Facile Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing and Wet Spinning of Polymeric Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microfluidic Spinneret Fabrication
2.2. Computational Model and Simulation
2.3. Flow Experiment
2.4. Thermoplastic Urethane (TPU) Fiber Spinning
2.5. Versatility Testing
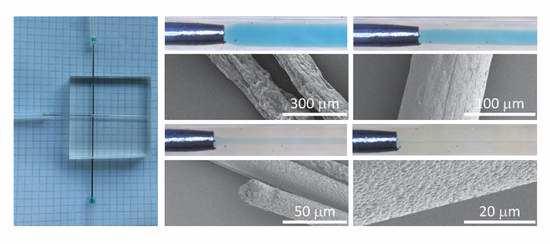
2.6. SEM Analysis of Produced Fibers
3. Results
3.1. PDMS Chip Fabrication
3.2. Fluid-Dynamics Simulation
3.3. Flow Experiment
3.4. Microfluidic Wet Spinning of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Fibers
3.5. Versatility in Microfluidic Wet-Spinning of Other Polymer Fibers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, M.; Deng, R.; Schumacher, K.M.; Kurisawa, M.; Ye, H.; Purnamawati, K.; Ying, J.Y. Hydrodynamic spinning of hydrogel fibers. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynl, C.; Hofmann, E.; Pawar, K.; Förster, S.; Scheibel, T. Microfluidics-Produced Collagen Fibers Show Extraordinary Mechanical Properties. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5917–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, F.; Bai, Z.; Montazami, R.; Hashemi, N. Mechanical and physical properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) microfibers fabricated by a microfluidic approach. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55343–55353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonhomme, O.; Leng, J.; Colin, A. Microfluidic wet-spinning of alginate microfibers: A theoretical analysis of fiber formation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10641–10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Kong, T.; Zhao, Y. Spinning and Applications of Bioinspired Fiber Systems. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2749–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozipek, B.; Karakas, H. 9—Wet spinning of synthetic polymer fibers. In Advances in Filament Yarn Spinning of Textiles and Polymers; Zhang, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 174–186. ISBN 978-0-85709-499-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lölsberg, J.; Linkhorst, J.; Cinar, A.; Jans, A.; Kuehne, A.J.C.; Wessling, M. 3D nanofabrication inside rapid prototyped microfluidic channels showcased by wet-spinning of single micrometre fibres. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, E.; Jeong, G.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Lee, S.H. Digitally tunable physicochemical coding of material composition and topography in continuous microfibres. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Park, D.; Jun, Y.; Lee, J.; Hyun, J.; Lee, S.H. Biomimetic spinning of silk fibers and: In situ cell encapsulation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, G.; Cheng, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. Microfluidic-spinning construction of black-phosphorus-hybrid microfibres for non-woven fabrics toward a high energy density flexible supercapacitor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Ostrovidov, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.; Kasuya, M.; Kurihara, K.; Nakajima, K.; Bae, H.; Wu, H.; Khademhosseini, A. Microfluidic spinning of cell-responsive grooved microfibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Shin, S.J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, S.H. Novel PDMS cylindrical channels that generate coaxial flow, and application to fabrication of microfibers and particles. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, G. Controllable preparation of microscale tubes with multiphase co-laminar flow in a double co-axial microdevice. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Ding, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, N.; Qu, L. Direct spinning of fiber supercapacitor. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12113–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håkansson, K.M.O. Online determination of anisotropy during cellulose nanofibril assembly in a flow focusing device. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18601–18608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tian, M.; Pan, N.; Sun, B.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Z.; Qu, L. Structure-tunable graphene oxide fibers via microfluidic spinning route for multifunctional textile. Carbon 2019, 152, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, S.; Cabot, J.M.; Macdonald, N.P.; Lewis, T.; Guijt, R.M.; Paull, B.; Breadmore, M.C. 3D printed microfluidic devices: Enablers and barriers. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pranzo, D.; Larizza, P.; Filippini, D.; Percoco, G. Extrusion-Based 3D Printing of Microfluidic Devices for Chemical and Biomedical Applications: A Topical Review. Micromachines 2018, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bressan, L.P.; Adamo, C.B.; Quero, R.F.; de Jesus, D.P.; da Silva, J.A.F. A simple procedure to produce FDM-based 3D-printed microfluidic devices with an integrated PMMA optical window. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.; Samuel, R.; Chaharlang, M.; Jafek, A.R.; Frost, A.; Gale, B.K. FDM 3D Printing of High-Pressure, Heat-Resistant, Transparent Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10450–10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.J.L.; Hidalgo San Jose, L.; Jamieson, W.D.; Wymant, J.M.; Song, B.; Stephens, P.; Barrow, D.A.; Castell, O.K. Simple and Versatile 3D Printed Microfluidics Using Fused Filament Fabrication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, M.; Kumar, H.; Wang, Z.; Martin, N.; Mills, B.; Kim, K. Rapid and Inexpensive Fabrication of Multi-Depth Microfluidic Device using High-Resolution LCD Stereolithographic 3D Printing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, A.P.; Bhattacharjee, N.; Lee, Y.; Castro, K.; Kim, Y.T.; Folch, A. High-Precision Stereolithography of Biomicrofluidic Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, N.; Parra-Cabrera, C.; Kim, Y.T.; Kuo, A.P.; Folch, A. Desktop-Stereolithography 3D-Printing of a Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Material with Sylgard-184 Properties. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, T.M.; DuBois, E.M.; Machnicki, C.E.; Bhaskar, D.; Cui, F.R.; Wong, I.Y. 3D printed self-adhesive PEGDA–PAA hydrogels as modular components for soft actuators and microfluidics. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrios, A.; Parra-Cabrera, C.; Bhattacharjee, N.; Gonzalez-Suarez, A.M.; Rigat-Brugarolas, L.G.; Nallapatti, U.; Samitier, J.; DeForest, C.A.; Posas, F.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; et al. 3D-printing of transparent bio-microfluidic devices in PEG-DA. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2287–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Bickham, B.P.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. Custom 3D printer and resin for 18 μm × 20 μm microfluidic flow channels. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.A.; Shields, A.R.; Naciri, J.; Ligler, F.S. Hydrodynamic Shaping, Polymerization, and Subsequent Modification of Thiol Click Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, E.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.H. Microfluidic wet spinning of chitosan-alginate microfibers and encapsulation of HepG2 cells in fibers. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 022208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Shin, S.J.; Kim, C.B.; Kim, J.K.; Cho, Y.W.; Chung, B.G.; Lee, S.H. Microfluidic synthesis of pure chitosan microfibers for bio-artificial liver chip. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.; Park, Y.D.; Lee, K.B.; Whang, C.M.; Lee, S.H. “On the fly” continuous generation of alginate fibers using a microfluidic device. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9104–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Park, Y.; Sun, K.; Lee, S.H. Microfluidic chip-based fabrication of PLGA microfiber scaffolds for tissue engineering. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6845–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Mensing, G.; Beebe, D.J. Hydrodynamic microfabrication via “on the fly” photopolymerization of microscale fibers and tubes. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoe, H.; Okitsu, T.; Itou, A.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Gojo, R.; Kiriya, D.; Sato, K.; Miura, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, K.; et al. Metre-long cell-laden microfibres exhibit tissue morphologies and functions. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Shang, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Design of capillary micro fl uidics for spinning cell-laden microfibers. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 2557–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.R. Diffusion during the coagulation step of wet-spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1968, 12, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, T.A.; Spruiell, J.E.; White, J.L. Wet spinning of aliphatic and aromatic polyamides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 21, 1227–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, G.; Popa, A.M.; Rossi, R.M.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Puigmartí-Luis, J.; Crespy, D.; Fortunato, G. Tunable release of hydrophilic compounds from hydrophobic nanostructured fibers prepared by emulsion electrospinning. Polymer 2015, 66, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, G.; Dmitriev, R.I.; Tyagi, V.; Jenkins, J.; Rotaru, G.-M.; Rottmar, M.; Rossi, R.M.; Toncelli, C.; Papkovsky, D.B.; Maniura-Weber, K.; et al. Steering surface topographies of electrospun fibers: Understanding the mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gursoy, A.; Iranshahi, K.; Wei, K.; Tello, A.; Armagan, E.; Boesel, L.F.; Sorin, F.; Rossi, R.M.; Defraeye, T.; Toncelli, C. Facile Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing and Wet Spinning of Polymeric Fibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030633
Gursoy A, Iranshahi K, Wei K, Tello A, Armagan E, Boesel LF, Sorin F, Rossi RM, Defraeye T, Toncelli C. Facile Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing and Wet Spinning of Polymeric Fibers. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030633
Chicago/Turabian StyleGursoy, Akin, Kamran Iranshahi, Kongchang Wei, Alexis Tello, Efe Armagan, Luciano F. Boesel, Fabien Sorin, René M. Rossi, Thijs Defraeye, and Claudio Toncelli. 2020. "Facile Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing and Wet Spinning of Polymeric Fibers" Polymers 12, no. 3: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030633
APA StyleGursoy, A., Iranshahi, K., Wei, K., Tello, A., Armagan, E., Boesel, L. F., Sorin, F., Rossi, R. M., Defraeye, T., & Toncelli, C. (2020). Facile Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing and Wet Spinning of Polymeric Fibers. Polymers, 12(3), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030633