Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Test Samples
2.3. Hydrothermal Aging
2.4. Experimental Methods
2.5. Modeling of Property Degradation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
3.2. Characterization before Hydrothermal Aging
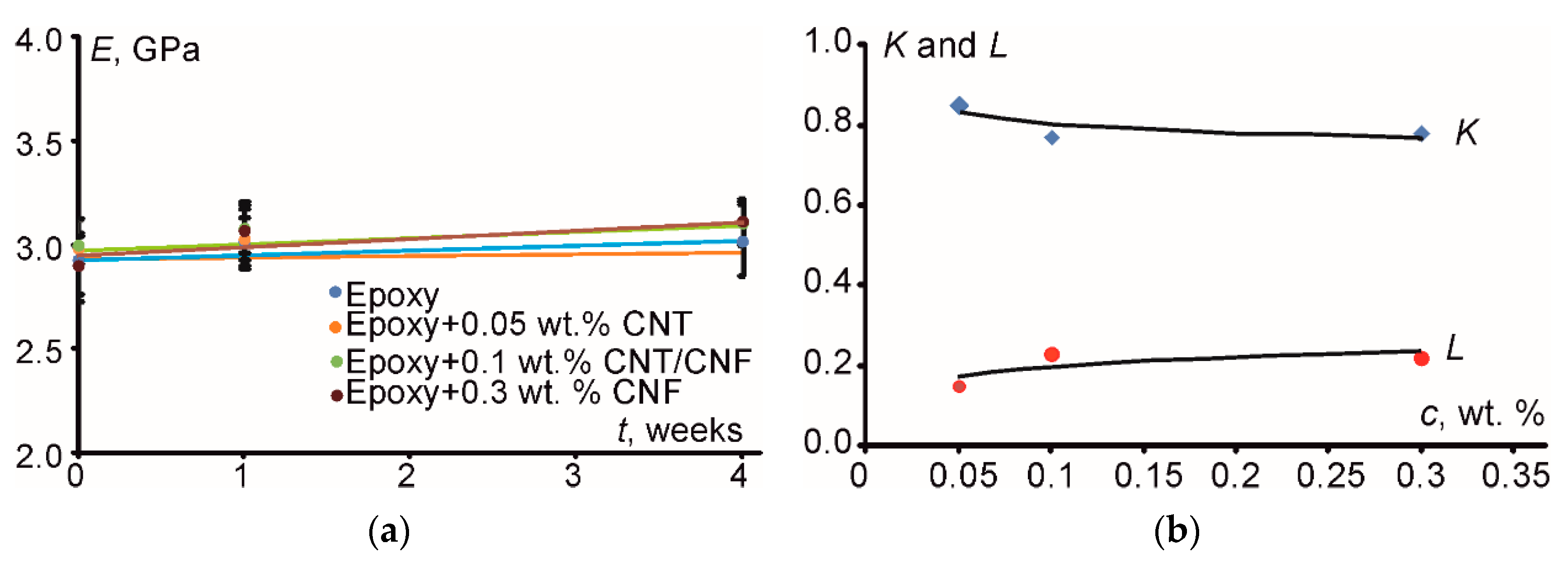
3.2.1. Flexural Properties
3.2.2. Thermomechanical Properties
3.3. Hydrothermal Aging
3.4. Characterization after Hydrothermal Aging
3.4.1. Flexural Properties
3.4.2. Thermomechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xin, H.; Liu, Y.; Mosallam, A.; Zhang, Y. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging of pultruded glass fiber reinforced polymer laminates in bridge application. Compos. Part B 2016, 100, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniskevich, K.K.; Glaskova, T.I.; Aniskevich, A.N.; Faitelson, Y.A. Effect of moisture on the viscoelastic properties of an epoxy-clay nanocomposite. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2011, 46, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chevali, V.S.; Xu, Z.; Hui, D.; Wang, H. A review of extending performance of epoxy resins using carbon nanomaterials. Compos. Part B 2018, 136, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniskevich, K.; Glaskova, T.; Jansons, J. Elastic and sorption characteristics of an epoxy binder in a composite during its moistening. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2005, 41, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoula, N.M.; Karabela, M.; Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Tsotra, P. Fast curing versus conventional resins—Degradation due to hygrothermal and UV exposure. Express Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Sevcenko, J.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Cyclic moisture sorption and its effects on the thermomechanical properties of epoxy and epoxy/MWCNT nanocomposite. Polymers 2019, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frigione, M.; Lettieri, M. Durability issues and challenges for material advancements in FRP employed in the construction industry. Polymers 2018, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Papaefthymiou, K.P.; Koutsomitopoulou, A.F.; Portan, D.V.; Zaoutsos, S.P. Effect of dispersion of MWCNTs on the static and dynamic mechanical behavior of epoxy matrix nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Koutsomitopoulou, A.F.; Sfakianakis, A. Effect of thermal fatigue on the mechanical properties of epoxy matrix composites reinforced with olive pits powder. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T. Near tip damage and subcritical crack growth in a participate composite material. Compos. Struct. 1997, 39, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Mannov, E.; Schulte, K.; Aniskevich, A. Water transport in epoxy/MWCNT composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Martone, A.; Giordano, M.; Zarrelli, M. Effect of moisture on elastic and viscoelastic properties of epoxy and epoxy-based carbon fibre reinforced plastic filled with multiwall carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part A 2016, 90, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova, T.; Aniskevich, K.; Borisova, A. Modeling of creep for multiwall carbon nanotube/epoxy nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3314–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. A review of multifunctional polymer-matrix structural composites. Compos. Part B 2019, 160, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Manara, A.E.; Kontaxis, L.C. Experimental and prediction study of displacement-rate effects on flexural behaviour in nano and micro TiO2 particles-epoxy resin composites. Polymers 2020, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Technical Data Sheet: NC7000™. Available online: https://www.nanocyl.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/DM-TI-02-TDS-NC7000-V08.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Technical Data Sheet: SA 719781. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/719781?lang=en®ion=LV (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Sevcenko, J.; Zotti, A.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Environmental effects on mechanical, thermophysical and electrical properties of epoxy resin filled with carbon nanofillers. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Structural Analysis of Advanced Materials—Icsaam, Ischia, Italy, 12–15 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Zotti, A.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Flexural properties of the epoxy resin filled with single and hybrid carbon nanofillers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1431, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Campo, M.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Ureña, A. Effect of the carbon nanotube functionalization on flexural properties of multiscale carbon fiber/epoxy composites manufactured by VARIM. Compos. Part B 2013, 45, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, A.C.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption of graphite-epoxy composition immersed in liquids and humid air. J. Compos. Mater. 1979, 13, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Fernandes, P.; Sena-Cruz, J.; Xavier, J.; Castro, F.; Soares, D.; Carneiro, V. Effects of different environmental conditions on the mechanical characteristics of a structural epoxy. Compos. Part B 2016, 88, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Kosmidou, T.V.; Vatalis, A.S.; Delides, C.G. Water absorption mechanism and some anomalous effects on the mechanical and viscoelastic behavior of an epoxy system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, G.C.; Pappa, A. Water sorption and temperature effects on the dynamic mechanical behaviour of epoxy-matrix particulates. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolongo, S.G.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Moriche, R.; Ureña, A. Influence of thickness and lateral size of graphene nanoplatelets on water uptake in epoxy/graphene nanocomposites. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allaoui, A.; Bounia, N.E. How carbon nanotubes affect the cure kinetics and glass transition temperature of their epoxy composites?—A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2009, 13, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Friedrich, K. Microstructure-related fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth behaviour in toughened, anhydride-cured epoxy resins. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1993, 48, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomula, S.S.R.; Rathore, D.K.; Ray, B.C.; Prusty, R.K. Creep performance of CNT reinforced glass fiber/epoxy composites: Roles of temperature and stress. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material Characteristics | CNT | CNF |
|---|---|---|
| Average diameter, nm | 9.5 | 130 |
| Average length, μm | 1.5 | 20 |
| Aspect ratio | 158 | 153 |
| Surface area, m2/g | 250–300 | 24 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.75 | 1.90 |
| Time, Weeks | Epoxy | Epoxy + 0.05 wt. % CNT | Epoxy + 0.1 wt. % CNF | Epoxy + 0.3 wt. % CNT/CNF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | |
| 0 | 2.93 ± 0.16 | 2.93 | 2.97 ± 0.06 | 2.93 | 2.99 ± 0.10 | 2.93 | 2.91 ± 0.12 | 2.91 |
| 1 | 3.02 ± 0.07 | 3.02 | 3.03 ± 0.07 | 3.03 | 3.07 ± 0.10 | 3.07 | 3.07 ± 0.11 | 3.07 |
| 4 | 3.03 ± 0.03 | 3.13 | 3.09 ± 0.07 | 3.18 | 3.09 ± 0.07 | 3.29 | 3.10 ± 0.09 | 3.31 |
| K = 0.89 L = 0.11 | K = 0.84 L = 0.16 | K = 0.88 L = 0.12 | ||||||
| Time, Weeks | Epoxy | Epoxy + 0.05 wt. % CNT | Epoxy + 0.1 wt. % CNF | Epoxy + 0.3 wt. % CNT/CNF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | |
| 0 | 2.93 ± 0.16 | 2.93 | 2.97 ± 0.06 | 2.93 | 2.99 ± 0.12 | 2.93 | 2.91 ± 0.10 | 2.93 |
| 1 | 2.99 ± 0.10 | 2.94 | 2.97 ± 0.12 | 3.01 | 3.02 ± 0.08 | 3.22 | 2.93 ± 0.15 | 2.89 |
| 4 | 3.14 ± 0.15 | 3.14 | 3.17 ± 0.07 | 3.17 | 3.20 ± 0.15 | 3.18 | 3.13 ± 0.03 | 2.98 |
| K = 0.57 L = 0.43 | K = 0.84 L = 0.16 | K = 0.00 L = 1.00 | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Papanicolaou, G.; Portan, D.; Zotti, A.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051153
Glaskova-Kuzmina T, Aniskevich A, Papanicolaou G, Portan D, Zotti A, Borriello A, Zarrelli M. Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051153
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlaskova-Kuzmina, Tatjana, Andrey Aniskevich, George Papanicolaou, Diana Portan, Aldobenedetto Zotti, Anna Borriello, and Mauro Zarrelli. 2020. "Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051153
APA StyleGlaskova-Kuzmina, T., Aniskevich, A., Papanicolaou, G., Portan, D., Zotti, A., Borriello, A., & Zarrelli, M. (2020). Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers. Polymers, 12(5), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051153











