Emerging Developments in the Use of Electrospun Fibers and Membranes for Protective Clothing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Integrating Electrospinning with Textiles
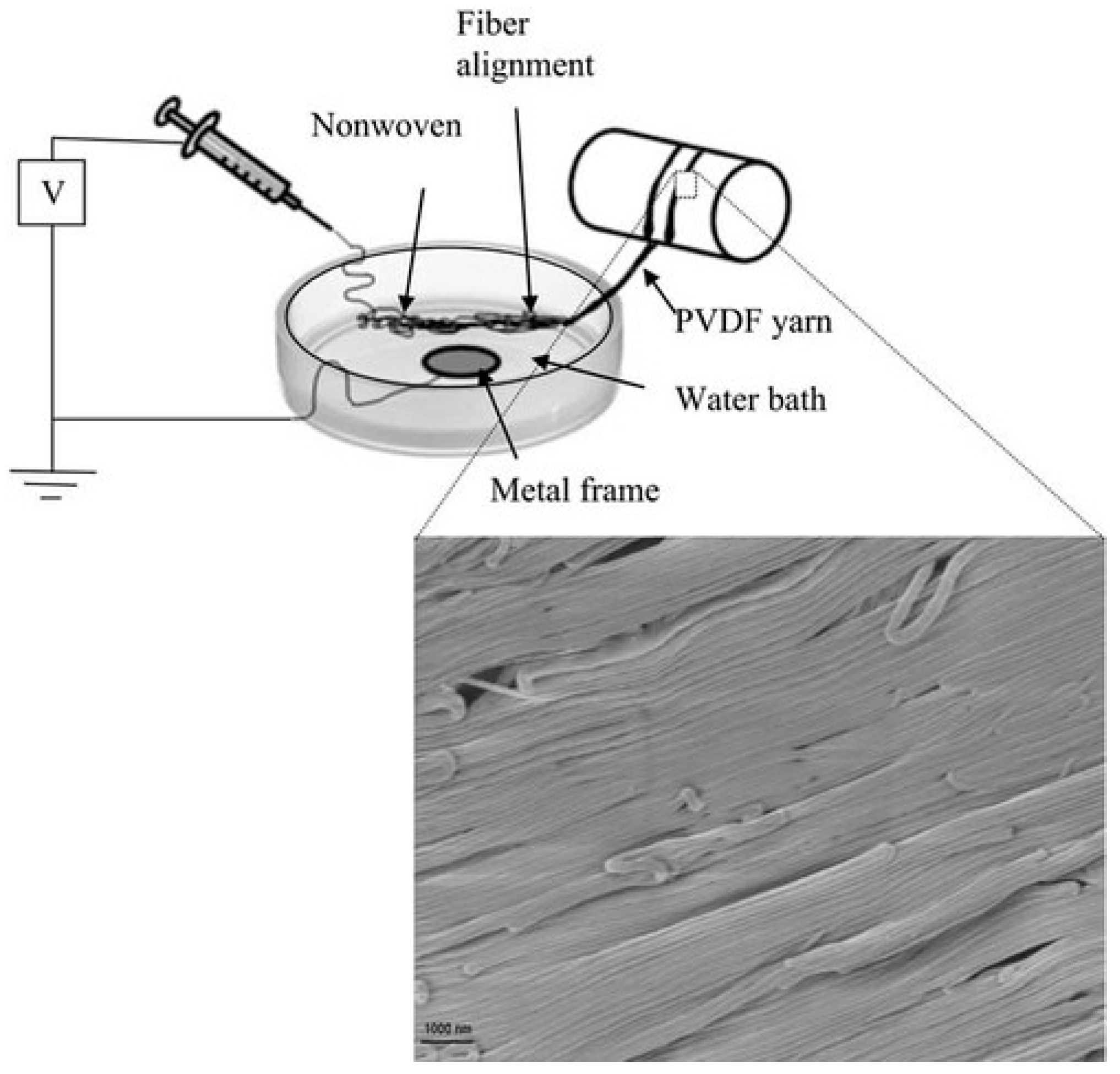
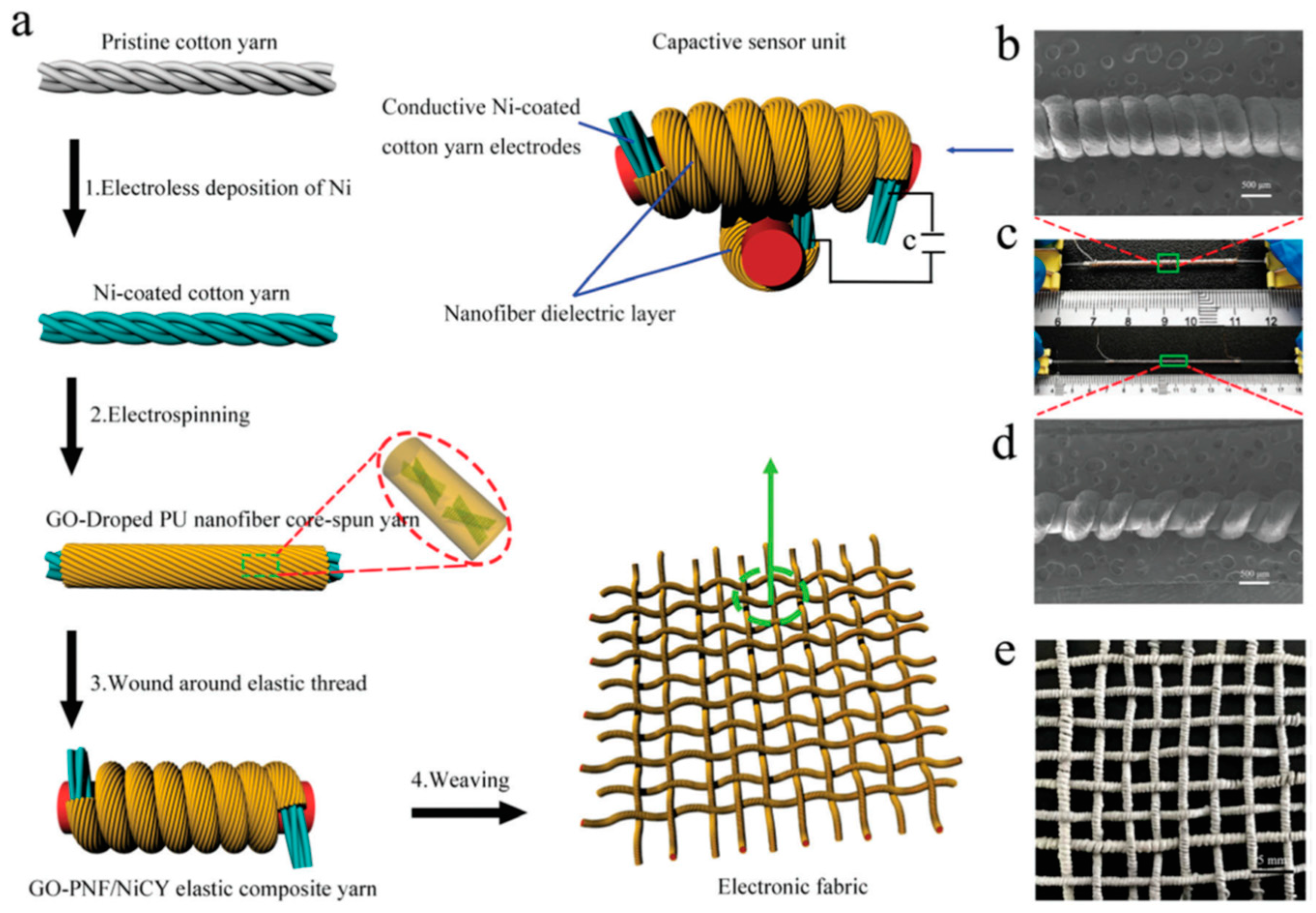
2.1. Yarns
2.2. Nonwovens
2.3. Composite Fibers and Multilayer Nanofiber Membrane
3. Protective Clothing
3.1. Protective Clothing against Micro and Nanoparticles
3.2. Protective Clothing against Liquid Penetration
3.3. Protective Clothing against Chemicals
3.4. Protective Clothing against Microbes
3.5. Protective Clothing against Heat and Thermal
3.6. Protective Clothing against Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, E.L.; Xu, Z.; Chur, L.K.; Behroozfar, A.; Baniasadi, M.; Moreno, S.; Huang, J.C.; Gilligan, J.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Nanofibrous Smart Fabrics from Twisted Yarns of Electrospun Piezopolymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24220–24229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Gibson, P.; Senecal, K.; Sennett, M.; Walker, J.; Yeomans, W.; Ziegler, D.; Tsai, P.P. Protective textile materials based on electrospun nanofibers. J. Adv. Mater. 2002, 34, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Obendorf, S.K. Developing protective textile materials as barriers to liquid penetration using melt-electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3430–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Developing UV-protective textiles based on electrospun zinc oxide nanocomposite fibers. Fibers Polym. 2009, 10, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Falco, F.; Guarino, V.; Gentile, G.; Cocca, M.; Ambrogi, V.; Ambrosio, L.; Avella, M. Design of functional textile coatings via non-conventional electrofluidodynamic processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 541, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teli, M.D.; Annaldewar, B.N. Superhydrophobic and ultraviolet protective nylon fabrics by modified nano silica coating. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G.W.; Ackerman, M.; Paskaluk, S.; Gholamreza, F. Characterization of textile fabrics under various thermal exposures. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S. Novel method for ultraviolet protection and flame retardancy of cotton fabrics by low-temperature plasma. Cellulose 2014, 21, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. A review on membrane engineering for innovation in wearable fabrics and protective textiles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bromberg, L.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Walker, J.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Chemical protection fabrics via surface oximation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile fiber mats. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.K.; Park, C.H.; Kim, J.; Kang, T.J. Application of electrospun polyurethane web to breathable water-proof fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2007, 8, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.G.; Shi, Z.J.; Deng, N.P.; Liang, Y.Y.; Kang, W.M.; Cheng, B.W. Designing waterproof breathable material with moisture unidirectional transport characteristics based on a TPU/TBAC tree-like and TPU nanofiber double-layer membrane fabricated by electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32155–32163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitchuli, N.; Shi, Q.; Nowak, J.; McCord, M.; Bourham, M.; Zhang, X.W. Electrospun Ultrathin Nylon Fibers for Protective Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.H.; Qin, X.H. Polyacrylonitrile nanofiber yarns and fabrics produced using a novel electrospinning method combined with traditional textile techniques. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtera, J.; Kalous, T.; Pokorny, P.; Batka, O.; Bilek, M.; Chvojka, J.; Mikes, P.; Kostakova, E.K.; Zabka, P.; Ornstova, J.; et al. Fabrication of dual-functional composite yarns with a nanofibrous envelope using high throughput AC needleless and collectorless electrospinning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gun, A.D. Dimensional, Physical and Thermal Properties of Plain Knitted Fabrics Made from 50/50 Blend of Modal Viscose Fiber in Microfiber Form with Cotton Fiber. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.R.; Zhu, H.J.; Hendrix, M.; Lousberg, N.; de With, G.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Xin, J.H. Temperature-Triggered Collection and Release of Water from Fogs by a Sponge-Like Cotton Fabric. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Integrating Substrate less Electrospinning with Textile Technology for Creating Biodegradable Three-Dimensional Structures. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5420–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, S.B.; Popovic, D.; Poparic, G.B. Thermal properties of textile fabrics made of natural and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.J.; Hong, W.G.; Kim, W.J.; Jun, Y.; Kim, B.H. A Novel Method for Applying Reduced Graphene Oxide Directly to Electronic Textiles from Yarns to Fabrics. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5701–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gora, A.; Anariba, F.; Baji, A. Enhanced tensile strength and electrical conductivity of electrospun polyacrylonitrile Yarns via post-treatment. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Du, X.S.; Wong, S.C. Improved Tensile Strength and Ferroelectric Phase Content of Self-Assembled Polyvinylidene Fluoride Fiber Yarns. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; He, J.X.; Wang, H.B.; Nan, N.; Qi, K.; Cui, S.Z. Fabrication of superhydrophobic nanofiber fabric with hierarchical nanofiber structure. E-Polymers 2017, 17, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.S.; Song, T.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Zein and Zein/Poly-L-lactide Nanofiber Yarns. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.Q.; Yao, C.; Song, T.Y.; Li, X.S. Fabrication of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanofiber yarns by conjugate electrospinning. J. Text. Inst. 2011, 102, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, H.; Sorrentino, L.; Laguna-Gutierrez, E.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Ardanuy, M. Gas Dissolution Foaming as a Novel Approach for the Production of Lightweight Biocomposites of PHB/Natural Fibre Fabrics. Polymers 2018, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.M.; Han, J.Q.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, M.; Vaquero, C.; Amantia, D. Development of Protective Clothing against Nanoparticle Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Nanomater. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Obendorf, S.K. Transport properties of layered fabric systems based on electrospun nanofibers. Fibers Polym. 2007, 8, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Rivin, D. Transport properties of porous membranes based on electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 187, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yin, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Li, C.J.; Pan, K. Wearable and Stretchable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Crumpled Nanofibrous Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12452–12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.L.; Zhu, M.M.; Shen, J.L.; Qiu, Q.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. All-Fiber Structured Electronic Skin with High Elasticity and Breathability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Y.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Liang, Z.W.; Li, H.F.; Ma, Y.J.; Feng, X. Fabrication of highly pressure-sensitive, hydrophobic, and flexible 3D carbon nanofiber networks by electrospinning for human physiological signal monitoring. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.X.; Kennedy, S.J.; Wu, Y.Q. Electrospinning materials for energy-related applications and devices. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 4886–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Domnner, M.; Chang, C.; Lin, L.W. Piezoelectric nanofibers for energy scavenging applications. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.E.; Tran, V.H.; Wang, J.B.; Fuh, Y.K.; Lin, L.W. Direct-Write Piezoelectric Polymeric Nanogenerator with High Energy Conversion Efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.F.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. One-Dimensional Composite Nanomaterials: Synthesis by Electrospinning and Their Applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ali, A.; Naguib, N.; Ye, H.H.; Yang, G.L.; Li, C.; Willis, P. Electrospinning of continuous carbon nanotube-filled nanofiber yarns. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.L.; He, J.X.; Nan, N.; Sun, X.Q.; Qi, K.; Zhou, Y.M.; Shao, W.L.; Liu, F.; Cui, S.Z. Stretchable capacitive fabric electronic skin woven by electrospun nanofiber coated yarns for detecting tactile and multimodal mechanical stimuli. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12981–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; He, J.X.; Wang, H.B.; Qi, K.; Nan, N.; You, X.L.; Shao, W.L.; Wang, L.D.; Ding, B.; Cui, S.Z. Highly sensitive, self-powered and wearable electronic skin based on pressure-sensitive nanofiber woven fabric sensor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Liu, K.; Zhang, R.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cui, Y. Roll-to-Roll Transfer of Electrospun Nanofiber Film for High-Efficiency Transparent Air Filter. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Wang, R.X.; Tang, G.S.; Mou, Z.P.; Lei, J.D.; Han, J.Q.; de Smedt, S.; Xiong, R.H.; Huang, C.B. Ecofriendly Electrospun Membranes Loaded with Visible-Light Responding Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Usages: Highly Efficient Air Filtration, Dye Scavenging, and Bactericidal Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12880–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambaer, W.; Zatloukal, M.; Kimmer, D. 3D modeling of filtration process via polyurethane nanofiber based nonwoven filters prepared by electrospinning process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barhate, R.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wei, H.H.; Wang, X.F. An electrospun polycarbonate nanofibrous membrane for high efficiency particulate matter filtration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65275–65281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, A.; Balazy, A.; Gradon, L. Application of nanofibers to improve the filtration efficiency of the most penetrating aerosol particles in fibrous filters. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Yap, C.C.; He, J.T.; Chen, C.; Wong, S.Y.; Li, X. Electrospinning: A facile technique for fabricating functional nanofibers for environmental applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strain, I.N.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Raza, A.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Tortuously structured polyvinyl chloride/polyurethane fibrous membranes for high-efficiency fine particulate filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, B.Y.; Shim, E.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Boehmite nanoparticles incorporated electrospun nylon-6 nanofiber web for new electret filter media. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cai, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.Y. Electret nanofibrous membrane with enhanced filtration performance and wearing comfortability for face mask. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolla, D.; Lolla, M.; Abutaleb, A.; Shin, H.U.; Reneker, D.H.; Chase, G.G. Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols. Materials 2016, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.X.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, X.; Wong, S.C.; Chase, G.G.; Qu, J.P.; Baji, A. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride containing nanoscale graphite platelets as electret membrane and its application in air filtration under extreme environment. Polymer 2017, 131, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, N.; Vijayalakshmi, E.; Robert, B.; Srinivasan, N.R. Development of PAN nano fibrous filter hybridized by SiO2 nanoparticles electret for high efficiency air filtration. J. Polym. Mater. 2018, 35, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.G.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Carbon Nanotubes Enhanced Fluorinated Polyurethane Macroporous Membranes for Waterproof and Breathable Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13538–13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Tailoring Water-Resistant and Breathable Performance of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibrous Membranes Modified by Polydimethylsiloxane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27218–27226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.F.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, G.N.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride fibrous membranes with simultaneously water/windproof and breathable performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87820–87827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Sheng, J.L.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, L.F.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Environmentally Friendly and Breathable Fluorinated Polyurethane Fibrous Membranes Exhibiting Robust Waterproof Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29302–29310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.X.; Wan, Y.Q.; Wu, W.W.; Yang, C.; He, J.H.; Cheng, J.H.; Jetter, R.; Ko, F.K.; Chen, Y.C. A lotus effect-inspired flexible and breathable membrane with hierarchical electrospinning micro/nanofibers and ZnO nanowires. Mater. Des. 2019, 162, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, X.H.; Si, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Waterproof and Breathable Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, e1800931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.L.; McAmish, L.; McCormick, A.V. Three-dimensional pore connectivity in bi-axially stretched microporous composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, R.S.; Cruz, M.; Mahfouz, N.G.A.; Qiu, Y.; Hurt, R.H. Breathable Vapor Toxicant Barriers Based on Multilayer Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5670–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.M.; Hong, Y.; Wan, Y.B.; Wang, Q.; Gong, M.L.; Wu, Z.G.; Guo, C.F. Thermal, Waterproof, Breathable, and Antibacterial Cloth with a Nanoporous Structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Clarizia, G.; Golemme, G.; Drioli, E. New breathable and waterproof coatings for textiles: Effect of an aliphatic polyurethane on the formation of PEEK-WC porous membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, F.F.; Yu, J.Y.; Ding, B. Hydrophobic Fibrous Membranes with Tunable Porous Structure for Equilibrium of Breathable and Waterproof Performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.M.; Wang, W.G.; Dong, A.J.; Zhang, J.H. A novel transdermal drug delivery system based on self-adhesive Janus nanofibrous film with high breathability and monodirectional water-penetration. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, A.S.; Baji, A. Electrospun Janus Membrane for Efficient and Switchable Oil-Water Separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaseshan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Zinc titanate nanofibers for the detoxification of chemical warfare simulants. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bromberg, L.; Lee, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Gibson, P.; Walker, J.; Hammond, P.T.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Multifunctional Electrospun Fabrics via Layer-by-Layer Electrostatic Assembly for Chemical and Biological Protection. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitchuli, N.; Shi, Q.; Nowak, J.; Kay, K.; Caldwell, J.M.; Breidt, F.; Bourham, M.; McCord, M.; Zhang, X.W. Multifunctional ZnO/Nylon 6 nanofiber mats by an electrospinning-electrospraying hybrid process for use in protective applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Park, M.K.; Kwak, S.Y. Silver-titania/polyurethane composite nanofibre mat for chemical and biological warfare protection. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 10, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, S.; Chandrasekaran, A.R.; Ramakrishna, S. An Update on Nanomaterials-Based Textiles for Protection and Decontamination. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3955–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Yimnirun, R.; Unruan, S. Electrospun barium titanate/cobalt ferrite composite fibers with improved magnetoelectric performance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55217–55223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Nanoscale investigation of ferroelectric properties in electrospun barium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride composite fibers using piezoresponse force microscopy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 44, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.G.; Wang, P.L.; Zhao, Z.G.; Ji, J.H. Antimicrobial Activity of Electrospun Poly(butylenes succinate) Fiber Mats Containing PVP-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, J.; Borges, J.P.; Boltes, K.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Rosal, R. Antimicrobial electrospun silver-, copper- and zinc-doped polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, N.L.; Ramaseshan, R.; Li, B.J.; Sundarrajan, S.; Barhate, R.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of nanofibers with antimicrobial functionality used as filters: Protection against bacterial contaminants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Argirova, M.; Rashkov, I. Antibacterial electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/ascorbyl palmitate nanofibrous materials. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Song, J.; Jung, Y.; Kweon, O.Y.; Song, H.; Jang, J. Electrospun ZnO/TiO2 composite nanofibers as a bactericidal agent. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9164–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Breu, J.; Hou, H.Q.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Gradient-Structured Nonflammable Flexible Polymer Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11876–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbezeanu, D.; Popa, A.M.; Stelzig, T.; Sava, I.; Rossi, R.M.; Fortunato, G. Preparation and characterization of thermally stable polyimide membranes by electrospinning for protective clothing applications. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.W.; Mandal, S.; Rossi, R.M. Effects of various factors on performance of thermal protective clothing. In Thermal Protective Clothing for Firefighters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 163–182. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.; Ku, B.C.; Emrick, T.; Coughlin, B.E.; Farris, R.J. Flame Resistant Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers from Deoxybenzoin-based Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Z.S.; Tan, L.H.; Cao, X.M.; Ju, F.Y.; Ying, S.J.; Xu, F.M. Preparation of melamine microfibers by reaction electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ma, B.C.; Reinholz, J.; Li, Q.F.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, K.A.I.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Efficient Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing and UV Protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29915–29922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.R.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.B.; Dong, W.J. The Formation and UV-blocking Property of Flower-like ZnO Nanorod on Electrospun Natural Cotton Cellulose Nanofibers. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.R.; Shu, S.X.; Chen, R.; Chen, B.Y.; Dong, W.J. Functionalization of electrospun nanofibers of natural cotton cellulose by cerium dioxide nanoparticles for ultraviolet protection. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, S.S.; Sariisik, M.; Aktas, A.H.; Ucar, M.C.; Erden, E. Modifying of Cotton Fabric Surface with Nano-ZnO Multilayer Films by Layer-by-Layer Deposition Method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becheri, A.; Durr, M.; Nostro, P.L.; Baglioni, P. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, M.M.A.; Farouk, A.; Sharaf, S. Flame retardancy and UV protection of cotton based fabrics using nano ZnO and polycarboxylic acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, H.R.; Bajgai, M.P.; Nam, K.T.; Seo, Y.A.; Pandeya, D.R.; Hong, S.T.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nylon-6 spider-net like nanofiber mat containing TiO2 nanoparticles: A multifunctional nanocomposite textile material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Song, Y.; Lee, S. Crosslinking of lignin/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite fiber webs and their antimicrobial and ultraviolet-protective properties. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baji, A.; Agarwal, K.; Oopath, S.V. Emerging Developments in the Use of Electrospun Fibers and Membranes for Protective Clothing Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020492
Baji A, Agarwal K, Oopath SV. Emerging Developments in the Use of Electrospun Fibers and Membranes for Protective Clothing Applications. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020492
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaji, Avinash, Komal Agarwal, and Sruthi Venugopal Oopath. 2020. "Emerging Developments in the Use of Electrospun Fibers and Membranes for Protective Clothing Applications" Polymers 12, no. 2: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020492
APA StyleBaji, A., Agarwal, K., & Oopath, S. V. (2020). Emerging Developments in the Use of Electrospun Fibers and Membranes for Protective Clothing Applications. Polymers, 12(2), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020492





