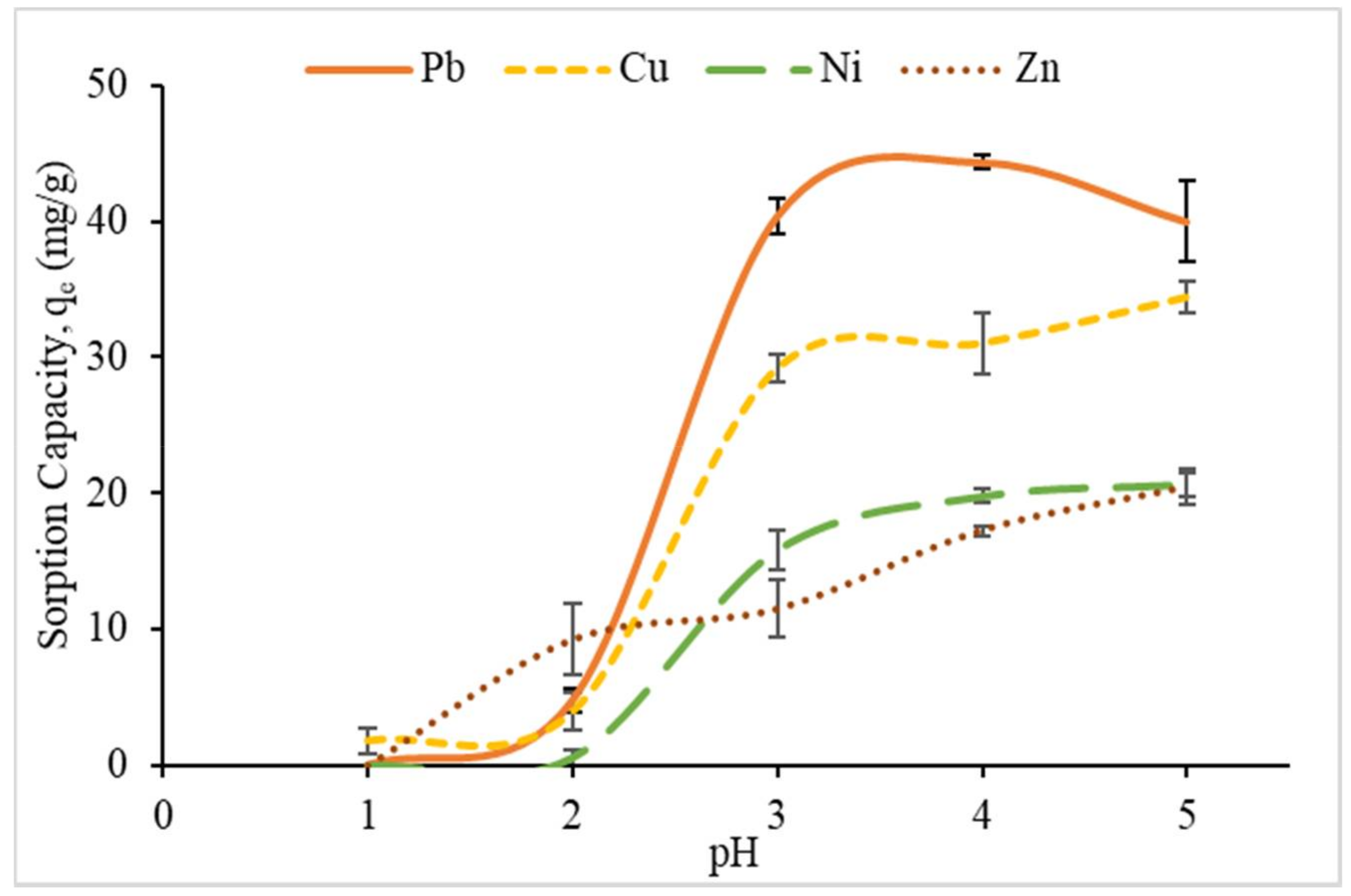
3.2.1. Effect of pH
3.2.2. Effect of Contact Time and Kinetic Study on Metal Sorption
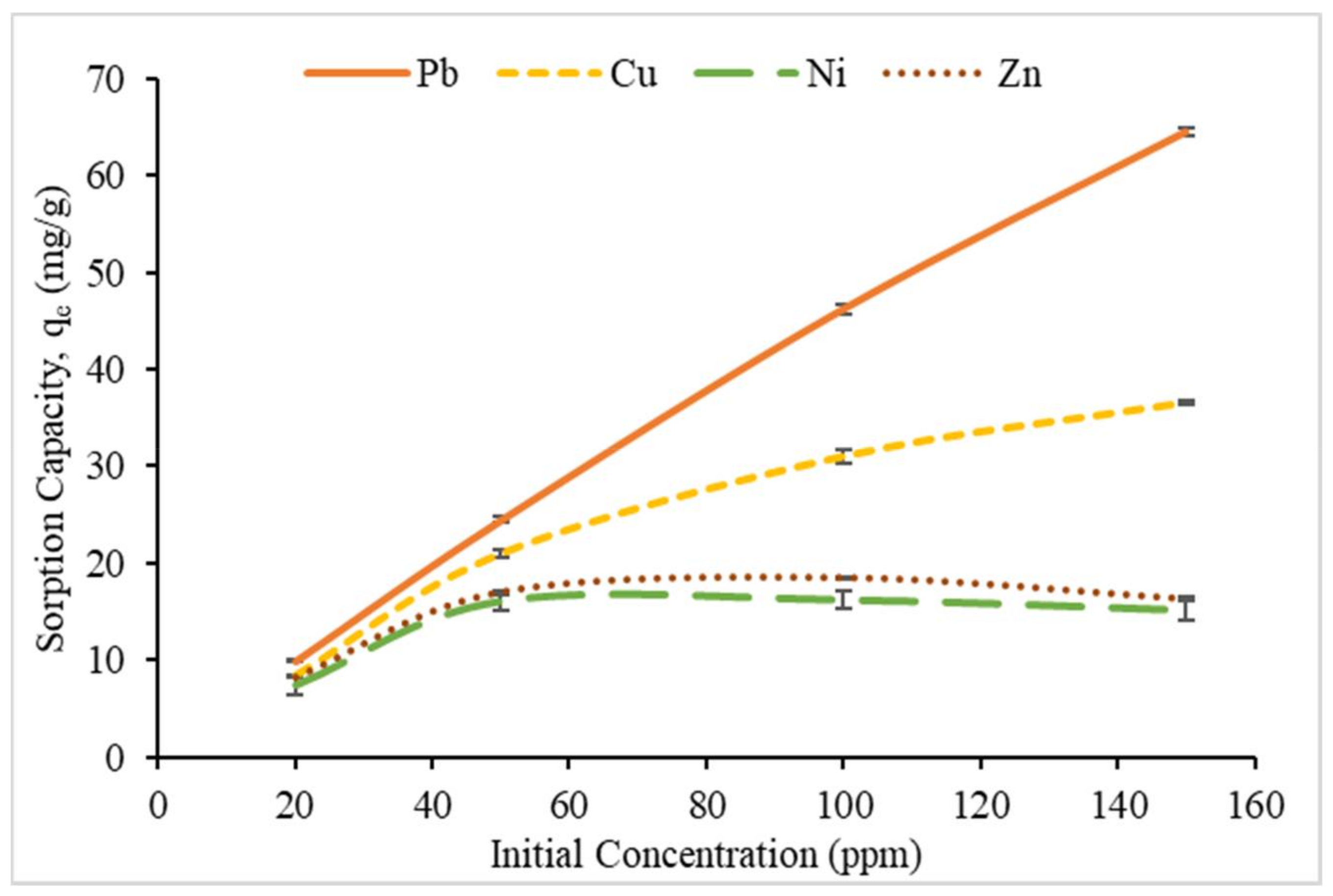
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Metal Ion Concentration
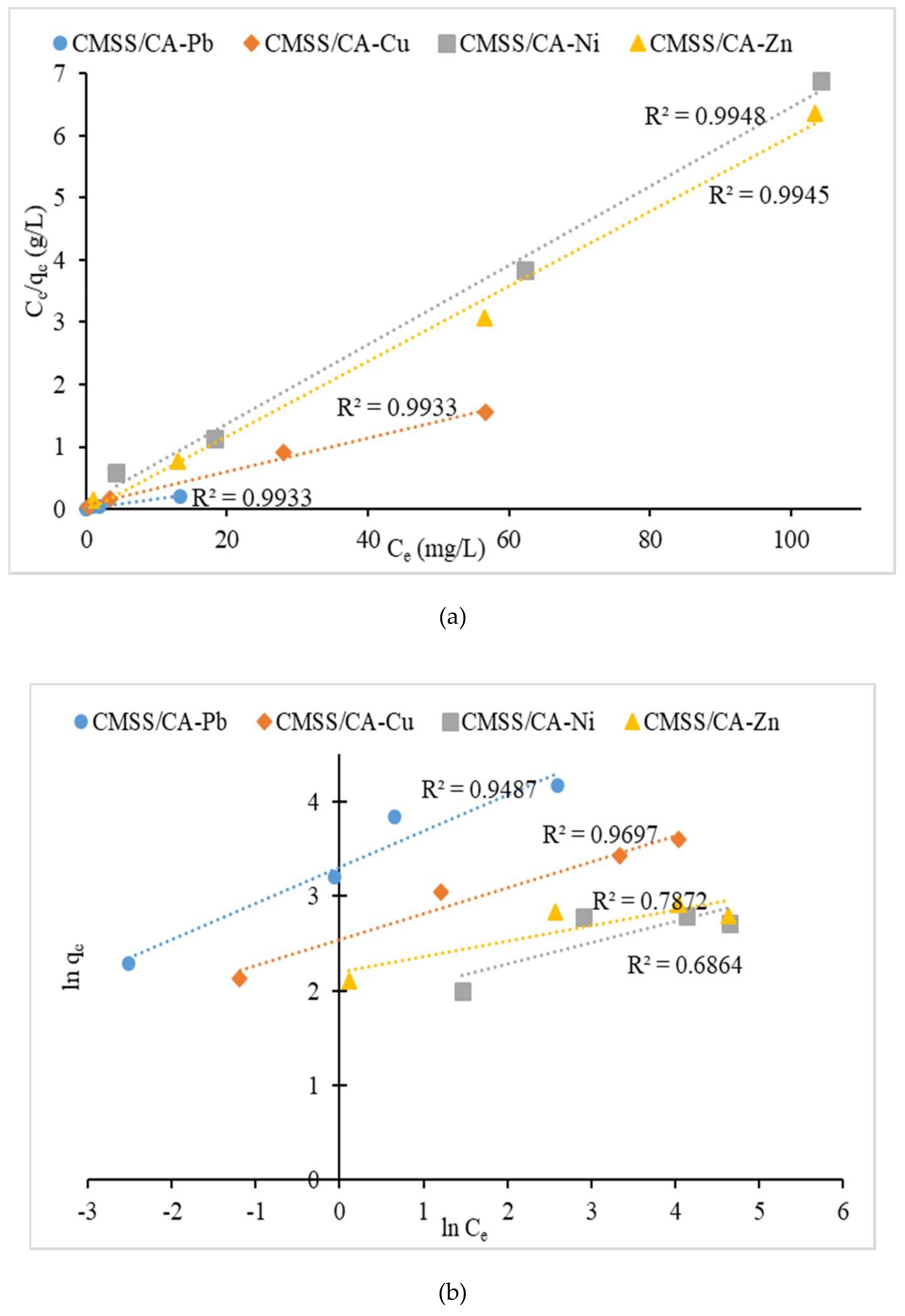
3.2.4. Isotherm Study
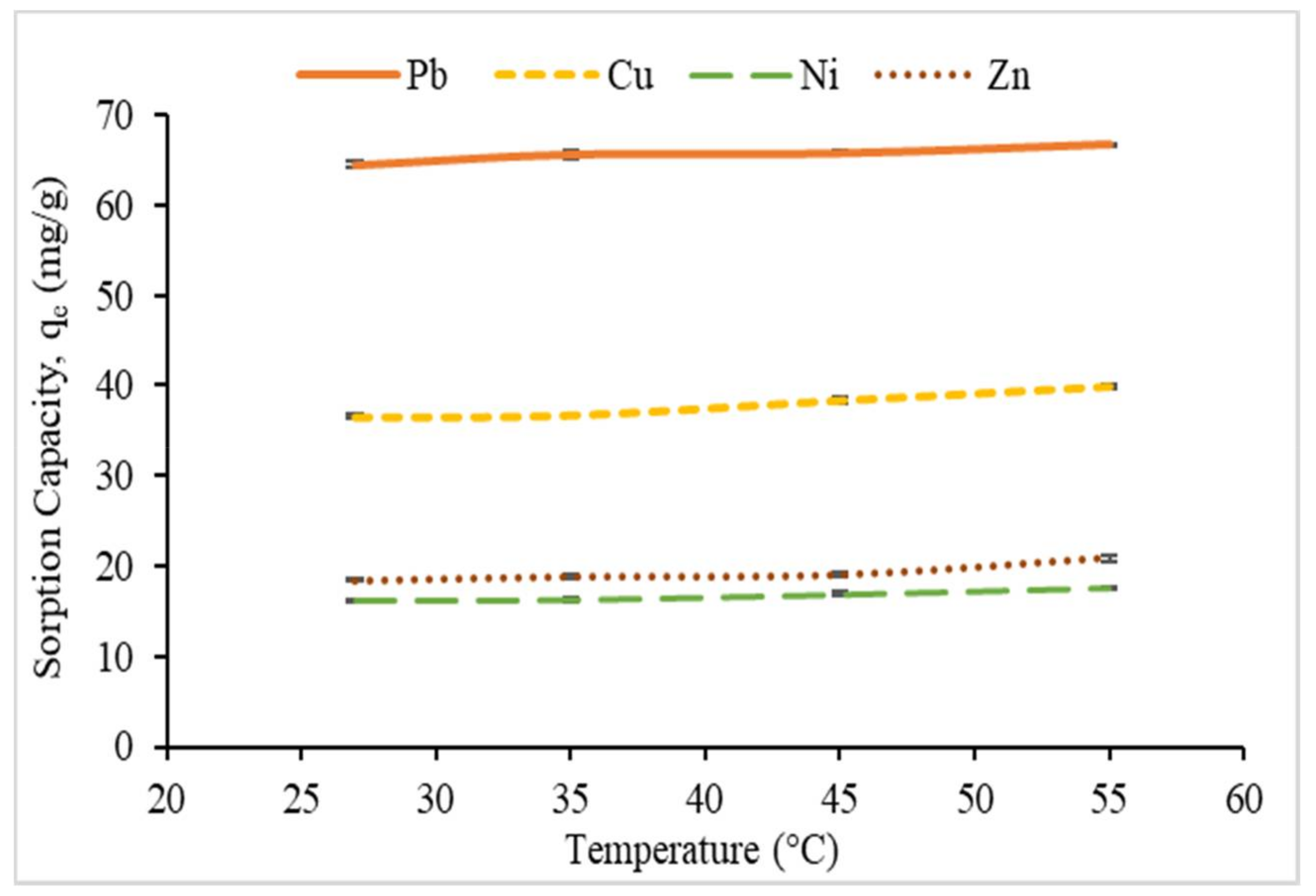
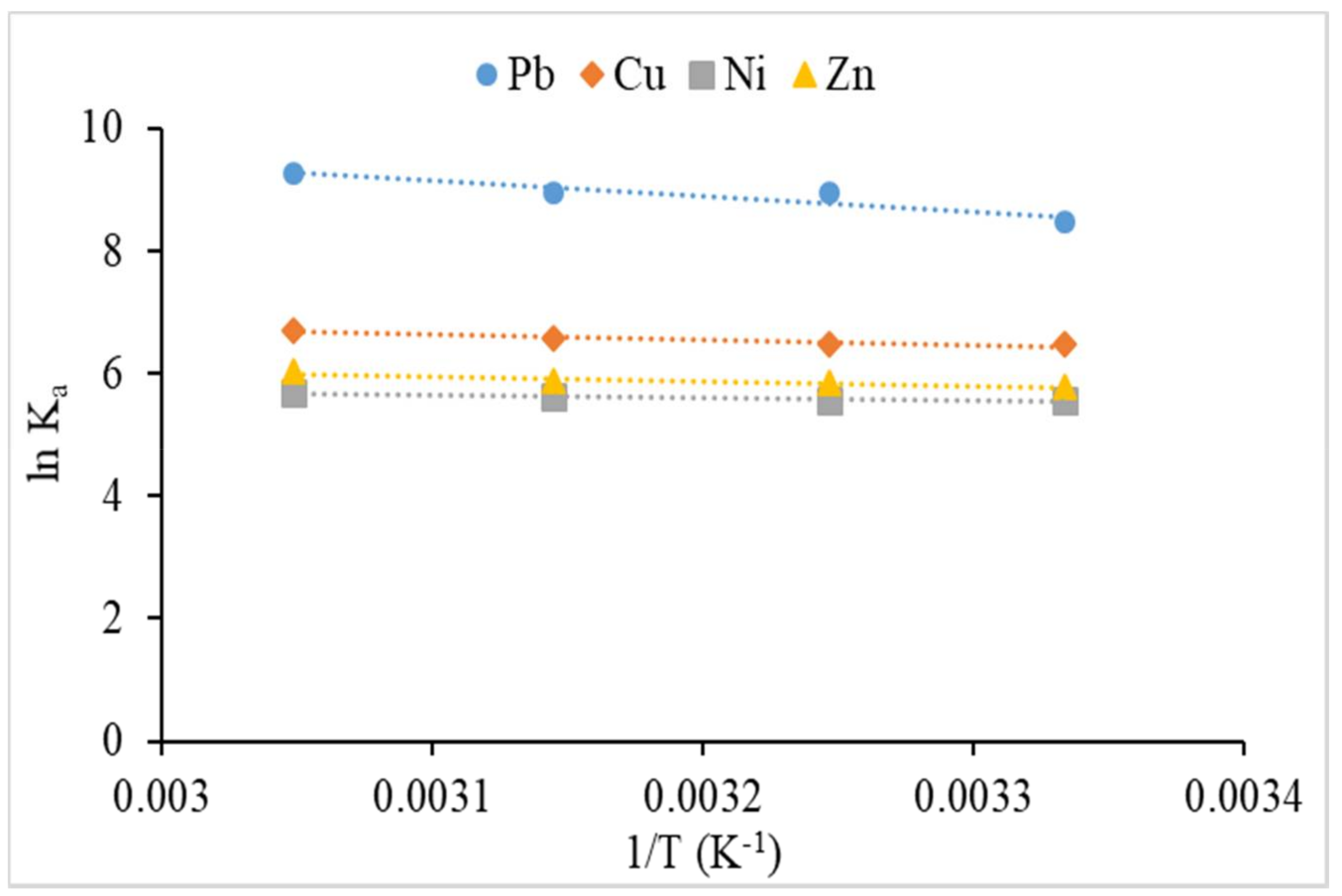
3.2.5. Effect of Temperature and Thermodynamic Study
3.2.6. Comparison of CMSS/CA Hydrogel with Polysaccharides-Based Hydrogel
3.3. Selectivity Study
3.4. Desorption Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadhum, S.A.; Ishak, M.Y.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Hashim, R.B. Evaluation of the status and distributions of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Langat River Basin in Selangor Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, N.F.; Aris, A.Z.; Praveena, S.M. Preliminary study of heavy metal (Zn, Pb, Cr, Ni) contaminations in Langat river estuary, selangor. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrogan, C.; Pandele, A.M.; Bobirică, C.; Dobrotă, D.; Dăncilă, A.M.; Gârleanu, G.; Orbuleț, O.D.; Borda, C.; Gârleanu, D.; Orbeci, C. Synthesis, characterization and sorption capacity examination for a novel hydrogel composite based on Gellan gum and Graphene oxide (GG/GO). Polymers 2020, 12, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Długosz, O.; Banach, M. Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations of the adsorption of Ag+ and Cu2+ on vermiculite. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 258, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharuddin, N.H.; Lai, S.H.; Aroua, M.K. Removal of heavy metal ions from mixed solutions via polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration using starch as a water-soluble biopolymer. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 34, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, A.; Guleria, A. Chemical modification of cellulosic biopolymer and its use in removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, R.; Pour, Z.S.; Ghaemy, M. Novel magnetic bio-sorbent hydrogel beads based on modified gum tragacanth/graphene oxide: Removal of heavy metals and dyes from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, M.B. Batch sorption experiments: Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm studies for the adsorption of textile metal ions onto Teff Straw ( Eragrostis tef ) agricultural waste. J. Thermodyn. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.; Mansur, A.A.; De Jesus, A.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; De Oliveira, L.C.; Mansur, H.S. Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1218–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, H. Characterization and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels crosslinked by polyethylene glycol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Hanif, M.; Ranjha, N.M. Methods of synthesis of hydrogels…A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 24, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Spychaj, T.; Lendzion-Bieluń, Z. Crosslinked carboxymethyl starch: One step synthesis and sorption characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Anderson, D.P.; Chang, P.R. Modification of porous starch for the adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.T.; Okabe, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Hara, K. Removal of metal ions from aqueous solutions using carboxymethyl cellulose/sodium styrene sulfonate gels prepared by radiation grafting. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalla, A.H.; Yaseen, Z.; Bhat, M.A.; Rangreez, T.A.; Maswal, M. Recent review for removal of metal ions by hydrogels. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Lechner, M.D.; Hartmann, B.; Kulicke, W.-M. Carboxymethyl cocoyam starch: Synthesis, Characterisation and influence of reaction parameters. Starch Stärke 2007, 59, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzlina, Z.A.N.; Karim, A.A.; Teng, T.T. Physicochemical properties of Carboxy-methylated sago (Metroxylon sagu) starch. J. Food Sci. 2006, 70, C560–C567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamood, N.F.A.-Z.T.; Zainuddin, N.; Ahmad, M.B.; Tan, S.W. Preparation, optimization and swelling study of carboxymethyl sago starch (CMSS)–acid hydrogel. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Abbasi, N.M.; Abdin, Z.-U.; Saleem, M.; Khan, R.U.; Ullah, R.S.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J. Chemical modification of starch and its application as an adsorbent material. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78264–78285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhalima, T.; Ferfera-Harrar, H.; Lerari, D. Optimization of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels beads generated by an anionic surfactant micelle templating for cationic dye uptake: Swelling, sorption and reusability studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Abdin, Z.-U.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, X.; Khan, R.U.; Zhang, H.; et al. Recent progress in chemical modification of starch and its applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67459–67474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, B.; Hu, X.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X.; Tian, Y. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl starch microgel with different crosslinking densities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demitri, C.; Del Sole, R.; Scalera, F.; Sannino, A.; Vasapollo, G.; Maffezzoli, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Nicolais, L. Novel superabsorbent cellulose-based hydrogels crosslinked with citric acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, K.K.; Dhawale, S.C.; Dias, R.J. Synthesis and characterization of hydrogel films of carboxymethyl tamarind gum using citric acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isah, S.; Oshodi, A.A.; Atasie, V.N. Physicochemical properties of cross linked acha (digitaria exilis) starch with citric acid. Chem. Int. 2017, 3, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Basri, S.N.; Zainuddin, N.; Hashim, K.; Yusof, N.A. Preparation and characterization of irradiated carboxymethyl sago starch-acid hydrogel and its application as metal scavenger in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychaj, T.; Zdanowicz, M.; Kujawa, J.; Schmidt, B. Carboxymethyl starch with high degree of substitution: Synthesis, properties and application. Polimery 2013, 58, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-P.; Dai, X.-Z.; Kan, J.-R.; Shilong, F.-D.; Zhu, M. Fabrication of carboxymethyl chitosan–hemicellulose resin for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by crosslinked carboxymethyl konjac glucomannan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainuddin, N. Carboxymethylation of Sago Starch and Sago Waste and the Formation of Carboxymethyl Starch-Hydrogel via Irradiation Technique. Master’s Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, January 2003. Available online: http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/9564/1/FSAS_2003_25_A.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Othman, Z.; Hassan, O.; Hashim, K. Physicochemical and thermal properties of gamma-irradiated sago (Metroxylon sagu) starch. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 109, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthumporn, U.; Wahidah, N.; Karim, A.A. Physicochemical properties of starch from sago (Metroxylon Sagu) palm grown in mineral soil at different growth stages. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 62, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ming, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, G. Synthesis, characterisation and in vitro digestibility of carboxymethyl potato starch rapidly prepared with microwave-assistance. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanli, W.; Gao, W.; Xia, L. Carboxymethyl Chinese yam starch: Synthesis, characterization, and influence of reaction parameters. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, M.; Sharaf, S.; El-Hady, M.A.; Hebeish, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels and carboxymethylcellulolse-hydrogel-ZnO-nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramachineni, A.K.; Sathasivam, T.; Muniyandy, S.; Janarthanan, P.; Langford, S.J.; Lim, Y.Y. Optimizing extraction of cellulose and synthesizing pharmaceutical grade Carboxymethyl sago cellulose from Malaysian sago pulp. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamingan, Z.; Ahmad, M.B.; Hashim, K.; Zainuddin, N. Sago starch based hydrogel prepared using electron beam irradiation technique for controlled release application. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2015, 19, 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Citric acid cross-linking of starch films. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuibo, X.; Shuibo, X.; Wang, G.; Yu, C.W.; Zeng, T.; Cai, P.; Huang, H. Fabrication and optimization of the thermo-sensitive hydrogel Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) for U(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Polymers 2020, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamshary, H.; Fouda, M.M.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Removal of heavy metal using poly (N-vinylimidazole)-grafted-carboxymethylated starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qudah, Y.H.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Khalek, M.A. Radiation crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol)/acrylic acid copolymer for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Mafize, A.A.; Kahar, N.A.M.A.; Johari, K.; Rabat, N.E. Efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by using oil palm bio-waste/MWCNTs reinforced PVA hydrogel composites: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic modeling. Polymers 2020, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dula, T.; Siraj, K.; Kitte, S.A. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using chemically activated carbon prepared from locally available waste of bamboo (Oxytenanthera abyssinica). ISRN Environ. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahchamani, J.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Behzad, M. Adsorption of methyl violet from aqueous solution by polyacrylamide as an adsorbent: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Desalination 2011, 267, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Mittal, H.; Waanders, F.; Ray, S.S. Thermodynamic properties and adsorption behaviour of hydrogel nanocomposites for cadmium removal from mine effluents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 48, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, S.N. Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Aqueous Solution by Carboxymethyl Sago Starch and Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Chitosan Hydrogels. Master’s Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, M.A.; Chisti, H.; Shah, S.A. Removal of heavy metal ions from water by cross-linked potato di-starch phosphate polymer. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.I.; Abdel-Halim, M.G. Preparation of anionic starch containing carboxyl groups and its utilization as chelating agent. Starch Stärke 2001, 53, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Metal | qe,exp (mg g−1) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe,calc (mg g−1) | R2 | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe,calc (mg g−1) | R2 | ||
| Pb | 46.23 | 0.0387 | 7.737 | 0.9130 | 0.0109 | 47.17 | 0.9992 |
| Cu | 31.79 | 0.0465 | 3.396 | 0.9553 | 0.0254 | 32.26 | 1.0000 |
| Ni | 16.58 | 0.0138 | 1.108 | 0.2446 | 0.0616 | 16.47 | 0.9983 |
| Zn | 19.27 | 0.0302 | 2.146 | 0.9745 | 0.0283 | 19.61 | 0.9997 |
| Metal | qe,exp (mg g−1) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L mg−1) | qmax (mg g−1) | R2 | KF (L1/n mg1/n−1 g−1) | n | R2 | ||
| Pb | 64.48 | 0.9536 | 69.44 | 0.9933 | 27.34 | 2.625 | 0.9487 |
| Cu | 36.56 | 0.3851 | 37.31 | 0.9933 | 12.73 | 3.638 | 0.9697 |
| Ni | 16.21 | 0.6175 | 15.72 | 0.9948 | 6.303 | 4.505 | 0.6864 |
| Zn | 18.46 | −1.317 | 16.58 | 0.9945 | 8.968 | 6.079 | 0.7872 |
| Metal | T (K) | 1/T (K−1 × 10−3) | Ka (mL/g) | ln Ka | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (J mol−1 K−1) | ΔG (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (II) | 300 | 3.33 | 4833 | 8.483 | −21.159 | ||
| 308 | 3.25 | 7632 | 8.940 | 20.484 | 0.1395 | −22.893 | |
| 318 | 3.15 | 7763 | 8.957 | −23.681 | |||
| 328 | 3.05 | 10627 | 9.271 | −25.282 | |||
| Cu (II) | 300 | 3.33 | 645.6 | 6.470 | −16.138 | ||
| 308 | 3.25 | 654.9 | 6.485 | 6.793 | 0.07622 | −16.605 | |
| 318 | 3.15 | 723.2 | 6.584 | −17.406 | |||
| 328 | 3.05 | 808.8 | 6.696 | −18.259 | |||
| Ni (II) | 300 | 3.33 | 260.7 | 5.563 | −13.876 | ||
| 308 | 3.25 | 263.2 | 5.573 | 3.649 | 0.05830 | −14.271 | |
| 318 | 3.15 | 276.4 | 5.622 | −14.863 | |||
| 328 | 3.05 | 294.7 | 5.686 | −15.506 | |||
| Zn (II) | 300 | 3.33 | 326.5 | 5.788 | −14.436 | ||
| 308 | 3.25 | 346.7 | 5.848 | 6.284 | 0.06896 | −14.975 | |
| 318 | 3.15 | 352.3 | 5.864 | −15.504 | |||
| 328 | 3.05 | 413.2 | 6.024 | −16.427 |
| Sorbent | Heavy Metal Ion | Sorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gellan Gum/Graphene Oxide | Zn2+ | 120.48 | [3] |
| Porous starch xanthate | Pb2+ | 107.36 | [15] |
| Porous starch citrate | Pb2+ | 48.30 | |
| Carboxymethyl Cellulose/sodium styrene | Pb2+ | 0.0036 | [16] |
| sulfonate | Cu2+ | 0.0252 | |
| Ni2+ | 0.0267 | ||
| Zn2+ | 0.0303 | ||
| Crosslinked carboxymethyl corn starch | Pb2+ | 76.53 | [23] |
| Carboxymethyl Sago Starch-lactic acid | Pb2+ | 56.08 | [28] |
| Cu2+ | 17.19 | ||
| Crosslinked carboxymethyl konjac | Cu2+ | 25.50 | [31] |
| glucomannan | Pb2+ | 29.20 | |
| Oil palm bio-waste/Chitosan/multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)/Polyvinyl alcohol | Pb2+ | 30.03 | [44] |
| CMSS/CA | Pb2+ | 64.48 | Present study |
| Cu2+ | 36.56 | ||
| Ni2+ | 16.21 | ||
| Zn2+ | 18.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keirudin, A.A.; Zainuddin, N.; Yusof, N.A. Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Citric Acid Hydrogel for Sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2020, 12, 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112465
Keirudin AA, Zainuddin N, Yusof NA. Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Citric Acid Hydrogel for Sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112465
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeirudin, Amyrah Auni, Norhazlin Zainuddin, and Nor Azah Yusof. 2020. "Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Citric Acid Hydrogel for Sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112465
APA StyleKeirudin, A. A., Zainuddin, N., & Yusof, N. A. (2020). Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Sago Starch/Citric Acid Hydrogel for Sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution. Polymers, 12(11), 2465. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112465




