The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
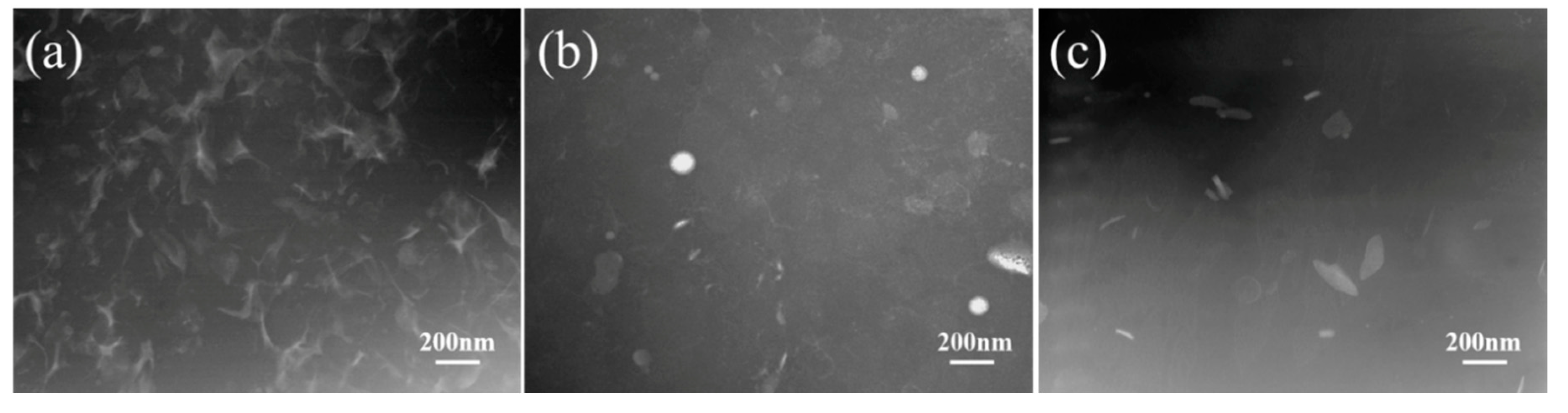
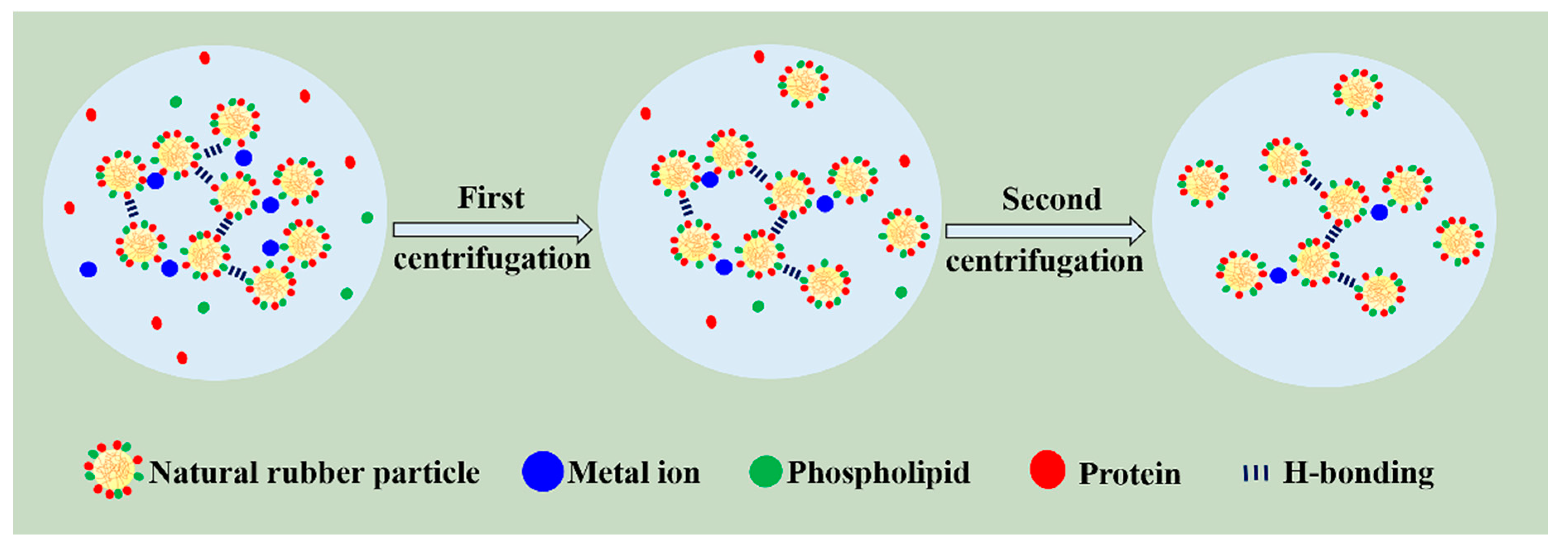
3.1. Non-Rubber Components and Structure of NR, CNR-1 and CNR-2
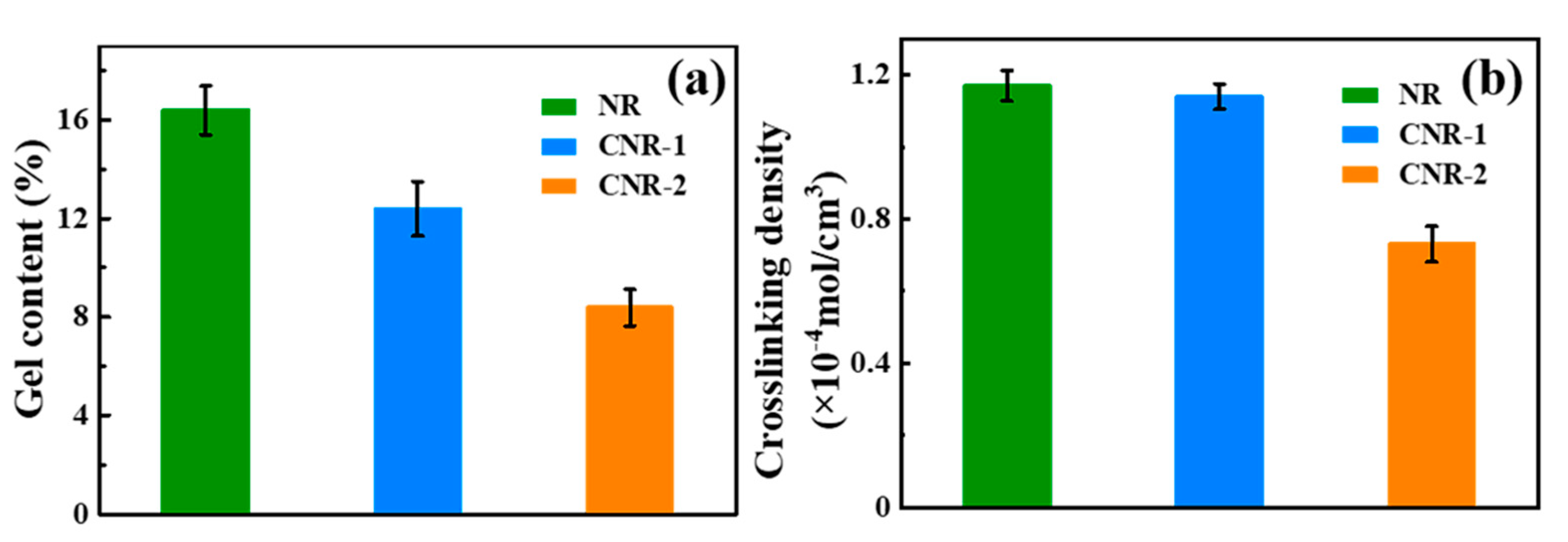
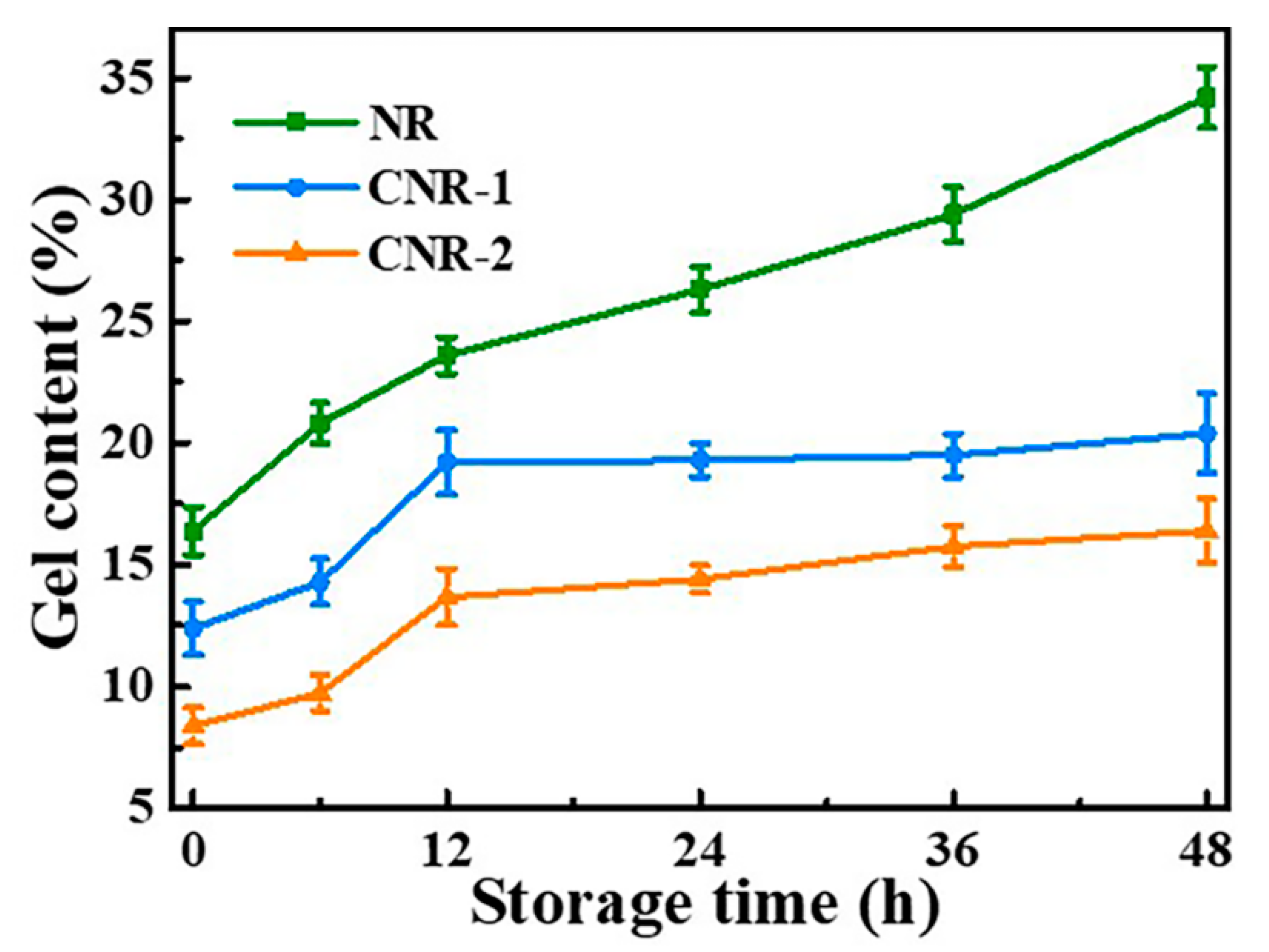
3.2. Crosslinking Density and Gel Content of NR, CNR-1, and CNR-2 Before and after Accelerated Storage
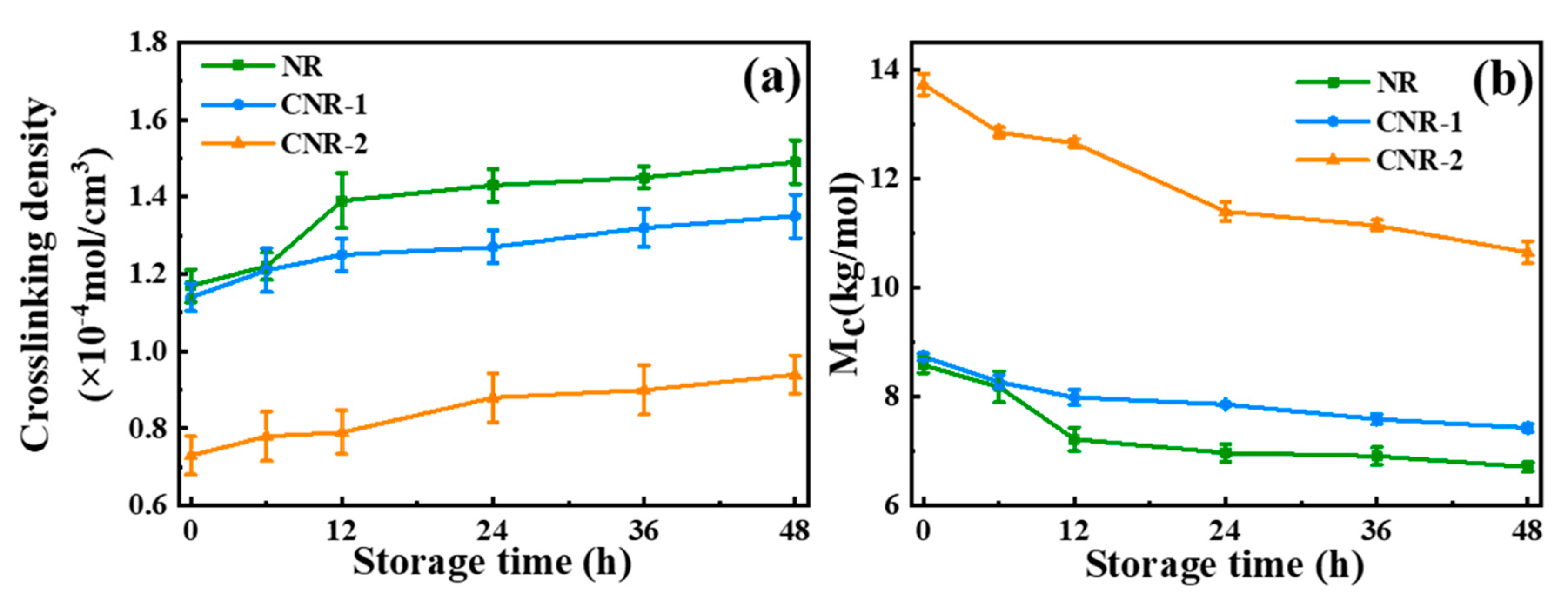
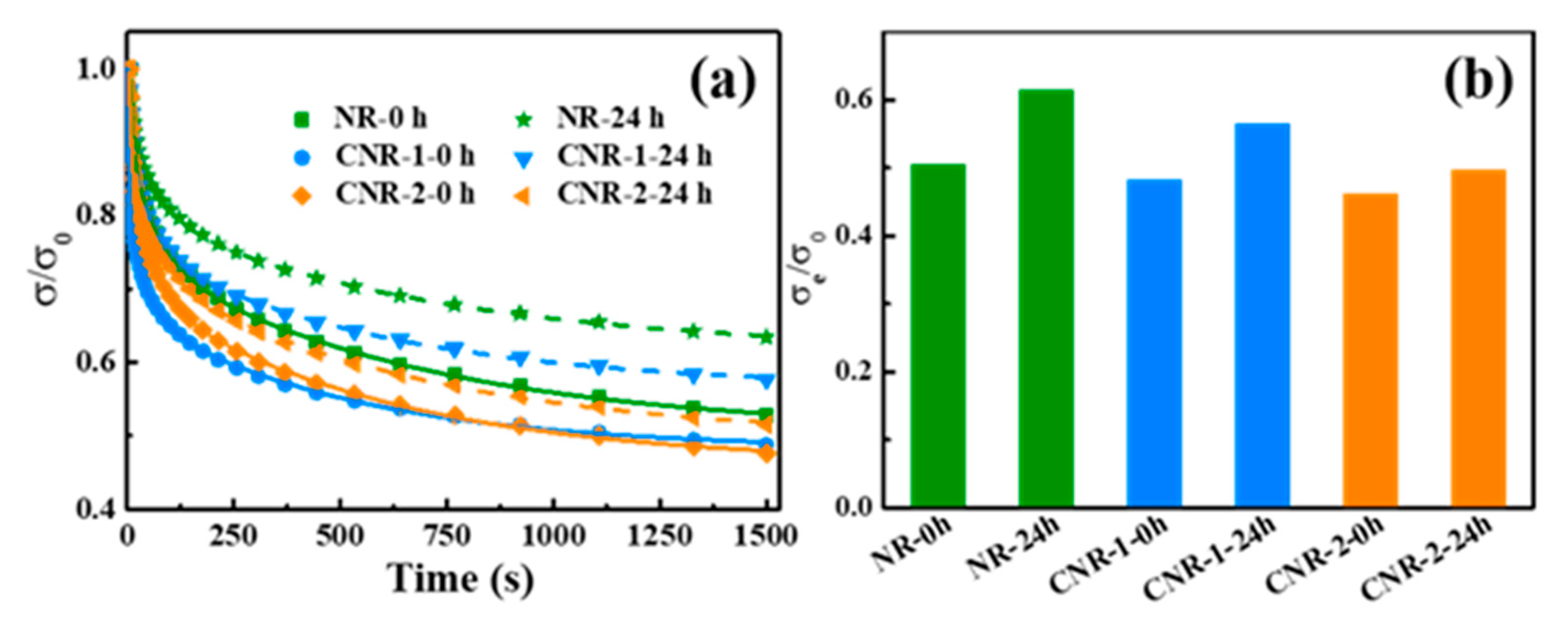
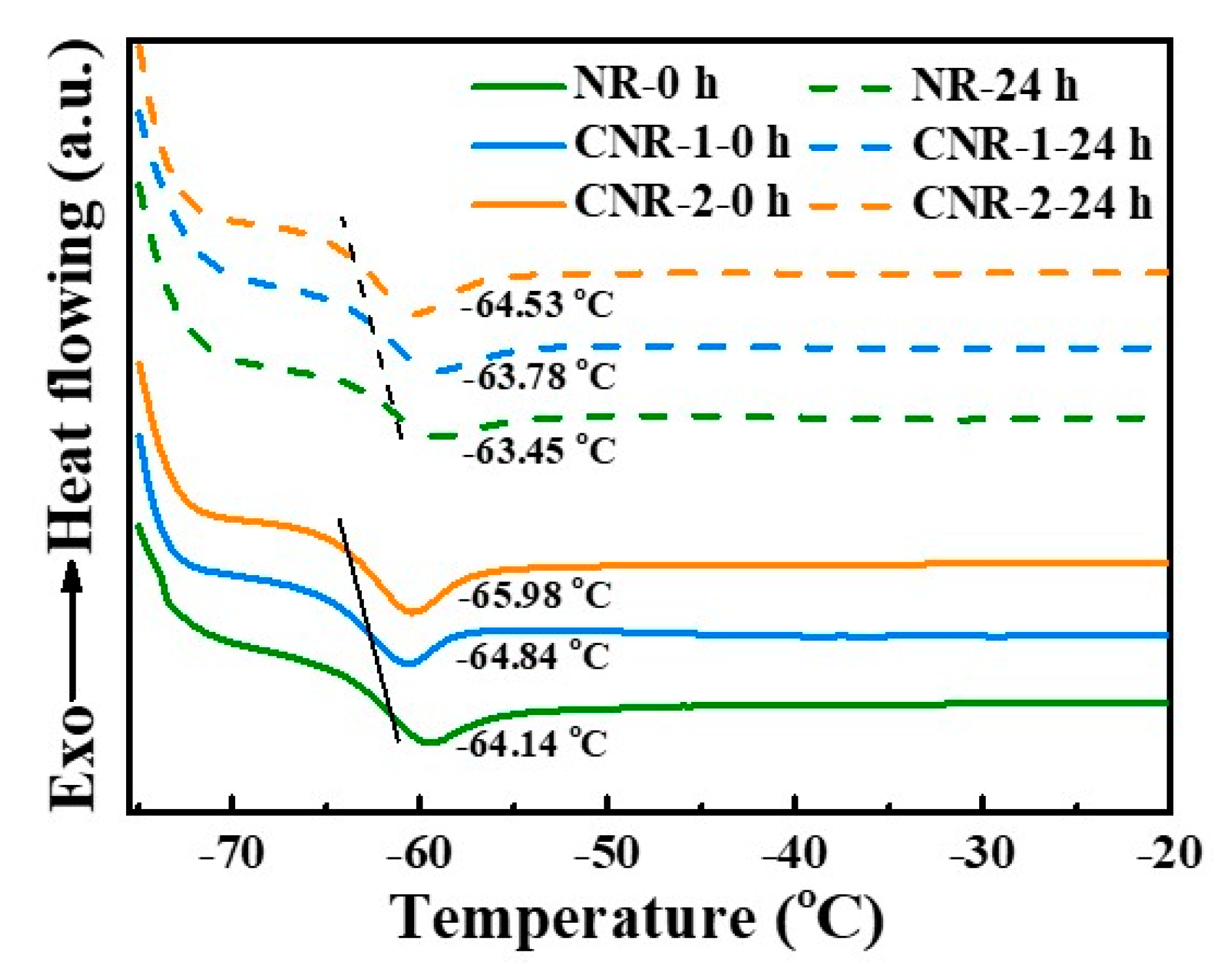
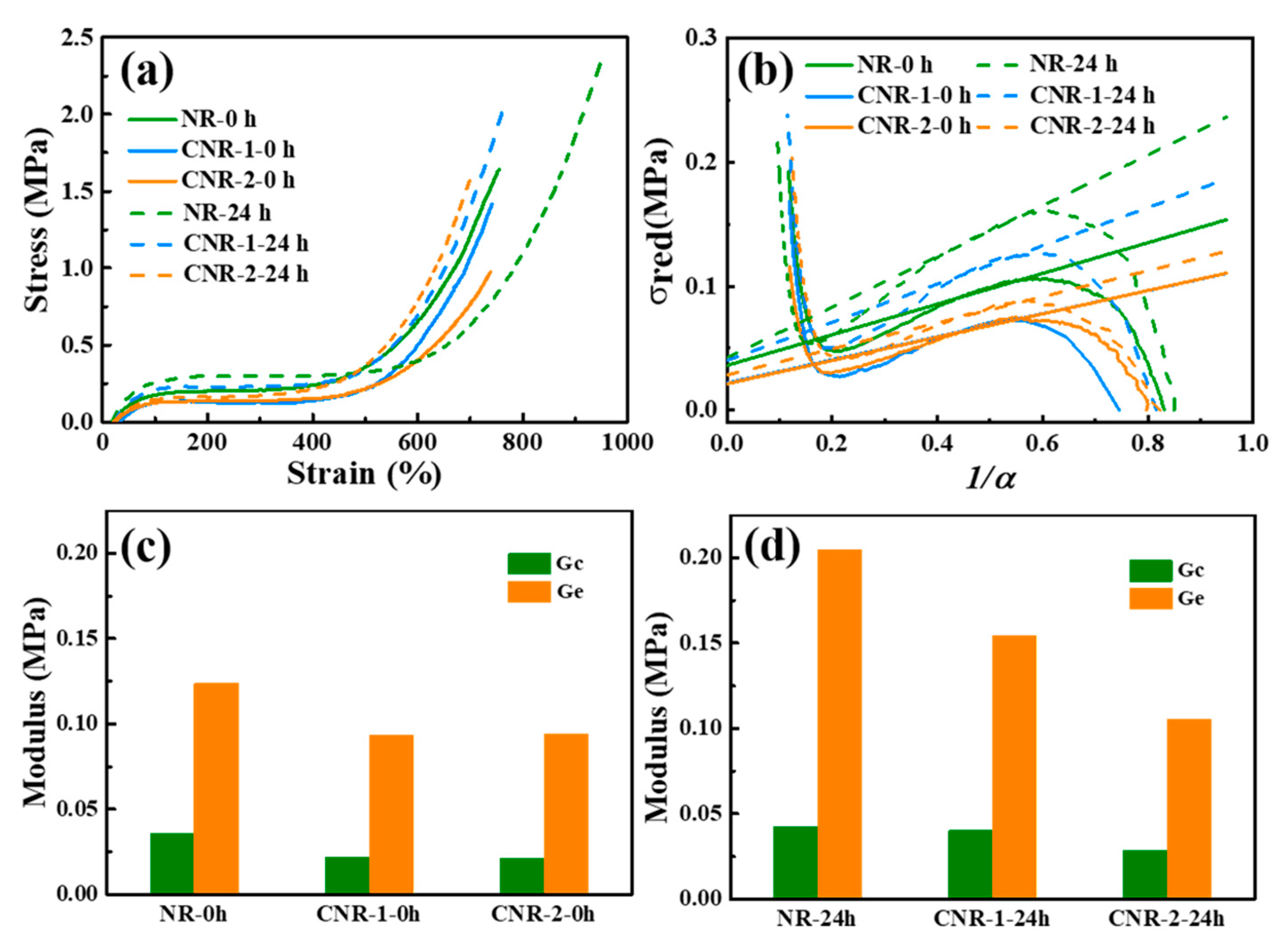
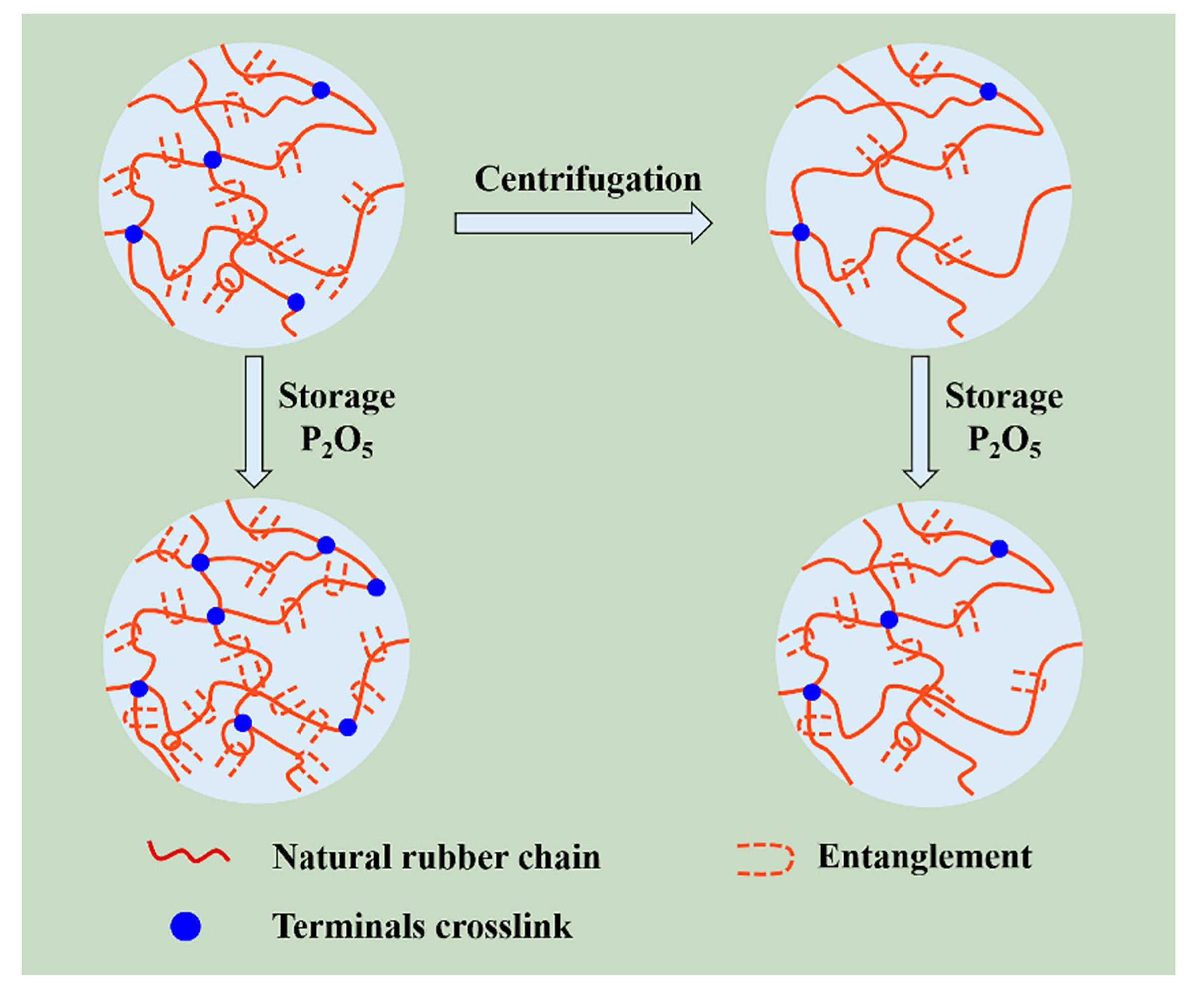
3.3. Molecular Network of NR, CNR-1, and CNR-2 Before and after Accelerated Storage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, Y.; Tarachiwin, L. Recent advances in structural characterization of natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2009, 82, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriring, M.; Nimpaiboon, A.; Kumarn, S.; Takahara, A.; Sakdapipanich, J. Enhancing viscoelastic and mechanical performances of natural rubber through variation of large and small rubber particle combinations. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolerea, A.S.; Liengprayoonb, S.; Vayssea, L.; Sainte-Beuvea, J.; Bonfilsa, F. Investigating natural rubber composition with Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy: A rapid and non-destructive method to determine both protein and lipid contents simultaneously. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansatsadeekul, J.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Rojruthai, P. Characterization of associated proteins and phospholipids in natural rubber latex. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomez, M.; Subileau, M.; Intapun, J.; Bonfils, F.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Vaysse, L.; Dubreucq, E. Micro-organisms in latex and natural rubber coagula of Hevea brasiliensis and their impact on rubber composition, structure and properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Liu, G.-X.; Zhang, H.-F.; Zhao, F.; Luo, M.-C.; Liao, S. Non-rubber components tuning mechanical properties of natural rubber from vulcanization kinetics. Polymer 2019, 183, 121911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Tanaka, Y. Green strength of natural rubber: The origin of the stress-strain behavior of natural rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, G.-S.; Wei, L.-Y.; Zeng, J.; Fu, X.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.-R. Inhomogeneous natural network promoting strain-induced crystallization: A mesoscale model of natural rubber. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qu, W.; Huang, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, C.; Liu, H. Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of spatial organization of proteins and lipids in natural rubber. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Suwanruji, P.; Tantatherdtam, P.; Smitthipong, W. New approach on structure-property relationships of stabilized natural rubbers. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, T.T.; Phan, T.N.; Seiichi, K. Factors influencing green strength of commercial natural rubber. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 7, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Ute, K.; Kitayama, T.; Tanaka, Y. Structural characterization of α-Terminal group of natural rubber. 2. Decomposition of branch-points by phospholipase and chemical treatments. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojruthai, P.; Kantaram, T.; Sakdapipanich, J. Impact of non-rubber components on the branching structure and the accelerated storage hardening in Hevea rubber. J. Rubber Res. 2020, 23, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promhuad, K.; Smitthipong, W. Effect of stabilizer states (solid vs liquid) on properties of stabilized natural rubbers. Polymers 2020, 12, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Sriring, M.; Kumarn, S. Reducing and stabilizing the viscosity of natural rubber by using sugars: Interference of the Maillard reaction between proteins and sugars. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Tang, Z.; Lin, T.; Guo, B.; Huang, G. New evidence disclosed for networking in natural rubber by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kosugi, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawahara, S. Effect of non-rubber components on the mechanical properties of natural rubber. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawamawat, K.; Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Ho, C.C. Effect of deproteinized methods on the proteins and properties of natural rubber latex during storage. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 288, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J. Role of gel content on the structural changes of masticated natural rubber. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 844, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunyongwattanakorn, J.; Tanakat, Y.; Kawahara, S.; Klinklai, W.; Sakdapipanich, J.T. Effect of non-rubber components on storage hardening and gel formation of natural rubber during accelerated storage under various conditions. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2003, 76, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burfield, D.R. Epoxy groups responsible for crosslinking in natural rubber. Nature 1974, 249, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burfield, D.R.; Gan, S.N. Nonoxidative crosslinking reactions in natural rubber. I. Determination of crosslinking groups. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1975, 13, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, B.C. Inhibition of hardening in natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1960, 35, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, B.C. Degradation and crosslinking of polyisoprene in Hevea Brasiliensis latex during processing and storage. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Pol. Chem. 1960, 48, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.N.; Ting, K.F. Effect of treating latex with some metal ions on storage hardening of natural rubber. Polymer 1993, 34, 2142–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, A.H.; Tangpakdee, J.; Kawahara, S.; Tanaka, Y. Distribution and origin of abnormal groups in NR. J. Rubber Res. 1997, 12, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Huang, G.; Li, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Qu, W.; Xie, Z.; Wu, J. Research on architecture and composition of natural network in natural rubber. Polymer 2018, 154, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaypornsri, S.; Toki, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Sakdapipanich, J. The effects of endlinking network and entanglement to stress–strain relation and strain-induced crystallization of un-vulcanized and vulcanized natural rubber. Polymer 2012, 53, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; He, D.; Gao, X.; Yu, H. Effect of lipids on the stability of natural rubber latex and tensile properties of its films. J. Rubber Res. 2017, 20, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, E.; Nicolai, T.; Durand, D. Effect of random end-linking on the viscoelastic relaxation of entangled star polymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5205–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montfort, J.P.; Marin, G.; Monge, P. Effects of constraint release on the dynamics of entangled linear polymer melts. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Huang, G.; Qu, L.; Wang, X.; Weng, G.; Wu, J. New insights into thermodynamic description of strain-induced crystallization of peroxide cross-linked natural rubber filled with clay by tube model. Polymer 2011, 52, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H.; Yee, L.; Cohen, C. Effect of network structure on the stress–strain behaviour of endlinked PDMS elastomers. Polymer 2010, 51, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.-H.; Wei, Y.-C.; Zhang, H.-F.; Luo, M.-C.; Zheng, T.-T.; Liao, S. Analysis of the thermogenesis mechanism of natural rubber under high speed strain. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 3, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Ute, K.; Kitayama, T.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E.; Kobayashi, A.; Tanaka, Y. Structural characterization of alpha-terminal group of natural rubber. 1. decomposition of branch-points by lipase and phosphatase treatments. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nun-anan, P.; Wisunthorn, S.; Pichaiyut, S.; Nathaworn, C.D.; Nakason, C. Influence of nonrubber components on properties of unvulcanized natural rubber. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 31, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Liu, G.-X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, F.; Liao, S.; Luo, M.-C. Exploring the unique characteristics of natural rubber induced by coordination interaction between proteins and Zn2+. Polymer 2020, 193, 122357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nun-anan, P.; Wisunthorn, S.; Pichaiyut, S.; Vennemann, N.; Nakason, C. Novel approach to determine non-rubber content in Hevea brasiliensis: Influence of clone variation on properties of un-vulcanized natural rubber. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 118, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Cai, X.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. The effects of proteins and phospholipids on the network structure of natural rubber: A rheological study in bulk and in solution. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.C.; Liu, G.X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.Z.; Liao, S.; Luo, M.C. Mimicking the mechanical robustness of natural rubber based on a sacrificial network constructed by phospholipids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14468–14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippel, M.M.; Leite, C.A.P.; Lee, L.-T.; Galembeck, F. Direct imaging and elemental mapping of microgels in natural rubber particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 283, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippel, M.M.; Paula Leite, C.A.; Galembeck, F. Elemental mapping in natural rubber latex films by electron energy loss spectroscopy associated with transmission electron microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oouchi, M.; Ukawa, J.; Ishii, Y.; Maeda, H. Structural analysis of the terminal groups in commercial hevea natural rubber by 2D-NMR with DOSY filters and multiple-wet methods using ultrahigh-field NMR. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Tarachiwin, L.; Kum-ourm, H.; Matsuura, A.; Fushihara, K.; Ute, K. Characterization of natural rubber end groups using high-sensitivity NMR. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkriengkrai, D.; Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Tanaka, Y. Structural characterization of terminal groups in natural rubber: Origin of nitrogenous groups. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2007, 79, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopoulos, S.X.; Forte, G.; Ronca, S. Relaxation dynamics in disentangled ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene via torsional rheology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4515–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaro, P.A.P.; da Cunha, G.P.; Pinto, J.M.; Munaro, M.; de Azevedo, E.R.; Akcelrud, L.C. Ageing and structural changes in PDMS rubber investigated by time domain NMR. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2019, 166, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, V.; Lavallata, V. Entanglement locking in the unique elasticity of polydimethylsiloxane rubbers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 1900497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, A.; Verron, E.; Huneau, B. A physically-based model for strain-induced crystallization in natural rubber. Part II: Derivation of the mechanical model. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 125, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Sriring, M.; Sakdapipanich, J.T. Molecular structure and storage hardening of natural rubber: Insight into the reactions between hydroxylamine and phospholipids linked to natural rubber molecule. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H. Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J. Rheol. 1986, 30, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, C.; Luo, M.; Qu, W.; Liu, H.; Gu, Z.; Jing, L.; Huang, G.; Zheng, J. A rheological study on non-rubber component networks in natural rubber. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91742–91750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeurle, S.A.; Hotta, A.; Gusev, A.A. A new semi-phenomenological approach to predict the stress relaxation behavior of thermoplastic elastomers. Polymer 2005, 46, 4344–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögl, S.; Trutschel, M.-L.; Chassé, W.; Riess, G.; Saalwächter, K. Entanglement effects in elastomers: Macroscopic vs microscopic properties. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2759–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Luo, M.; Liao, S. The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage. Polymers 2020, 12, 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122880
Zhang H, Zhang L, Chen X, Wang Y, Zhao F, Luo M, Liao S. The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122880
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huifeng, Lu Zhang, Xu Chen, Yueqiong Wang, Fuchun Zhao, Mingchao Luo, and Shuangquan Liao. 2020. "The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122880
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhang, L., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, F., Luo, M., & Liao, S. (2020). The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage. Polymers, 12(12), 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122880




