Microstructural Contributions of Different Polyolefins to the Deformation Mechanisms of Their Binary Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Mechanical Characterization
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of Blends
3.2. Crystallinity
3.2.1. Mono Materials
3.2.2. Blends
3.3. Tensile Deformation and Properties
3.3.1. Mono Materials
3.3.2. Blends
LLDPE + LDPE
HDPE + PP
LLDPE + HDPE
LLDPE + PP
LDPE + HDPE
LDPE + PP
4. Discussion
4.1. LLDPE + LDPE
4.2. HDPE + PP
4.3. LLDPE + HDPE
4.4. LLDPE + PP
4.5. LDPE + HDPE
4.6. LDPE + PP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PlasticsEurope Plastics—The Facts 2019; PlasticsEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Utracki, L.A.; Wilkie, C.A. Polymer Blends Handbook; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9789400760646. [Google Scholar]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullo, A.H. The cost of plastic packaging. CEN Glob. Enterp. 2016, 94, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Schmid, M.; Schlummer, M. Recycling of Polymer-Based Multilayer Packaging: A Review. Recycling 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serranti, S.; Bonifazi, G. Post-consumer polyolefins (PP-PE) recognition by combined spectroscopic sensing techniques. Open Waste Manag. J. 2010, 3, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiss, R.; Hobeika, S.; Lynn, C.; Strobl, G. Network stretching, slip processes, and fragmentation of crystallites during uniaxial drawing of polyethylene and related copolymers. A comparative study. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, B.A.G.; Janssen, R.P.M.; Govaert, L.E.; Meijer, H.E.H. Intrinsic deformation behavior of semicrystalline polymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6069–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrauwen, B.A.G.; Breemen, L.C.A.V.; Spoelstra, A.B.; Govaert, L.E.; Peters, G.W.M.; Meijer, H.E.H. Structure, deformation, and failure of flow-oriented semicrystalline polymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8618–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Galeski, A. Plastic deformation of crystalline polymers: The role of cavitation and crystal plasticity. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9688–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Choi, P. A review of the miscibility of polyethylene blends. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2006, 21, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, K.; Lee, H.; Choe, S. Rheological and Mechanical Properties in Polyethylene Blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Abe, S. LLDPE/LDPE Blends. I. Rheological, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.A. Melt miscibility and mechanical properties of metallocene linear low-density polyethylene blends with high-density polyethylene: Influence of comonomer type. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rana, S.K.; Deopura, B.L. Mechanical properties and morphology of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 46, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Stein, R.S.; Hsu, S.L. Cocrystallization and Phase Segregation of Polyethylene Blends. 1. Thermal and Vibrational Spectroscopic Study by Utilizing the Deuteration Technique. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rana, S.K.; Deopura, B.L. Crystallization kinetics of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 51, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Men, Y.; Strobl, G. Understanding of the tensile deformation in HDPE/LDPE blends based on their crystal structure and phase morphology. Polymer 2003, 44, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhel, G.; Banerjee, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Rheological and mechanical properties of LDPE/HDPE blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2006, 45, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.A.; Harrison, I.R. An investigation of co-crystallization in LDPE/HDPE blends using DSC and TREF. Thermochim. Acta 1998, 313, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shanks, R.A.; Olley, R.H.; Greenway, G.R. Miscibility and isothermal crystallisation of polypropylene in polyethylene melts. Polymer 2001, 42, 7685–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strapasson, R.; Amico, S.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Sydenstricker, T.H.D. Tensile and impact behavior of polypropylene/low density polyethylene blends. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, T.G.; Ojijo, V.; Ray, S.S. The Influence of Blend Ratio on the Morphology, Mechanical, Thermal, and Rheological Properties of PP/LDPE Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolley, E.; Barlow, J.W.; Paul, D.R. Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Low Density Polyethylene Blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalygina, E.E.; Popov, A.A.; Kolesnikova, N.N.; Karpova, S.G. Morphology, thermal behaviour and dynamic properties of the blends based on isotactic polypropylene and low-density polyethylene. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2015, 19, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.M.; Li, R.K.Y.; Ng, C.N. Impact behaviour of polypropylene / polyethylene blends. Polym. Test. 2000, 19, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shanks, R.A.; Long, Y. Miscibility and crystallisation of polypropylene-linear low density polyethylene blends. Polymer 2001, 42, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoulin, M.M.; Carreau, P.J.; Utracki, L.A. Rheological properties of linear low density polyethylene/polypropylene blends. Part 2: Solid state behavior. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1987, 27, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebergall, U.; Bohse, J.; Seidler, S.; Grellmann, W.; Schürmann, B.L. Relationship of fracture behavior and morphology in polyolefin blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Aprem, A.S.; Francis, B.; Chandy, M.C.; Werner, P.; Alstaedt, V.; Thomas, S. Phase morphology, crystallisation behaviour and mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene/high density polyethylene blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, A.J.; Williams, M.L. Tensile Properties and Morphology of Blends of Polyethylene and Polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1980, 25, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, J.; Sheppard, S.; Tookey, S.; Hill, M.J.; Barham, P.J. Unexpectedly High Young’s Moduli Recorded for iPP / HDPE blends. J. Polym. Sci. 2001, 39, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Bringuier, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Baker, A.M.; Macosko, C.W. Adhesion between polyethylenes and different types of polypropylenes. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, B.C.; Chum, S.P.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Adhesion of polyethylene blends to polypropylene. Polymer 2004, 45, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.M.; Kim, K.; Soetrisno, D.; Hannah, J.; Bates, F.S.; Jaffer, S.A.; Lhost, O.; Macosko, C.W. Role of Crystallization on Polyolefin Interfaces: An Improved Outlook for Polyolefin Blends. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.T.; Laabs, F.C.; Narasimhan, B. Interfacial adhesion mechanisms in incompatible semicrystalline polymer systems. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, K.A.; Bates, F.S.; Brant, P.; Brown, G.M. Semicrystalline blends of polyethylene and isotactic polypropylene: Improving mechanical performance by enhancing the interfacial structure. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, J.S.; Cunha, A.; Crawford, R.J. Influence of thermomechanical conditions on structure development and mechanical properties of polyethylene mouldings produced using different moulding methods. Plast. Rubber Compos. Process. Appl. 2000, 29, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, J.; Li, H. Morphology and mechanical properties of injection-molded ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/polypropylene blends and comparison with compression molding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 111, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.-C.; Yen, H.-Z.; Chen, C.-C. Phase morphology and physical properties of PP/HDPE/organoclay (nano) composites with and without a maleated EPDM as a compatibilizer. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Paul, D.R. Formation of co-continuous structures in melt-mixed immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 87–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, G.N. Polyethylene: Linear Low-density. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Elsevier: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 7184–7188. [Google Scholar]
- Michler, G.H. Electron Microscopy of Polymers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783540363507. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, H.P.; Teh, J.W.; Bremner, T.; Rudin, A. Isothermal and non-isothermal crystallization of PP: Effect of annealing and of the addition of HDPE. Polymer 1998, 39, 4011–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Grade | Producer | MFI (g/10 min) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | ExceedTM 1012HA | ExxonMobil | 1.0 |
| LDPE | LD150AC | ExxonMobil | 0.8 |
| HDPE | 25055E | Dow | 25.0 |
| PP | PP6272NE1 | ExxonMobil | 2.8 |
| Blend (A + B) | Composition (A/B) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 80/20 | 50/50 | 20/80 | |
| LLDPE + PP | 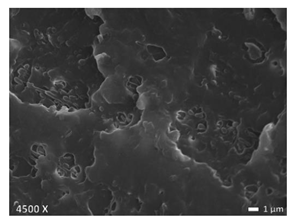 | 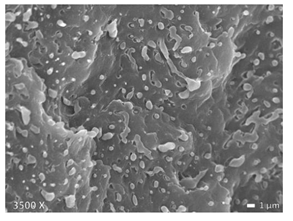 | 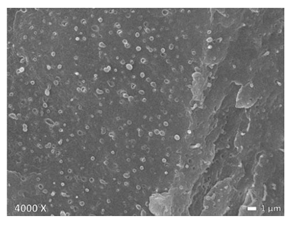 |
| LDPE + PP |  | 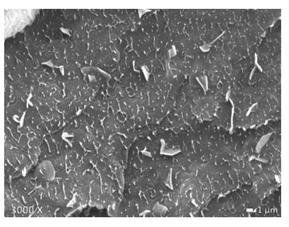 | 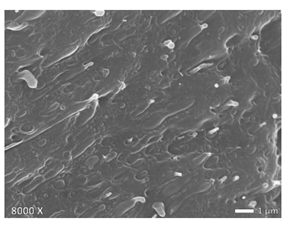 |
| HDPE + PP | 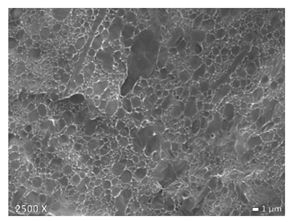 | 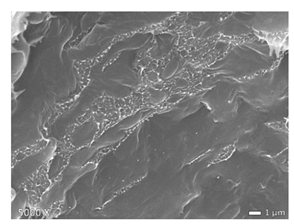 | 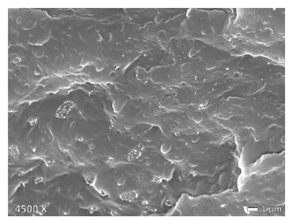 |
| Material | Tprocessing (°C) | Xc (%) 1 | E (MPa) 2 | σy (MPa) 2 | εy (MPa) 2 | εb (%) 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | 190 | 28.8 | 114 | ± | 2 | 4.75 | ± | 0.05 | 3.41 | ± | 0.07 | 557 | ± | 12 |
| 230 | 29.1 | 101 | ± | 2 | 5.26 | ± | 0.03 | 3.79 | ± | 0.08 | 427 | ± | 23 | |
| LDPE | 190 | 32.7 | 192 | ± | 4 | 6.64 | ± | 0.09 | 3.08 | ± | 0.09 | 89.0 | ± | 2.0 |
| 230 | 33.8 | 172 | ± | 4 | 7.51 | ± | 0.10 | 3.57 | ± | 0.10 | 114 | ± | 3 | |
| HDPE | 190 | 65.1 | 953 | ± | 33 | 24.34 | ± | 0.15 | 9.77 | ± | 0.08 | 463 | ± | 110 |
| 230 | 63.7 | 864 | ± | 51 | 23.83 | ± | 0.38 | 10.62 | ± | 0.14 | 269 | ± | 57 | |
| PP | 230 | 42.2 | 1771 | ± | 28 | 37.11 | ± | 0.17 | 8.09 | ± | 0.06 | 68 | ± | 9 |
| Code | Curve | Test Bar Deformation | Deformation Mechanism Polymers/Blends |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 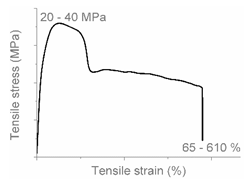 |  | Neck shear yielding HDPE (pure, εb: 270%–465%) PP (pure, εb: 70%) |
| B |  |  | Local shear yielding LDPE (pure, εb: 90%–115%) |
| C |  |  | Uniform shear yielding with strain hardening LLDPE (pure, εb: 430%–555%) |
| AB | 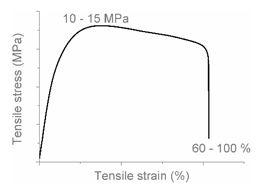 |  | Combined (neck + local) shear yielding LDPE + HDPE LDPE + PP |
| AC | 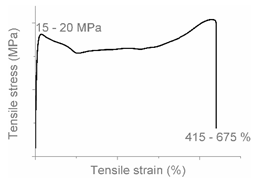 |  | Progressive shear yielding with strain hardening LLDPE + HDPE |
| AA | 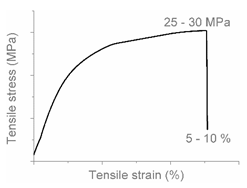 |  | Brittle HDPE + PP |
| Amount of A (wt.%) | A | B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | LDPE | HDPE | ||
| 0 | LDPE | C | ||
| 5 | C | |||
| 10 | C | |||
| 20 | C | |||
| 50 | B | |||
| 80 | B | |||
| 90 | B | |||
| 95 | B | |||
| 100 | B | |||
| 0 | HDPE | C | B | |
| 5 | C | B | ||
| 10 | C | B | ||
| 20 | C | B | ||
| 50 | AC | AB | ||
| 80 | AC | A | ||
| 90 | A | A | ||
| 95 | A | A | ||
| 100 | A | A | ||
| 0 | PP | C | B | A |
| 5 | C | B | AA | |
| 10 | C | B | AA | |
| 20 | C | B | AA | |
| 50 | A | AB | AA | |
| 80 | A | A | A | |
| 90 | A | A | A | |
| 95 | A | A | A | |
| 100 | A | A | A | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Belle, A.; Demets, R.; Mys, N.; Van Kets, K.; Dewulf, J.; Van Geem, K.; De Meester, S.; Ragaert, K. Microstructural Contributions of Different Polyolefins to the Deformation Mechanisms of Their Binary Blends. Polymers 2020, 12, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051171
Van Belle A, Demets R, Mys N, Van Kets K, Dewulf J, Van Geem K, De Meester S, Ragaert K. Microstructural Contributions of Different Polyolefins to the Deformation Mechanisms of Their Binary Blends. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051171
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Belle, Astrid, Ruben Demets, Nicolas Mys, Karen Van Kets, Jo Dewulf, Kevin Van Geem, Steven De Meester, and Kim Ragaert. 2020. "Microstructural Contributions of Different Polyolefins to the Deformation Mechanisms of Their Binary Blends" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051171
APA StyleVan Belle, A., Demets, R., Mys, N., Van Kets, K., Dewulf, J., Van Geem, K., De Meester, S., & Ragaert, K. (2020). Microstructural Contributions of Different Polyolefins to the Deformation Mechanisms of Their Binary Blends. Polymers, 12(5), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051171








