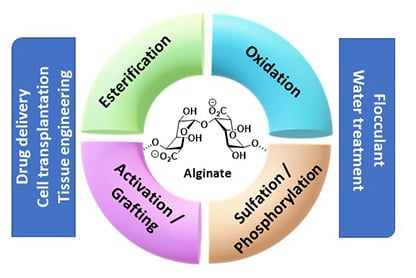
Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Alginate: Composition and Physicochemical Properties
2.1. Chemical Description of Alginate
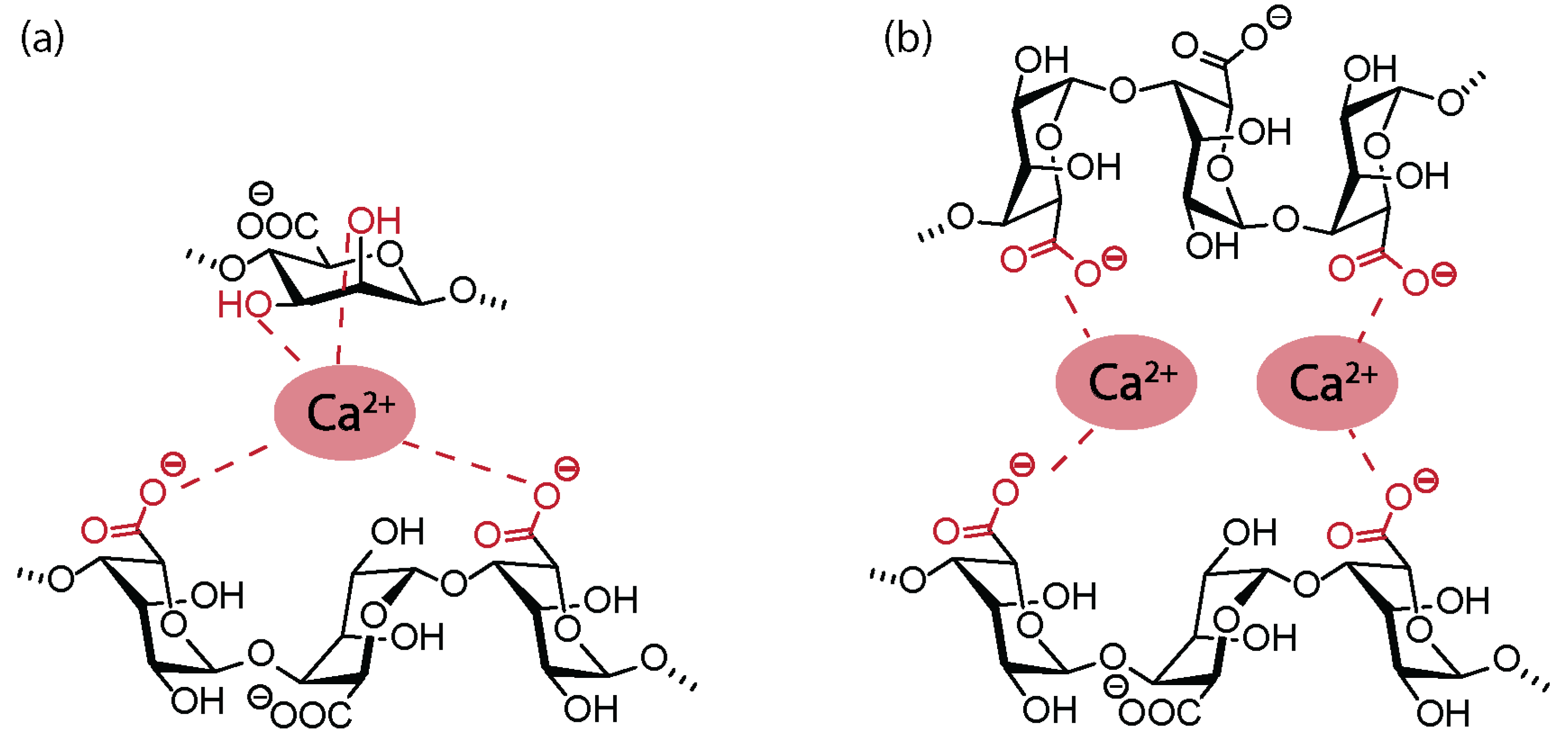
2.2. Physicochemical and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics of Alginate
3. Modification with Partial Conservation of the Carboxyl Groups
4. Modification with Complete Conservation of the Alginate Carboxyl Groups
4.1. Ester Formation
4.1.1. Acetylation
4.1.2. Other Esterification Methods
4.2. Sulfation
4.3. Phosphorylation
4.4. Epoxide Ring-Opening Reactions
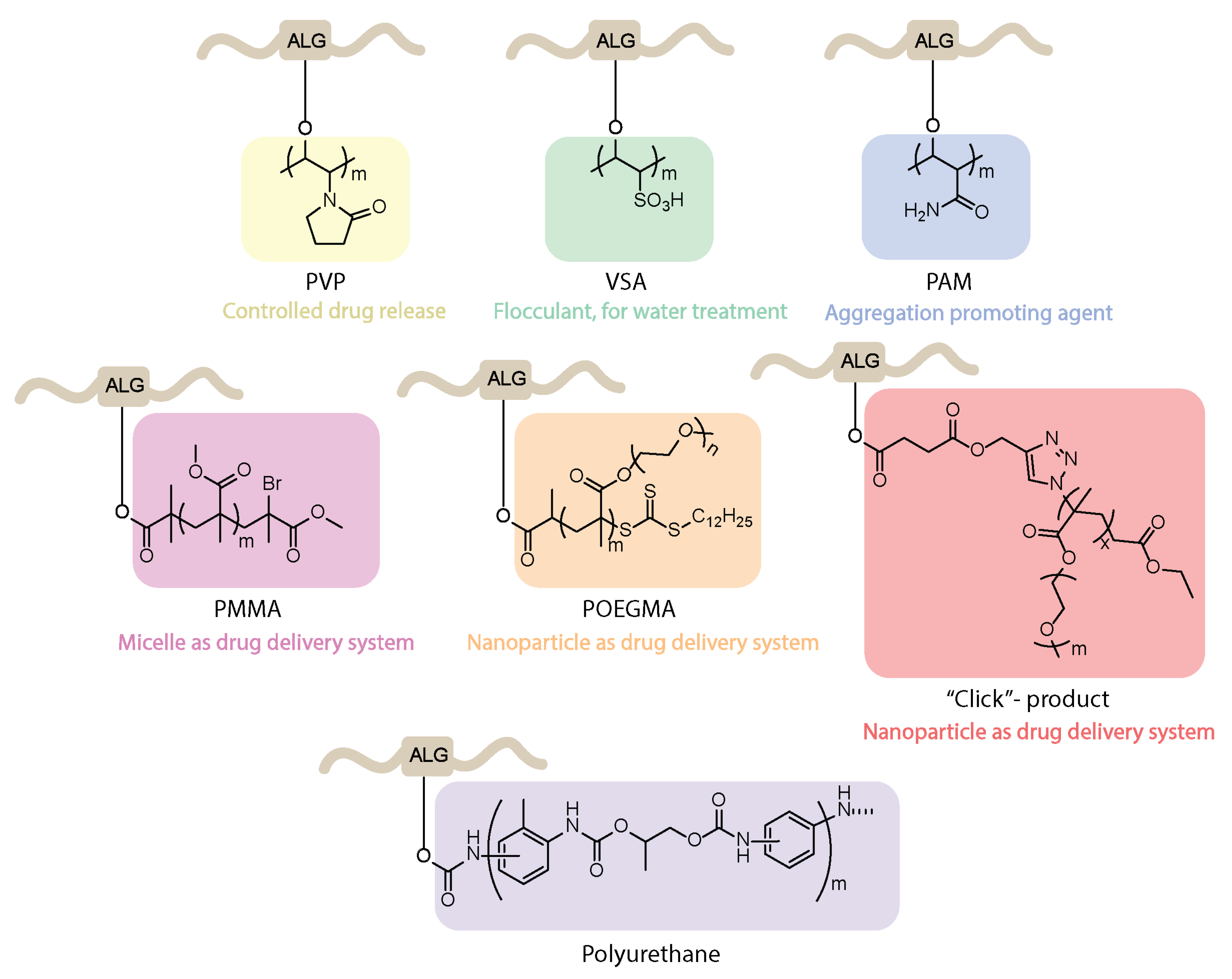
4.5. Synthesis of Graft Copolymers
4.6. Oxidation of Alginates
4.6.1. Oxidation without Further Modification
4.6.2. Chemical Modification of Oxidized Alginates
4.6.3. Cross-Linked Hydrogels from Oxidized Alginates
4.7. Other Functionalization Methods
5. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Draget, K.I. Alginates. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 379–395. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, V.J. Algin and alginates. In Seaweeds and Their Uses, 3rd ed.; Chapman, V.J., Chapman, D.J., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 194–225. [Google Scholar]
- Valla, S.; Ertesvåg, H.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Genetics and biosynthesis of alginates. Carbohydr. Eur. 1996, 14, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, I.D.; Rehman, Z.U.; Moradali, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Rehm, B.H.A. Microbial alginate production, modification and its applications. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottrell, I.W.; Kovacs, P. Alginates. In Handbook of Water-Soluble Gums and Resins; Davidson, R.L., Ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, S.T.; Draget, K.J.; Skjåk -Bræk, G.; Smidsrød, O. Alginates. In Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications; Stephen, A.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 245–286. [Google Scholar]
- Draget, K.J.; Moe, S.T.; Skjåk -Bræk, G.; Smidsrød, O. Alginates. In Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications, 2nd ed.; Stephen, A.M., Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 289–334. [Google Scholar]
- Grasdalen, H.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrød, O. A PMR study of the composition and sequence of uronic residues in alginate. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 68, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Myklestad, S.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrød, O. Correlation between chemical structure and physical properties of alginate. Acta Chem. Scand. 1967, 21, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Larsen, B. The solubility of alginates at low pH. Acta Chem. Scand. 1963, 17, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Haug, A. Dependence upon uronic acid composition of some ion-exchange properties of alginates. Acta Chem. Scand. 1968, 22, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Glover, R.M.; Whittington, S.G. The relative extension of alginates having different chemical composition. Carbohydr. Res. 1973, 27, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Xie, Y.-J.; He, W. Research Progress on Chemical Modification of Alginate: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, Q.; Chen, A. Influence of Different Divalent Metal Ions on the Properties of Alginate Microcapsules and Microencapsulated Cells. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Su, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y. A Novel Anti-calcification Method for Bioprosthetic Heart Valves Using Dopamine-Modified Alginate. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Gepp, M.M.; Stracke, F.; von Briesen, H.; Neubauer, J.C.; Zimmermann, H. Tyramine-Conjugated Alginate Hydrogels as a Platform for Bioactive Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107A, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, S.-W.; Ko, B.; Shin, J.; Ahn, C.H. Alginate-Catechol Cross-Linking Interferes with Insulin Secretion Capacity in Isolated Murine Islet Cells. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattás-Asfura, K.M.; Fraker, C.A.; Stabler, C.L. Perfluorinated Alginate for Cellular Encapsulation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100A, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breger, J.C.; Fisher, B.; Samy, R.; Pollack, S.; Wang, N.S. Synthesis of “Click” Alginate Hydrogel Capsules and Comparison of their Stability, Water Swelling, and Diffusion Properties with that of Ca+2 Crosslinked Alginate Capsules. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2015, 103B, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettignano, A.; Grijalvo, S.; Häring, M.; Eritja, R.; Tanchoux, N.; Quignard, F.; Diaz Diaz, D. Boronic-Acid-Modified Alginate Enables Direct Formation of Injectable, Self-Healing and Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3350–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanian, M.H.; Mirzadeh, H.; Baharvand, H. In Situ Forming, Cytocompatible, and Self-Recoverable Tough Hydrogels Based on Dual Ionic and Cross-Linked Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1646–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattás-Asfura, K.M.; Stabler, C.L. Chemoselective Cross-Linking and Functionalization of Alginate via Staudinger Ligation. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3122–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, A.J.; Veiseh, O.; Doloff, J.C.; Ma, M.; Tam, H.H.; Bratlie, K.; Li, J.; Bader, A.R.; Langan, E.; Olejnik, K.; et al. Combinatorial Hydrogel Library Enables Identification of Materials that Mitigate the Foreign Body Response in Primates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, A.J.; Veiseh, O.; Gürtler, M.; Millman, J.R.; Pagliuca, F.W.; Bader, A.R.; Doloff, J.C.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Olejnik, K.; et al. Long-Term Glycemic Control Using Polymer-Encapsulated Human Stem Cell-Derived Beta Cells in Immune-Competent Mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenikova, S.; Stancu, I.-C.; Kalinovska, L.; Schacht, E.; Lippens, E.; Declercq, H.; Cornelissen, M.; Santin, M.; Amblard, M.; Martinez, J. Chemoselective Cross-Linking of Alginate with Thiol-Terminated Peptides for Tissue Engineering Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, M.; Gabano, E.; Bonzani, D.; Zanellato, I.; Arrais, A.; Cantamessa, S.; Biggiogera, M.; Osella, D. Hybrid Inorganic (Nonporous Silica)/Organic (Alginate) Core-Shell Platform for Targeting a Cisplatin-Based Pt(IV) Anticancer Prodrug. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 189, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassermann, A. Alginic Acid-Acetate. Nature 1946, 158, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassermann, A. Alginic Acid Acetate. J. Chem. Soc. 1948, 48, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, N.C.; Cunningham, G.E.; Speakman, J.B. Alginic Acid Diacetate. Nature 1946, 158, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, R.G. Acetylation of Alginic Acid. I. Preparation and Viscosities of Algin Acetates. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 1786–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, R.G. Acetylation of Alginic Acid. II. Reaction of Algin Acetates with Calcium and Other Divalent Ions. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological Interactions between Polysaccharides and Divalent Cations: The Egg-Box Model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtuvia, V.; Maturana, N.; Acevedo, F.; Peña, C.; Díaz-Barrera, A. Bacterial Alginate Production: An Overview of Its Biosynthesis and Potential Industrial Production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjåk-Braek, G. Selective Acetylation of Mannuronic Acid Residues in Calcium Alginate Gels. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 185, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjåk-Braek, G.; Paoletti, S.; Gianferrara, T. Effect of Acetylation on Some Solution and Gelling Properties of Alginates. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 185, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N. Chemical Modification of Alginates in Organic Media. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le-Tien, C.; Mateescu, M.-A.; Millette, M.; Lacroix, M. Modified Alginate and Chitosan for Lactic Acid Bacteria Immobilization. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2004, 39, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahou, R.; Borcard, F.; Crivelli, V.; Montanari, E.; Passemard, S.; Noverraz, F.; Gerber-Lemaire, S.; Bühler, L.; Wandrey, C. Tuning the Properties of Hydrogel Microspheres by Adding Chemical Cross-Linking Functionality to Sodium Alginate. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4380–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, C.G.; Huang, Z.H.; Xue, F.F. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoparticles Based on Hydrophobic Alginate Derivative as Carriers for Sustained Release of Vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ishii, D.; Iwata, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Alginic Acid Ester Derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Acharya, P.C.; Bhatt, S. Preparation of Lauroyl Grafted Alginate-Psyllium Husk Gel Composite Film with Enhanced Physicochemical, Mechanical and Antimicrobial Properties. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, C. Heparin and Related Drugs: Beyond Anticoagulant Activity. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronghua, H.; Yumin, D.; Jianhong, Y. Preparation and in Vitro Anticoagulant Activities of Alginate Sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 52, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, G.; Guan, H.; Yue, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Preparation of Low-Molecular-Weight Polyguluronate Sulfate and Its Anticoagulant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øystein, A.; Finn, L.A.; Anders, S.; Terje, E.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Heparin-Like Properties of Sulfated Alginates with Defined Sequences and Sulfation Degrees. Biomacromolecules 2014, 45, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, E.; Arlov, Ø.; Aksel, S.; Ling, L.; Ornitz, D.M.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Sulfated Hydrogel Matrices Direct Mitogenicity and Maintenance of Chondrocyte Phenotype through Activation of FGF Signaling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3649–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Mashayekhi, M.; Pezeshki Modaress, M. Facile Fabrication of Sulfated Alginate Electrospun Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Qiu, P.; Xin, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Yu, R.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship of Propylene Glycol Alginate Sodium Sulfate Derivatives for Blockade of Selectins Binding to Tumor Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xie, W.; Long, Z.; Zhou, J. Synthesis and Anticoagulant Activity of Sodium Alginate Sulfates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, I.; Kedem, A.; Cohen, S. The Effect of Sulfation of Alginate Hydrogels on the Specific Binding and Controlled Release of Heparin-Binding Proteins. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3260–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhanna, R.; Kashyap, A.; Palazzolo, G.; Vallmajo-Martin, Q.; Becher, J.; Möller, S.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Chondrocyte Culture in Three Dimensional Alginate Sulfate Hydrogels Promotes Proliferation While Maintaining Expression of Chondrogenic Markers. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Astani, A.; Ghosh, T.; Schnitzler, P.; Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Sargassum Tenerrimum: Structural Features, Chemical Modification and Anti-Viral Activity. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, D.; Qiu, P.; Han, Z.; Zeng, P.; He, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xu, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Efficacy of Heparinoid PSS in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases and beyond-A Review of 27 Years Clinical Experiences in China. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2016, 22, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.J.; Lawrie, G.; Lambert, L.K.; Whittaker, M.; Jack, K.S.; Grndahl, L. Phosphorylation of Alginate: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of in Vitro Mineralization Capacity. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Song, M.; Lee, E.J.; Shin, U.S. Injectable Hydrogels Derived from Phosphorylated Alginic Acid Calcium Complexes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 51, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueqin, Y.; Caifeng, L.; Zhe, L.; Fengjun, J.; Yi, Z.; Kunshan, Y.; Shaopeng, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Biosurfactant Based on Hydrophobically Modified Alginate. Colloid J. 2014, 76, 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C. Amphiphilic Alginate as a Drug Release Vehicle for Water-Insoluble Drugs. Colloid J. 2015, 77, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, S.; Lu, Q.; Yu, Y. Synthesis and Micelle Properties of the Hydrophobic Modified Alginate. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panão, C.O.; Campos, E.L.S.; Lima, H.H.C.; Rinaldi, A.W.; Lima-Tenório, M.K.; Tenório-Neto, E.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Asefa, T.; Rubira, A.F. Ultra-Absorbent Hybrid Hydrogel Based on Alginate and SiO2 Microspheres: A High-Water-Content System for Removal of Methylene Blue. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuran, I.; Murat, I.; Mustafa, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(N-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone) Grafted Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Beads for the Controlled Release of Indomethacin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Arpit, S.; Mithilesh, Y.; Kunj, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Alginate-g-Vinyl Sulfonic Acid with a Potassium Peroxydiphosphate/Thiourea System. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 3685–3694. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, S.; Ram Prakash, S.; Sagar, P. Microwave-Initiated Synthesis of Polyacrylamide Grafted Sodium Alginate: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vitaliy, K.; Ralph, A.W.; Pascale, C.; Michael, F.C.; Ronald, J.N. Polymerization Induced Self-Assembly of Alginate Based Amphiphilic Graft Copolymers Synthesized by Single Electron Transfer Living Radical Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.N.; Pang, V.Y.T.; Aik, S.X.L. Calcium Triggered Self-Assembly of Alginate-: Graft -POEGMA via RAFT for the Encapsulation of Lipophillic Actives. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8254–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.N.; Wu, Y.L.; Loh, X.J.; Ho, N.Y.; Aik, S.X.; Pang, V.Y. The Effective Treatment of Multi-Drug Resistant Tumors with Self-Assembling Alginate Copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Barikani, M. Molecular Engineering of Manipulated Alginate-Based Polyurethanes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, T.; Larsen, B. Formation of Hemiacetals between Neighbouring Hexuronic Acid Residues during the Periodate Oxidation of Alginate. Acta Chem. Scand. 1970, 24, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Painter, T. Effect of Periodate Oxidation upon the Stiffness of the Alginate Molecule in Solution. Carbohydr. Res. 1973, 26, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.E.; Tigwell, M.J. Periodate-Induced Viscosity Decreases in Aqueous Solutions of Acetal- and Ether-Linked Polymers. Carbohydr. Res. 1973, 28, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.E.; Tigwell, M.J. On the Mechanism of Scission of Alginate Chains by Periodate. Carbohydr. Res. 1976, 47, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, I.L.; Painter, T.; Smidsrød, O. Concerning the Effect of Periodate Oxidation upon the Intrinsic Viscosity of Alginate. Carbohydr. Res. 1977, 59, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.G.; Rinaudo, M.; Villar, M.A. Oxidation of Sodium Alginate and Characterization of the Oxidized Derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Lesieur, S.; Labarre, D.; Jayakrishnan, A. Periodate Oxidation of Sodium Alginate in Water and in Ethanol-Water Mixture: A Comparative Study. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, D.J.; Damm, K.L.; Bouhadir, K.H.; Anderson, K.W.; Alsberg, E.; Lee, K.Y. Degradation of Partially Oxidized Alginate and Its Potential Application for Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Study on Partially Oxidized Sodium Alginate with Potassium Permanganate as the Oxidant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar]
- Boontheekul, T.; Kong, H.J.; Mooney, D.J. Controlling Alginate Gel Degradation Utilizing Partial Oxidation and Bimodal Molecular Weight Distribution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.J.; Kaigler, D.; Kim, K.; Mooney, D.J. Controlling Rigidity and Degradation of Alginate Hydrogels via Molecular Weight Distribution. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, M.-C.; Delestre, C.; Hubert, P.; Dellacherie, E. Covalent Coupling of a Short Polyether on Sodium Alginate: Synthesis and Characterization of the Resulting Amphiphilic Derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 1991, 16, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.A.; Jeon, G.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Yang, J.W. Effectiveness Test of Alginate-Derived Polymeric Surfactants. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun-Ah, K.; Moon Sik, S.; Ji-Won, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobically Modified Alginate. Polym. Bull. 2002, 47, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Laurienzo, P.; Malinconico, M.; Motta, A.; Vicinanza, A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Alginate-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Graft Copolymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptstein, S.; Dezorzi, S.; Prüfert, F.; Matuszczak, B.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Synthesis and in Vitro Characterization of a Novel S-Protected Thiolated Alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalheim, M.; Vanacker, J.; Najmi, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Strand, B.L.; Christensen, B.E. Efficient Functionalization of Alginate Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2016, 80, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueckgen, A.; Garske, D.S.; Ellinghaus, A.; Desai, R.M.; Stafford, A.G.; Mooney, D.J.; Duda, G.N.; Cipitria, A. Hydrolytically-Degradable Click-Crosslinked Alginate Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2018, 181, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Lei, J.; Cui, H.; Lu, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Zheng, H.; Yin, Y. Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanospheres from Sodium Alginate Derivative for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Drug Release Behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A.D.; Chiu, H.I.; Mat Yusuf, S.N.A.; Abd Kadir, E.; Ngalim, S.H.; Lim, V. Biocompatible Disulphide Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate Derivative Nanoparticles for Oral Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Tang, F.; Gong, G.; Zhang, J.; Hoi, M.P.M.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Wang, R. pH-Responsive Prodrug Nanoparticles Based on a Sodium Alginate Derivative for Selective Co-Release of Doxorubicin and Curcumin into Tumor Cells. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12533–12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova, B.M.; Jacinto, C.R.; Alarcón, H.; Mejía, I.M.; López, R.C.; de Oliveira Silva, D.; Cavalheiro, E.; Venâncio, T.; Dávalos, J.Z.; Valderrama, A.C. Chemical Modification of Sodium Alginate with Thiosemicarbazide for the Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2259–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huamani-Palomino, R.G.; Jacinto, C.R.; Alarcón, H.; Mejía, I.M.; López, R.C.; de Oliveira Silva, D.; Cavalheiro, E.T.; Venâncio, T.; Dávalos, J.Z.; Valderrama, A.C. Chemical Modification of Alginate with Cysteine and Its Application for the Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Sun, J.; Tan, H.; Yuan, G.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Xiong, D.; Chen, G.; Lai, J.; Ling, Z.; et al. Covalently Polysaccharide-Based Alginate/Chitosan Hydrogel Embedded Alginate Microspheres for BSA Encapsulation and Soft Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, J.; Krause, A.; Möller, L.; Kensah, G.; Möwes, M.; Diekmann, A.; Martin, U.; Kirschning, A.; Gruh, I.; Dräger, G. Fully Defined in Situ Cross-Linkable Alginate and Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Myocardial Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.; Jofri, A.; Thomas, D.S.; Vittorio, O.; Kavallaris, M.; Boyer, C. Tuneable Catechin Functionalisation of Carbohydrate Polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadir, K.H.; Hausman, D.S.; Mooney, D.J. Synthesis of Cross-Linked Poly (Aldehyde Guluronate) Hydrogels (Alginate Oxidised). Polymer 1999, 40, 3575–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Bouhadir, K.H.; Mooney, D.J. Degradation Behavior of Covalently Cross-Linked Poly(Aldehyde Guluronate) Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipan, P.; Nguyen, A.; Narayan, R.J. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. MRS Commun. 2017, 7, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, B.; Papageorgiou, D.G.; Silva, R.; Zehnder, T.; Gul-E-Noor, F.; Bertmer, M.; Kaschta, J.; Chrissafis, K.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Fabrication of Alginate-Gelatin Crosslinked Hydrogel Microcapsules and Evaluation of the Microstructure and Physico-Chemical Properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Jayakrishnan, A. Self-Cross-Linking Biopolymers as Injectable In Situ Forming Biodegradable Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgis, T.A.; Wilder, J. Polyelectrolyte Networks: Elasticity, Swelling, and the Violation of the Flory-Rehner Hypothesis. Comput. Theor. Polym. Sci. 1998, 8, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Patchan, M.; Maranchi, J.; Elisseeff, J.; Trexler, M. Determination of Crosslinking Density of Hydrogels Prepared from Microcrystalline Cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4537–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, B.; Singh, R.; Silva, R.; Roether, J.A.; Kaschta, J.; Detsch, R.; Schubert, D.W.; Cicha, I.; Boccaccini, A.R. Evaluation of Fibroblasts Adhesion and Proliferation on Alginate-Gelatin Crosslinked Hydrogel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigore, A.; Sarker, B.; Fabry, B.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Detsch, R. Behavior of Encapsulated MG-63 Cells in RGD and Gelatine-Modified Alginate Hydrogels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, B.; Rompf, J.; Silva, R.; Lang, N.; Detsch, R.; Kaschta, J.; Fabry, B.; Boccaccini, A.R. Alginate-Based Hydrogels with Improved Adhesive Properties for Cell Encapsulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, T.; Sarker, B.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Detsch, R. Evaluation of an Alginate-Gelatine Crosslinked Hydrogel for Bioplotting. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovska, J.; Lennert, P.; Hartmann, A.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Zehnder, T.; Sarker, B.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Detsch, R. Biofabrication of 3D Alginate-Based Hydrogel for Cancer Research: Comparison of Cell Spreading, Viability, and Adhesion Characteristics of Colorectal HCT116 Tumor Cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, B.; Zehnder, T.; Rath, S.N.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Alginate-Gelatin Hydrogel: A Favorable Matrix for Growth and Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in 3D. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Ooi, H.; Morgan, F.; Mota, C.; Dettin, M.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Moroni, L.; Baker, M. Viscoelastic Oxidized Alginates with Reversible Imine Type Crosslinks: Self-Healing, Injectable, and Bioprintable Hydrogels. Gels 2018, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Whitney, R.A.; Neufeld, R.J. Kinetic Controlled Synthesis of PH-Responsive Network Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2536–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Whitney, R.A.; Neufeld, R.J. Semisynthesis of a Controlled Stimuli-Responsive Alginate Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluemsab, W.; Sakairi, N.; Furuike, T. Synthesis and Inclusion Property of α-Cyclodextrin-Linked Alginate. Polymer (Guildf) 2005, 46, 9778–9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluemsab, W.; Fukazawa, Y.; Furuike, T.; Nodasaka, Y.; Sakairi, N. Cyclodextrin-Linked Alginate Beads as Supporting Materials for Sphingomonas Cloacae, a Nonylphenol Degrading Bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benettayeb, A.; Guibal, E.; Morsli, A.; Kessas, R. Chemical Modification of Alginate for Enhanced Sorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Khalifa, R.E.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, X.K. Fabrication of Tetraethylenepentamine Functionalized Alginate Beads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passemard, S.; Szabó, L.; Noverraz, F.; Montanari, E.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Bühler, L.H.; Wandrey, C.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Synthesis Strategies to Extend the Variety of Alginate-Based Hybrid Hydrogels for Cell Microencapsulation. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, L.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Montanari, E.; Noverraz, F.; Bornet, A.; Bühler, L.H.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Cross-Reactive Alginate Derivatives for the Production of Dual Ionic–Covalent Hydrogel Microspheres Presenting Tunable Properties for Cell Microencapsulation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noverraz, F.; Montanari, E.; Pimenta, J.; Szabó, L.; Ortiz, D.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Bühler, L.H.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Antifibrotic Effect of Ketoprofen-Grafted Alginate Microcapsules in the Transplantation of Insulin Producing Cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levato, R.; Jungst, T.; Scheuring, R.G.; Blunk, T.; Groll, J.; Malda, J. From Shape to Function: The Next Step in Bioprinting. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, F.L.C.; Moroni, L.; Baker, M.B. Dynamic Bioinks to Advance Bioprinting. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 1901798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Y. Four-dimensional bioprinting: Current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matai, I.; Kaur, G.; Seyedsalehi, A.; McClinton, A.; Laurencin, C.T. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 226, 119536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.; Kampleitner, C.; Brennan, M.Á.; Hoornaert, A.; Layrolle, P. Reconstruction of Large Skeletal Defects: Current Clinical Therapeutic Strategies and Future Directions Using 3D Printing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Gao, Q.; Fu, J.; He, Y. Grafting of 3D Bioprinting to In Vitro Drug Screeing: A Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 1901773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Starting Polymer | Sulfation Agent | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na-alg | ClSO3H/formamide | Anticoagulant heparin analogue | [43] |
| Poly-G-alg | ClSO3H/formamide | Anticoagulant heparin analogue and anti-inflammatory compound | [44] |
| TBA-alg | DCC, H2SO4/DMF | Heparin-binding proteins release | [50] |
| Na-alg | N(SO3Na)3/H2O | Anticoagulant heparin analogue | [49] |
| Na-alg, various G:M ratios | ClSO3H/formamide | Evaluation of heparin-like properties of sulfated-alg | [45] |
| TBA-alg | SO3/pyridine | Chondrocyte encapsulation | [51] |
| Na-alg | ClSO3H/formamide | Chondrocyte encapsulation | [46] |
| Na-alg | ClSO3H/formamide | Nanofiber electrospinning | [47] |
| Alginic acid, Poly-M-alg and Poly-G-alg | ClSO3H/formamide | Structure-activity relationship of propylene glycol alginate sodium sulfate (PSS) derivatives | [48] |
| [Ox] Degree | R-NH2 | Reducing Agent | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% |  | NaBH3CN | Amphiphilic alginate | [78] |
| 40% |  | NaBH3CN | Hydrophobically modified alginate, surfactant, removal of heavy metals | [79] |
| 30% |  | NaBH3CN | Hydrophobically modified alginate, polymeric surfactant | [80] |
| 20% |  (Further modified with PEG) | NaBH3CN | High biocompatibility material | [81] |
| 44% |  | NaBH4 | Drug delivery | [85] |
| n.d. |  | NaBH3CN | Drug delivery | [82] |
| 8% |  Peptide sequences: GRGDYP, GRGDSP, KHIFSDDSSE | pic-BH3 | Material with cell attachment sites, induction of cell interaction | [83] |
| 48% | Doxorubicin | - | Self-assembly pH sensitive nanoparticle for drug delivery | [87] |
| n.d. |  | NaBH4 | Heavy metal removal from water | [88] |
| 30% |  | NaBH4 | Heavy metal removal from water | [89] |
| 3–11% |  | NaBH4 | Drug delivery | [86] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, L.; Gerber-Lemaire, S.; Wandrey, C. Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040919
Szabó L, Gerber-Lemaire S, Wandrey C. Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040919
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Luca, Sandrine Gerber-Lemaire, and Christine Wandrey. 2020. "Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties" Polymers 12, no. 4: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040919
APA StyleSzabó, L., Gerber-Lemaire, S., & Wandrey, C. (2020). Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties. Polymers, 12(4), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040919