Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Epoxy Resin Specimens
2.2.2. Preparation of CFRP Plates
2.3. Immersion Conditions
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
2.4.2. Tensile Test
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
3.1.1. DMA of the Aged Epoxy Resins
3.1.2. DMA of Aged CFRP Composites
3.2. Tensile Properties
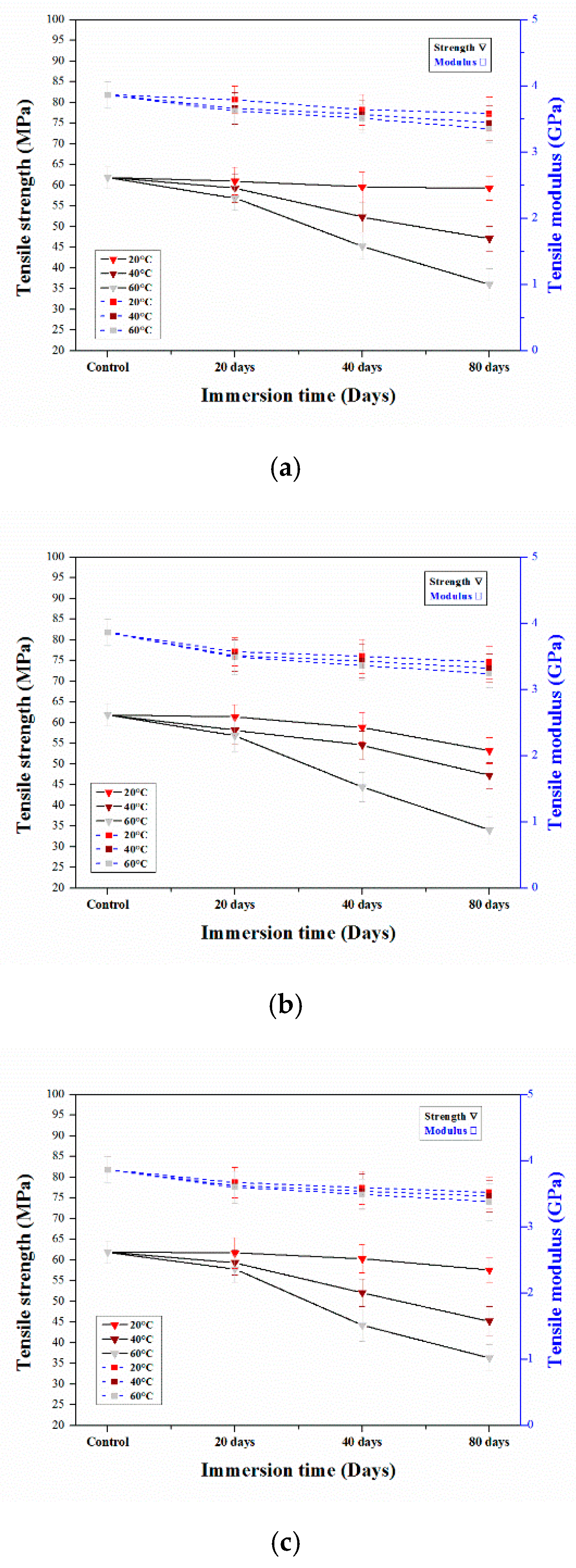
3.2.1. Tensile Properties of Aged Epoxy Resins
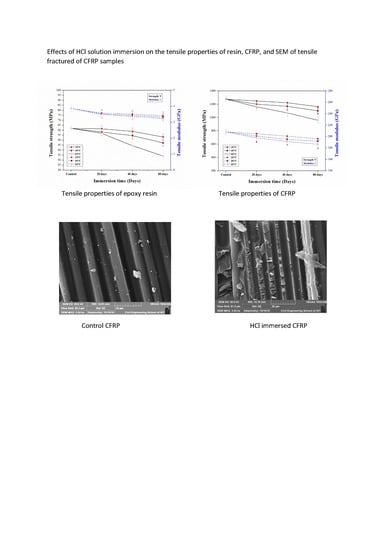
3.2.2. Tensile Properties of Aged CFRP Composites
3.3. Service Life Prediction of the CFRP Composite in the Three Solutions
3.3.1. Arrhenius Relationship
3.3.2. Degradation Prediction Procedure
3.3.3. Long-Term Tensile Strength Retention Prediction
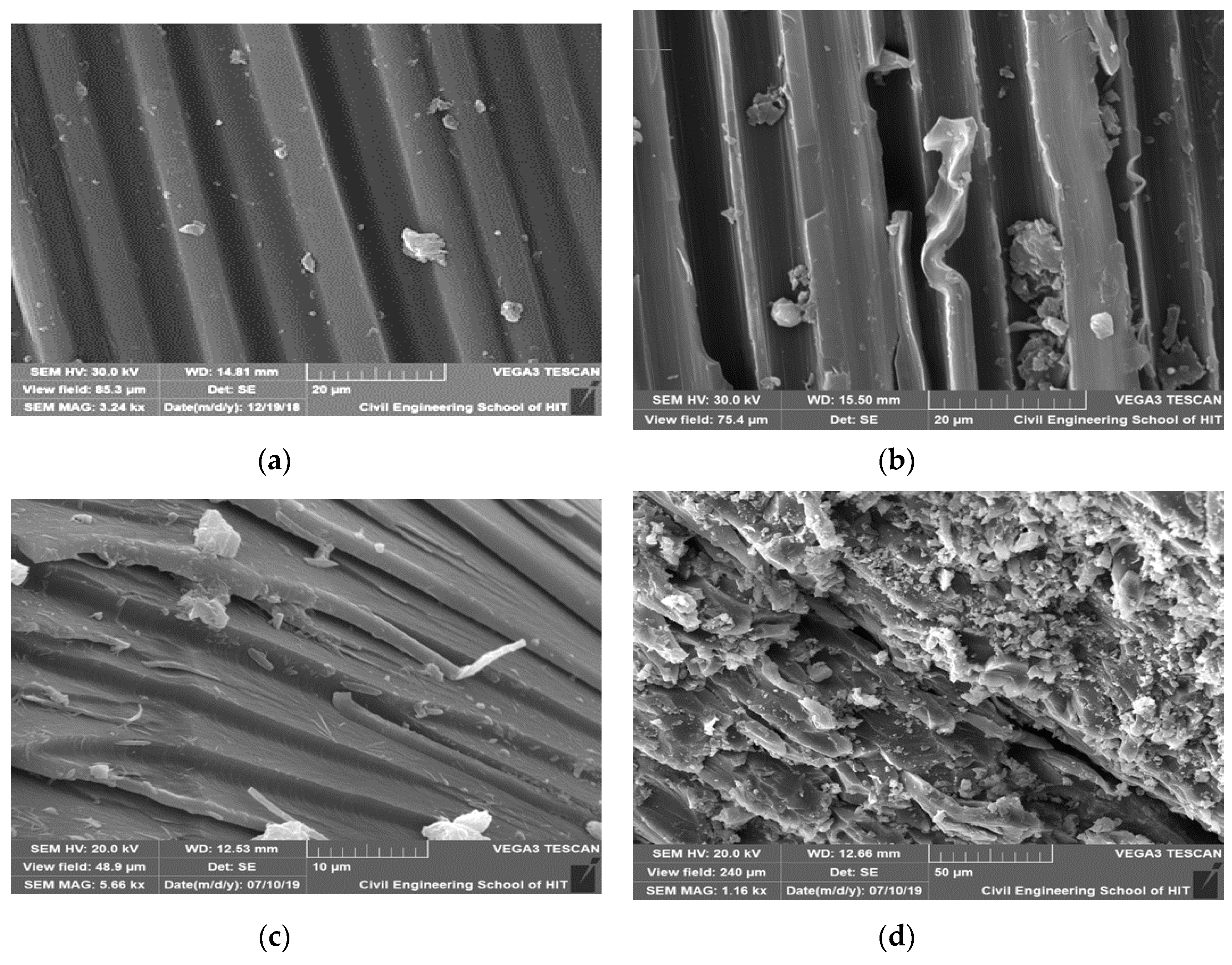
3.4. Morphological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzmán, E.; Cugnoni, J.; Gmür, T. Multi-factorial models of a carbon fibre/epoxy composite subjected to accelerated environmental ageing. Compos. Struct. 2014, 111, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C. Introduction: Engineering Requirements for Aerospace Composite Materials. In Polymer Composites in the Aerospace Industry; The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, A.J. Fracture Mechanics Characterization of Polymer Composites for Aerospace Applications. In Polymer Composites in the Aerospace Industry; Empa: Dubendorf, Switzerland; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, Z.K.; Aravinthan, T.; Zhuge, Y.; Gonzalez, F. A review of optimization techniques used in the design of fibre composite structures for civil engineering applications. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xian, G.; Karbhari, V.M. DMTA Based Investigation of Hygrothermal Ageing of an Epoxy System Used in Rehabilitation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Li, H.; Xian, G. Hygrothermal Ageing of Basalt Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. In Proceedings of the CICE 2010—The 5th International Conference on FRP Composites in Civil Engineering, Beijing, China, 27–29 September 2010; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, G.; Li, H.; Su, X. Effects of immersion and sustained bending on water absorption and thermomechanical properties of ultraviolet cured glass fiber-reinforced acylate polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, S.A.; Evernden, M.; Mitchels, J.; Zafari, B.; Mottram, J.T.; Papanicolaou, G.C. On the response to hygrothermal aging of pultruded FRPs used in the civil engineering sector. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dharsini, S.P.; Bhuvaneshwari, B.; Palani, G.S.; Ganesh, G.M.; Iyer, N.R. FEA Studies on the Interfacial Behavior of Epoxy-CFRP Composites. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2014, 4, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Abanilla, M.A. Design factors, reliability, and durability prediction of wet layup carbon/epoxy used in external strengthening. Compos. Part B 2007, 38, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, M.R.; Prolongo, S.G.; Ureña, A. Hygrothermal ageing of adhesive joints with nanoreinforced adhesives and different surface treatments of carbon fibre/epoxy substrates. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 40, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Lee, S.; Park, S. Polymer matrices for carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Carbon Lett. 2013, 14, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, A.; Douglas, E.P. Accelerated Testing of Epoxy-FRP Composites for Civil Infrastructure Applications : Property Changes and Mechanisms of Degradation. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pacheco, E.; Cauich-Cupul, J.I.; Valadez-González, A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xian, G.; Zhao, X.L. Effects of hydrothermal aging on carbon fibre/epoxy composites with different interfacial bonding strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.G.; Singh, R.P.; Nakamura, T. Degradation of Carbon Fiber-reinforced Epoxy Composites by Ultraviolet Radiation and Condensation. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2713–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.G.; Singh, R.P.; Nakamura, T. Factors governing water absorption by composite matrices. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 487–492. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Effects of Surface Treatment of Carbon Fiber : Tensile Property, Surface Characteristics, and Bonding to Epoxy. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 2921–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kolstein, H.; Bijlaard, F.S.K. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in pultruded fibre reinforced polymer composites of bridge decks. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertzen, W.K.; Kessler, M.R. Dynamic mechanical analysis of carbon/epoxy composites for structural pipeline repair. Compos. Part B 2007, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, B.; Hodgkin, J.; Krstina, J.; Mardel, J.; Tian, W. Accelerated aging versus realistic aging in aerospace composite materials. II. Chemistry of thermal aging in a structural composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3221–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, F.A.; Carlsson, L.A.; Acha, B.A. Evaluation of water degradation of vinylester and epoxy matrix composites by single fiber and composite tests. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 5230–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi, N.; Elleuch, K.; Ayedi, H.F. The effect of time and aging temperature on structural and mechanical properties of pipeline coating. Mater. Des. 2010, 30, 2006–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouani, S.; Curtil, L.; Hamelin, P. Ageing of carbon/epoxy and carbon/vinylester composites used in the reinforcement and/or the repair of civil engineering structures. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, S.; Pitarresi, G.; Spadaro, G. Effect of hydrothermal ageing on the thermal and delamination fracture behaviour of CFRP composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajorncheappunngam, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Gangarao, H.V.S. Effect of Aging Environment on Degradation of Glass-Reinforced Epoxy. J. Compos. Constr. 2002, 6, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, W.; Jaunich, M.; Mchugh, J. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of epoxy carbon- fibre prepregs partially cured in a discontinued autoclave analogue process. Polym. Test. 2015, 41, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, K.; Joseph, K.; Joseph, J.M.; Mathew, T.V. Degradation studies of coir fiber/polyester and glass fiber/polyester composites under different conditions. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 1571–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Bertocco, F.; Schjødt-Thomsen, J.; Rauhe, J.C. Investigation of the long term effects of moisture on carbon fibre and epoxy matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.B.C.M.; Raijmaekers, S.; Nijssen, R.P.L.; vander Meer, F.P.; Sluys, L.J. Hygrothermal ageing behaviour of a glass/epoxy composite used in wind turbine blades. Compos. Struct. 2017, 174, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Xian, G. Composites : Part B Hygrothermal effects on high V F pultruded unidirectional carbon/epoxy composites : Moisture uptake. Compos. Part B 2009, 40, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Haddar, N.; Elleuch, K.; Bienvenu, Y. Impact of aging conditions on mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4194–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Y.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, D.H.; Sun, T.; Xiao, H.Y.; Jia, J. Tensile strength of hygrothermally conditioned carbon/epoxy composites with voids. Energy Procedia 2011, 16, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Alzeebaree, R.; Çevik, A.; Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J. Mechanical properties and durability of unconfined and confined geopolymer concrete with fiber reinforced polymers exposed to sulfuric acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 215, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xian, G. Ageing of a thermosetting polyurethane and its pultruded carbon fiber plates subjected to seawater immersion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, N.; Ray, B.C. Acidic degradation of FRP composites. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Developments In Composites, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 14–15 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Amaro, A.M.; Reis, P.N.B.; Neto, M.A.; Louro, C. Effects of alkaline and acid solutions on glass/epoxy composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Mechanical properties and water absorption behaviour of recycled cellulose fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Haddar, N.; Elleuch, K.; Bienvenu, Y. Influence of thermal aging on tensile and creep behavior of thermoplastic polyurethane. Comptes Rendus Mec. 2011, 339, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, D.; Crane, R.L.; Pethrick, R.A.; Armstrong, G.S.; Banks, W.M. Dielectric and mechanical studies of the durability of adhesively bonded CFRP structures subjected to aging in various solvents. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2004, 218, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Abanilla, M.A.; Karbhari, V.M.; Li, Y. Interlaminar and intralaminar durability characterization of wet layup carbon/epoxy used in external strengthening. Compos. Part B 2006, 37, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xian, G.; Wu, G.; Raman, R.K.S.; Al-saadi, S. Durability study on interlaminar shear behaviour of basalt-, glass- and carbon-fibre reinforced polymer (B/G/CFRP) bars in seawater sea sand concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.-S. Prediction of Long-Term Performance and Durability of BFRP Bars under the Combined Effect of Sustained Load and Corrosive Solutions. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Davalos, J.F.; Ray, I. Durability Prediction for GFRP Reinforcing Bars Using Short-Term Data of Accelerated Aging Tests. J. Compos. Constr. 2007, 10, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.; Karbhari, V.M. Effect of Water Sorption on Performance of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. ASCE 2005, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chouw, N. Effect of water, seawater and alkaline solution ageing on mechanical properties of flax fabric/epoxy compos, ites used for civil engineering applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wang, X.F.; Heng, Y.J.; Zhi, J.H. Effect of carbon fiber surface functionality on the moisture absorption behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites. Surf. Interface Anal. 2016, 48, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xian, G.; Wang, Z. Durability study opultruded carbon fiber reinforced polymer plates subjected to water immersion. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2018, 21, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Solutions | Temperatures (°C) | Duration (Days) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 20/40/60 | 20/40/80 |
| Acid (HCl) | 20/40/60 | 20/40/80 |
| Alkaline (NaOH) | 20/40/60 | 20/40/80 |
| Samples | Immersion Time (Days) | Water | HCl | NaOH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | ||
| Epoxy resin C 1: 152.8 | 20 | 139.0 | 138 | 141.7 | 135.5 | 132.52 | 133 | 140.8 | 141.0 | 141.3 |
| 40 | 141.0 | 141.3 | 136.2 | 133.6 | 129.3 | 129.0 | 141.0 | 139.1 | 131.8 | |
| 80 | 140.6 | 142.4 | 147.6 | 132.6 | 127.0 | 139.9 | 139.5 | 141.0 | 147.0 | |
| CFRP C 1: 135.8 | 20 | 142.3 | 139.0 | 135.8 | 137.9 | 139.0 | 136.7 | 144.6 | 142.5 | 140.7 |
| 40 | 133.1 | 128.1 | 132.7 | 135.0 | 136.2 | 132.6 | 135.7 | 135.1 | 132.7 | |
| 80 | 133.0 | 130.5 | 132.1 | 131.6 | 132.0 | 133.1 | 132.2 | 133.0 | 133.4 | |
| Samples | Immersion Time (Days) | Water | HCl | NaOH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | ||
| Epoxy resin | 20 | 1.5 | 4.2 | 8.09 | 1 | 6.1 | 8.1 | 0.3 | 4.1 | 6.6 |
| 40 | 3.8 | 15.5 | 27 | 5 | 11.9 | 28.3 | 2.6 | 15.8 | 28.5 | |
| 80 | 4.2 | 23.9 | 41.8 | 14 | 23.7 | 45 | 7 | 27 | 41.3 | |
| CFRP | 20 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 9.1 | 2.2 | 6.0 | 9.0 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 10.0 |
| 40 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 17.7 | 4.2 | 8.4 | 16.2 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 12.2 | |
| 80 | 2.8 | 6.0 | 20.0 | 9.0 | 14.0 | 25.0 | 4.3 | 10.8 | 24.0 | |
| Samples | Immersion Time (Days) | Water | HCl | NaOH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | ||
| Epoxy resin | 20 | 1.9 | 5.3 | 6.3 | 7.6 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 6.3 | 6.8 |
| 40 | 6.0 | 7.6 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 11.2 | 13.0 | 7.1 | 8.4 | 10.0 | |
| 80 | 7.3 | 11.0 | 13.3 | 11.7 | 14.1 | 16.1 | 8.9 | 10.5 | 12.5 | |
| CFRP | 20 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 1.6 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 5.0 |
| 40 | 2.9 | 5.1 | 6.3 | 3.6 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 6.4 | |
| 80 | 5.3 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 6.0 | 7.9 | 10.5 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 7.4 | |
| Immersion Solutions | Temperatures (°C) | τ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 20 | 2425 | 0.95 |
| 40 | 1127 | 0.87 | |
| 60 | 288 | 0.86 | |
| HCl | 20 | 2341 | 0.87 |
| 40 | 445 | 0.96 | |
| 60 | 263 | 0.97 | |
| NaOH | 20 | 1641 | 0.91 |
| 40 | 503 | 0.92 | |
| 60 | 240 | 0.91 |
| Immersion Solutions | Tensile Strength Retention (%) | Ea/R | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 60 | 6379 | 0.96 |
| 70 | 6379 | 0.96 | |
| 80 | 6379 | 0.96 | |
| 90 | 6379 | 0.96 | |
| HCl | 60 | 5660 | 0.95 |
| 70 | 5660 | 0.95 | |
| 80 | 5660 | 0.95 | |
| 90 | 5660 | 0.95 | |
| NaOH | 60 | 6197 | 0.99 |
| 70 | 6197 | 0.99 | |
| 80 | 6197 | 0.99 | |
| 90 | 6197 | 0.99 |
| Immersion Solutions | Immersion TEMPERATURES (°C) | Time Shift Factor (TSF) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hall’s Harbor Wharf 7.6 °C | Joffre Bridge (4.1 °C) | Chatham Bridge (4.6 °C) | Crowchild Trail Bridge (3.9 °C) | Waterloo Creek Bridge (9.9 °C) | ||
| Water | 20 | 2.61 | 3.48 | 3.34 | 3.54 | 2.17 |
| 40 | 10.50 | 13.99 | 13.42 | 14.22 | 8.73 | |
| 60 | 35.67 | 47.52 | 45.59 | 48.32 | 29.66 | |
| HCl | 20 | 2.35 | 3.03 | 2.92 | 3.07 | 1.99 |
| 40 | 8.05 | 10.39 | 10.01 | 10.54 | 6.84 | |
| 60 | 23.83 | 30.74 | 29.63 | 31.19 | 20.23 | |
| NaOH | 20 | 2.54 | 3.36 | 3.23 | 3.41 | 2.12 |
| 40 | 9.80 | 12.94 | 12.43 | 13.15 | 8.19 | |
| 60 | 32.10 | 42.41 | 40.74 | 43.10 | 26.84 | |
| Conditions | Reference Temperature Cites | Average Annual Temperature (°C) | τ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Hall’s Harbor Wharf | 7.6 | 11,927 | 0.97 |
| Joffre Bridge | 4.1 | 15,890 | 0.97 | |
| Chatham Bridge | 4.6 | 15,246 | 0.97 | |
| Crowchild Trail Bridge | 3.9 | 16,156 | 0.97 | |
| Waterloo Creek Bridge | 9.9 | 9916 | 0.97 | |
| HCl | Hall’s Harbor Wharf | 7.6 | 5218 | 0.96 |
| Joffre Bridge | 4.1 | 6731 | 0.96 | |
| Chatham Bridge | 4.6 | 6487 | 0.96 | |
| Crowchild Trail Bridge | 3.9 | 6831 | 0.96 | |
| Waterloo Creek Bridge | 9.9 | 4430 | 0.96 | |
| NaOH | Hall’s Harbor Wharf | 7.6 | 7807 | 0.91 |
| Joffre Bridge | 4.1 | 10,313 | 0.91 | |
| Chatham Bridge | 4.6 | 9907 | 0.91 | |
| Crowchild Trail Bridge | 3.9 | 10,483 | 0.91 | |
| Waterloo Creek Bridge | 9.9 | 6524 | 0.91 |
| Reference Temperature Cites | Average Annual Temperature (°C) | Time in Years to Reach 70% Tensile Strength Retention of CFRP Composites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFRP Composites in Water | CFRP Composites in Acid Medium | CFRP Composites in Acid Medium | ||
| Hall’s Harbor Wharf | 7.6 | 11.7 | 5.1 | 7.6 |
| Joffre Bridge | 4.1 | 15.5 | 6.6 | 10.1 |
| Chatham Bridge | 4.6 | 14.9 | 6.3 | 9.7 |
| Crowchild Trail Bridge | 3.9 | 15.8 | 6.7 | 10.2 |
| Waterloo Creek Bridge | 9.9 | 9.7 | 4.3 | 8.3 |
| Immersion Solutions | Time (Years) | Time in Years to Reach 70% Tensile Strength Retention of CFRP Composites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hall’s Harbor Wharf | Joffre Bridge | Chatham Bridge | Crowchild Trail Bridge | Waterloo Creek Bridge | ||
| Water | 5 | 86 | 89.1 | 88.7 | 89.3 | 83.2 |
| 10 | 73.6 | 79.5 | 78.7 | 79.8 | 69.2 | |
| 15 | 63.2 | 70.9 | 69.8 | 71.3 | 57.6 | |
| 20 | 54.2 | 63.2 | 62 | 63.6 | 48 | |
| HCl | 5 | 70.5 | 76.3 | 75.5 | 76.6 | 66.2 |
| 10 | 49.7 | 58.1 | 57 | 58.6 | 44 | |
| 15 | 35 | 44.3 | 43 | 44.9 | 29.1 | |
| NaOH | 5 | 79.2 | 83.8 | 83 | 84 | 75.6 |
| 10 | 62.7 | 70.2 | 69.2 | 70.6 | 57.2 | |
| 15 | 49.6 | 58.8 | 57.5 | 59.3 | 43.2 | |
| 20 | 39.3 | 49.3 | 47.9 | 49.8 | 32.7 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uthaman, A.; Xian, G.; Thomas, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, X. Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions. Polymers 2020, 12, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030614
Uthaman A, Xian G, Thomas S, Wang Y, Zheng Q, Liu X. Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030614
Chicago/Turabian StyleUthaman, Arya, Guijun Xian, Sabu Thomas, Yunjia Wang, Qiang Zheng, and Xiaoling Liu. 2020. "Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions" Polymers 12, no. 3: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030614
APA StyleUthaman, A., Xian, G., Thomas, S., Wang, Y., Zheng, Q., & Liu, X. (2020). Durability of an Epoxy Resin and Its Carbon Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Composite upon Immersion in Water, Acidic, and Alkaline Solutions. Polymers, 12(3), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030614