Effect of Polyaniline on Sulfur/Sepiolite Composite Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sepiolite Acid Treatment
2.2. Thermal Activation Method
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Electrochemical Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis
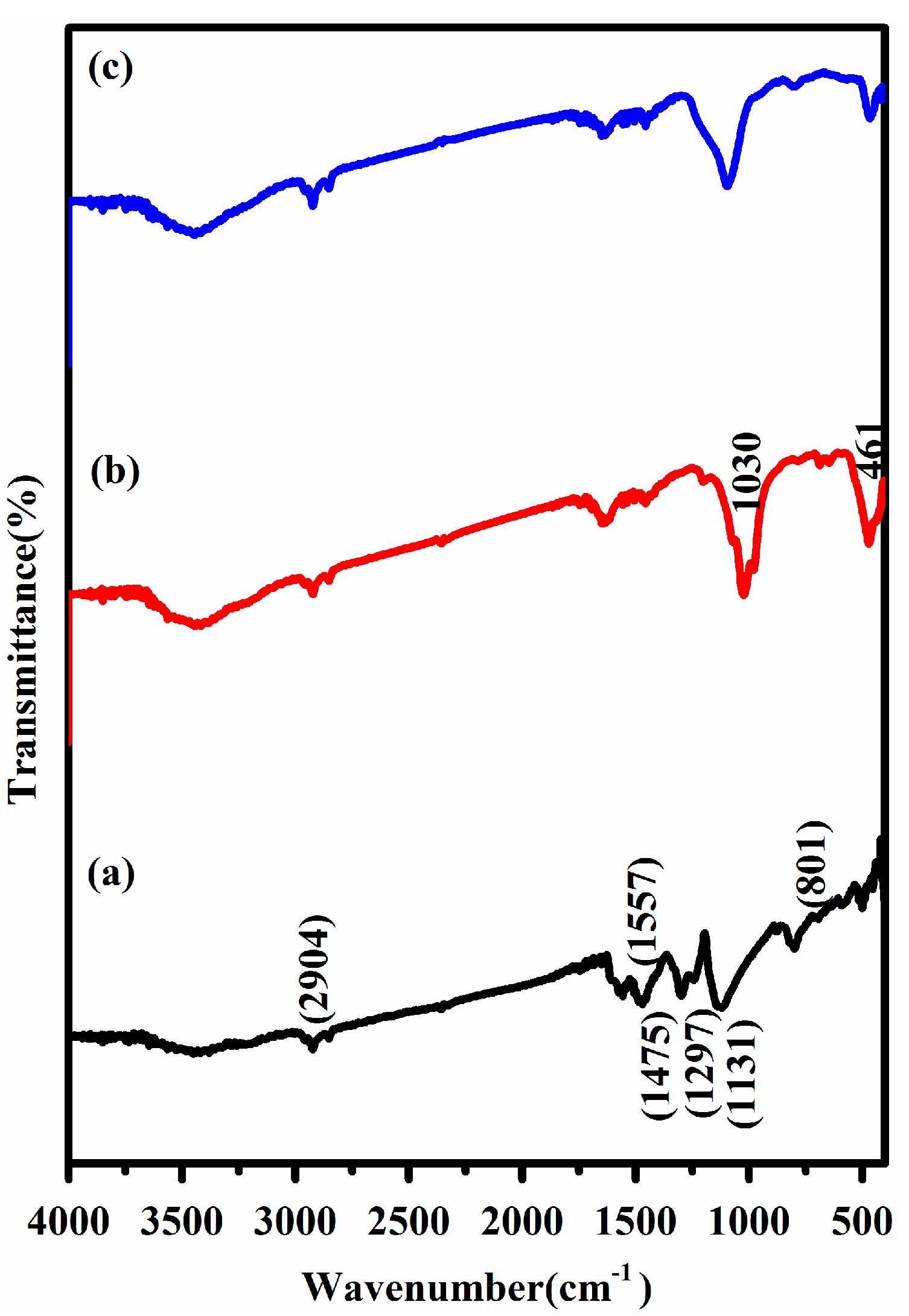
3.2. FTIR Analysis
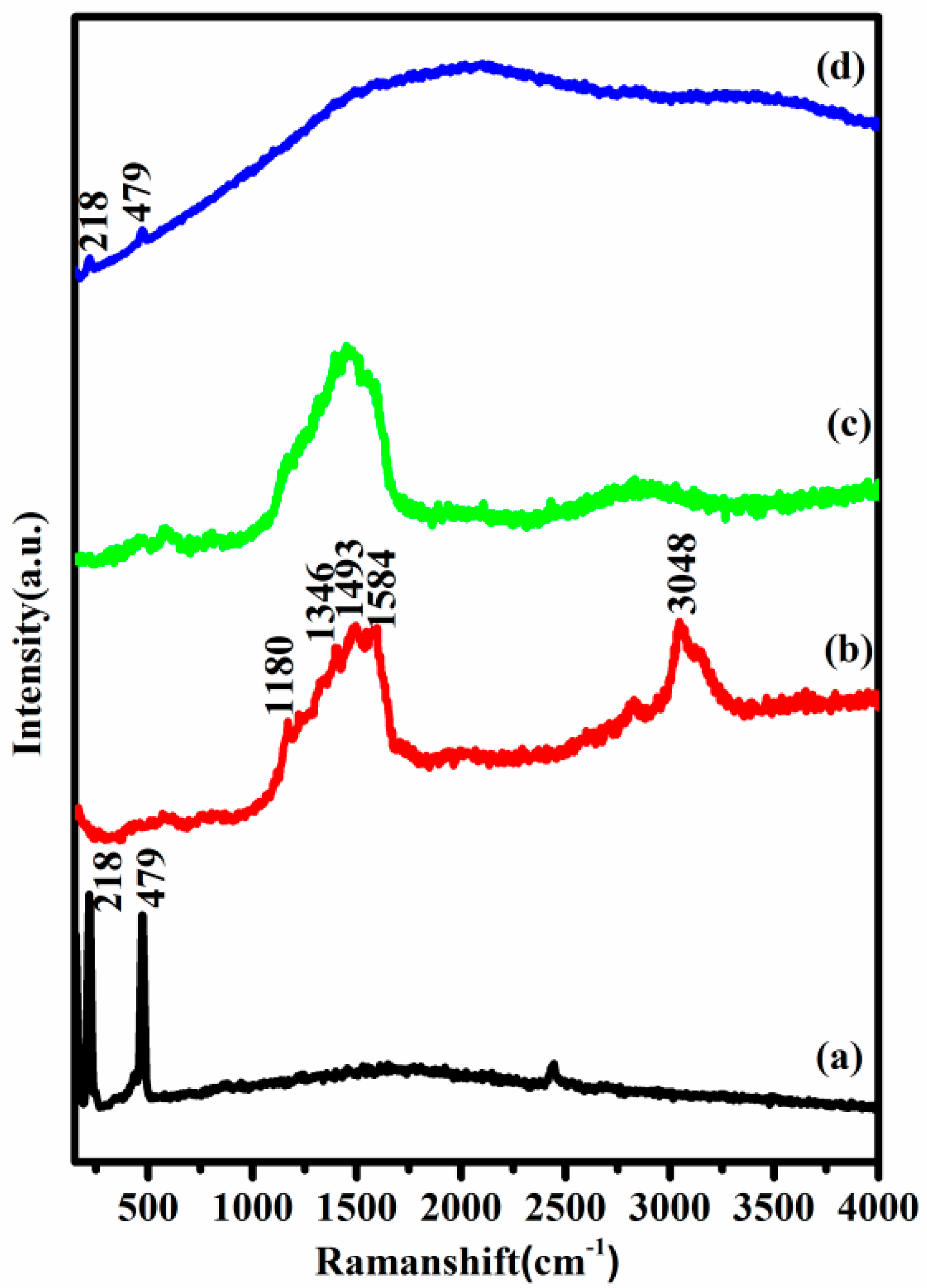
3.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. Morphological Analysis
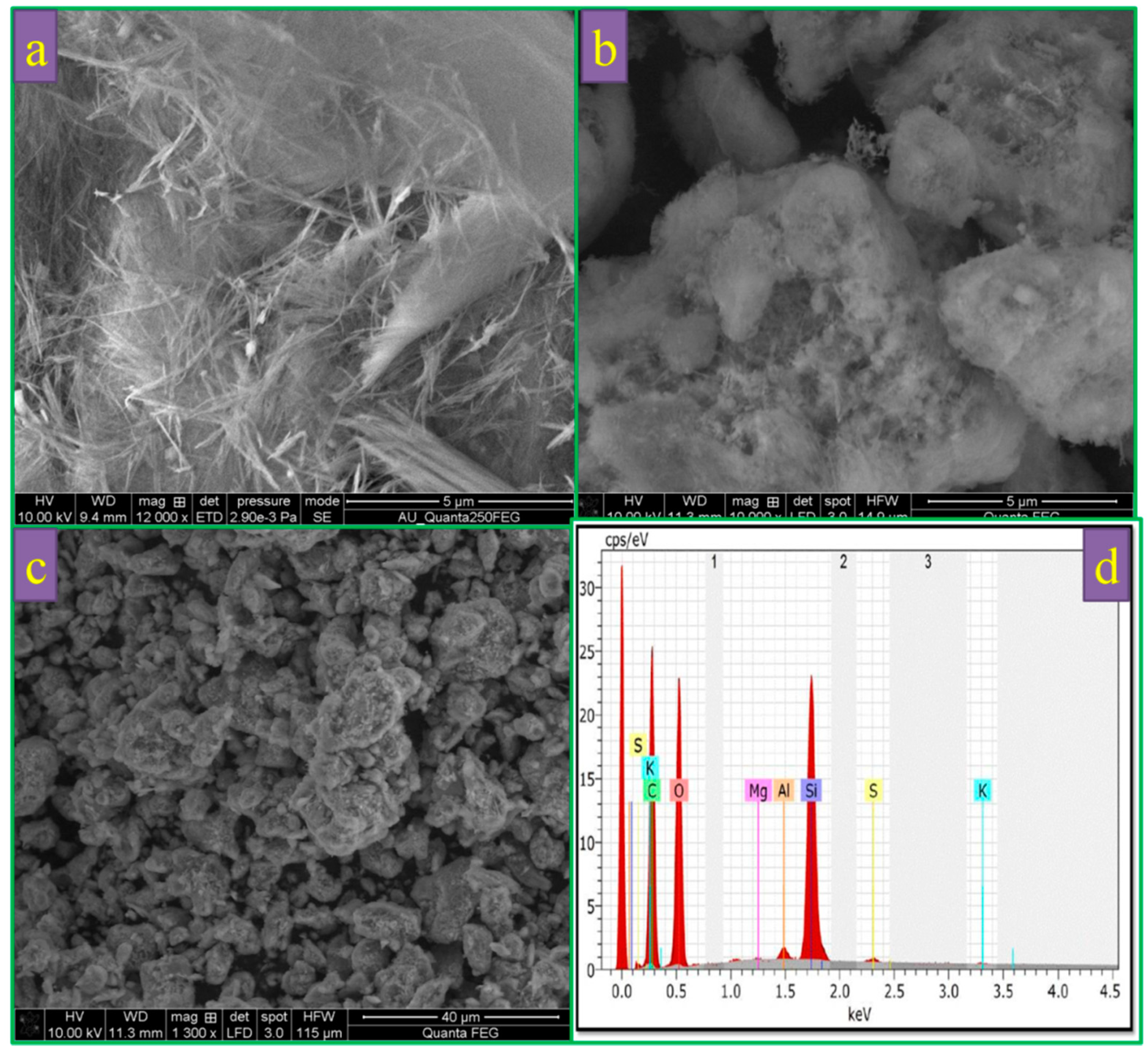
3.4.1. SEM Analysis
3.4.2. TEM Analysis
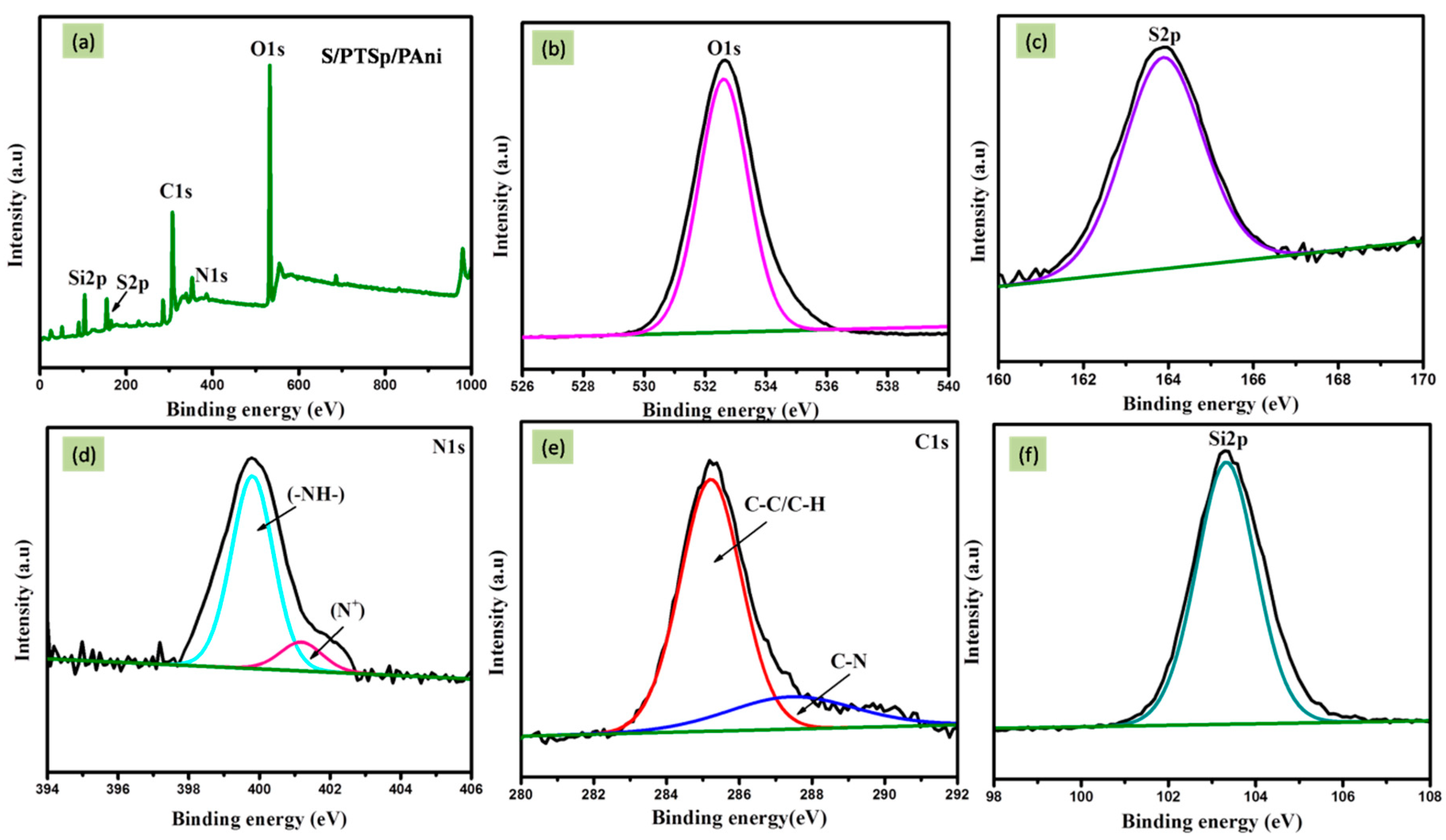
3.5. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
3.6. Nitrogen Adsorption-Desorption Isotherms
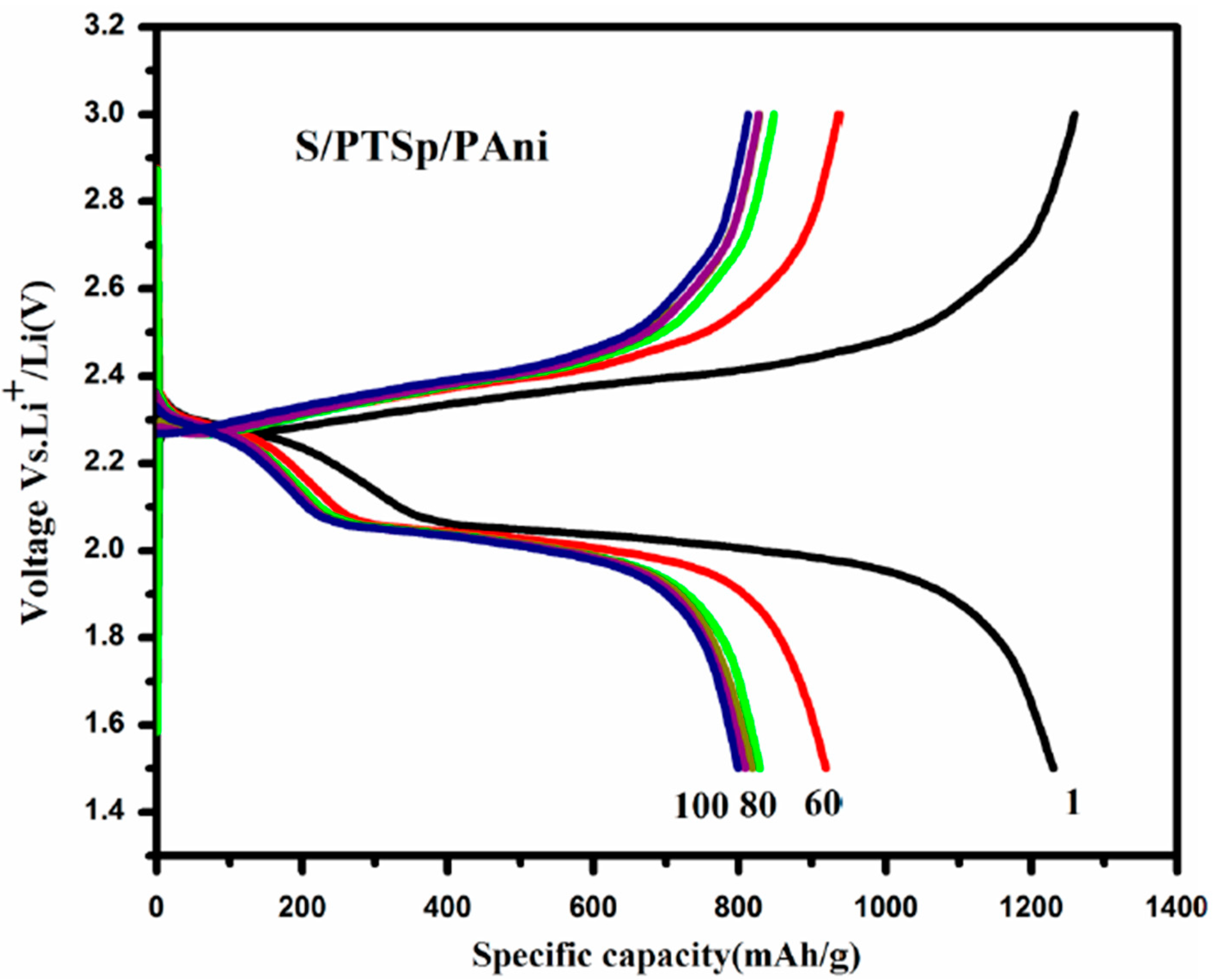
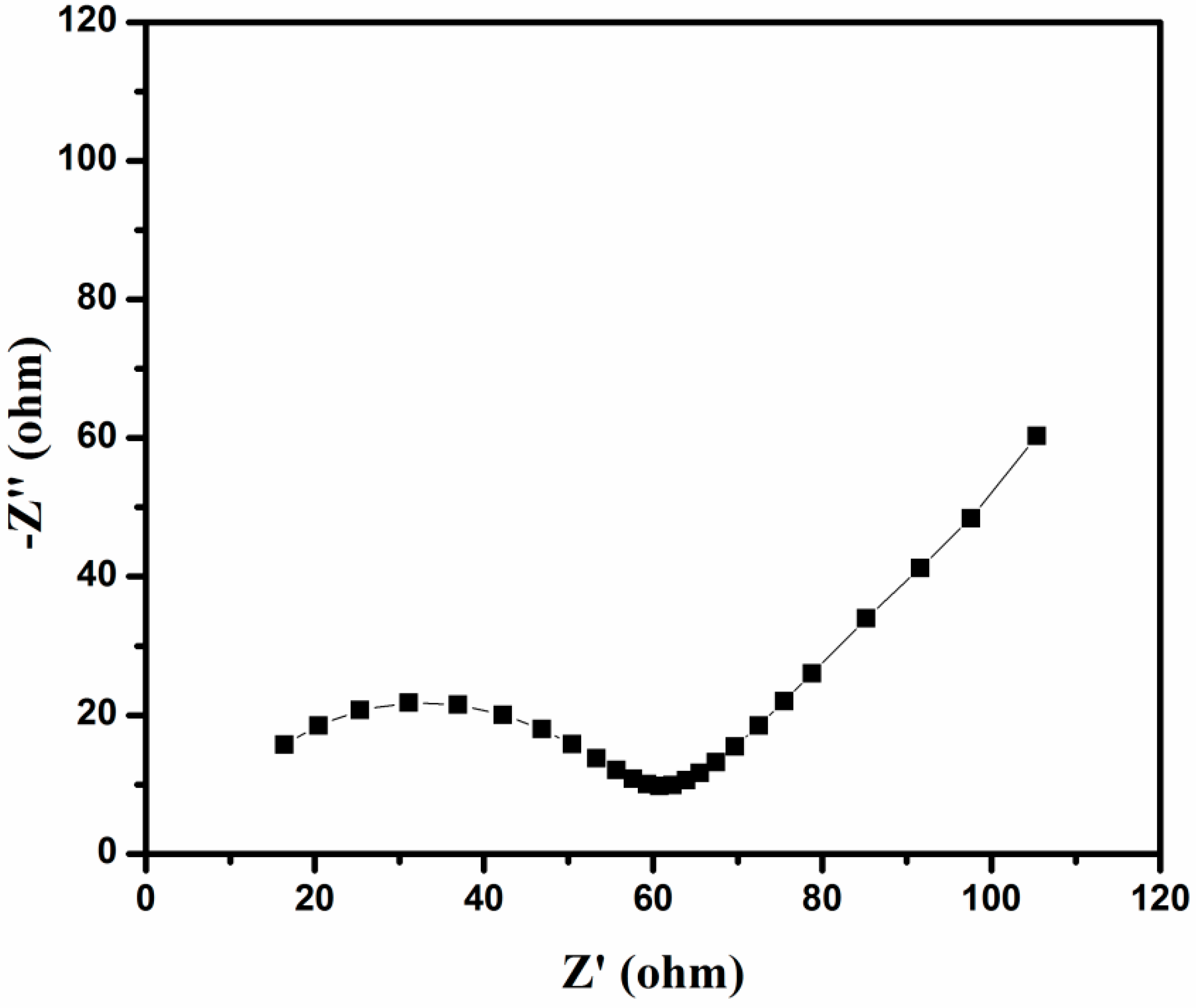
3.7. Electrochemical Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Ge, Y.; Kim, D.; Lu, Y.; Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, X. A novel separator coated by carbon for achieving exceptional high performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Energy 2016, 20, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.J.; Wang, D.W.; Huang, J.Q.; Cheng, X.B.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, F.; Zhang, Q. Janus separator of polypropylene-supported cellular graphene framework for sulfur cathodes with high utilization in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; Cheng, H.M.; Li, F.; Ren, W. 3D graphene-foam–reduced-graphene-oxide hybrid nested hierarchical networks for high-performance Li–S batteries. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaibani, M.; Akbari, A.; Sheath, P.; Easton, C.D.; Banerjee, P.C.; Konstas, K.; Fakhfouri, A.; Barghamadi, M.; Musameh, M.M.; Best, A.S.; et al. Suppressed polysulfide crossover in Li–S batteries through a high-flux graphene oxide membrane supported on a sulfur cathode. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7768–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthiram, A.; Chung, S.H.; Zu, C. Lithium–sulfur batteries: Progress and prospects. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1980–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Li, J.C.M.; Lu, J.; Amine, K.; Belharouak, I. Demonstration of highly efficient lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4170–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenman, A.; Markevich, E.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D.; Garsuch, A.; Chesneau, F.F. Review on Li-Sulfur battery systems: An integral perspective. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwiuk, A.; Berkes, B.B.; Wei, T.; Sommer, H.; Janek, J.; Brezesinski, T. The critical role of lithium nitrate in the gas evolution of lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2603–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.H.; Manthiram, A. Bifunctional separator with a light-weight carbon-coating for dynamically and statically stable Lithium-Sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5299–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.R.; Bella, F.; Angulakshmi, N.; Stephan, A.M.; Gerbaldi, C. Nanocellulose-laden composite polymer electrolytes for high performing lithium–sulphur batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 3, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Lee, K.T.; Nazar, L.F. A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, M.J.; Jeschull, F.; Edstrom, K.; Brandell, D. Porosity blocking in highly porous carbon black by PVDF binder and its implications for the Li–S system. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 25890–25898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Cui, Y. Nanostructured sulfur cathodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3018–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan, E. Properties and applications of palygorskite-sepiolite clays. Clay Miner. 1996, 31, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A. Sepiolite:Properties and uses. Dev. Sedimentol. 1984, 37, 253–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bokobza, L.; Burr, A.; Garnaud, G.; Perrin, M.Y.; Pagnotta, S. Fibre reinforcement of elastomers: Nanocomposites based on sepiolite and poly (hydroxyethyl acrylate). Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.Y.; Xu, N.X. A novel conductive polymer–sulfur composite cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Wan, C.; Du, K.; Xie, J.; Xu, N. Sulfur composite cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003, 13, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.E.; Lee, P.C.; Tatsumi, I. Preparation and electrochemical properties of sulfur-polypyrrole composite cathodes for electric vehicle applications. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A.; Fu, Y.; Chung, S.H.; Zu, C.; Su, Y.S. Rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11751–11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Debarnot, D.; Poncin-Epaillard, F. Polyaniline as a new sensitive layer for gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 475, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; DiSalvo, J.F.; Abruña, D.H. Yolk–shell structure of polyaniline-coated sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Su, Y. Sepiolite/CNT/S @ PAni composite with stable network structure for lithium-sulfur batteries. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17950–17957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, T.; Chen, R. Improvement of rate and cycle performence by rapid polyaniline coating of a MWCNT/sulfur cathode. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 24411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh, R.; Viswanathan, K. Determination of electron and hole effective masses in thermal oxide utilizing an n-channel silicon MOSFET. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 6, 2278–4861. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Chung, S.H.; Manthiram, A. Ultra-lightweight PANiNF/MWCNT-functionalized separators with synergistic suppression of polysulfide migration for Li–S batteries with pure sulfur cathodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18829–18834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, Q. Preparation and characterization of mercapto functionalized sepiolite and their application for sorption of lead and cadmium. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Dunsch, L. The stabilization of charged states at phenazine-like units in polyaniline under p-doping: An in situ ATR-FTIR spectroelectrochemical study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchova, M.; Matejka, P.; Brodinova, J.; Kalendovac, A.; Prokesd, J.; Stejskal, J. Structural and conductivity changes during the pyrolysis of polyaniline base. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchasz, C.; Molton, F.; Duboc, C.; Lepretre, J.C.; Patoux, S.; Alloin, F. Lithium/sulfur cell discharge mechanism: An original approach for intermediate species identification. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3973–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Morbidelli, M. Conductive framework of inverse opal structure for sulfur cathode in lithium-sulfur batteries. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Kong, L.L.; Liu, S.; Li, G.R.; Gao, X.P. A High-Efficiency Sulfur/Carbon Composite Based on 3D Graphene Nanosheet@ Carbon Nanotube Matrix as Cathode for Lithium–Sulfur Battery. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 7, 1602543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wei, W.; Yuan, K.; Lu, W.; Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Song, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.G.; Shen, C. Towards dendrite-free lithium deposition via structural and interfacial synergistic effects of 3D graphene@ Ni scaffold. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2016, 8, 26091–26097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Pu, W.; Ren, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Wan, C. Charge/discharge characteristics of sulfur composite cathode materials in rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7372–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Ahn, H.J. Improvement of cycle property of sulfur electrode for lithium/sulfur battery. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 449, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.E.; Ko, K.S.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Chin, E.Y.; Kim, H.T. Rechargeable lithium sulfur battery I. Structural change of sulfur cathode during discharge and charge. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A796–A799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, P.; Diwakar, K.; Radhika, G.; Krishnaveni, K.; Subadevi, R.; Sivakumar, M. Effect of silicon dioxide in sulfur/carbon black composite as a cathode material for lithium sulfur batteries. Vacuum 2019, 161, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, D.W.; Li, F.; Hou, P.X.; Yin, L.; Liu, C.; Lu, G.Q.; Gentle, I.R.; Cheng, H.M. A flexible nanostructured sulphur–carbon nanotube cathode with high rate performance for Li-S batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8901–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Rao, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Duan, W.; Guo, J.; Cairns, E.J.; Zhang, Y. Graphene oxide as a sulfur immobilizer in high performance lithim/sulfur cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18522–18525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J. Nano-wire networks of sulfur–polypyrrole composite cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, W.; Lu, Q. The catalytic activity of manganese dioxide supported on graphene promoting the electrochemical performance of lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Pan, L.; Wang, H.; Su, Q.; Du, G. Nanosulfur/polyaniline/graphene composites for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries: One pot in-situ synthesis. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Li, G.R.; Ye, S.H.; Gao, X.P. A polyaniline-coated sulfur/carbon composite with an enhanced high-rate capability as a cathode material for lithium/sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.; Gordin, M.L.; Regula, M.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Song, J.; Wang, D. Porous spherical polyacrylonitrile-carbon nanocomposite with high loading of sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 302, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chelladurai, K.; Venkatachalam, P.; Rengapillai, S.; Liu, W.-R.; Huang, C.-H.; Marimuthu, S. Effect of Polyaniline on Sulfur/Sepiolite Composite Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Polymers 2020, 12, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040755
Chelladurai K, Venkatachalam P, Rengapillai S, Liu W-R, Huang C-H, Marimuthu S. Effect of Polyaniline on Sulfur/Sepiolite Composite Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040755
Chicago/Turabian StyleChelladurai, Kalaiselvi, Priyanka Venkatachalam, Subadevi Rengapillai, Wei-Ren Liu, Chia-Hung Huang, and Sivakumar Marimuthu. 2020. "Effect of Polyaniline on Sulfur/Sepiolite Composite Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries" Polymers 12, no. 4: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040755
APA StyleChelladurai, K., Venkatachalam, P., Rengapillai, S., Liu, W.-R., Huang, C.-H., & Marimuthu, S. (2020). Effect of Polyaniline on Sulfur/Sepiolite Composite Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Polymers, 12(4), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040755





