Insoluble Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Improving Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Properties and Physicochemical Characterization of SDs
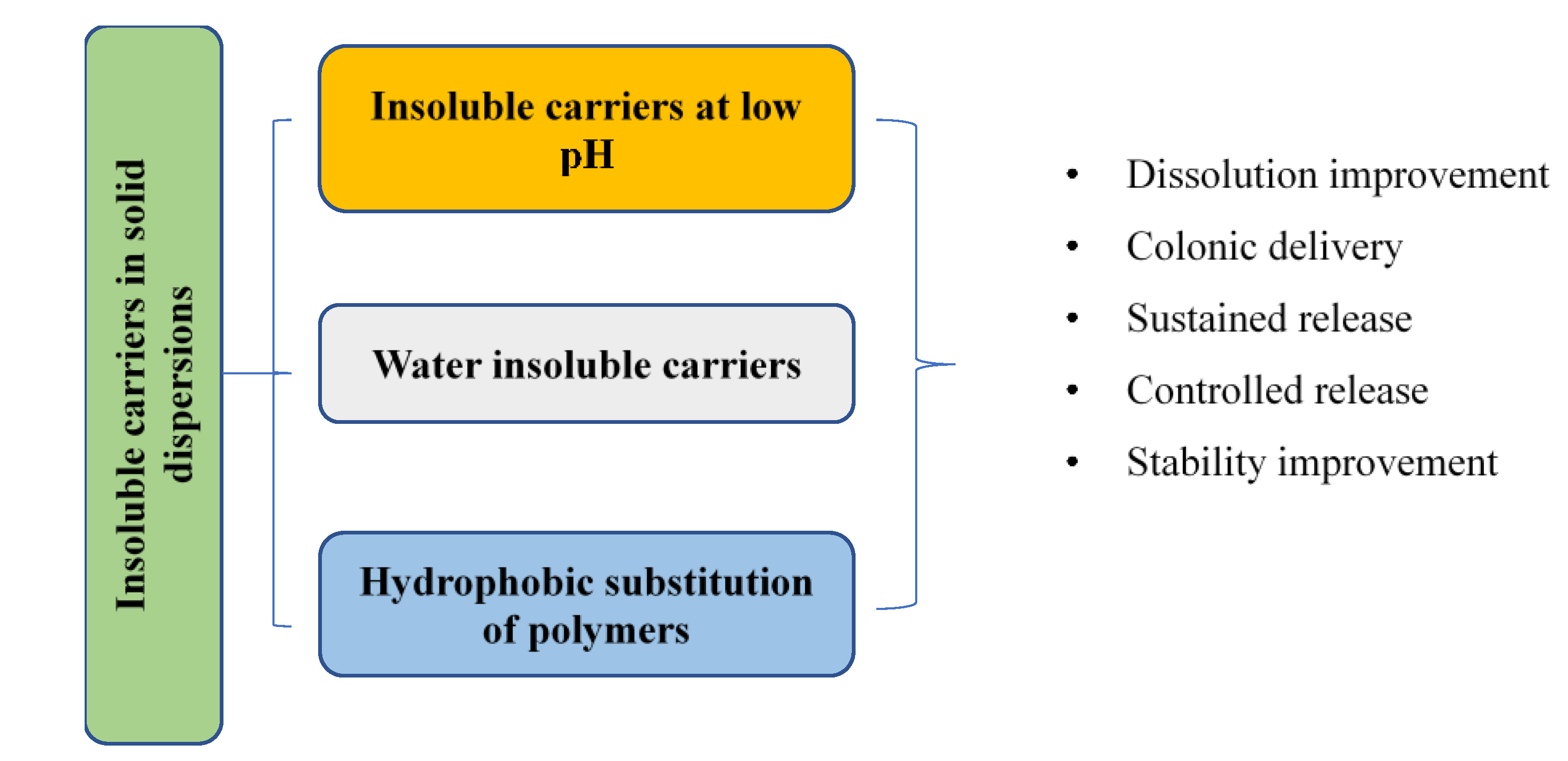
3. Insoluble Carriers at Low pH Levels in SDs
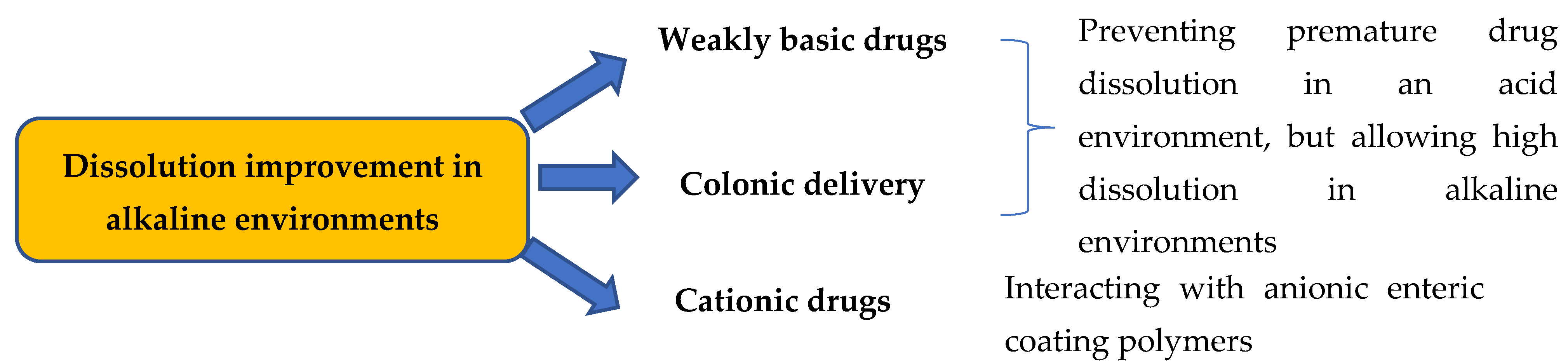
3.1. Dissolution Improvement in Alkaline Environments and for Colonic Delivery
3.2. Effects of Enteric Coating Polymers and Preparation Methods on Amorphous SDs
3.3. Nano-Sized SDs from Enteric Coating Polymers
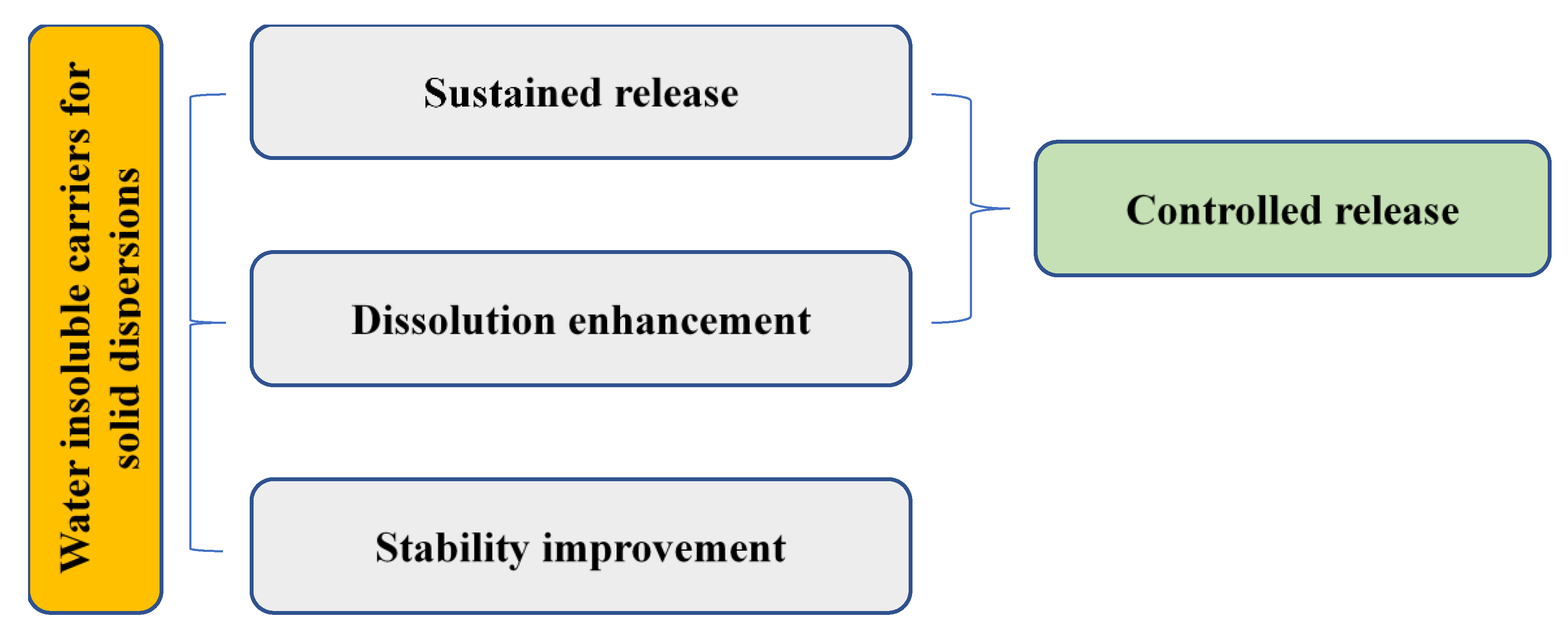
4. Water-Insoluble Carriers for SDs
4.1. Sustained Release and Stability Improvement
4.2. Dissolution Improvement
4.3. Controlled Release of SDs with Water-Insoluble Carriers
5. Hydrophobic Substitution of Polymers in SDs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahloul, B.; Safta, F.; Lassoued, M.A.; Dhotel, H.; Seguin, J.; Mignet, N.; Sfar, S. Use of mouse model in pharmacokinetic studies of poorly water soluble drugs: Application to fenofibrate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Lorenz, T.; Repanas, A.; Schneider, F.; Steiner, D.; Baumann, K.; Bunjes, H.; Dietzel, A.; Finke, J.H.; Glasmacher, B.; et al. Novel strategies for the formulation and processing of poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Ziemba, T.; Huang, C.; Chang, M.; Xu, C.; Qiao, J.X.; Wang, T.C.; Finlay, H.J.; Salvati, M.E.; Adam, L.P.; et al. Oral Delivery of Highly Lipophilic, Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs: Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems to Improve Oral Absorption and Enable High-Dose Toxicology Studies of a Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Inhibitor in Preclinical Species. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, M.; Moreno, J.; Bilgili, E.; Davé, R. Fast dissolution of poorly water soluble drugs from fluidized bed coated nanocomposites: Impact of carrier size. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. The use of zein in the controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, B.M.A.; Ferreira, E.I. Is prodrug design an approach to increase water solubility? Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; Nti-Addae, K.W. Prodrug strategies to overcome poor water solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, J.; Kumpulainen, H.; Heimbach, T.; Oliyai, R.; Oh, D.; Järvinen, T.; Savolainen, J. Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clas, S.-D.; Sanchez, R.I.; Nofsinger, R. Chemistry-enabled drug delivery (prodrugs): Recent progress and challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Jannin, V.; Pouton, C.W.; Boyd, B.J. Colloidal aspects of dispersion and digestion of self-dispersing lipid-based formulations for poorly water-soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y. Nanosizing—Oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings1PII of original article: S0169-409X(96)00423-1. The article was originally published in Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 23 (1997) 3–25.1. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C. Poor aqueous solubility—An industry wide problem in drug discovery. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2002, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Erickson, B.; Jayasankar, A.; Lu, L.; Marsh, K.; Menon, R.; Gao, P. Assessing Supersaturation and Its Impact on In Vivo Bioavailability of a Low-Solubility Compound ABT-072 With a Dual pH, Two-Phase Dissolution Method. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R. Nanotechnology based approaches to enhance aqueous solubility and bioavailability of griseofulvin: A literature survey. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Song, S.; Ding, Z.; Fan, B.; Huang, W.; Xu, T. Improving the Solubility, Dissolution, and Bioavailability of Ibrutinib by Preparing It in a Coamorphous State With Saccharin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3020–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, N.; Hiramatsu, T.; Suzuki, R.; Okamoto, R.; Shibagaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, C.; Kawashima, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Improvement in the water solubility of drugs with a solid dispersion system by spray drying and hot-melt extrusion with using the amphiphilic polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer and d-mannitol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, G.O.K.; Tan, Y.T.F.; Peh, K.K. Hydrophilic polymer solubilization on norfloxacin solubility in preparation of solid dispersion. Powder Technol. 2014, 256, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekes, M.K.; Kuminek, G.; Rauber, G.S.; de Campos, C.E.M.; Bortoluzzi, A.J.; Stulzer, H.K. HPMC as a potential enhancer of nimodipine biopharmaceutical properties via ball-milled solid dispersions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, I.; Snyder, J.; Vippagunta, R.; Alvine, M.; Vakil, R.; Tong, W.-Q.; Vippagunta, S. Comparison of HPMC based polymers performance as carriers for manufacture of solid dispersions using the melt extruder. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-T.; Balakrishnan, P.; Oh, D.H.; Joe, K.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Hwang, D.H.; Lee, Y.-B.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.-G. Development of novel sibutramine base-loaded solid dispersion with gelatin and HPMC: Physicochemical characterization and pharmacokinetics in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelić, D.; Liavitskaya, T.; Vyazovkin, S. Thermal stability of indomethacin increases with the amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone in solid dispersion. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 676, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Osman, Y.; Liavitskaya, T.; Vyazovkin, S. Polyvinylpyrrolidone affects thermal stability of drugs in solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smikalla, M.M.; Urbanetz, N.A. The influence of povidone K17 on the storage stability of solid dispersions of nimodipine and polyethylene glycol. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L.; Lee, B.J. Dissolution-modulating mechanism of alkalizers and polymers in a nanoemulsifying solid dispersion containing ionizable and poorly water-soluble drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L.; Choi, H.G.; Han, H.K.; Lee, B.J. The roles of acidifiers in solid dispersions and physical mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.L.; Malekar, S.A.; Cote, C.; Worthen, D.R. Hydroxypropyl cellulose stabilizes amorphous solid dispersions of the poorly water soluble drug felodipine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B.; Rathi, S.; Jyothi, V.G.S.S.; Shastri, N.R. Cellulose based polymers in development of amorphous solid dispersions. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, C.J.; Nichols, B.L.B.; Novo, D.C.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J.; Neilson, A.P. Cellulose-based amorphous solid dispersions enhance rifapentine delivery characteristics in vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinović, T.; Medarević, D.; Vranić, E.; Potpara, Z.; Krstić, M.; Djuriš, J.; Ibrić, S. Development of ternary solid dispersions with hydrophilic polymer and surface adsorbent for improving dissolution rate of carbamazepine. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, S.; de Armas, H.N.; Roberts, C.J.; Van den Mooter, G. Characterization of Ternary Solid Dispersions of Itraconazole, PEG 6000, and HPMC 2910 E5. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddeeris, C.; Willems, T.; Van den Mooter, G. Formulation of fast disintegrating tablets of ternary solid dispersions consisting of TPGS 1000 and HPMC 2910 or PVPVA 64 to improve the dissolution of the anti-HIV drug UC 781. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Mintoo, M.J.; Mondhe, D.M.; Bharate, S.B.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Bharate, S.S. Binary and ternary solid dispersions of an anticancer preclinical lead, IIIM-290: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzoli, R.; Lyons, J.G.; Gately, N.; Higginbotham, C.L. Stability studies of hot-melt extruded ternary solid dispersions of poorly-water soluble indomethacin with poly(vinyl pyrrolidone-co-vinyl acetate) and polyethylene oxide. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Meckel, J.; Zhang, F. Investigation of itraconazole ternary amorphous solid dispersions based on povidone and Carbopol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Padrela, L.; Faucher, A.; O’Reilly, E.; Walker, G. Spray drying ternary amorphous solid dispersions of ibuprofen—An investigation into critical formulation and processing parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 120, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, S.; Nagels, S.; De Armas, H.N.; D’Autry, W.; Van Schepdael, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Formulation and characterization of ternary solid dispersions made up of Itraconazole and two excipients, TPGS 1000 and PVPVA 64, that were selected based on a supersaturation screening study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.T.; Potter, C.B.; Walker, G.M. Downstream processing of a ternary amorphous solid dispersion: The impacts of spray drying and hot melt extrusion on powder flow, compression and dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.-P.; Zhang, W.-L.; Yang, J.-K.; Fan, Y.-Q. Novel Tanshinone II A ternary solid dispersion pellets prepared by a single-step technique: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.T.; Potter, C.B.; Mohammadpour, M.; Albadarin, A.B.; Walker, G.M. Design of spray dried ternary solid dispersions comprising itraconazole, soluplus and HPMCP: Effect of constituent compositions. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yi, S.; Xiong, S. Enhanced felodipine dissolution from high drug loading amorphous solid dispersions with PVP/VA and sodium dodecyl sulfate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Nguyen, J.H.; Becker, C.; Francke, N.M.; Jørgensen, E.B.; Holm, P.; Holm, R.; Mu, H.; Rades, T.; Langguth, P. Influence of polymer molecular weight on in vitro dissolution behavior and in vivo performance of celecoxib:PVP amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhao, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, G.; Ma, X. Evaluate the ability of PVP to inhibit crystallization of amorphous solid dispersions by density functional theory and experimental verify. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaee, A.; O’Dea, S.; Howard-Hildige, A.; Padrela, L.; Potter, C.; Iqbal, J.; Albadarin, A.B.; Walker, G.; O’Reilly, E.J. Amorphous solid dispersion of ibuprofen: A comparative study on the effect of solution based techniques. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 118816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fan, N.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; He, Z. The tracking of interfacial interaction of amorphous solid dispersions formed by water-soluble polymer and nitrendipine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, N.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q.; He, Z. Interfacial interaction track of amorphous solid dispersions established by water-soluble polymer and indometacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, D.; Carter, D.; Foong Ng, L.Y.; Davis, M.; Walker, G.M.; Lyons, J.G.; Higginbotham, C.L. An investigation of the inter-molecular interaction, solid-state properties and dissolution properties of mixed copovidone hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L.; Lim, J.; Park, J.B.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, B.J. Physicochemical principles of controlled release solid dispersion containing a poorly water-soluble drug. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.L.T.; Wei, D.; Beom-Jin, L.; Thao, T.D.T. Current Designs of Polymer Blends in Solid Dispersions for Improving Drug Bioavailability. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. Dosage form designs for the controlled drug release of solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Xiong, H.; Ye, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T.; Jing, Q.; Lu, J.; Pan, H.; Ren, F.; Ouyang, D. Predicting physical stability of solid dispersions by machine learning techniques. J. Control. Release 2019, 311–312, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, S.; Lowinger, M.B.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Su, Y.; Williams, R.O. Influence of mechanical and thermal energy on nifedipine amorphous solid dispersions prepared by hot melt extrusion: Preparation and physical stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.W.; Kang, M.J. Improved oral absorption and chemical stability of everolimus via preparation of solid dispersion using solvent wetting technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Konecke, S.; Wegiel, L.A.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Both solubility and chemical stability of curcumin are enhanced by solid dispersion in cellulose derivative matrices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Marques, S.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Amorphous solid dispersions: Rational selection of a manufacturing process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, P.; Bulusu, R.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W.; Singh, M. Amorphous solid dispersions: An update for preparation, characterization, mechanism on bioavailability, stability, regulatory considerations and marketed products. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Williams, R.O. Characterization of amorphous solid dispersions: An update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beten, D.B.; Gelbcke, M.; Diallo, B.; Moës, A.J. Interaction between dipyridamole and Eudragit S. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 88, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, G.; Wu, T.; Bai, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Solid dispersion of berberine hydrochloride and Eudragit® S100: Formulation, physicochemical characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 40, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monschke, M.; Wagner, K.G. Amorphous solid dispersions of weak bases with pH-dependent soluble polymers to overcome limited bioavailability due to gastric pH variability—An in-vitro approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overhoff, K.A.; Moreno, A.; Miller, D.A.; Johnston, K.P.; Williams, R.O. Solid dispersions of itraconazole and enteric polymers made by ultra-rapid freezing. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayersohn, M. Principles of drug absorption. In Modern Pharmaceutics, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 23–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, L. Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Morgan, D.J.; Mendham, A.P.; Pang, J.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Drug–polymer intermolecular interactions in hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Boateng, J.S.; Bonnefille, M.; Aranyos, A.; Mitchell, J.C.; Douroumis, D. Taste masking of paracetamol by hot-melt extrusion: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong, H.L.T.; Wei, D.; Beom-Jin, L.; Thao, T.D.T. Modulation of Drug Crystallization and Molecular Interactions by Additives in Solid Dispersions for Improving Drug Bioavailability. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.L.; Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Malick, W.; Zia, H. Hot melt extrusion (HME) for amorphous solid dispersions: Predictive tools for processing and impact of drug–polymer interactions on supersaturation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.; Hassouna, F.; Malinová, L.; Merna, J.; Růžička, K.; Fulem, M. Impact of Hot-Melt Extrusion Processing Conditions on Physicochemical Properties of Amorphous Solid Dispersions Containing Thermally Labile Acrylic Copolymer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 109, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, T.; Gupta, S.S.; Meena, A.; Serajuddin, A.T. Investigation of thermal and viscoelastic properties of polymers relevant to hot melt extrusion-III: Polymethacrylates and polymethacrylic acid based polymers. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2016, 5, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, A.; Kawamura, R.I.E.; Nakagawa, H.; Sugimoto, I. Physical Properties of Solid Dispersions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs with Enteric Coating Agents. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotthivirat, S.; McKelvey, C.; Moser, J.; Rege, B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, D. Development of amorphous solid dispersion formulations of a poorly water-soluble drug, MK-0364. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Effect of HPMCAS on recrystallization inhibition of nimodipine solid dispersions prepared by hot-melt extrusion and dissolution enhancement of nimodipine tablets. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.Q.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Repka, M.A. Dual mechanism of microenvironmental pH modulation and foam melt extrusion to enhance performance of HPMCAS based amorphous solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, N.G.; Lam, K.; Tahsin, M.; Gumaste, S.G.; Shah, A.V.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Effects of Surfactants on Itraconazole-HPMCAS Solid Dispersion Prepared by Hot-Melt Extrusion I: Miscibility and Drug Release. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. The effect of drug and EUDRAGIT® S 100 miscibility in solid dispersions on the drug and polymer dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zemlyanov, D.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Nie, H.; Lubach, J.W.; Smith, D.; Byrn, S.; Pinal, R. Acid-base interactions in amorphous solid dispersions of lumefantrine prepared by spray-drying and hot-melt extrusion using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Sandhu, H.; Phuapradit, W.; Pinal, R.; Iyer, R.; Albano, A.; Chatterji, A.; Anand, S.; Choi, D.S.; Tang, K.; et al. Development of novel microprecipitated bulk powder (MBP) technology for manufacturing stable amorphous formulations of poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 438, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Choi, D.S.; Chokshi, H.; Shah, N.; Sandhu, H. Highly efficient miniaturized coprecipitation screening (MiCoS) for amorphous solid dispersion formulation development. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Iyer, R.M.; Mair, H.-J.; Choi, D.; Tian, H.; Diodone, R.; Fahnrich, K.; Pabst-Ravot, A.; Tang, K.; Scheubel, E.; et al. Improved Human Bioavailability of Vemurafenib, a Practically Insoluble Drug, Using an Amorphous Polymer-Stabilized Solid Dispersion Prepared by a Solvent-Controlled Coprecipitation Process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Taylor, L.S. Dissolution performance of high drug loading celecoxib amorphous solid dispersions formulated with polymer combinations. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.V.; Tran, P.H.L.; Lee, B.J.; Tran, T.T.D. The roles of a surfactant in zein-HPMC blend solid dispersions for improving drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, K.; Verreck, G.; Peeters, J.; Brewster, M.; Van den Mooter, G. Increased physical stability and improved dissolution properties of itraconazole, a class II drug, by solid dispersions that combine fast-and slow-dissolving polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thao, T.D.T.; Phuong, H.L.T. Perspectives on Strategies Using Swellable Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Controlled Drug Release. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyagi, N.; Ueda, K.; Higashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawakami, K.; Moribe, K. Synergetic Role of Hypromellose and Methacrylic Acid Copolymer in the Dissolution Improvement of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.A.; Wegiel, L.A.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Pairwise Polymer Blends for Oral Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, Í.; Corvo, M.L.; Serôdio, P.; Vicente, J.; Pinto, J.F.; Temtem, M. Production of nano-solid dispersions using a novel solvent-controlled precipitation process—Benchmarking their in vivo performance with an amorphous micro-sized solid dispersion produced by spray drying. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Domokos, A.; Farkas, A.; Démuth, B.; Borbás, E.; Nagy, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Controlled-release solid dispersions of Eudragit® FS 100 and poorly soluble spironolactone prepared by electrospinning and melt extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, A.; Farkas, B.; Pálvölgyi, Á.; Domokos, A.; Démuth, B.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Novel Alternating Current Electrospinning of Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose Acetate Succinate (HPMCAS) Nanofibers for Dissolution Enhancement: The Importance of Solution Conductivity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.; Hu, J.; Gao, P.; Li, L.; Ali-Reynolds, A.; Chal, B.; Gupta, V.; Ma, C.; Mahajan, N.; Akrami, A.; et al. Enhanced Bioavailability of a Poorly Soluble VR1 Antagonist Using an Amorphous Solid Dispersion Approach: A Case Study. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Lee, P.I. Probing the mechanisms of drug release from amorphous solid dispersions in medium-soluble and medium-insoluble carriers. J. Control. Release 2015, 211, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, A.; Koekoekx, R.; Clasen, C.; Van den Mooter, G. Amorphous solid dispersions of darunavir: Comparison between spray drying and electrospraying. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouna, F.; Abo El Dahab, M.; Fulem, M.; De Lima Haiek, A.; Laachachi, A.; Kopecký, D.; Šoóš, M. Multi-scale analysis of amorphous solid dispersions prepared by freeze drying of ibuprofen loaded acrylic polymer nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, R.; Amico, D.; Chiechio, S.; Spadaro, C.; Puglisi, G.; Giunchedi, P. Preparation and Analgesic Activity of Eudragit RS100® Microparticles Containing Diflunisal. Drug Deliv. 2001, 8, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Tsay, R.-J.; Lin, H.-I.; Chen, H.; Chao, S.-C.; Ku, H. Stabilization and sustained-release effect of Misoprostol with Methacrylate copolymer. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 203, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Alaei-Beirami, M.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Mohammadi, G.; Hamidi, A.; Andalib, S.; Adibkia, K. Comparison of physicochemical characteristics and drug release of diclofenac sodium–eudragit® RS100 nanoparticles and solid dispersions. Powder Technol. 2012, 219, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, J.M.; Cruz, R.; Hernandez, E. Preparation and characterization of Furosemide-Eudragit controlled release systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 195, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiranidchapong, C.; Tucker, I.G.; Rades, T.; Kulvanich, P. Miscibility and interactions between 17β-estradiol and Eudragit® RS in solid dispersion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4879–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, R.; Ferro, M.; De Guidi, G.; Salemi, G.; Vandelli, M.A.; Guccione, S.; Geppi, M.; Forte, C.; Puglisi, G. Preparation, characterisation and photosensitivity studies of solid dispersions of diflunisal and Eudragit RS100® and RL100®. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 218, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarahmieh, E.A.; Qi, S.; Craig, D.Q.M. Hot melt extruded transdermal films based on amorphous solid dispersions in Eudragit RS PO: The inclusion of hydrophilic additives to develop moisture-activated release systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, J.; Kaur Lamba, A.; Lamba, H.S. Development, characterization and solubility study of solid dispersion of Quercetin by solvent evaporation method. Mater. Today: Proc. 2017, 4, 10128–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kar, N.; Edgar, K.J. Direct synthesis of cellulose adipate derivatives using adipic anhydride. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.; Nguyen, P.K.; Van Vo, T.; Duan, W.; Tran, V.T.; Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. Hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer blend for modulation of crystalline changes and molecular interactions in solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.-S.; Cui, F.-D.; You, B.-G.; Fan, Y.-L.; Wang, L.; Yue, P.; Yang, H. Preparation of sustained-release nitrendipine microspheres with Eudragit RS and Aerosil using quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion method. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 259, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wigent, R.J.; Schwartz, J.B. Nifedipine Molecular Dispersion in Microparticles of Ammonio Methacrylate Copolymer and Ethylcellulose Binary Blends for Controlled Drug Delivery: Effect of Matrix Composition. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wigent, R.J.; Bentzley, C.M.; Schwartz, J.B. Nifedipine solid dispersion in microparticles of ammonio methacrylate copolymer and ethylcellulose binary blend for controlled drug delivery: Effect of drug loading on release kinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 319, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orienti, I.; Bigucci, F.; Luppi, B.; Cerchiara, T.; Zuccari, G.; Giunchedi, P.; Zecchi, V. Polyvinylalcohol substituted with triethyleneglycolmonoethylether as a new material for preparation of solid dispersions of hydrophobic drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Higashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. The effect of HPMCAS functional groups on drug crystallization from the supersaturated state and dissolution improvement. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 464, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.T.T.; Tran, P.H.L.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. Nano-sized solid dispersions based on hydrophobic-hydrophilic conjugates for dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.T.M.; Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. pH-independent dissolution enhancement for multiple poorly water-soluble drugs by nano-sized solid dispersions based on hydrophobic–hydrophilic conjugates. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrecich, M.; Nobile, F.; Rubessa, F.; Zingone, G. Effect of ageing on the release of indomethacin from solid dispersions with Eudragits. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 131, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelboe, J.; Knopp, M.M.; Khan, F.; Chourak, N.; Rades, T.; Holm, R. Importance of in vitro dissolution conditions for the in vivo predictability of an amorphous solid dispersion containing a pH-sensitive carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L. Insoluble Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Improving Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Polymers 2020, 12, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081679
Tran TTD, Tran PHL. Insoluble Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Improving Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081679
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Thao T.D., and Phuong H.L. Tran. 2020. "Insoluble Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Improving Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081679
APA StyleTran, T. T. D., & Tran, P. H. L. (2020). Insoluble Polymers in Solid Dispersions for Improving Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Polymers, 12(8), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081679



