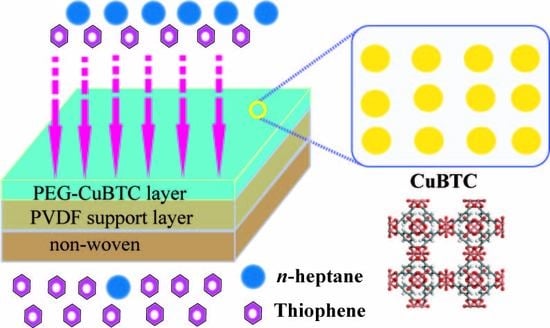
Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC
Abstract
Share and Cite
Cai, C.; Fan, X.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Vardhan, H. Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC. Polymers 2020, 12, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020414
Cai C, Fan X, Han X, Li J, Vardhan H. Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020414
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Caibin, Xiaotao Fan, Xiaolong Han, Jiding Li, and Harsh Vardhan. 2020. "Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC" Polymers 12, no. 2: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020414
APA StyleCai, C., Fan, X., Han, X., Li, J., & Vardhan, H. (2020). Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC. Polymers, 12(2), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020414