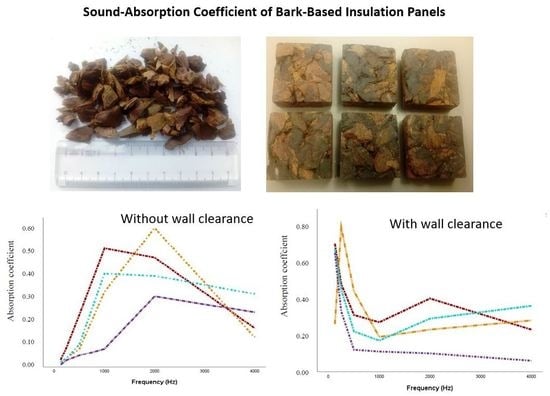
Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Acoustical Measurements in Impedance Tube
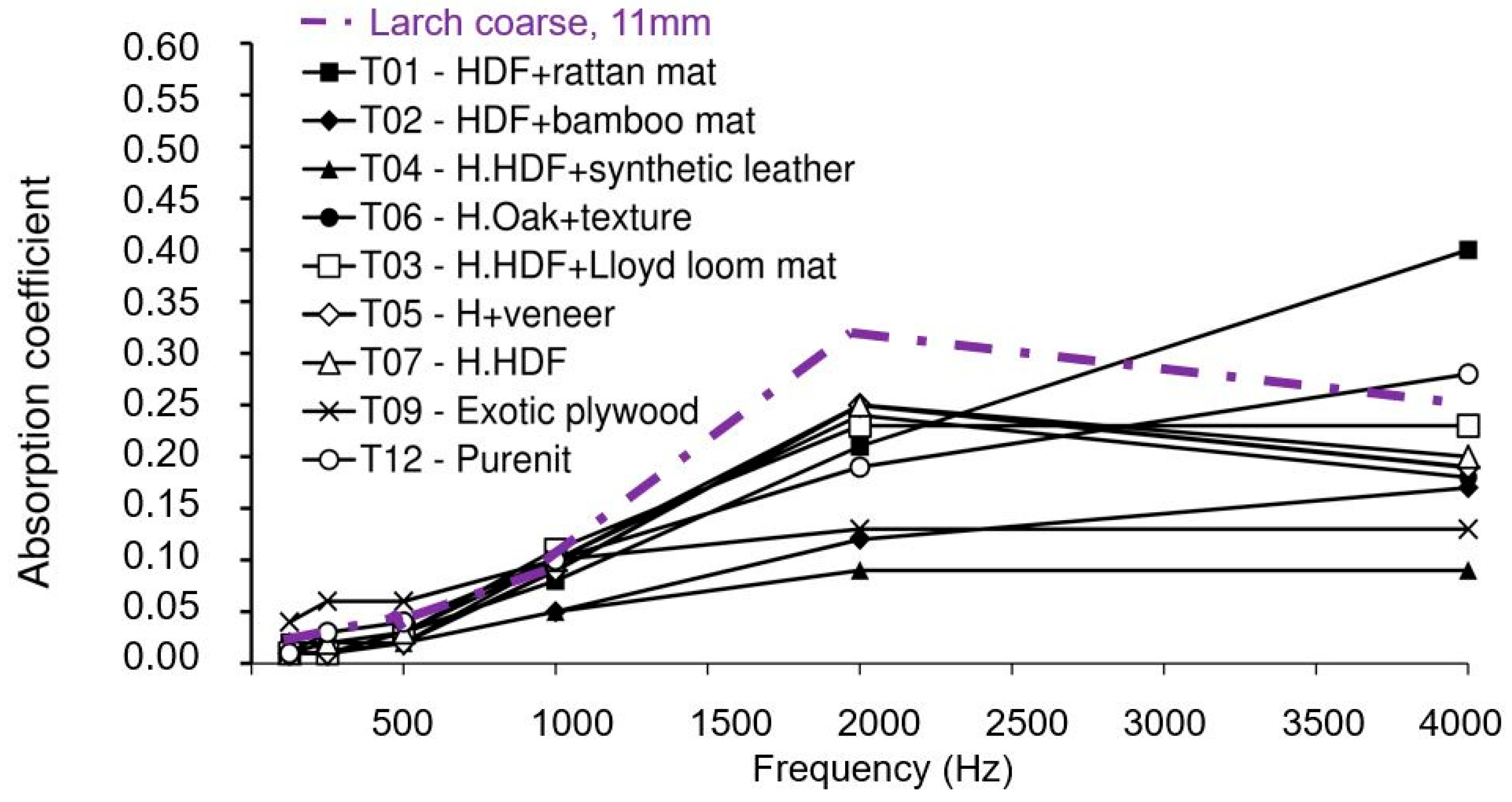
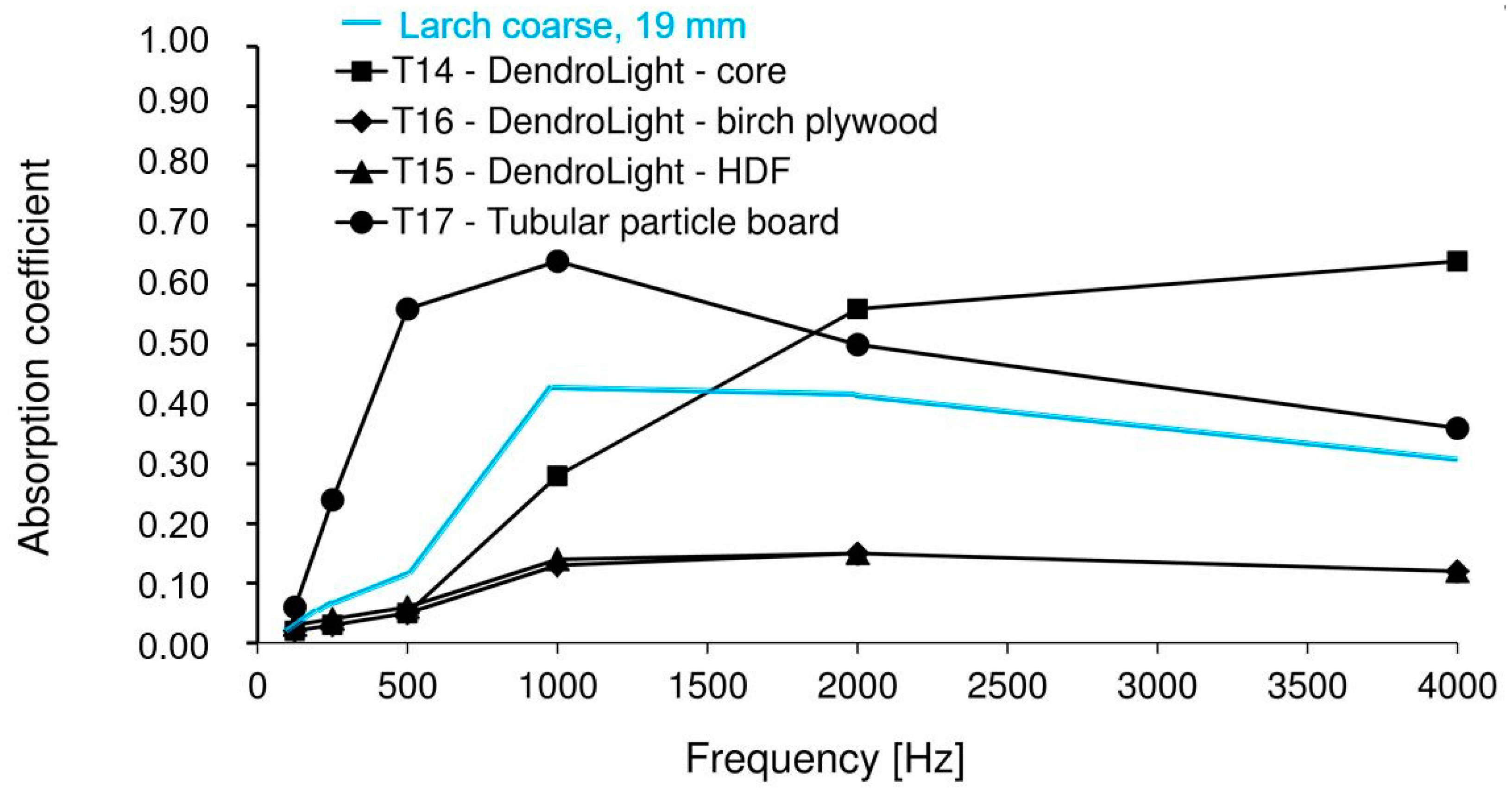
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohatkiewicz, J. Noise Control Plans in Cities–Selected Issues and Necessary Changes in Approach to Measures and Methods of Protectin. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 2744–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, E.; King, E.A. Strategic environmental noise mapping: Methodological issues concerning the implementation of the EU Environmental Noise Directive and their policy implications. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Godshall, W.; Davis, J. Acoustical Absorption Properties of Wood-Based Panel Materials; USDA Forest Service: Madison, WI, USA, 1969.
- Casas-Ledón, Y.; Salgado, K.D.; Cea, J.; Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Fuentealba, C. Life cycle assessment of innovative insulation panels based on eucalyptus bark fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszynski, P. Who warns noise pollution is a gowing harard health in Europe. BMJ 2011, 342, d2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, A. Short review: Air pollution, noise and lack of greenness as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease–epidemiologic and experimental evidence. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 134, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompmaker, J.O.; Janssen, N.A.; Bloemsma, L.D.; Gehring, U.; Wijga, A.H.; Brink, C.V.D.; Lebret, E.; Brunekreef, B.; Hoek, G. Residential surrounding green, air pollution, traffic noise and self-perceived general health. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pépiot, E. Male and female speech: A study of mean f0, f0 range, phonation type and speech rate in Parisian French and American English speakers. Speech Prosody 2014, 7, 305–309. Available online: https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs-00999332 (accessed on 23 February 2020).
- Smardzewski, J.; Kamisiński, T.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R.; Majewski, A.; Flach, A.; Pilch, A. Sound absorption of wood-based materials. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsby, B.; Ricketts, T. The effects of hearing loss on the contribution of high- and low-frequency speech information to speech understanding. II. Sloping hearing loss. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L. Sound absorption and insulation functional composites. In Advanced High Strength Natural Fibre Composites in Construction; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 333–373. [Google Scholar]
- Tsalagkas, D.; Börcsök, Z.; Pásztory, Z. Thermal, physical and mechanical properties of surface overlaid bark-based insulation panels. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pásztory, Z.; Börcsök, Z.; Tsalagkas, D. Density optimization for the manufacturing of bark-based thermal insulation panels. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Environment and Renewable Energy, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 25–28 February 2019; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 307. [Google Scholar]
- Karlinasari, L.; Hermawan, D.; Maddu, A.; Martianto, B.; Lucky, I.K.; Nugroho, N.; Hadi, Y.S. Acosutical properties of particleboards made from betung bamboo as building construction material. Bioresources 2012, 7, 5700–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bucur, V. Acoustic of Wood, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berling/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 7–36. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.; Crocker, M.J. Recent trends in porous sound-absorbing materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- McMullan, R. Environmental Science in Building, 5th ed.; Palgrave: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 200–251. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, M.; Johnson, J.; Rocafort, J. Architectural Acoustics Principles and Design; Pearson: London, UK, 1999; pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Chen, J.Y.; Parikh, D.V. Acoustical evaluation of carbonized and activated cotton nonwovens. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6533–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krucińska, I.; Gliścińska, E.; Michalak, M.; Ciechańska, D.; Kazimierczak, J.; Bloda, A. Sound-absorbing green composites based on cellulose ultrashort/ultra-fine fibers. Text Res. J. 2014, 85, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahani, F.; Soltani, P.; Zarrebini, M. The analysis of acoustic characteristics and sound absorption coefficient of needle punched nonwoven fabrics. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2014, 9, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwawiire, S.; Tomkova, B.; Gliscinska, E.; Krucinska, I.; Michalak, M.; Militky, J.; Jabbar, A. Investigation of sound absorption properties of bark cloth nonwoven fabric and composites. Autex Res. J. 2015, 15, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berge, B. The Ecology of Building Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Fua, Q.; Yang, S.; Dinga, B.; Yu, J. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, M.C.; Reh, R.; Çavdar, A.D. Non-Wood Lignocellulosic Composites. Materials Science and Engineering: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réh, R.; Igaz, R.; Krišťák, Ľ.; Ružiak, I.; Gajtanska, M.; Božíková, M.; Kučerka, M. Functionality of Beech Bark in Adhesive Mixtures Used in Plywood and Its Effect on the Stability Associated with Material Systems. Materials 2019, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, T.; Jamshaid, H.; Mishra, R.; Khan, M.Q.; Petru, M.; Novak, J.; Choteborsky, R.; Hromasova, M. Acoustic, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Green Composites Reinforced with Natural Fibers Waste. Polymers 2020, 12, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danihelová, A.; Němec, M.; Gergel, T.; Gejdoš, M.; Gordanová, J.; Sčensný, P. Usage of recycled technical textiles as thermal insulation and an acoustic absorber. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Němec, M.; Igaz, R.; Gergel, T.; Danihelová, A.; Ondrejka, V.; Krišťák, L.; Gejdoš, M.; Kminiak, R. Acoustic and thermophysical properties of insulation materials based on wood wool. Akustika 2019, 33, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, E.M.; Barbu, M.C.; Petutschnigg, A.; Réh, R.; Krišťák, Ľ. Analysis of Larch-Bark Capacity for Formaldehyde Removal in Wood Adhesives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliačik, J. Environmentally-Friendly High-Density Polyethylene-Bonded Plywood Panels. Polymers 2019, 11, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balali, A.; Hakimelahi, A.; Valipour, A. Identification and prioritization of passive energy consumption optimization measures in the building industry: An Iranian case study. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazieschi, G.; Gori, P.; Lombardi, L.; Asdrubali, F. Life cycle energy minimization of autonomous buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koezjakov, A.; Urge-Vorsatz, D.; Crijns-Graus, W.; van den Broek, M. The relationship between operational energy demand and embodied energy in Dutch residential buildings. Energy Build. 2018, 165, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincová, S.; Hitka, M.; Štarchoň, P.; Stachová, K. Strategic Instrument for Sustainability of Human Resource Management in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Using Management Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, W. Life-Cycle Assessment of Envelope Structure of Typical Residential Buildings in Cities and Towns in Severe Cold Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brás, A.; Gomes, V. LCA implementation in the selection of thermal enhanced mortars for energetic rehabilitation of school buildings. Energy Build. 2015, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kong, L.; Tong, H.; Wang, X. Evaluation Model of Environmental Impacts of Insulation Building Envelopes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestre, J.D.; Pargana, N.; De Brito, J.; Pinheiro, M.D.; Durão, V. Insulation Cork Boards—Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of an Organic Construction Material. Materials 2016, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowoświat, A.; Dulak, L. Impact of Cement Dust Pollution on the Surface of Sound-Absorbing Panels on Their Acoustic Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hýsek, Š.; Neuberger, P.; Sikora, A.; Schönfelder, O.; Ditommaso, G. Waste Utilization: Insulation Panel from Recycled Polyurethane Particles and Wheat Husks. Materials 2019, 12, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanciu, M.; Curtu, I.; Cosereanu, C.; Vasile, O.; Olarescu, C. Evaluation of Absorption Coefficient of Biodegradable Composite Materials with Textile Inserts. Rom. J. Acoust. Vib. 2011, 2, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Towards an inclusive circular economy: Quantifying the spatial flows of e-waste through the informal sector in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lee, C.; Lim, J.; Klemeš, J. Cross-disciplinary approaches towards smart, resilient and sustainable circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiades, K.; Blom, J.; Buyle, M.; Audenaerta, A. Translating the circular economy to bridge construction: Lessons learnt from a critical literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 15149-1:2011 Solid Biofuels-Determination of Particle size Distribution—Part 1: Oscillat-ing Screen Method Using Sieve Apertures of 1 mm and Above, -Test Method; CEN, European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Tudor, E.; Barbu, M.; Petutschnigg, A.; Réh, R. Added-value for wood bark as a coating layer for flooring tiles. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 180, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, G.; Lienbacher, B.; Barbu, M.; Senck, S.; Petutschnigg, A. Water vapour diffusion resistance of larch (Larix decidua) bark insulation panels and application considerations based on numeric modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, G.; Lienbacher, G.; Barbu, M.C.; Richter, K.; Petutschnigg, A. Larch (Larix decidua) bark insulation board: Interactions of particle orientation, physical-mechanical and thermal properties. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2018, 76, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kain, G.; Barbu, M.C.; Richter, K.; Plank, B.; Tondi, G.; Petutschnigg, A. Use of tree bark as insulation material. For. Prod. J. 2015, 65, S16–S25. [Google Scholar]
- Kain, G.; Stratev, D.; Tudor, E.; Lienbacher, B.; Weigl, M.; Barbu, M.C.; Petutschnigg, A. Qualitative investigation on VOC-emissions from spruce (Picea abies) and larch (Larix decidua) loose bark and bark panels. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2020, 78, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kain, G.; Charwat-Pessler, J.; Barbu, M.C.; Plank, B.; Richter, K.; Petutschnigg, A. Analyzing wood bark insulation board structure using X-ray computed tomography and modeling its thermal conductivity by means of finite difference method. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 326-1:1994: Wood-Based Panels-Sampling, Cutting and Inspection—Part 1: Sampling and Cutting of Test Pieces and Expression of Test Results, -Test Method; CEN, European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1994.
- ISO16999, Wood-Based Panels—Sampling and Cutting of Test Pieces; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EN 322:2005 Wood-Based Panels-Determination of Moisture Content, -Test Method; CEN, European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- ISO 10534-2:1998: Acoustics-Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method; ISO/TC 43/SC2 Building Acoustics; CEN, European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1998.
- Stegmaier, K. Akustikbüro Krämer&Stegmaier, Ingenieurbüro für Schallschutz und Technische Akustik. 2018. Available online: http://www.akustik-berlin.de/ (accessed on 14 April 2018).
- Dettendorfer, A. Hetta. Ein Ressourcenschonendes Möbel für IKEA. Bachelor’s Thesis, Salzburg University of Applied Sciences, Kuchl, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Niresh, J.A.; Neelakrishnan, S.; Subharani, S.; Kannaian, T.; Prabhakaran, R. Review of acoustic characteristics of materials using impedance tube. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar]
- Kundt, A. Acoustic Experiments. Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 2009, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahani, F.; Soltani, P.; Zarrebini, M. The analysis of acoustical characteristics and sound absorption coefficient of woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Agnhage, T.; Cho, G. Sound Absorption of Multiple Layers of Nanofiber Webs and the Comparison of Measuring Methods for Sound Absorption Coefficients. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlinasari, L.; Hermawan, D.; Maddu, A.; Martiandi, B.; Hadi, Y.S. Development of particleboard for acoustical panel from tropical fast growing species. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2012, 24, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H.J. Rice straw-wood particle composite for sound absorbing wooden construction materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, R.; Mohd Nor, M.J.; Mat Tahir, M.F.; Ismail, A.R.; Nuawi, M.Z. Acoustic properties of multi-layer coir fibers sound absorption panel. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 3709–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulkifli, R.; Nor, M.J.M. Noise control using coconut coir fiber sound absorber with porous layer backing and perforated panel. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smardzewski, J.; Batko, W.; Kamisinski, T.; Flach, A.; Pilch, A.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R.; Roszyk, E.; Majewski, A. Experimental study of wood acoustic absorption characteristics. Holzforschung 2013, 68, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassilieff, C. Sound absorption of wood-based materials. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 48, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, M.; Ashori, A.; Mehrabi, R. Mechanical and acoustical properties of particleboards made with date palm branches and vermiculite. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, T.; Danihelova, A.; Danihelova, Z. Acoustic comfort in wooden buildings made from cross laminated timber. Akustika 2016, 25, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ilgun, A.; Cogurcu, M.T.; Ozdemir, C.; Kalipci, E.; Sahinkaya, S. Determination of sound transfer coefficient of boron added waste cellulosic and paper mixture panels. Sci. Res. Essay 2010, 5, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar]

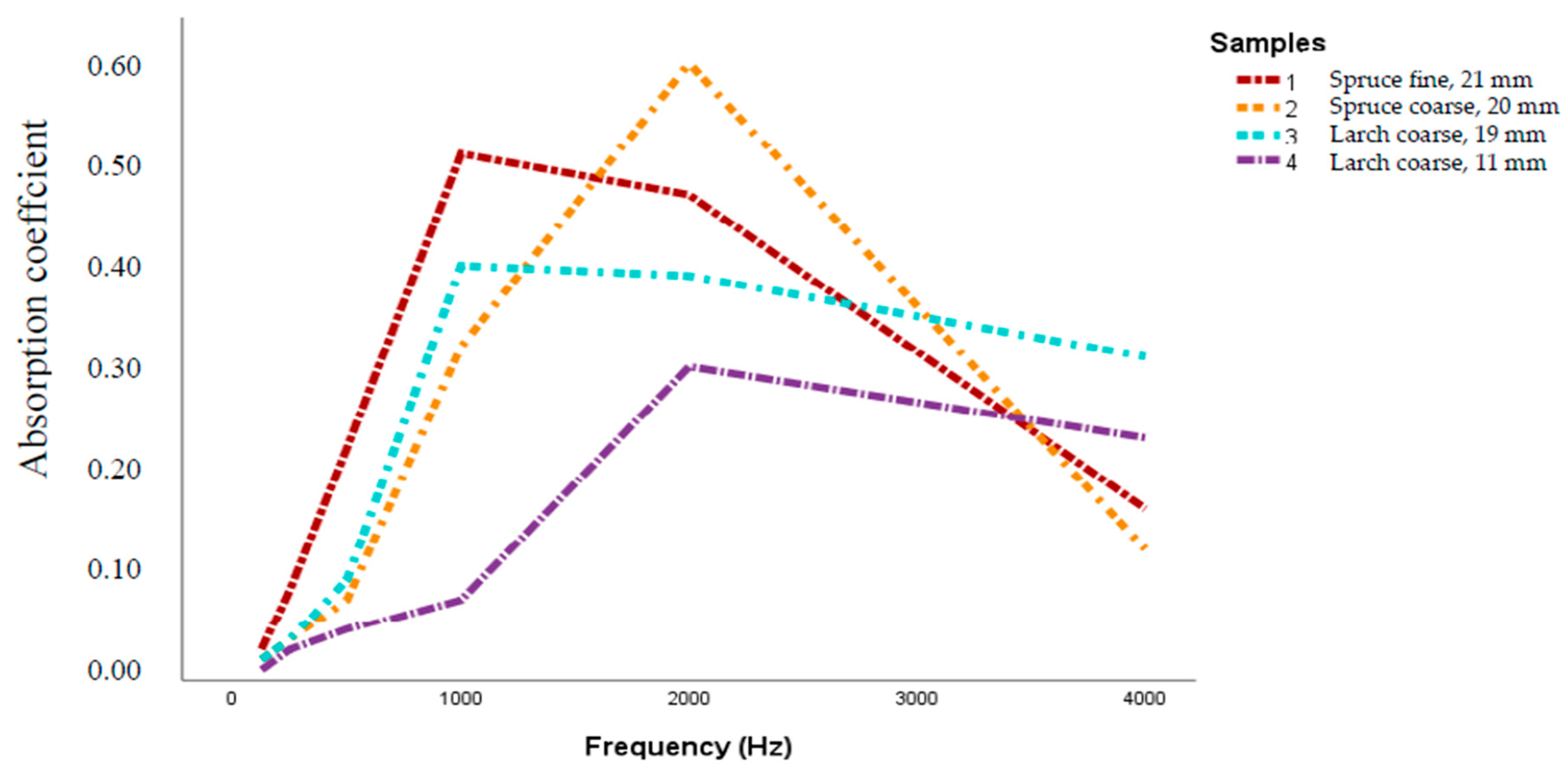


| Board Type | Bark Particle Size (mm) | Board Thickness (mm) | Boards Dimension (mm) | Board Density (kg/m³) | Adhesive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spruce fine | 8–13 | 21 | 500 × 500 | 500 | 10% UF |
| Spruce coarse | 10–30 | 20 | 500 × 500 | 414 | 10% UF |
| Larch coarse, thin | 10–30 | 11 | 500 × 500 | 690 | 10% tannin |
| Larch coarse, thick | 10–30 | 19 | 500 × 500 | 571 | 10% tannin |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tudor, E.M.; Dettendorfer, A.; Kain, G.; Barbu, M.C.; Réh, R.; Krišťák, Ľ. Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051012
Tudor EM, Dettendorfer A, Kain G, Barbu MC, Réh R, Krišťák Ľ. Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051012
Chicago/Turabian StyleTudor, Eugenia Mariana, Anna Dettendorfer, Günther Kain, Marius Catalin Barbu, Roman Réh, and Ľuboš Krišťák. 2020. "Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051012
APA StyleTudor, E. M., Dettendorfer, A., Kain, G., Barbu, M. C., Réh, R., & Krišťák, Ľ. (2020). Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels. Polymers, 12(5), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051012