Synthesis of Copper(II) Trimesinate Coordination Polymer and Its Use as a Sorbent for Organic Dyes and a Precursor for Nanostructured Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Adsorbates
2.3. Synthesis of MOF
2.3.1. Synthesis Using Slow Evaporation (A)
2.3.2. Solvothermal Synthesis Using a PEG-1500 Modulator (B)
2.3.3. Synthesis in Water (C)
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Determination of Kinetic and Thermodynamic Parameters of Thermal Decomposition
2.6. Measurement of Sorption Equilibrium Properties
2.7. Dye Equilibrium Adsorption Experiments
2.8. Studying the Kinetics of Adsorption
2.9. pH Experiments
2.10. Study of Adsorption Isotherms
2.10.1. Langmuir Isotherm
2.10.2. Freundlich Isotherm
2.11. Determination of Thermodynamic Parameters of Dye Adsorption
2.12. Thermolysis Technique
3. Results and Discussion
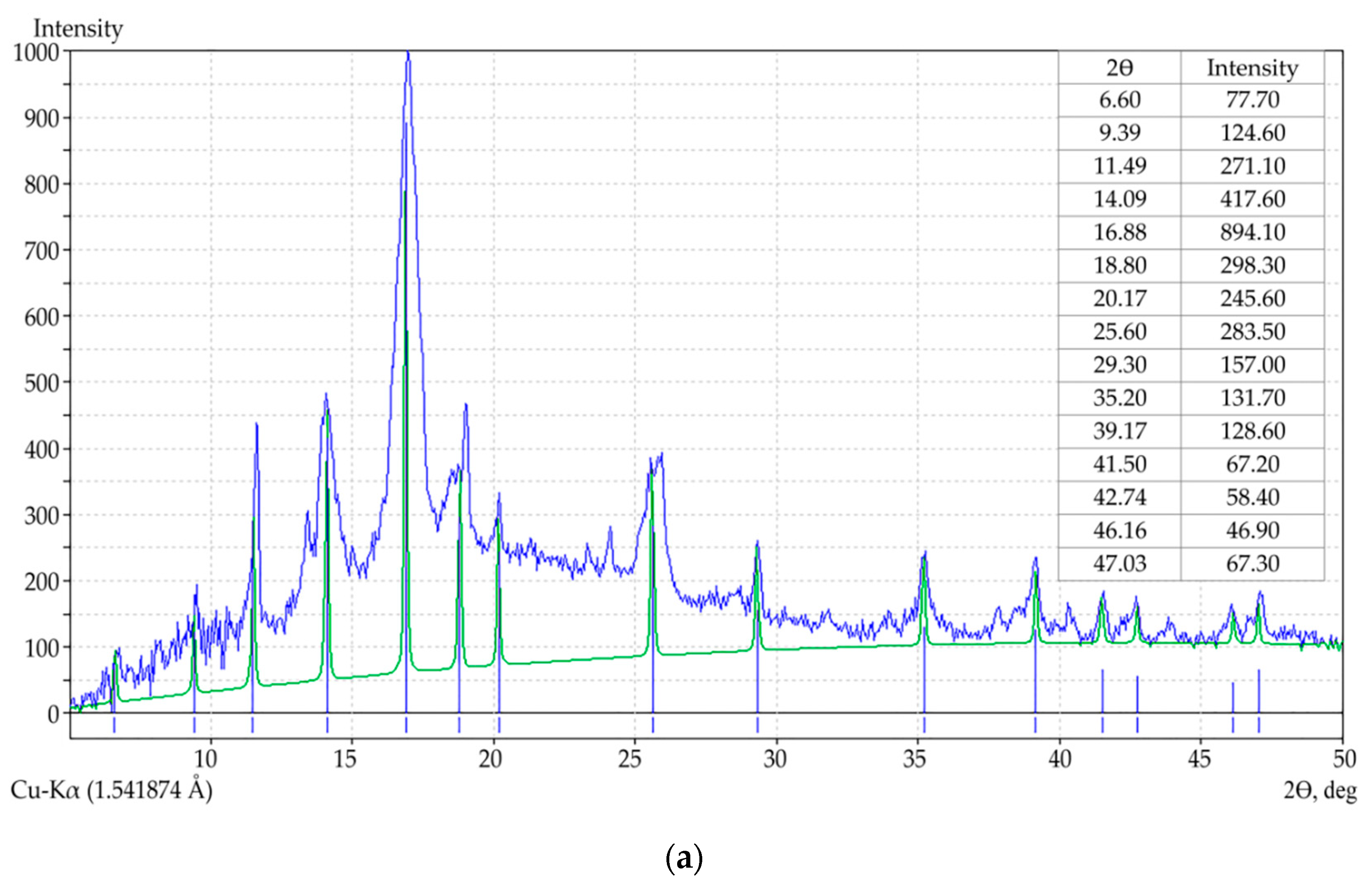
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of MOFs
3.2. The Adsorption Capacity and Surface Area Analysis of Copper Trimesinate
3.3. Dye Adsorption on MOF
3.4. Thermolysis of MOFs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Chen, X. Quantification of the Driving Factors of Water Use in the Productive Sector Change Using Various Decomposition Methods. Water Resour. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 33, 4105–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, J.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Zhang, P.; Song, B.; Cao, W.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Huan, S.-Y. Zirconium-based metal organic frameworks loaded on polyurethane foam membrane for simultaneous removal of dyes with different charges. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Adsorption and biodegradation of dye in wastewater with Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) core-shell bio-nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, J.; Vossoughi, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Alemzadeh, I. Synthesis of metal-organic framework hybrid nanocomposites based on GO and CNT with high adsorption capacity for dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadari, M.; Yousefi, F.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K. A simple approach for the sonochemical loading of Au, Ag and Pd nanoparticle on functionalized MWCNT and subsequent dispersion studies for removal of organic dyes: Artificial neural network and response surface methodology studies. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Hao, J. Fabrication of Titanium Dioxide and Tungstophosphate Nanocomposite Films and Their Photocatalytic Degradation for Methyl Orange. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13590–13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ghorai, S.; Das, C.; Samrat, S.; Ghosh, A.; Panda, A.B. Carboxymethyl Tamarind-g-poly(acrylamide)/Silica: A High Performance Hybrid Nanocomposite for Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15546–15556. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, M.; Guan, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Brusseau, M.L.; Chi, H. Synthesis of iron-based metal-organic framework MIL-53 as an efficient catalyst to activate persulfate for the degradation of Orange G in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 549, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sar, A.; Saleh, A. Response surface optimization, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for effective removal of rhodamine B by magnetic AC/CeO2 nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Sharma, N.R.; Singh, J.; Kanwar, R.S. Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1836–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Agnihotri, R.; Wasewar, K.L.; Uslu, H.; Yoo, C. Status of adsorptive removal of dye from textile industry effluent. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 50, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801–30818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletta, O.A.A.; Mustapha, S.I.; Ajayi, O.A.; Ahmed, A.T. Optimization of Dye Removal from Textile Wastewater using Activated Carbon from Sawdust. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2018, 15, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-M.; Ying, R.-J.; Han, C.-X.; Hu, Q.-T.; Xu, H.-M.; Li, J.-H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W. Adsorptive removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution by a Zr-based metal–organic framework: Effects of Ce(iii) doping. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; et al. Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.K. Dye removal from wastewater using activated carbon developed from sawdust: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 113, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, V.; Larrechi, M.S.; Callao, M.P. Kinetic and adsorption study of acid dye removal using activated carbon. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, D. Mechanisms for strong adsorption of tetracycline to carbon nanotubes: A comparative study using activated carbon and graphite as adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7870–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Studies on adsorption of dyes on beta-cyclodextrin polymer. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 90, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljerf, L. High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: Kinetics and equilibrium study. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousha, M.; Daneshvar, E.; Esmaeli, A.R.; Jokar, M.; Khataee, A.R. Optimization of Acid Blue 25 removal from aqueous solutions by raw, esterified and protonated Jania adhaerens biomass. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 69, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimvand, J.; Didehban, K.; Mirshokraie, S.A. Preparation and Characterization of Nano-lignin Biomaterial to Remove Basic Red 2 dye from aqueous solutions. Pollution 2018, 4, 395–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, L.; Morsali, A. Pillared Metal-Organic Frameworks: Properties and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Uflyand, I.E. Chemistry of Polymeric Metal Chelates; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 633–760. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.; Han, T.; Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. Rational construction of defects in a metal–organic framework for highly efficient adsorption and separation of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Voorde, B.; Bueken, B.; Denayer, J.; De Vos, D. Adsorptive separation on metal–organic frameworks in the liquid phase. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5766–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Li, J.R.; Lv, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Guo, G.S. Photocatalytic organic pollutants degradation in metal–organic frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2831–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qin, S.; Li, X.; Qi, S. An enhanced adsorption of organic dyes onto NH2 functionalization titanium-based metal-organic frameworks and the mechanism investigation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 263, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Salam, H.M.; Zaki, T. Removal of hazardous cationic organic dyes from water using nickel-based metal-organic frameworks. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Peng, Y.; Han, G.; Huang, H.; Zhong, C. Synthesis of hierarchical-pore metal-organic framework on liter scale for large organic pollutants capture in wastewater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 525, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavi, H.; Hakimian, A.; Shojaei, A.; Raeiszadeh, M. Selective dye adsorption by highly water stable metal-organic framework: Long term stability analysis in aqueous media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Yu, B.; Van Hecke, K.; Cui, G.H. Four cobalt(ii) coordination polymers with diverse topologies derived from flexible bis(benzimidazole) and aromatic dicarboxylic acids: Syntheses, crystal structures and catalytic properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61281–61289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racles, C.; Zaltariov, M.-F.; Iacob, M.; Silion, M.; Avadanei, M.; Bargan, A. Siloxane-based metal–organic frameworks with remarkable catalytic activity in mild environmental photodegradation of azo dyes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 205, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.-W.; An, W.-J.; Van Hecke, K.; Cui, G.-H. Two copper(I) cyanide coordination polymers modified by semi-rigid bis(benzimidazole) ligands: Syntheses, crystal structures, and electrochemical and photocatalytic properties. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 17474–17484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Uflyand, I.E. Nanomaterials Preparation by Thermolysis of Metal Chelates; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 247–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kharisov, B.I.; Kharissova, O.V.; Méndez, U.O. Coordination and organometallic compounds as precursors of classic and less-common nanostructures: Recent advances. J. Coord. Chem. 2013, 66, 3791–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, L. Metal/metal oxide nanostructures derived from metal–organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7267–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-K.; Xu, Q. Functional materials derived from open framework templates/precursors: Synthesis and applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2071–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Uflyand, I.E. Design and synthesis of coordination polymers with chelated units and their application in nanomaterials science. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42242–42288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chui, S.S.-Y.; Lo, S.M.-F.; Charmant, J.P.H.; Guy Orpen, A.; Williams, I.D. A Chemically Functionalizable Nanoporous Material [Cu3(TMA)2(H2O)3]n. Science 1999, 283, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, J.; Aguado, S.; Kapteijn, F. Manufacture of dense coatings of Cu3(BTC)2 (HKUST-1) on α-alumina. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 113, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, D.; Breynaert, E.; Bajpe, S.R.; Martens, J.A.; Kirschhock, C.E.A. Stability improvement of Cu3(BTC)2 metal–organic frameworks under steaming conditions by encapsulation of a Keggin polyoxometalate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8037–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, Y.K.; Hundal, G.; Jang, I.T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Jun, C.H.; Chang, J.-S. Microwave synthesis of hybrid inorganic–organic materials including porous Cu3(BTC)2 from Cu(II)-trimesate mixture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 119, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, T.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, G.; Weng, L.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Synthesis and Structure of a New 3D Porous Cu(II)–Benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate Coordination Polymer, [Cu2(OH)(BTC)(H2O)]n·2nH2O. Chem. Lett. 2003, 32, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Shi, L.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Ye, Z.; Peng, X. Mesoporous separation membranes of {[Cu(BTC–H2)2·(H2O)2]·3H2O} nanobelts synthesized by ultrasonication at room temperature. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Seoane, B.; Zamaro, J.M.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Combination of MOFs and zeolites for mixed-matrix membranes. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 2781–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameloot, R.; Vermoortele, F.; Vanhove, W.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; Sels, B.F.; De Vos, D.E. Interfacial synthesis of hollow metal–organic framework capsules demonstrating selective permeability. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-Fabra, M.; Munn, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Drage, T.C.; Grant, D.M.; Kashtiban, R.J.; Sloan, J.; Lester, E.; Walton, R.I. Instant MOFs: Continuous synthesis of metal–organic frameworks by rapid solvent mixing. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10642–10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carné-Sánchez, A.; Imaz, I.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Maspoch, D. A spray-drying strategy for synthesis of nanoscale metal-organic frameworks and their assembly into hollow superstructures. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-J.; Li, Y.J.; Kreider, P.B.; Chang, C.-H.; Wannenmacher, N.; Thallapally, P.K.; Ahn, H.-G. High-rate synthesis of Cu–BTC metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11518–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Singh, K.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Bandosz, T.J. Cu–BTC MOF–graphene-based hybrid materials as low concentration ammonia sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11417–11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Abdi, J. Nanoporous metal-organic framework (MOF-199): Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of Basic Blue 41. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, X.; Lester, E.; Wu, T. High efficiency synthesis of HKUST-1 under mild conditions with high BET surface area and CO2 uptake capacity. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2018, 28, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loera-Serna, S.; Solis, H.; Ortiz, E.; Martínez-Hernandéz, A.L.; Noreña, L. Elimination of Methylene Blue and Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solution Using HKUST-1. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2017, 8, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Song, Z.; Che, G.; Ren, A.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Adsorption behavior of metal–organic frameworks for methylene blue from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 193, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W.; Schindler, B.J.; Killops, K.L.; Browe, M.A.; Mahle, J.J. The effect of water adsorption on the structure of the carboxylate containing metal–organic frameworks Cu-BTC, Mg-MOF-74, and UiO-66. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11922–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, N.; Alfutimie, A.; Siperstein, F.R.; Fan, X. Underlying mechanism of the hydrothermal instability of Cu3(BTC)2 metal-organic framework. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2016, 1, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, A.; Ho, C.-H. Preparation of AC/Cu-BTC composite and its adsorption mechanisms. J. Environ. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, L.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M. Metal-organic frameworks/carbon-based materials for environmental remediation: A state-of-the-art mini-review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, V.; Veleta, J.; Zarei-Chaleshtori, M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Villagrán, D. Green synthesis of magnetic MOF@GO and MOF@CNT hybrid nanocomposites with high adsorption capacity towards organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sule, R.; Mishra, A.K. Synthesis of Mesoporous MWCNT/HKUST-1 Composite for Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Jabbari, V.; Islam, M.T.; Turley, R.S.; Dominguez, N.; Kim, H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of Bisphenol A from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tranchemontagne, D.J.; Hunt, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Room temperature synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks: MOF-5, MOF-74, MOF-177, MOF-199, and IRMOF-0. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 8553–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichte, K.; Kratzke, T.; Kaskel, S. Improved synthesis, thermal stability and catalytic properties of the metal-organic framework compound Cu3(BTC)2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 73, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, E.S.; Carroll, B. The Application of Thermoanalytical Techniques to Reaction Kinetics: The Thermogravimetric Evaluation of the Kinetics of the Decomposition of Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate. J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-State, M.A.M.; Saleh, Y.E.; Hazaa, H.A. Decolorization of Congo Red dye by bacterial isolates. J. Ecol. Health Environ. 2017, 5, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Tong, C. Synchronous fluorescence determination of DNA based on the interaction between methylene blue and DNA. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Ramavandi, B. Elimination performance of methylene blue, methyl violet, and Nile blue from aqueous media using AC/CoFe2O4 as a recyclable magnetic composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 19523–19539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Boyjoo, Y.; Choueib, A. A comparative study of dye removal using fly ash treated by different methods. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Krishni, R.R.; Sata, S.A. A novel agricultural waste adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdaoui, O. Batch study of liquid-phase adsorption of methylene blue using cedar sawdust and crushed brick. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsey, G.D. The role of surface heterogeneity. Adv. Catal. 1952, 4, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Pehlivan, E.; Arslan, G. Comparison of adsorption capacity of young brown coals and humic acids prepared from different coal mines in Anatolia. J. Hazard. Mater. B 2006, 138, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, R.H. The Organometallic Chemistry of the Transition Metals, 5th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.L.; Geng, H.Y.; Hu, B.; Song, G.W.; Xu, Z.S. A MOF/graphite oxide hybrid (MOF: HKUST-1) material for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10292–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.-C. Increasing the Stability of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Adv. Chem. 2014, 2014, 182327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailian, L.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M.; Eddaoudi, M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, T.V.N.; Luu, C.L.; Hoang, T.C.; Nguyen, T.; Bui, T.H.; Nguyen, P.H.D.; Thi, T.P.P. Synthesis of MOF-199 and application to CO2 adsorption. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 035016. [Google Scholar]
- Hafizovic, J.; Bjørgen, M.; Olsbye, U.; Dietzel, P.D.; Bordiga, S.; Prestipino, C.; Lamberti, C.; Lillerud, K.P. The Inconsistency in Adsorption Properties and Powder XRD Data of MOF-5 Is Rationalized by Framework Interpenetration and the Presence of Organic and Inorganic Species in the Nanocavities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3612–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Wang, H.; Zacher, D.; Fischer, R.A.; Wöll, C. Growth mechanism of metal-organic frameworks: Insights into the nucleation by employing a step-by-step route. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5038–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gan, Z.; Fisenko, S.; Wang, D.; El-Kaderi, H.M.; Wang, W.-N. Rapid Formation of Metal−Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based Nanocomposites in Microdroplets and Their Applications for CO2 Photoreduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9688–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, L.H.; Lohe, M.R.; Janssens, N.; Kaskel, S.; Martens, J.A. Fine tuning of the metal–organic framework Cu3(BTC)2 HKUST-1 crystal size in the 100 nm to 5 micron range. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13742–13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. The Strengthening Role of the Amino Group in Metal–Organic Framework MIL-53 (Al) for Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Dye Adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3414–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahryari, Z.; Goharrizi, A.S.; Azadi, M. Experimental study of methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solutions onto carbon nano tubes. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2010, 2, 16–28. [Google Scholar]














| Sample (Estimated Formula) | Method of Synthesis | Elemental Content, wt. % (Found/Calc.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | Сu | ||
| Cu3(BTC)2·2DMF·2H2O | A | 36.92/36.81 | 3.63/3.07 | 24.14/24.35 |
| Cu3(BTC)2·2DMF·2H2O | B | 34.63/36.81 | 3.54/3.07 | 24.95/24.35 |
| Cu3(BTC)2·2H2O | C | 35.74/33.72 | 1.21/1.56 | 31.54/29.74 |
| Z, s−1 | Ea, kJ/mol | ∆H, kJ/mol | ∆G, kJ/mol | ∆S, J/mol | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | |
| Stage 1 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 85.68 | 71.09 | 82.7 | 88.11 | 331.7 | −182.9 | −698.04 | 701.1 |
| Stage 2 | 0.18 | 0.9 | 132.9 | 140.7 | 128.64 | 137 | −232 | −106.6 | −703.03 | −690 |
| Stage 3 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 145.15 | 96.26 | 140.06 | 91.17 | 581.42 | 534.37 | −720 | −723 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Vmicro (cm3/g) | Average Pore Radius (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1348 | 0.7 | 0.51 | 14 |
| B | 830 | 0.9 | 0.31 | 28 |
| C | 1562.3 | 0.85 | 0.61 | 10.9 |
| Dye | 283 K | 308 K |
|---|---|---|
| CR | 0.47 | 0.9 |
| MB | 0.36 | 0.41 |
| MV | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| Model | CR | MB | MV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm = 170.9 mg g−1 | qm = 173.8 mg g−1 | qm = 34.9 mg g−1 |
| KL = 1 L mg−1 | KL = 1.0034 L mg−1 | KL = 0.7 L mg−1 | |
| R2 = 0.98 | R2 = 0.97 | R2 = 0.95 | |
| Freundlich | qe = 30 mg g−1 | qe = 80 mg g−1 | qe = 125 mg g−1 |
| KF = 0.3 | KF = 0.1 | KF = 0.57 | |
| R2 = 0.98 | R2 = 0.97 | R2 = 0.95 |
| Dye | ∆G0 (kJ mol−1) | ∆H0293 (kJ mol−1) | ∆S0293 (J mol−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 283 K | −11.288 | −10.31 | 11.5 |
| 293 K | −12.3 | |||
| 308 K | −11.72 | |||
| MB | 283 K | −7.058 | −6.6 | 16 |
| 293 K | −7.8 | |||
| 308 K | −8.8 | |||
| MV | 283 K | −7.082 | 2.9 | 4.7 |
| 293 K | −7.31 | |||
| 308 K | −7.5 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Baimuratova, R.K.; Knerelman, E.I.; Davydova, G.I.; Kudaibergenov, S.E.; Kharissova, O.V.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Uflyand, I.E. Synthesis of Copper(II) Trimesinate Coordination Polymer and Its Use as a Sorbent for Organic Dyes and a Precursor for Nanostructured Material. Polymers 2020, 12, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051024
Dzhardimalieva GI, Baimuratova RK, Knerelman EI, Davydova GI, Kudaibergenov SE, Kharissova OV, Zhinzhilo VA, Uflyand IE. Synthesis of Copper(II) Trimesinate Coordination Polymer and Its Use as a Sorbent for Organic Dyes and a Precursor for Nanostructured Material. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDzhardimalieva, Gulzhian I., Rose K. Baimuratova, Evgeniya I. Knerelman, Galina I. Davydova, Sarkyt E. Kudaibergenov, Oxana V. Kharissova, Vladimir A. Zhinzhilo, and Igor E. Uflyand. 2020. "Synthesis of Copper(II) Trimesinate Coordination Polymer and Its Use as a Sorbent for Organic Dyes and a Precursor for Nanostructured Material" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051024
APA StyleDzhardimalieva, G. I., Baimuratova, R. K., Knerelman, E. I., Davydova, G. I., Kudaibergenov, S. E., Kharissova, O. V., Zhinzhilo, V. A., & Uflyand, I. E. (2020). Synthesis of Copper(II) Trimesinate Coordination Polymer and Its Use as a Sorbent for Organic Dyes and a Precursor for Nanostructured Material. Polymers, 12(5), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051024








