Preparation and Characterization of a Composite Dust Suppressant for Coal Mines
Abstract
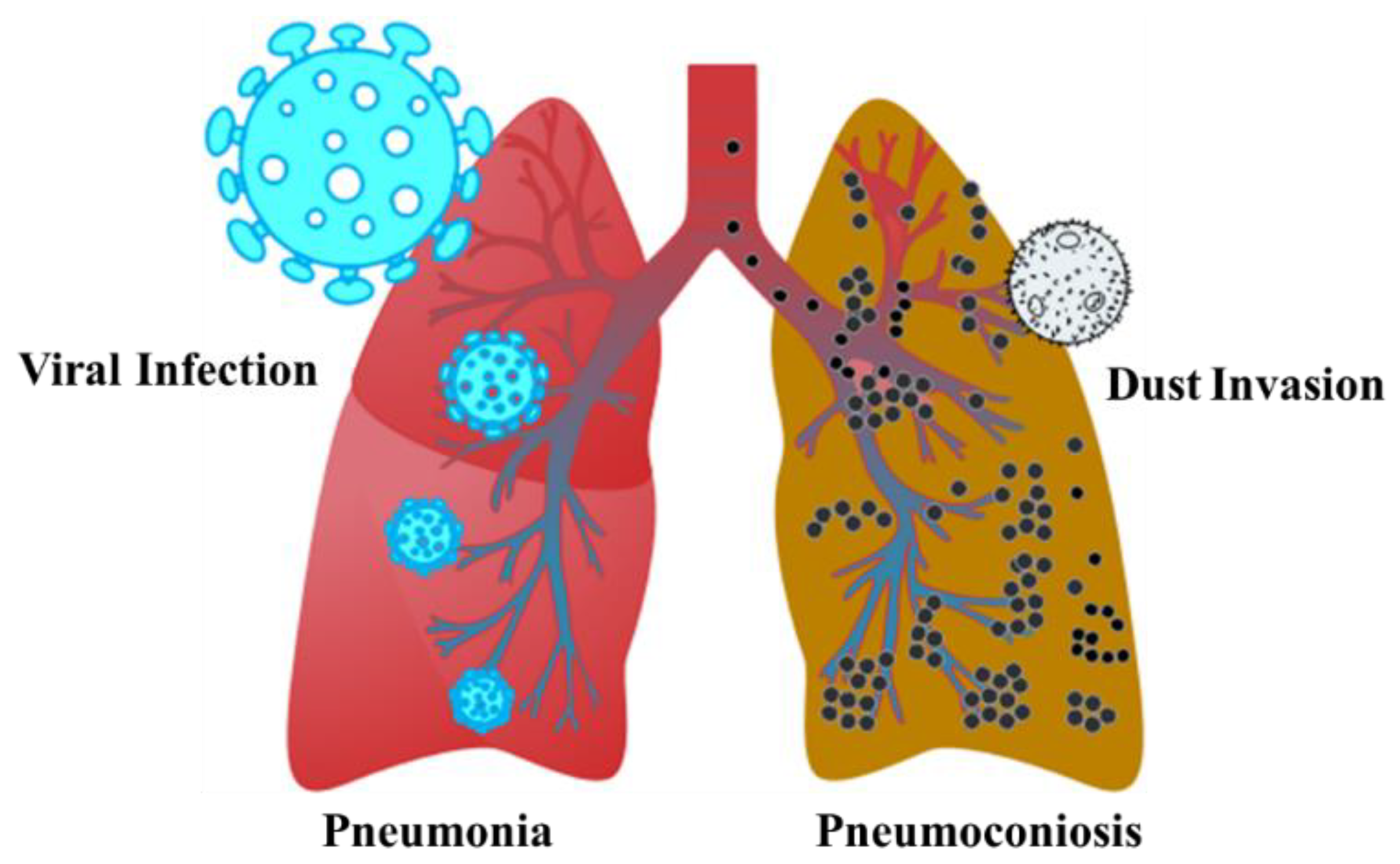
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Reagents and Equipment
2.2. Test of Coal Dust Particle Size
2.3. Optimization of Surfactants
2.3.1. Dynamic Contact Angle Test
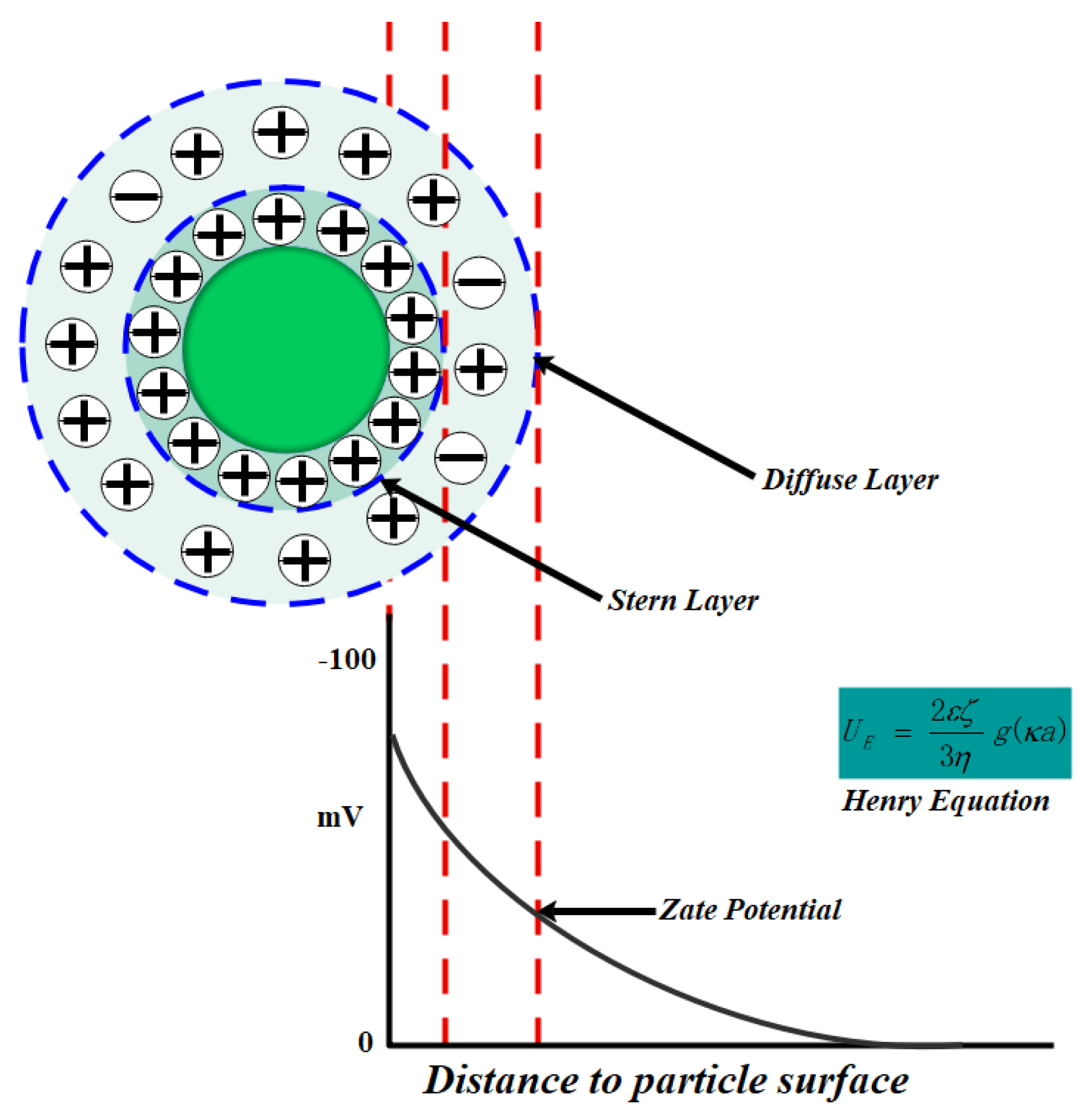
2.3.2. Zeta Potential Test of Coal Dust
- (1)
- First, surfactant solutions of different concentrations were prepared in deionized water. Each equal amount of coal powder was put into the surfactant solution for ultrasonic dispersion for 20 min, and the mixture was configured into a uniform suspension. The suspension was prepared in a neutral environment at a room temperature of 23 °C.
- (2)
- The suspension was poured into the sample cell and the lid closed, and the sample cell was put into the zeta potential measuring instrument.
- (3)
- The test software was opened, the parameter values of the sample to be tested were set, such as shading, refractive index, concentration, dielectric constant, etc., and three measurements were taken.
- (4)
- After waiting for the result to come out, the data was recorded and the results saved.
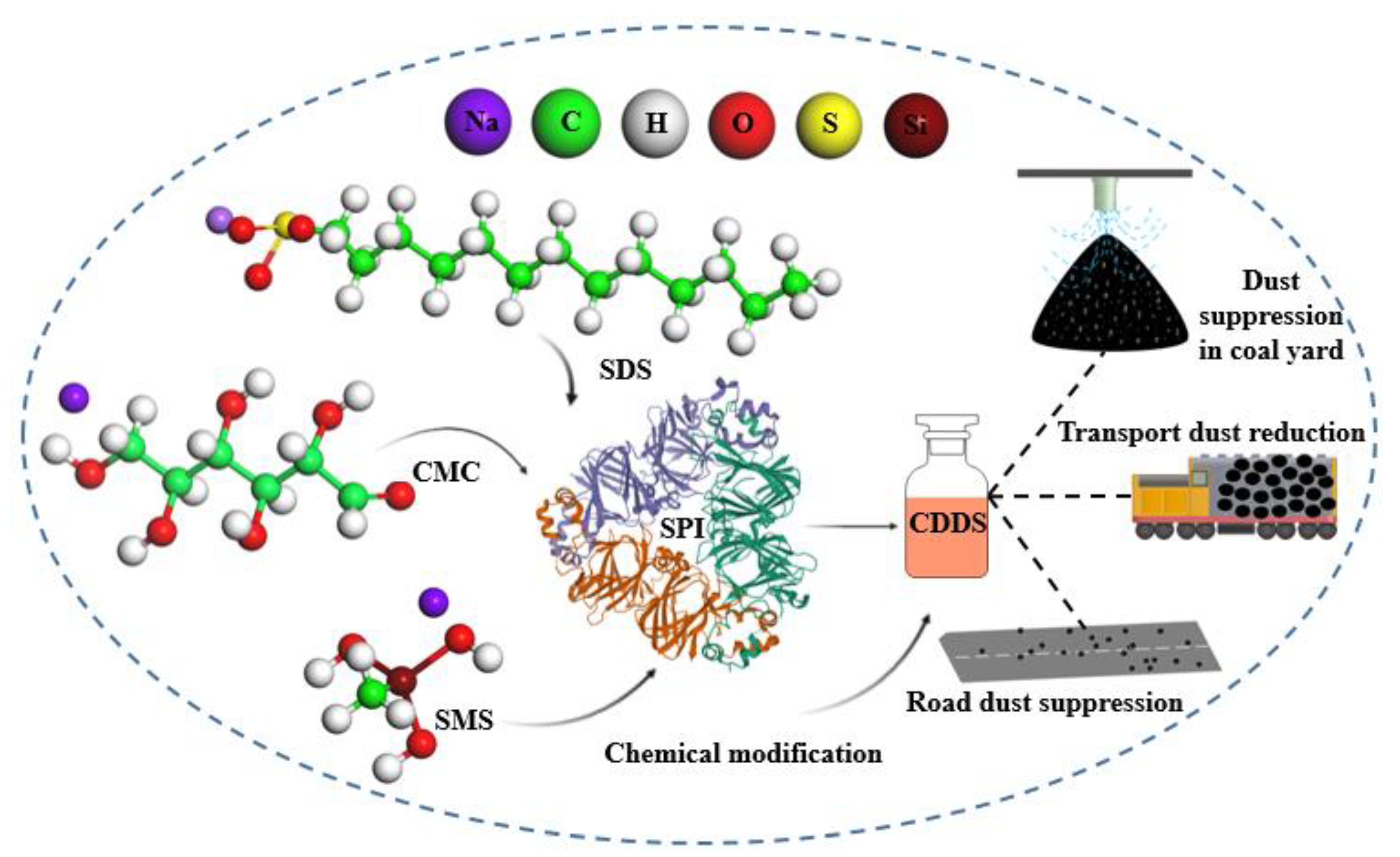
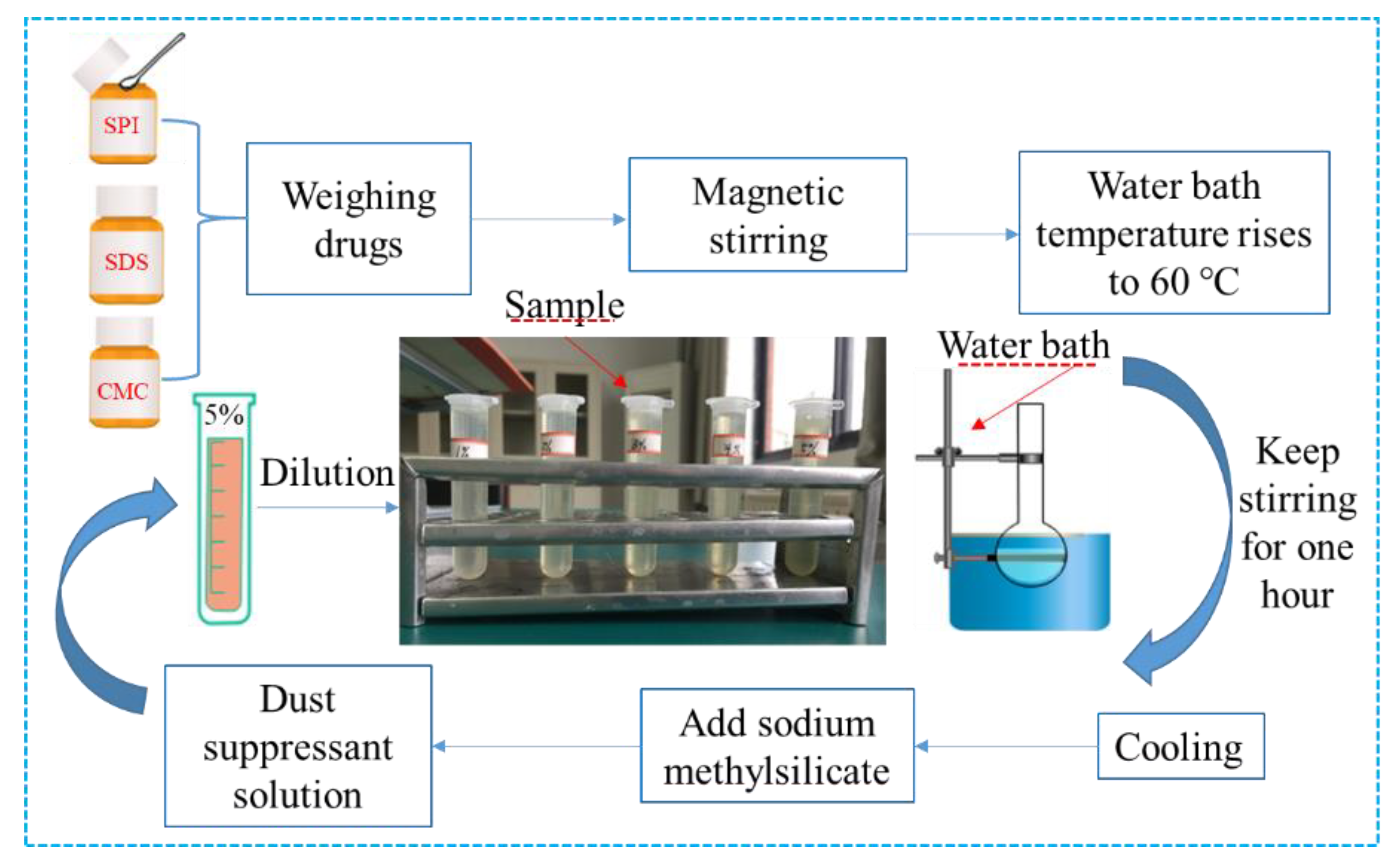
2.4. Preparation of Composite Dust Suppressant
2.5. Viscosity Experiment Test of Dust Suppressant
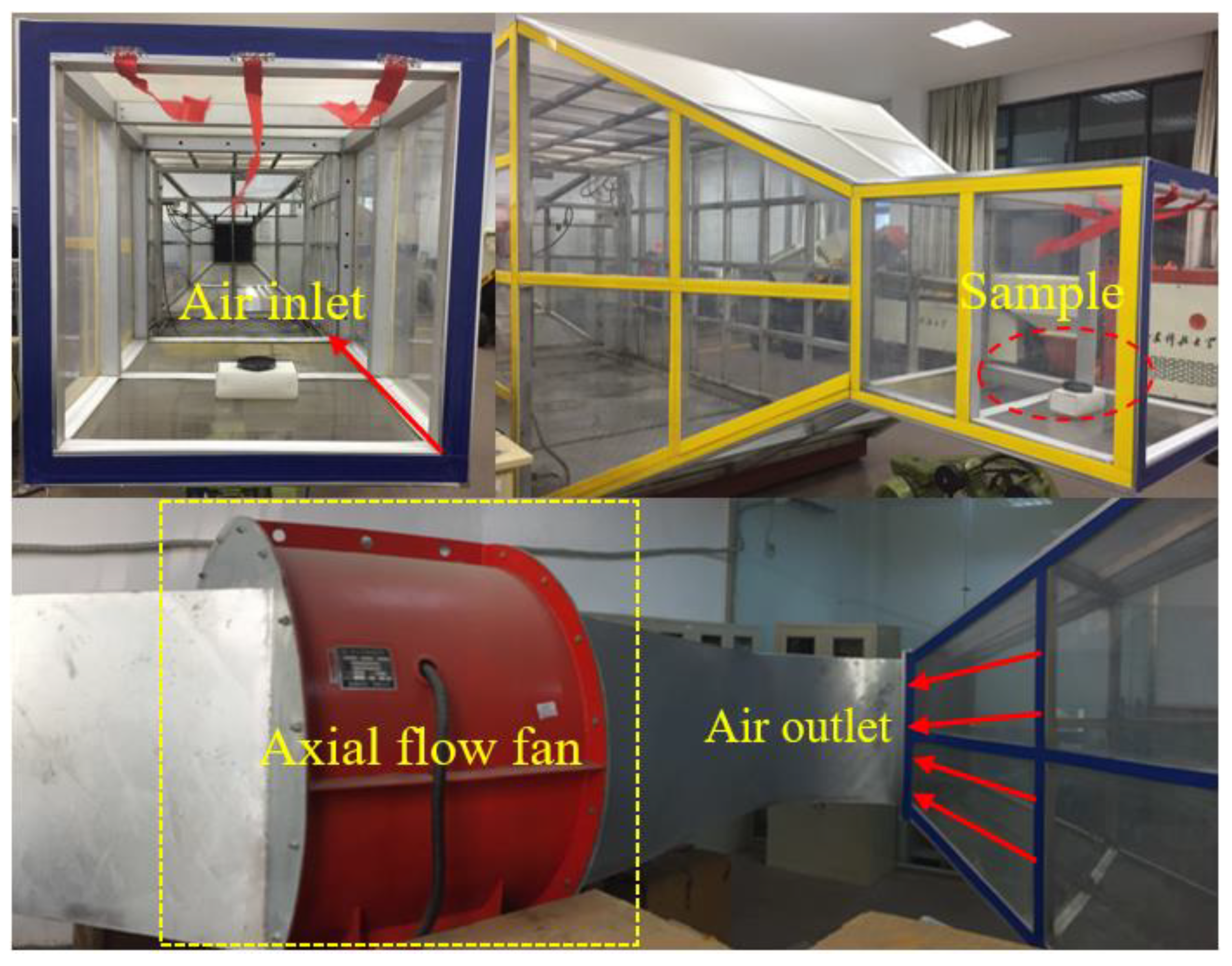
2.6. Anti-Wind Erosion Test of Dust Suppressant
2.7. Characterization Method of Dust Suppressant
- (1)
- Observation with scanning electron microscope (SEM)
- (2)
- X-ray diffraction test (XRD).
- (3)
- Thermogravimetric test (TGA).
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Coal Dust Particle Size Analysis
3.2. Dynamic Contact Angle Experiment Analysis
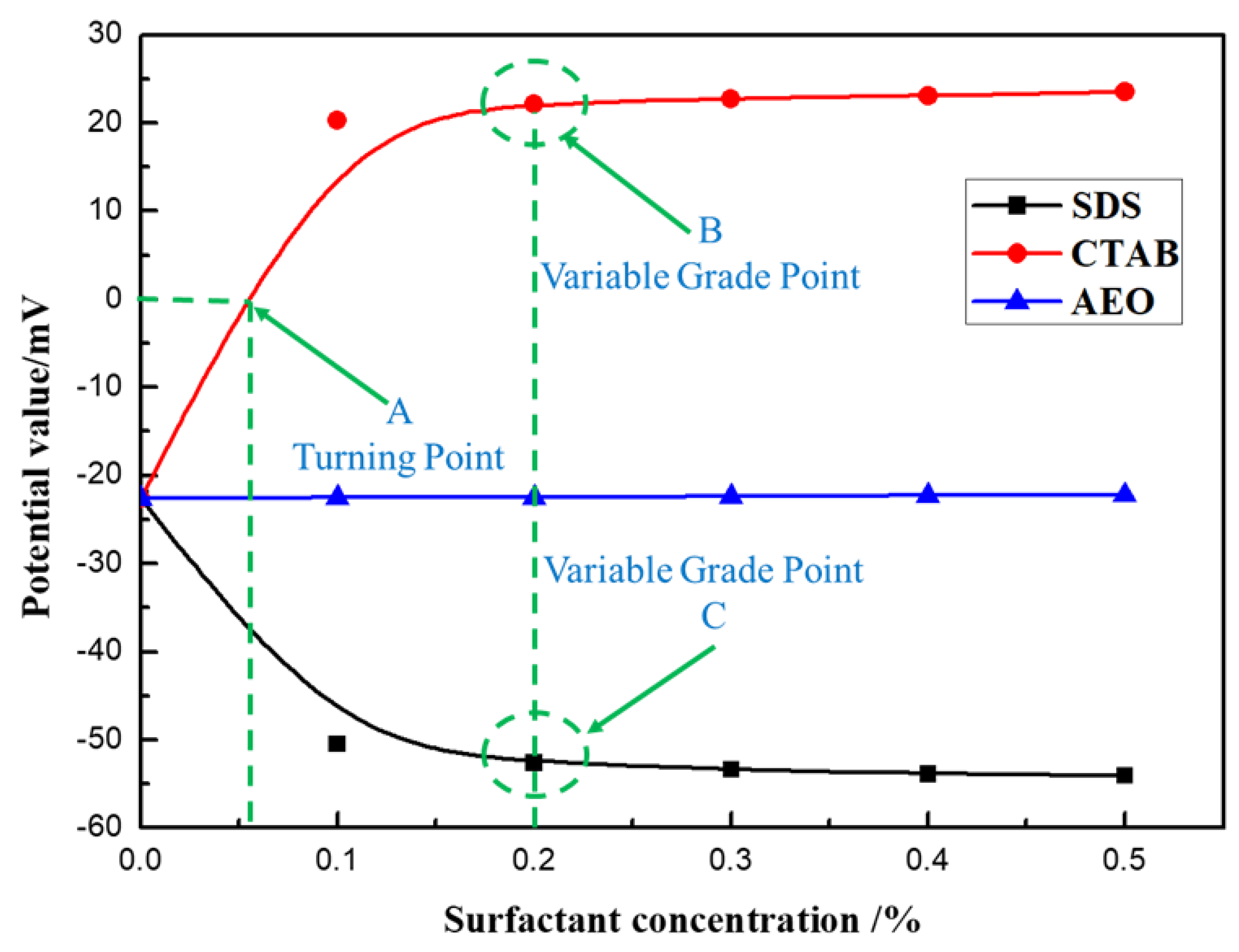
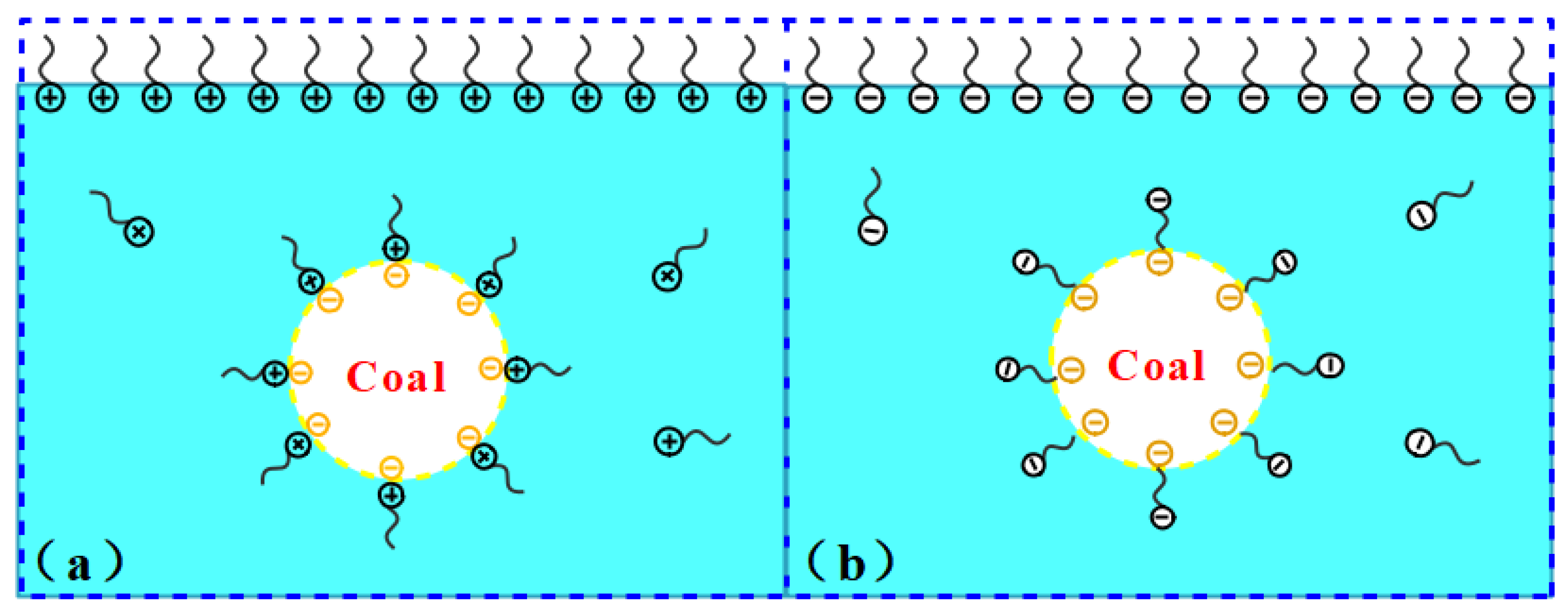
3.3. Zeta Potential Test Analysis
3.4. Viscosity Experiment Analysis
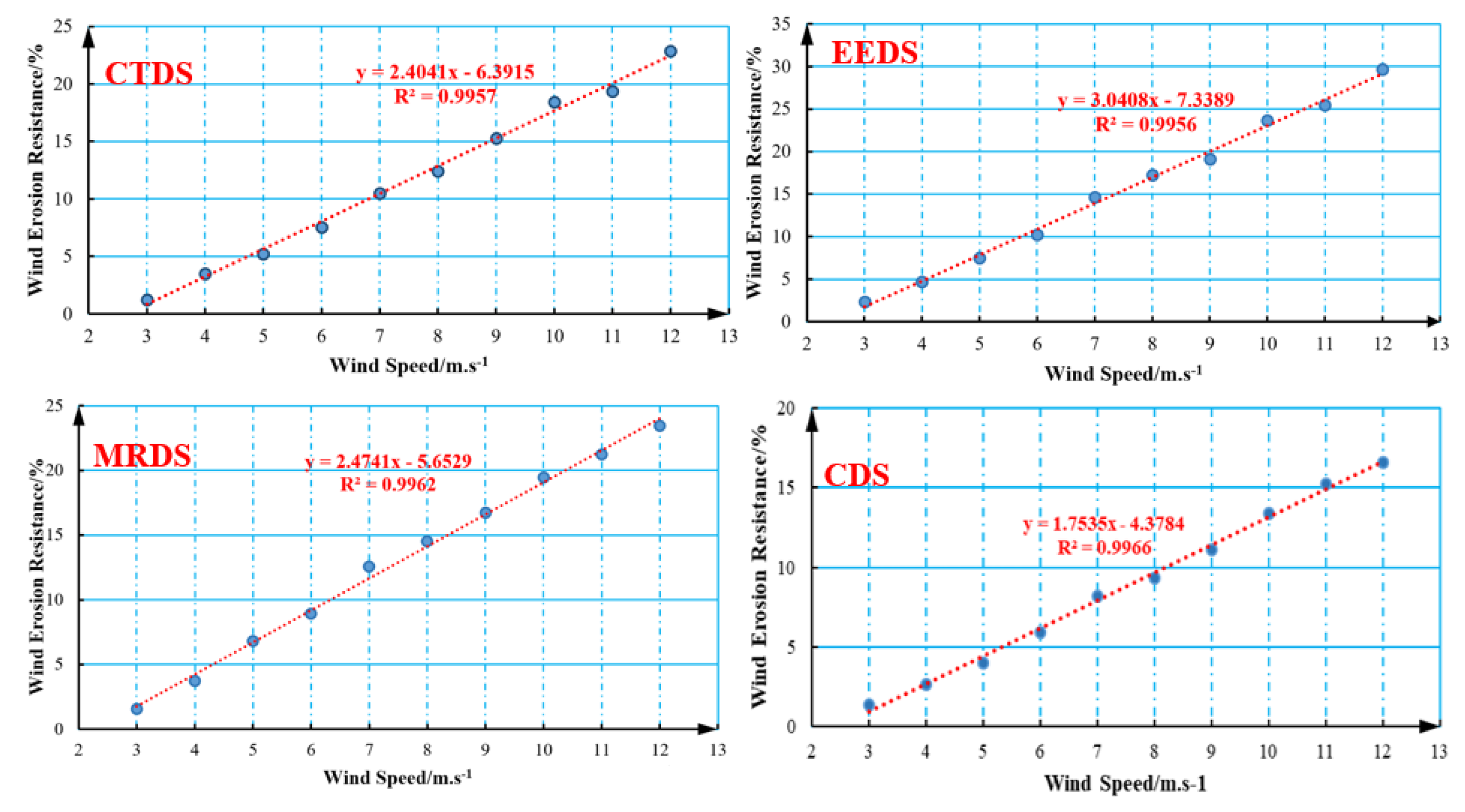
3.5. Analysis of Anti-Wind Erosion Test of Dust Suppressant
3.6. Characterization Results and Discussion
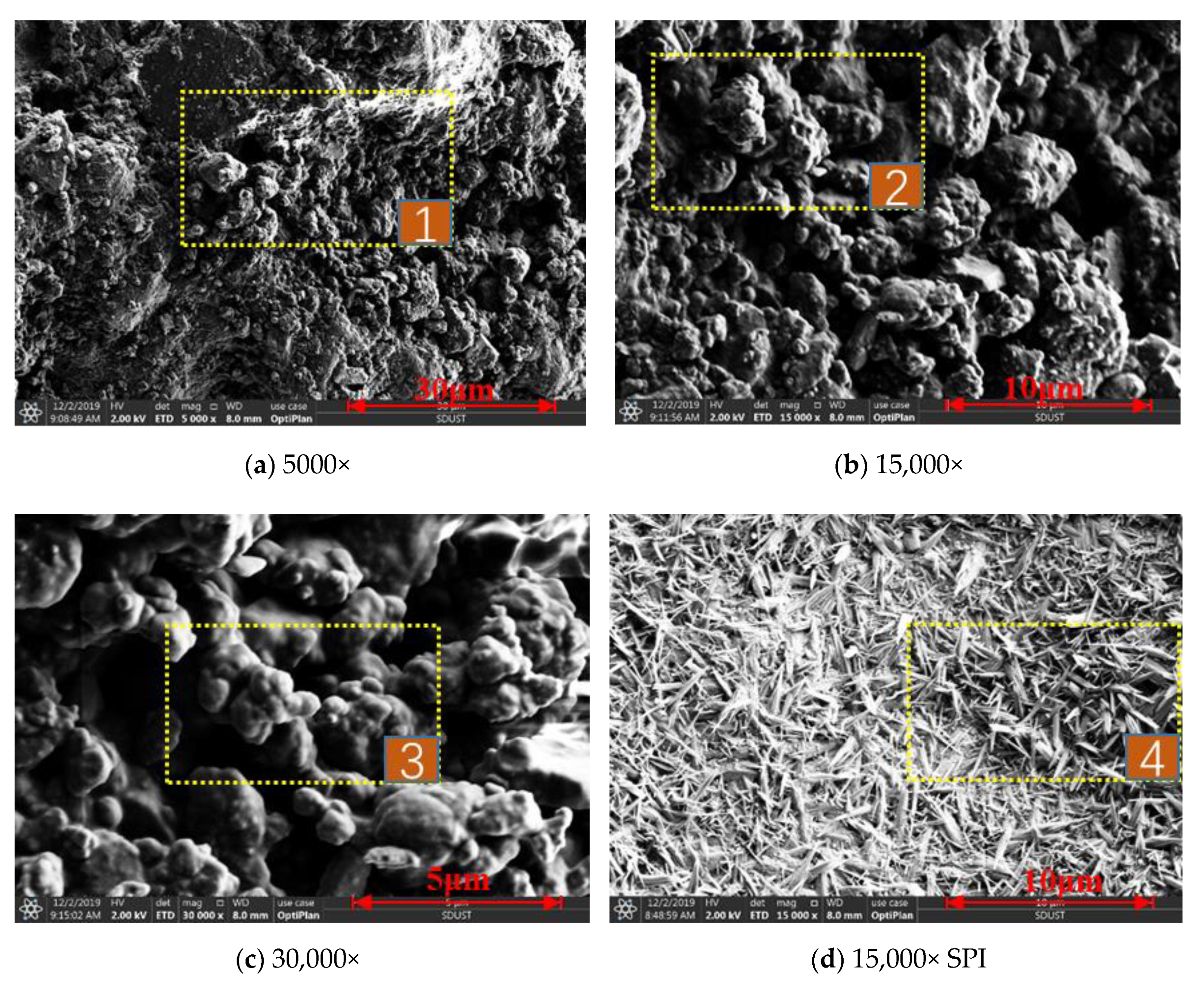
- (1)
- The morphology of the surface of coal dust sprayed with CDS as well as the surface of CDS was observed with SEM. The scanned image is shown in Figure 12.
- (2)
- The crystallization of soy protein isolate and CDS after film formation was observed with XRD.
- (3)
- The TG-DTG curve is obtained by testing the dust suppressant samples. As shown in Figure 14.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Dynamic contact angle measurements showed that the anionic surfactant SDS had good wetting of coal briquette samples, with a minimum contact angle of 40.09°. SDS reduced the zeta potential of a pulverized coal solution, increasing its electronegativity and also its wetting ability. Among the three surfactants tested, the anionic surfactant SDS at a concentration of 2 wt% was preferred as an additive to the for the composite dust suppressant CDS.
- (2)
- The performance of CDS prepared by the chemical modification method was compared to common, commercially available chemical dust suppressants. It was found that the viscosity of the four different types of dust suppressants increased with an increase in dust suppressant concentration. CDS had a maximum viscosity of 22.7 mPa·s at a concentration of 5 wt%. Moreover, it had relatively good anti-wind erosion ability, good dust suppression capacity, and could effectively inhibit dust pollution.
- (3)
- SEM, XRD, and TGA were used to characterize the properties of CDS. Modification of the soy protein isolate caused its crystallinity density to improve. After spraying the coal dust surface with CDS, it could effectively coat the coal dust to form a dense and hard solidified shell. CDS exhibited good wind erosion resistance and had good thermal stability, indicating that it should be adaptable to harsh environments.
- (4)
- The soy protein isolate used in the experiment is a green and environment-friendly polymer material with a wide range of sources, a relatively low processing cost, and a low price, and it is also biodegradable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, M.Y.; Nie, W.; Zhou, W.W.; Yan, J.Y.; Bao, Q.; Guo, C.J.; Tong, P.; Zhang, H.H.; Guo, L.D. Determining the effect of the non-ionic surfactant AEO9 on lignite adsorption and wetting via molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and experiment comparisons. Fuel 2020, 278, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollipara, V.K.; Chugh, Y.P.; Mondal, K. Physical, mineralogical and wetting characteristics of dusts from Interior Basin coal mines. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 127, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Wei, W.L.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.H.; Peng, H.T.; Liu, Q. The effects of ventilation parameters on the migration behaviors of head-on dusts in the heading face. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 70, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Nie, W.; Wei, W.L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Peng, H.T. Research on multi-radial swirling flow for optimal control of dust dispersion and pollution at a fully mechanized tunnelling face. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 79, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Wei, W.L.; Peng, H.T.; Cai, P.; Hua, Y.; Jin, H. The development and testing of a novel external-spraying injection dedusting device for the heading machine in a fully-mechanized excavation face. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Nie, W.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, H.K.; Jin, H.; Bao, Q. Synthesis and performance measurement of environment-friendly solidified dust suppressant for open pit coalmine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Nie, W.; Wang, H.K.; Bao, Q.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y.H. Preparation and experimental dust suppression performance characterization of a novel guar gum-modification-based environmentally-friendly degradable dust suppressant. Powder Technol. 2018, 339, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Nie, W.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.H.; Wang, H.K.; Jin, H. Preparation and characterization of a binary-graft-based, water-absorbing dust suppressant for coal transportation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 136, 47065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.B.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.T.; Pan, H.W.; Liu, D. Experimental study on modification of physicochemical characteristics of acidified coal by surfactants and ionic liquids. Fuel 2020, 266, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L. Trend of Dust Pollution, Prevalence Characteristics and Prediction of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis in a Mine in East China; Nanjing Medical University: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.X.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.Q.; Gu, Y.J. Study on LiFe0.2Mn0.8PO4/C cathode materials coated with different carbon contents. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, M.; Perera, H.; Gunawardana, B.; Manatunge, J. Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: A critical review on the unresolved dichotomy. Environ Res. 2020, 188, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Hama, S.; Omidvarborna, H.; Sharma, A.; Sahani, J.; Abhijith, K.V.; Debele, S.E.; Zavala-Reyes, J.C.; Barwise, Y.; Tiwari, A. Temporary reduction in fine particulate matter due to ‘anthropogenic emissions switch-off’ during COVID-19 lockdown in Indian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xu, H.H.; Shu, X.Q. Application of chemical dust suppressor in coal dust suppression. China Coal. 2007, 8, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.D. Study on Coal Dust Suppression and Crusting for Coal Pile Based on a Compound Binder; China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, M.J.; Wen, H. Research application status and development of dust suppressant. Safety Coal Mines. 2018, 49, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Li, X.F.; Yang, J.L.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.W. Analysis of hydrogenation product by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.S.; Yang, K.; Li, H.X.; Han, H. Screening and Property of Composite Dust Suppressant in Coal Mine. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.A.; Jiang, L.; Chen, J.S. Experiments on the foaming agent formula of froth dedusting during down-the-hole drilling in open-pit mine. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, L.J.; Yang, C. Inhibition characteristics of polymer suppressant on fine particles in lignite mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysztof, C.; Bogdan, M. ANETA W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of coal and mine dust wetting. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inyang, H.I.; Bae, S.; Pando, M.A. Contaminant dust suppression materials: A cost-effectiveness estimation methodology. Measurement 2016, 93, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardsson, K.; Magnusson, R. Impact of Fine Materials Content on the Transport of Dust Suppressants in Gravel Road Wearing Courses. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhou, G.; Li, S.L.; Wang, C.M.; Liu, R.L.; Jiang, W.J. Molecular dynamics simulation and experimental characterization of anionic surfactant: Influence on wettability of low-rank coal. Fuel 2020, 279, 118323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Nie, W.; Cai, P.; Liu, Z.Q. The diffusion of dust in a fully-mechanized mining face with a mining height of 7 m and the application of wet dust-collecting nets. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G. Acoustic emission monitoring and early warning method for stress-dominated coal-gas dynamic disasters in deep mines. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 39, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.G.; Jia, R.L. The Effect of Polyethylene Glycol (300) on the Performance SPI/GF Composite. Lastics Addit. 2013, 3, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.H.; Liang, H.; Gong, W.R.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y.M.; Tian, W.Q.; Chen, Y. Effects of Storage Conditions on the Structure and Properties of Cellulose/Soy Protein Isolate Composite Membranes. J. Wuhan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 58, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, N.; Maruyama, Y.; Tsuruki, T.; Okuda, E.; Yoshikawa, M.; Utsumi, S. Crystal Structure of Soybean beta-Conglycinin Beta Homotrimer (I122M/K124W). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1648, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.D.; Lin, M.S.; Luo, Y.B.; Dong, J.F. Preparation and properties of a new type of coal dust suppressant. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Nie, W.; Zhang, H.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Bao, Q.; Wang, H.K.; Huang, D.M. The preparation and characterization of a novel environmentally-friendly coal dust suppressant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Nie, W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, H.K.; Zhang, H.H.; Bao, Q.; Yan, J.Y. Development of environmental friendly dust suppressant based on the modification of soybean protein isolate. Processes 2019, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, S.C.; Kang, Z.W.; Jing, D.J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.X. Experimental study on performance of a new type macromolecule dust suppressant. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 12, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.S. The improvement of addition of sodium sulfate on wettability of coal dust by anionic surfactants. J. Saf. Environ. 2001, 1, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.C.; Ruan, Q.; Lv, Z.Y.; Wang, M.J. Research Progress and Application of Surfactants in Analytical Chemistry. Yunnan Chem. Technol. 2013, 40, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tan, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.H.; Shang, Y.D.; Zhao, W.B. Study on the coal dust surface characteristics and wetting mechanism. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 7, 737–740. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Valiullina, Y.A.; Faizullin, D.A.; Kurbanov, R.K.h.; Ermakova, E.A. Spectroscopic, zeta potential and molecular dynamics studies of the interaction of antimicrobial peptides with model bacterial membrane. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 242, 118785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.Z.; Wen, X.L.; Ding, Y.M.; Ouyang, J.M. Adsorption of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide on Different-sized Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals. J. Inorg. Mater. 2016, 31, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Panchal, A.; Rawil, F.; Anna, S.; Vladimir, V.; Yuri, L. An assembly of organic-inorganic composites using halloysite clay nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 45, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, L.; Giuseppe, C.; Pooria, P.; Stefana, M.; Giuseppe, L. Why does vacuum drive to the loading of halloysite nanotubes? The key role of water confinement. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 547, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.S.; Zhu, L.J.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Xia, D.H. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Structural Properties and Catalytic Performance of Novel Amorphous NiP/Hβ Catalyst for n-Hexane Isomerization. Catalysts. 2020, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Hu, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Cheng, W.M.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhu, S.C.; Lu, W.; Song, C.Y. Preparation and performance evaluation of environment-friendly biological dust suppressant. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Hu, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.L. Study on preparation and properties of environmentally-friendly dust suppressant with semi-interpenetrating network structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.T.; Nie, W.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xiu, Z.H.; Yang, S.B.; Xu, C.W.; Ma, Q.X.; Guo, C. Optimization of external spray negative-pressure mist-curtain dust suppression devices for roadheaders based on a multi-factor orthogonal experiment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H. Experiment Study on Performance of Adhesive Dust-Suppressor Used in Coal Storage and Transport; North China University of Science and Technology: Qinhuangdao, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Meng, X.B. An investigation on the aluminum dustexplosion suppression efficiency and mechanism of a NaHCO3/DE composite powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3246–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, X.B.; Yan, K.; Ma, X.S.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Bai, J.C. Inhibition effects of Al(OH)(3) and Mg(OH)(2) on Al-Mg alloy dust explosion. J. Loss Prevent. Proc. 2020, 66, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Types of Raw Materials | Raw Material Name | English Abbreviations | Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main reagents | Soy protein isolate | SPI | BR | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China |
| Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | CMC | CP | Xiya Reagent Co., Ltd., China | |
| Sodium methyl silicate | SMS | GR | Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong, China | |
| Surfactant | Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether | AEO | Tech | Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong, China |
| Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide | CTAB | Tech | Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong, China | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | SDS | Tech | Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shandong, China | |
| Dust Suppressant | Crust-type dust suppressant | CTDS | Tech | Dacheng County Yibo Chemical Co., Ltd., China |
| Mine road dust suppressant | MRDS | Tech | Langfang Tianshuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., China | |
| Efficient environmental dust suppressant | EEDS | Tech | Hebei Lankai Energy Saving Technology Co., Ltd., China |
| Experimental Apparatus | Model Name | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Malvern laser particle size analyzer | Mastersizer 3000 | Malvern, UK |
| Dynamic contact angle measuring instrument | KRUSS | KRüSS company |
| Zeta Potentiometer | ELSZ-2000 | Suzhou Otsuka Electronics Co., Ltd, China |
| Constant temperature magnetic heating stirrer | 85-1 | Shanghai meiyingpu Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd., China |
| Rotational viscometer | NDI-79 | Shanghai Precision Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| High resolution scanning electron microscope | APREO | Shanghai Casting Gold Analytical Instruments and Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| X-ray diffractometer | Rigaku Utima IV | Rigaku corperation |
| Thermogravimetric Analyzer | Labsys Evo | Mettler Toledo International Trading (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., China |
| Electronic analytical balance | ME104E | Tianjin Tianma Instruments Co., Ltd, China |
| Vacuum drying oven | DHG-9030 | Shanghai Yiheng technology mailbox company, China |
| Wind Speed | 3 m/s | 4 m/s | 5 m/s | 6 m/s | 7 m/s | 8 m/s | 9 m/s | 10 m/s | 11 m/s | 12 m/s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTDS | M1 | 90.23 | 90.43 | 89.23 | 88.45 | 90.28 | 89.24 | 87.98 | 89.56 | 90.23 | 90.85 |
| M2 | 89.10 | 87.25 | 84.58 | 81.76 | 80.81 | 78.15 | 74.55 | 73.07 | 72.74 | 70.07 | |
| δ1 | 1.25 | 3.52 | 5.21 | 7.56 | 10.49 | 12.43 | 15.27 | 18.41 | 19.38 | 22.87 | |
| MRDS | M3 | 88.35 | 89.56 | 88.65 | 89.23 | 89.28 | 89.67 | 88.79 | 88.63 | 89.25 | 88.39 |
| M4 | 86.96 | 86.22 | 82.60 | 81.26 | 78.07 | 76.65 | 73.94 | 71.37 | 70.28 | 67.65 | |
| δ2 | 1.57 | 3.73 | 6.82 | 8.93 | 12.56 | 14.52 | 16.72 | 19.47 | 21.25 | 23.46 | |
| EEDS | M5 | 87.36 | 87.23 | 87.64 | 87.98 | 88.23 | 88.25 | 87.68 | 87.73 | 88.15 | 88.24 |
| M6 | 85.31 | 83.15 | 81.04 | 79.00 | 75.29 | 73.03 | 70.90 | 66.96 | 65.69 | 62.04 | |
| δ3 | 2.35 | 4.68 | 7.53 | 10.21 | 14.67 | 17.25 | 19.14 | 23.67 | 25.48 | 29.69 | |
| CDS | M7 | 88.34 | 88.75 | 89.21 | 88.72 | 88.96 | 88.31 | 89.25 | 89.41 | 89.16 | 88.47 |
| M8 | 88.15 | 87.59 | 86.82 | 84.97 | 83.45 | 80.91 | 79.22 | 76.61 | 74.38 | 70.23 | |
| δ4 | 0.22 | 1.31 | 2.68 | 4.23 | 6.19 | 8.38 | 11.24 | 14.32 | 16.58 | 20.62 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Niu, K.; Wu, G.; Wei, X.; Wang, H. Preparation and Characterization of a Composite Dust Suppressant for Coal Mines. Polymers 2020, 12, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122942
Jin H, Zhang Y, Chen K, Niu K, Wu G, Wei X, Wang H. Preparation and Characterization of a Composite Dust Suppressant for Coal Mines. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122942
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Hu, Yansong Zhang, Kun Chen, Kuo Niu, Guangan Wu, Xiangrui Wei, and Houwang Wang. 2020. "Preparation and Characterization of a Composite Dust Suppressant for Coal Mines" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122942
APA StyleJin, H., Zhang, Y., Chen, K., Niu, K., Wu, G., Wei, X., & Wang, H. (2020). Preparation and Characterization of a Composite Dust Suppressant for Coal Mines. Polymers, 12(12), 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122942




