Surface Modification of Carbon Microspheres with Guanidine Phosphate and Its Application as a Flame Retardant in PET
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material and Instruments
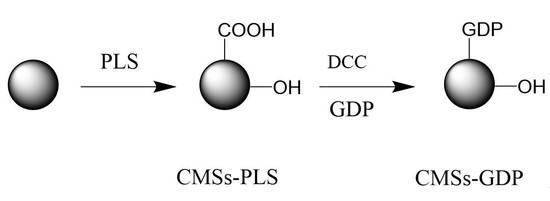
2.2. Preparation of Composite Material
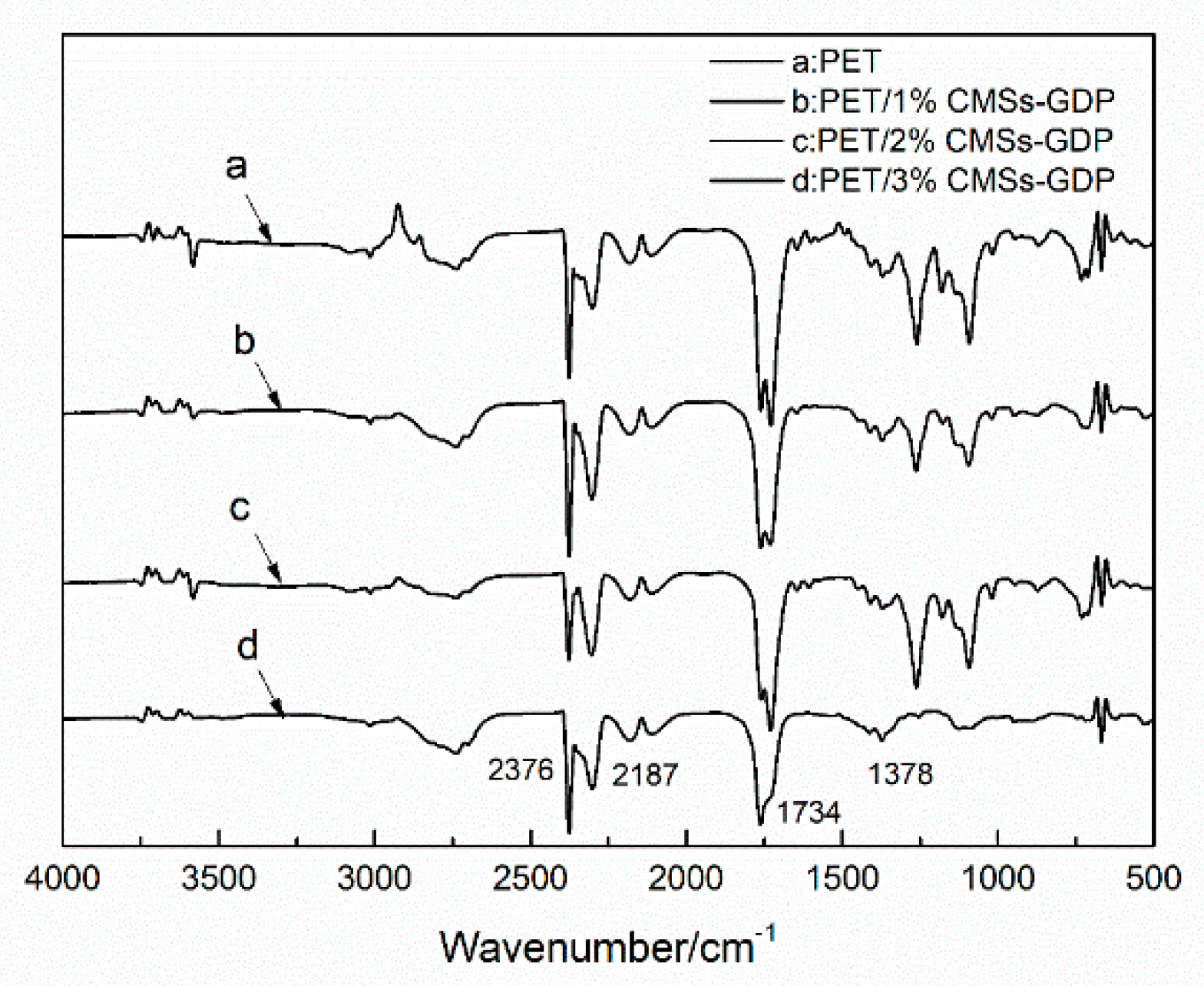
2.3. Characterization of Composite Material
3. Results and Discussion
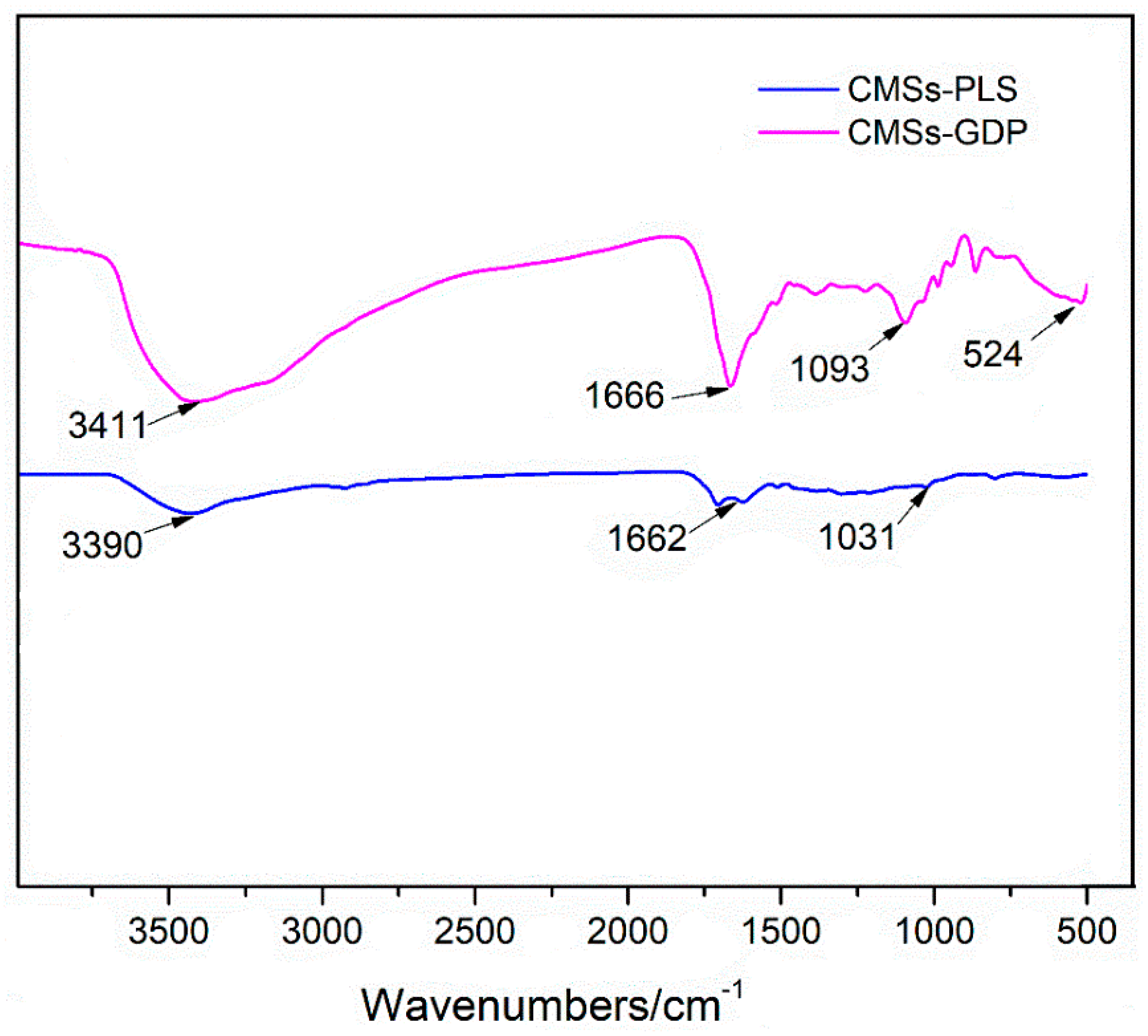
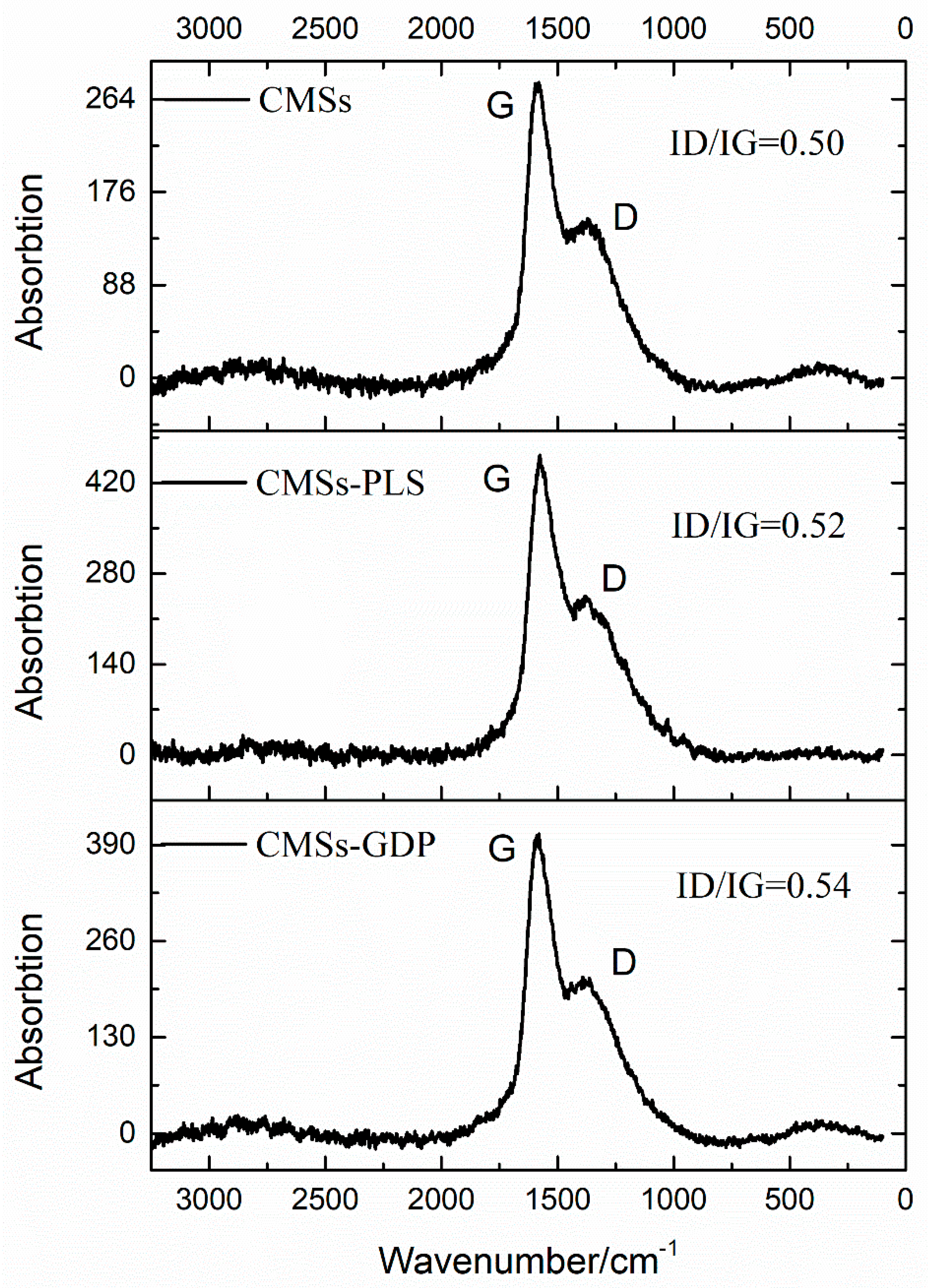
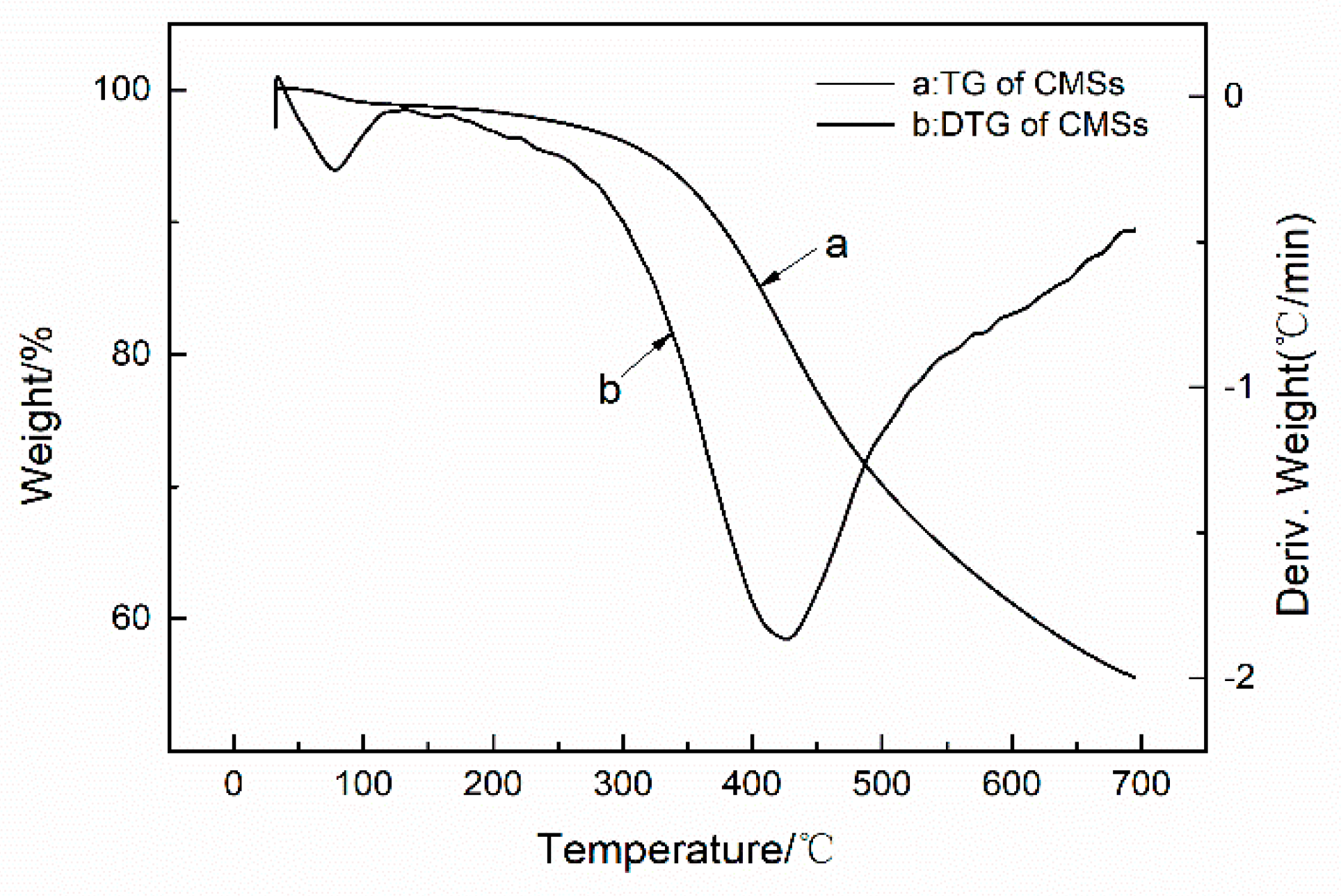
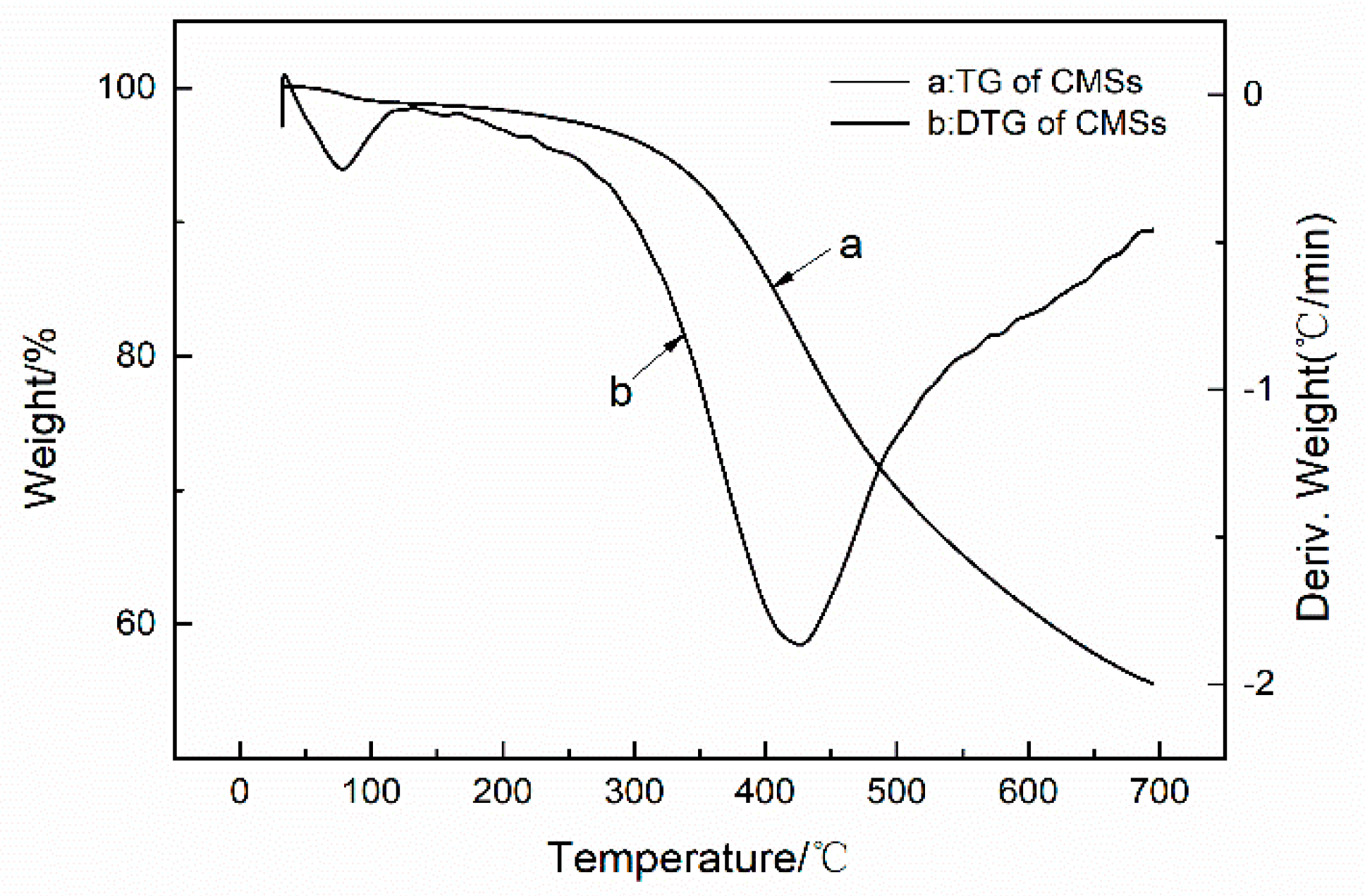
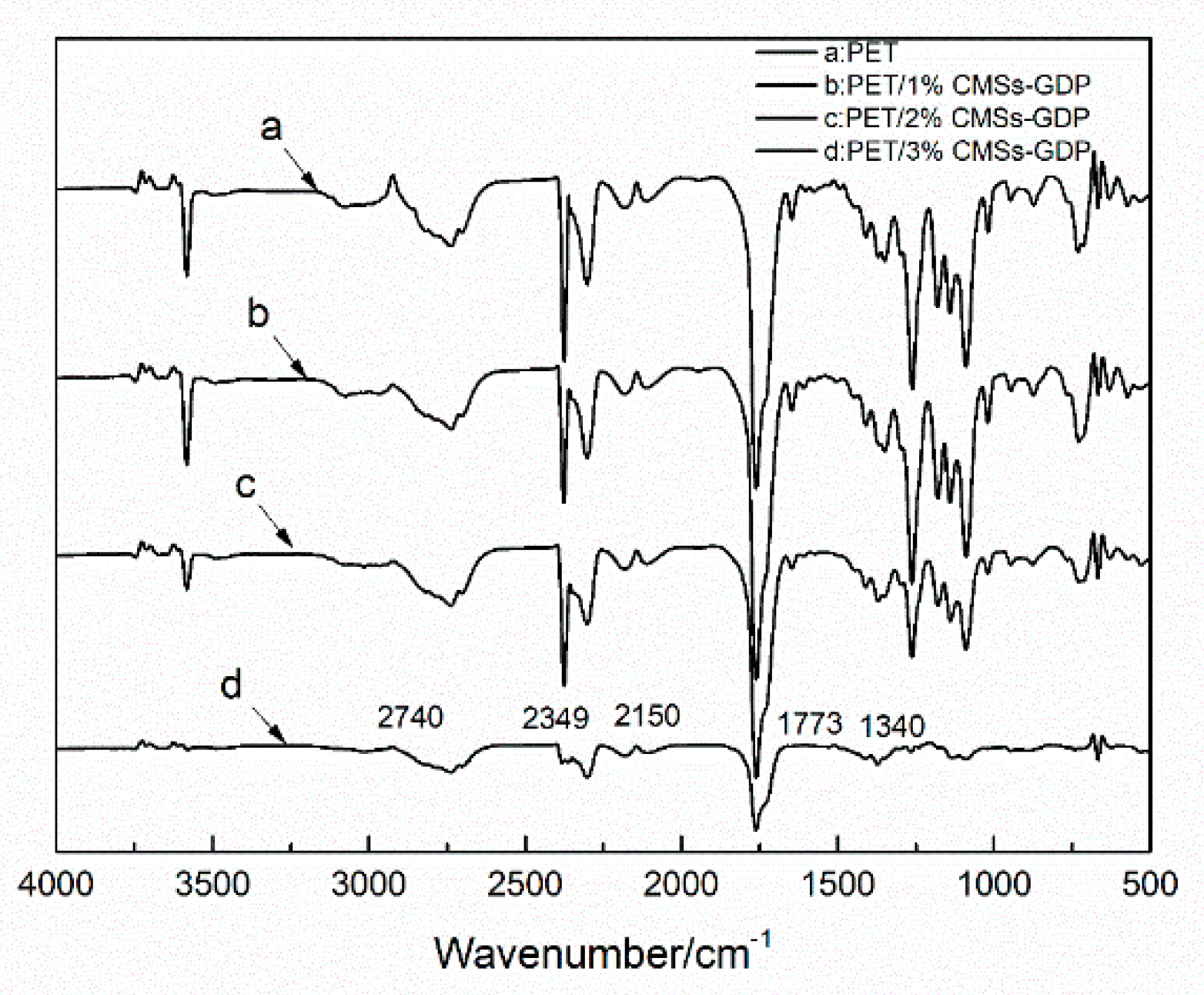
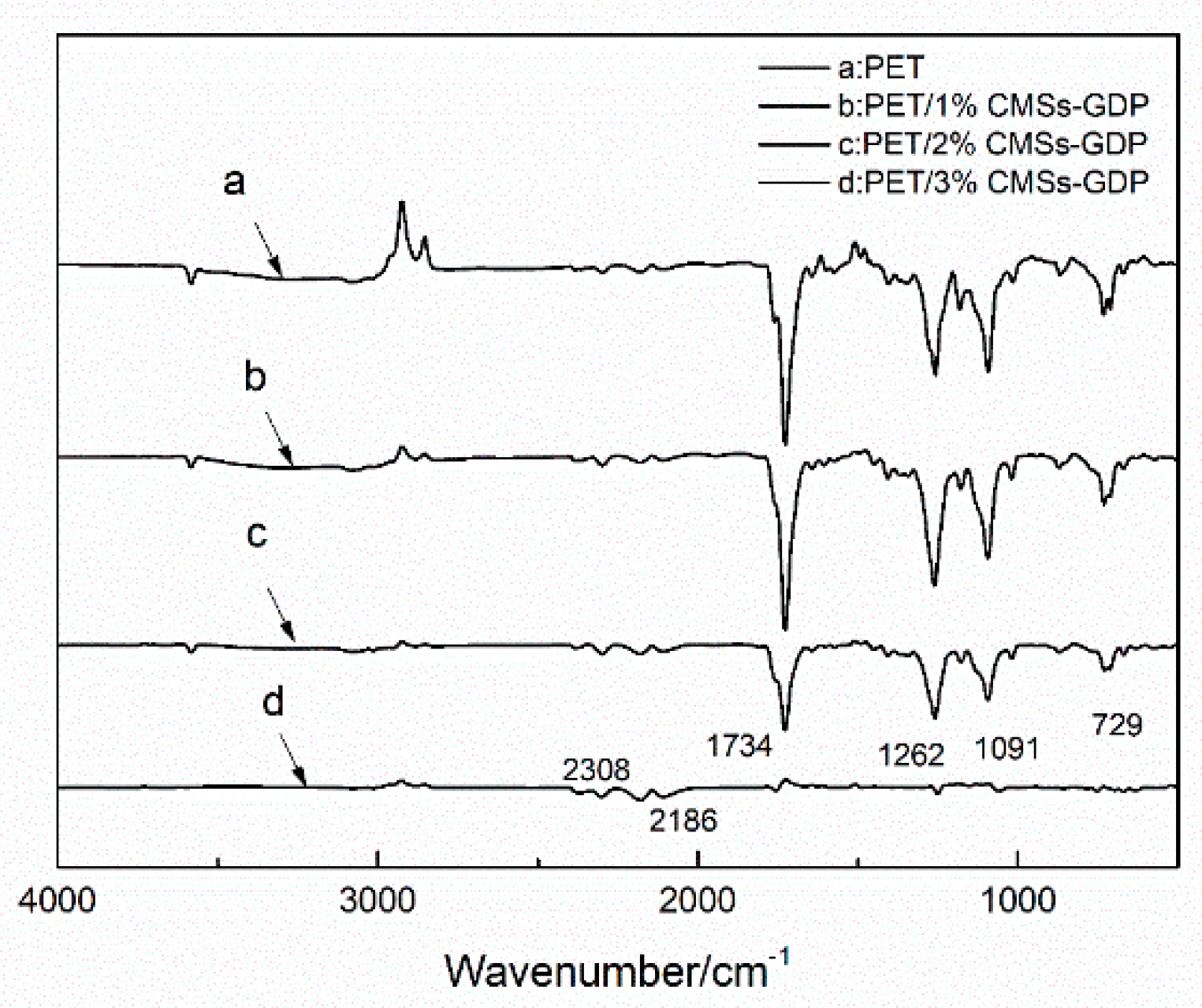
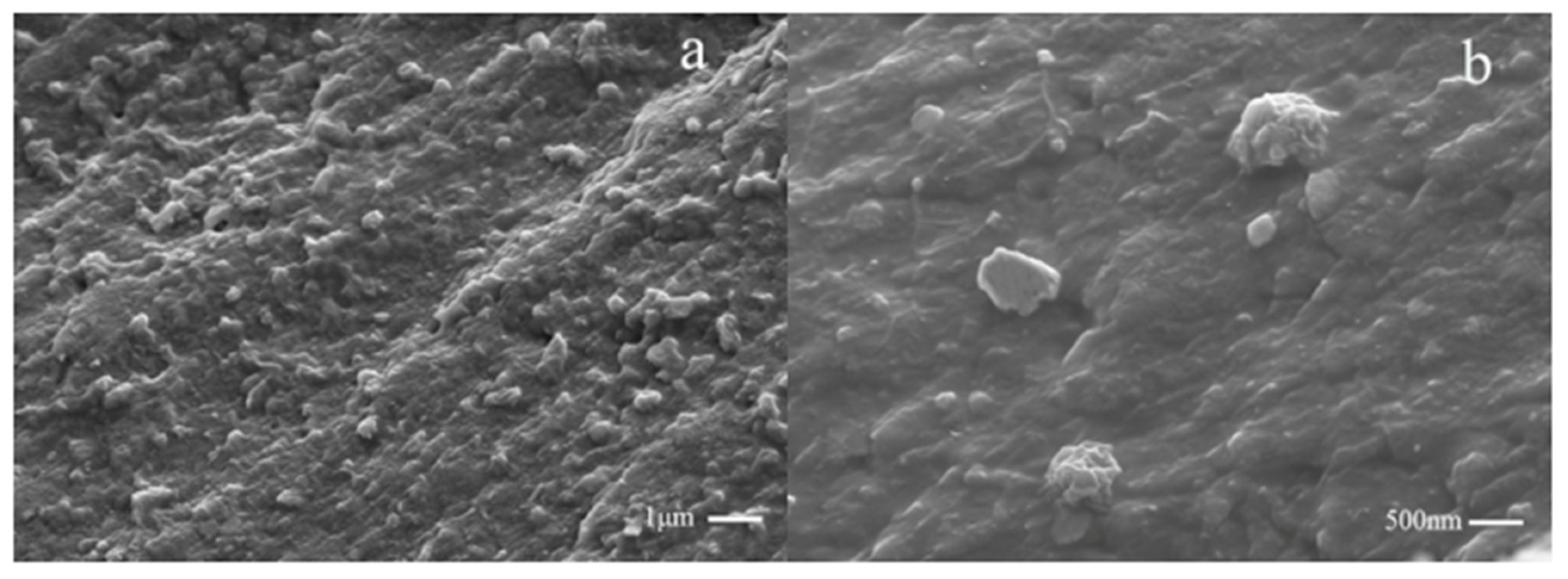
3.1. Characterization of CMSs
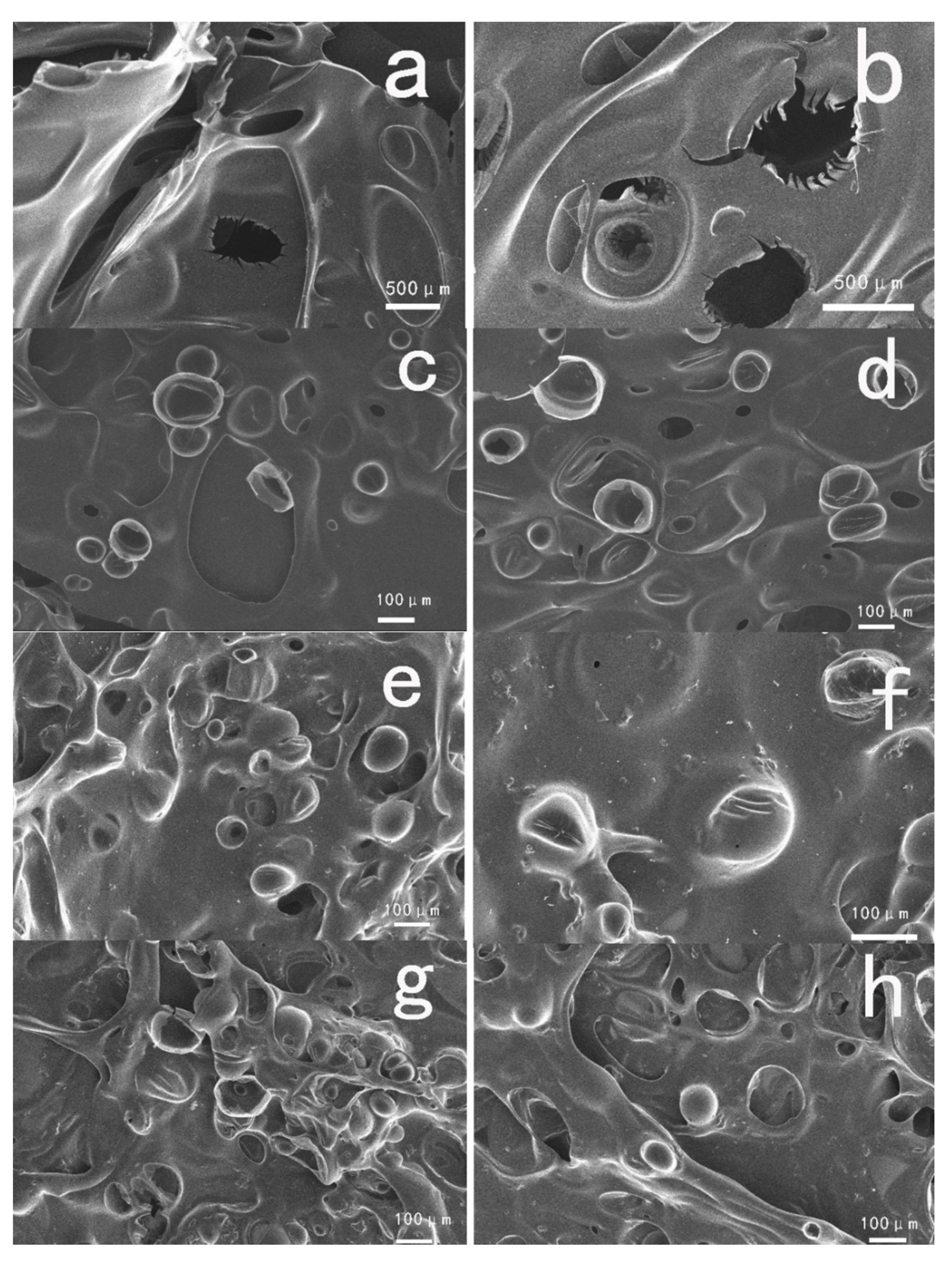
3.2. Flammability of PET and Composite Materials
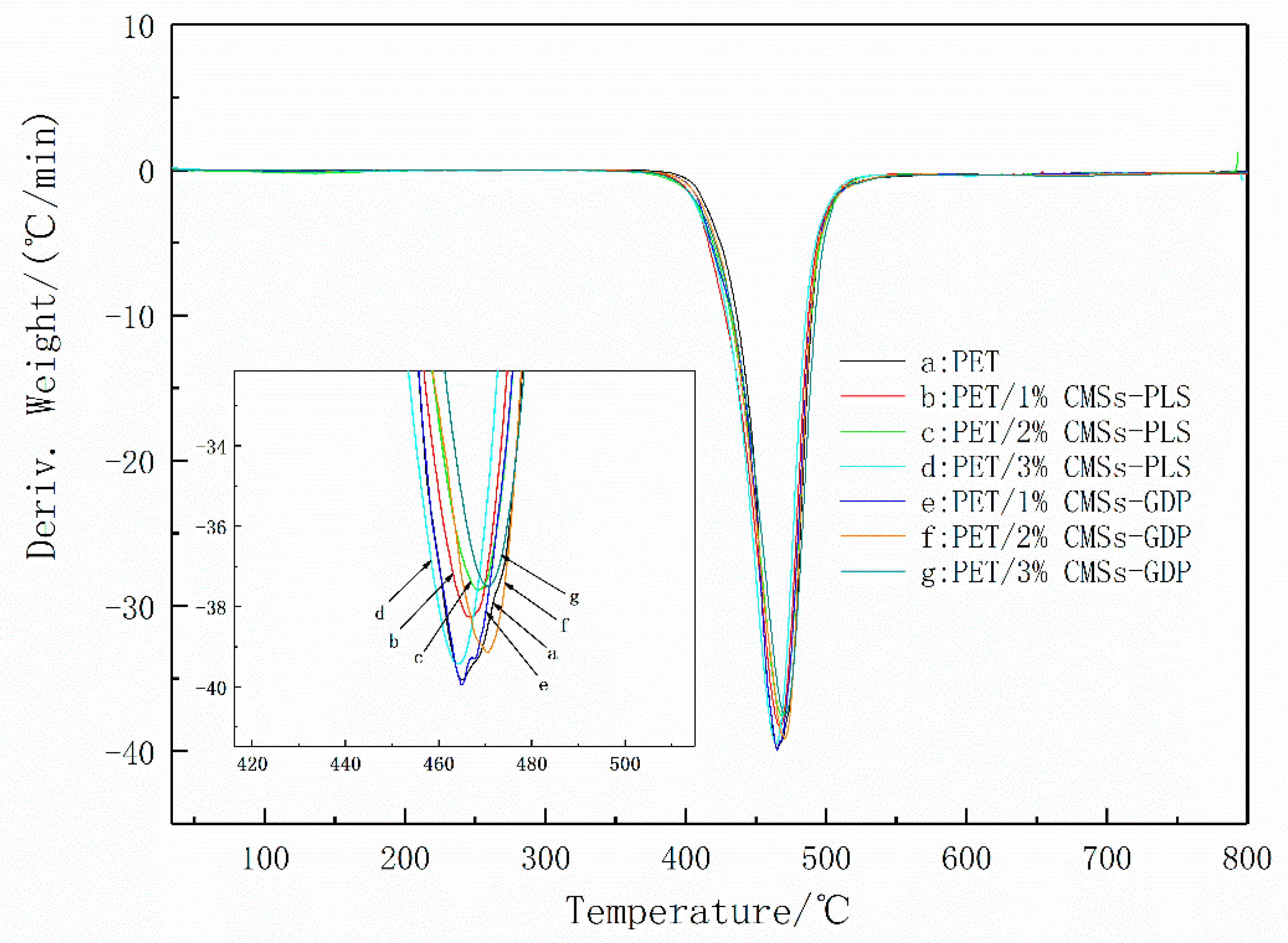
3.3. Thermal Properties and Degradation Mechanism of PET Composite Material
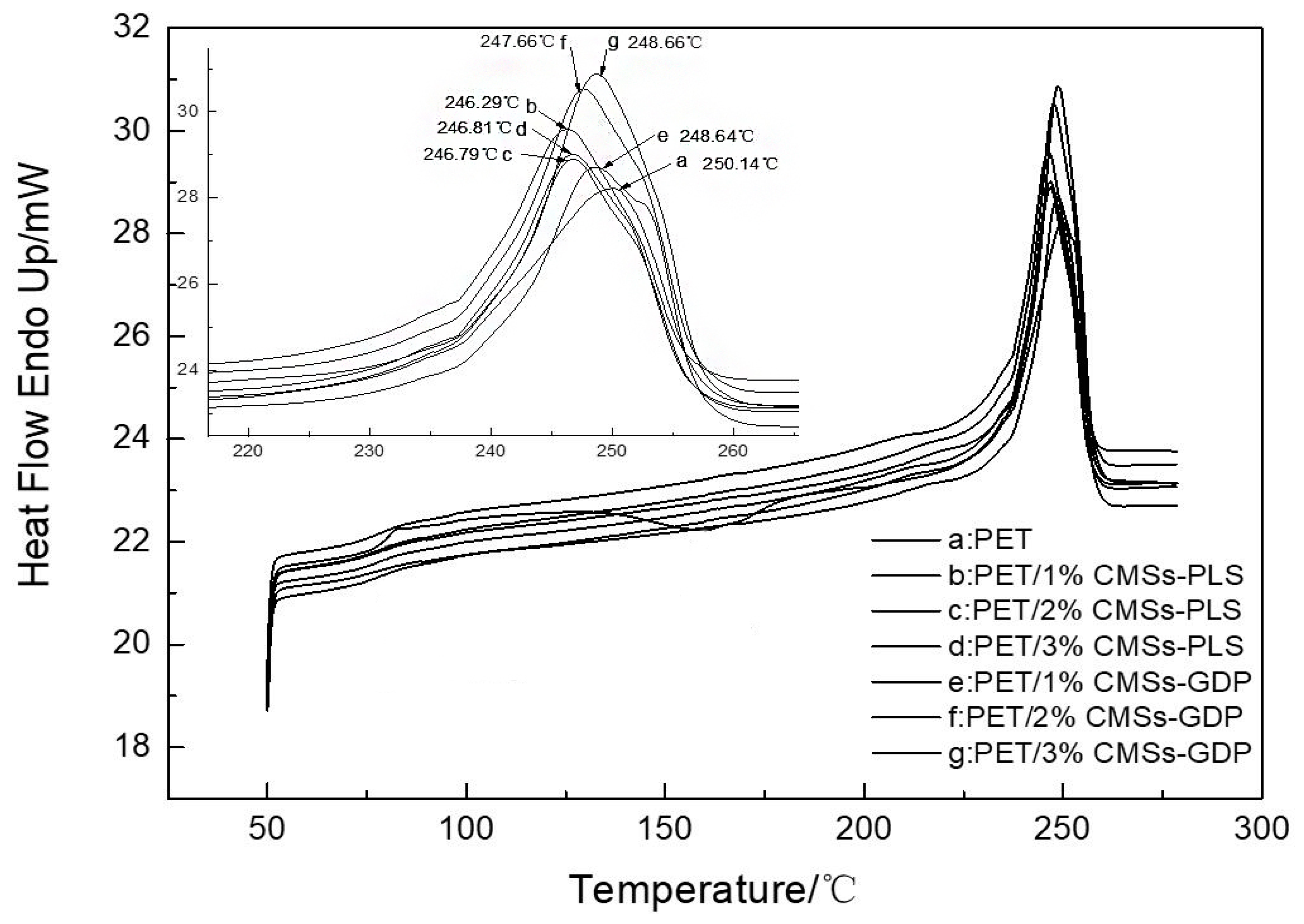
3.4. Crystallization Performance of PET Composite Material
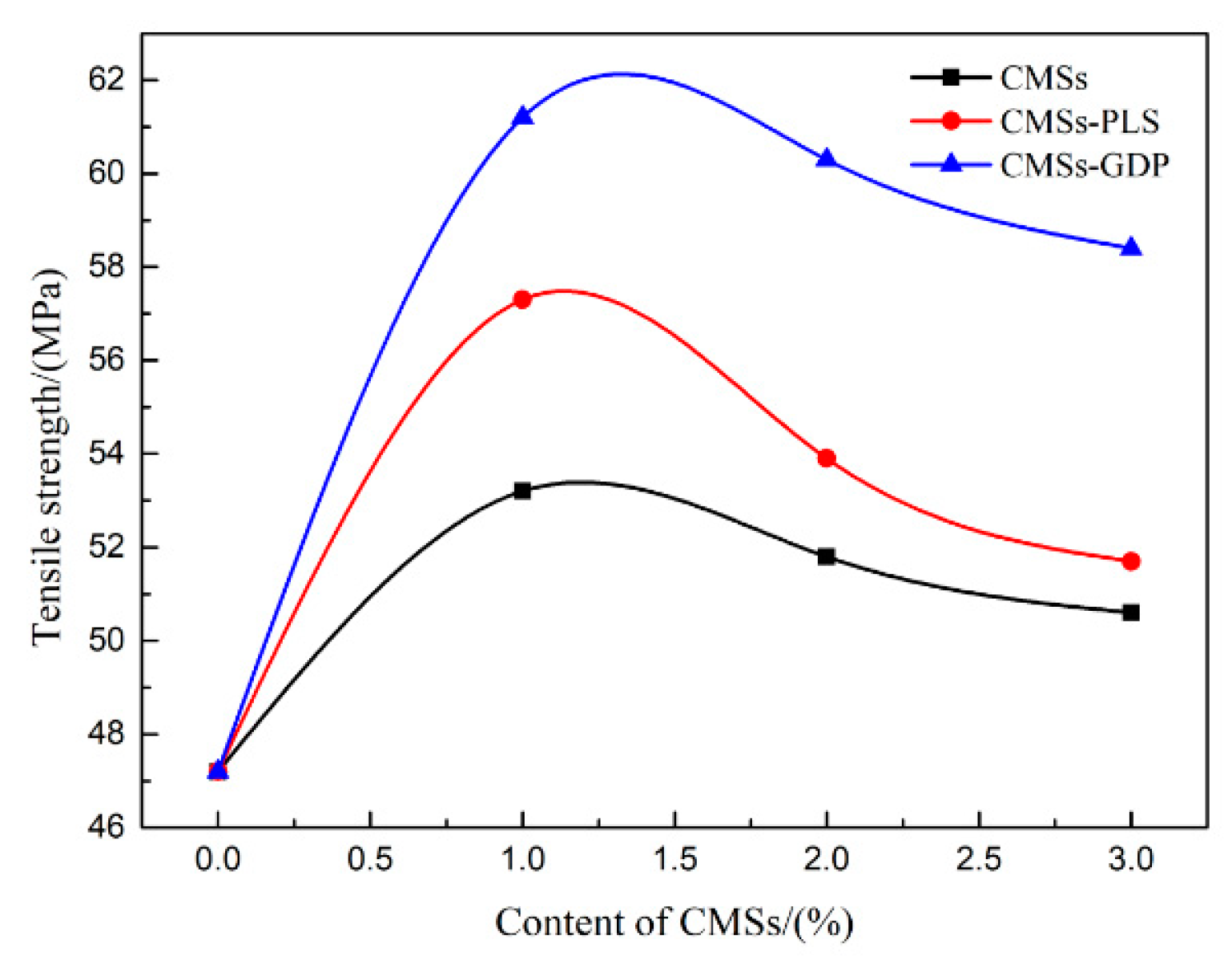
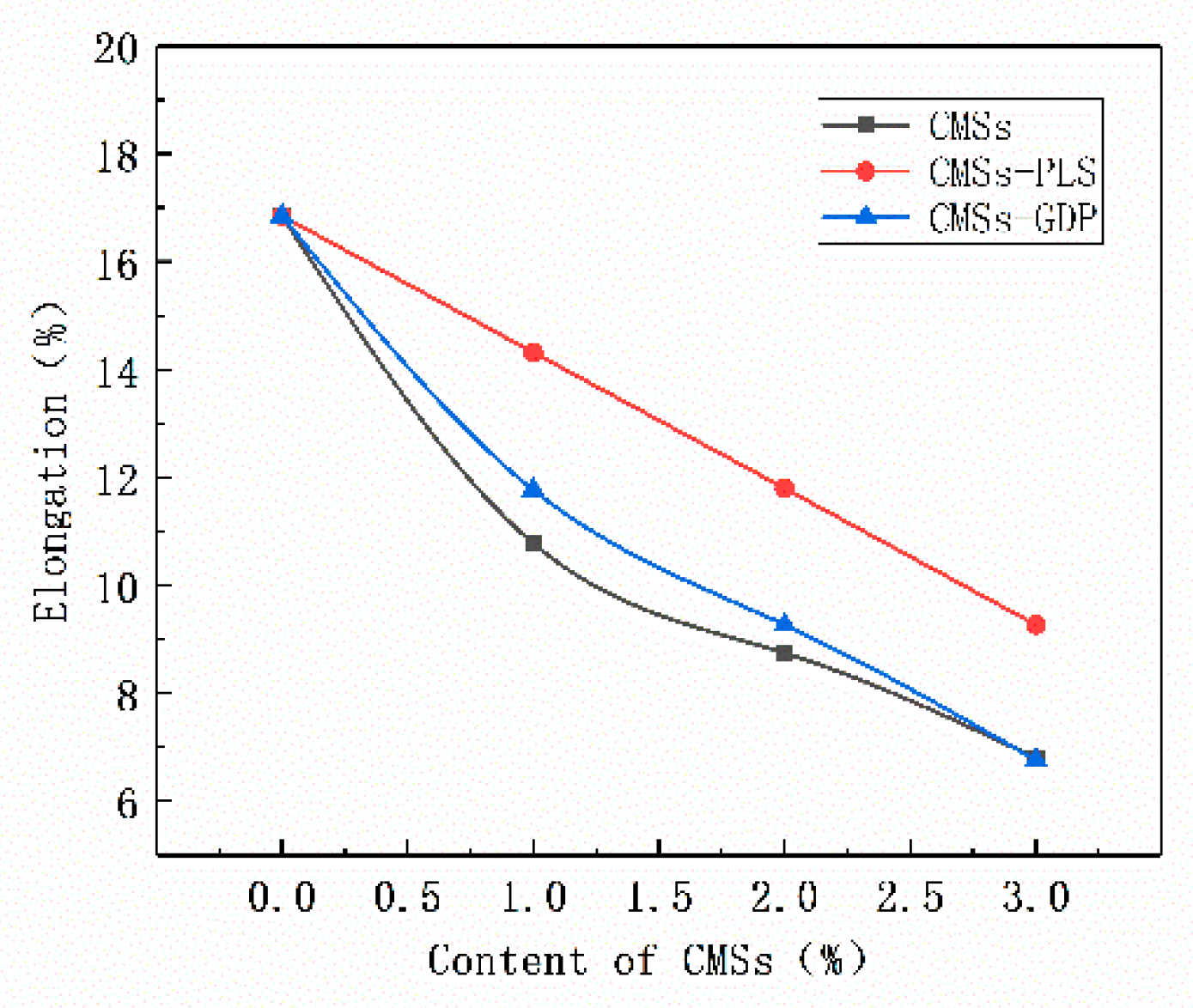
3.5. Mechanical Properties of PET Composite Material
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levchik, G.F.; Grigoriev, Y.V.; Balabanovich, A.I.; Levchik, S.V.; Klatt, M. Phosphorus–nitrogen containing fire retardants or poly(butylene terephthalate). Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. A review on thermal decomposition and combustion of thermoplastic polyesters. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xia, Y.; Kong, Q. Thermal stability and flame-retardancy mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/boehmite nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, Z.; Fang, Z.; Cao, Z. Effects of layered lanthanum phenylphosphonate on flame retardancy of glass-fiber reinforced poly(ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 10, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xue, M.; Wang, H.; Tian, X.; Ding, X.; Zheng, K.; Cui, P. Electrical and flame-retardant properties of carbon nanotube/poly(ethylene terephthalate) composites containing bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate). Polymer 2013, 54, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Kong, D.; Xu, H. Synergistic effects of a novel silicon-containing triazine charring agent on the flame-retardant properties of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/hexakis (4-phenoxy) cyclotriphosphazene composites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 7, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Hou, W.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. The structure of microencapsulated carbon microspheres and its flame retardancy in poly(ethylene terephthalate). Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 3, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusteri, L.; Cannilla, C.; Bonura, G.; Chuvilin, A.L.; Perathoner, S.; Centi, G.; Frusteri, F. Carbon microspheres preparation, graphitization and surface functionalization for glycerol etherification. Catal. Today 2016, 2, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, X. Preparation of multilayer carbon microspheres by using graphitic carbon nitride as precursor. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 8, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Luan, C.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Thermal stability and surface chemistry evolution of oxidized carbon microspheres. Full. Nanotub. Carb. Nanostruct. 2014, 22, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Characteristics of carbon microspheres and study on its adsorption isotherms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. Surface modification and characterization of carbon spheres by grafting polyelectrolyte brushes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, E.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, W.I.; Oh, S.H. Sulfur/graphitic hollow carbon sphere nano-composite as a cathode material for high-power lithium-sulfur battery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.; Suh, Y.W.; Dong, J.S.; Ahn, D.J. Hydrothermal preparation of carbon microspheres from mono-saccharides and phenolic compounds. Carbon 2010, 48, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Grafting molecularly imprinted poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid) onto the surface of carbon microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6441–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y. Waxberry-like carbon@polyaniline microspheres with high-performance microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 9, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, M.; Li, J.; Xue, B.; Dai, J. Preparation of carbon microspheres coated magnesium hydroxide and its application in polyethylene terephthalate as flame retardant. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, G. Surface modification of carbon nanomaterials by plasma technique and their applications in environmental pollution cleanup. In Abstract Book of China NANO, Proceedings of the International Conference on Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, China, 5–7 September 2013; National Nanoscience Center: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Nie, X.; Dai, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, H. Surface modification of carbon nanotubes modulate immune response with potential application in tumor immunotherapy. In Abstract Book of the 6th International Conference on Nanoscience & Technology, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Nanoscience & Technology, Beijing, China, 3 September 2013; National Nanoscience Center: Beijing, China, 2013; p. 402. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Y.; Ping, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Application of Raman spectroscopy in carbon nanotube-based polymer composites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar]
- Wiacek, J.; Molenda, M. Effect of particle polydispersity on micromechanical properties and energy dissipation in granular mixtures. Particuology 2014, 16, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Fard, F.G.; Khatibi, E.; Sarpoolaky, H. Dispersion and stability of carbon black nanoparticles, studied by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2009, 3, 524–527. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.Y.; Yuan, T.Q.; He, J. Study on thermal degradation kinetics of cellulose graft poly (l-lactic acid) by thermogravimetric analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 99, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Discharge Power/W | Time/min | Grain Size/nm | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 5 | 574 | 1.00 |
| 250 | 5 | 343 | 0.58 |
| 300 | 5 | 632 | 1.00 |
| 250 | 10 | 264 | 0.66 |
| 250 | 15 | 439 | 0.80 |
| Sample | t1/s | t2/s | t3/s | t1+t2/s | t2+t3/s | Melt Drip | Complete Combustion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100%PET | 15.77 | 15.74 | 0.4 | 31.51 | 16.14 | Y | Y |
| 99%PET/1%CMSs | 9.64 | 10.57 | 0.5 | 20.21 | 11.07 | Y | Y |
| 98%PET/2%CMSs | 6.45 | 6.72 | 0.3 | 13.17 | 7.02 | Y | Y |
| 97%PET/3%CMSs | 3.37 | 3.12 | 0.3 | 6.49 | 3.42 | Y | N |
| 99%PET/1%CMSs-PLS | 9.34 | 7.78 | 0.6 | 17.12 | 8.38 | Y | Y |
| 98%PET/2%CMSs-PLS | 4.21 | 5.35 | 0.5 | 9.56 | 5.85 | Y | Y |
| 97%PET/3%CMSs-PLS | 3.21 | 3.44 | 0.2 | 6.65 | 3.46 | Y | N |
| 99%PET/1%CMSs-GDP | 8.72 | 8.36 | 0.4 | 17.08 | 8.76 | Y | Y |
| 98%PET/2%CMSs-GDP | 4.33 | 4.19 | 0.4 | 8.52 | 4.59 | N | N |
| 97%PET/3%CMSs-GDP | 2.19 | 3.21 | 0.2 | 5.40 | 3.41 | N | N |
| Sample | T5% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | The rate of Tmax (wt % min−1) | Residue at 800 °C (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | |||
| CMSs | 352 | - | 440 | - | 10.8 | 55.31 |
| CMSs-GDP | 221 | 276 | 443 | 1.3 | 2.55 | 44.61 |
| PET | 420 | - | 464 | - | 39.8 | 11.91 |
| PET/1%CMSs | 422 | - | 464 | - | 38.2 | 13.20 |
| PET/2%CMSs | 423 | - | 466 | - | 37.5 | 13.21 |
| PET/3%CMSs | 426 | - | 468 | - | 36.4 | 13.78 |
| PET/1%CMSs-GDP | 428 | - | 470 | - | 35.9 | 14.18 |
| PET/2%CMSs-GDP | 431 | - | 472 | - | 35.1 | 14.65 |
| PET/3%CMSs-GDP | 435 | - | 473 | - | 34.4 | 15.42 |
| Sample | Tm/°C | Tmc/°C | △Hm/(J/g) | △Hmc/(J/g) | Crystallinity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 250.14 | 164.61 | 38.90 | 26.06 | 22.27 |
| PET/1%CMSs-PLS | 246.29 | 209.05 | 43.16 | 45.48 | 30.82 |
| PET/2%CMSs-PLS | 246.79 | 211.32 | 44.80 | 46.32 | 32.00 |
| PET/3%CMSs-PLS | 246.81 | 211.78 | 43.35 | 47.33 | 30.96 |
| PET/1%CMSs-GDP | 248.64 | 214.87 | 51.00 | 49.98 | 36.43 |
| PET/2%CMSs-GDP | 247.66 | 215.55 | 47.55 | 50.46 | 33.96 |
| PET/3%CMSs-GDP | 248.66 | 216.87 | 48.00 | 52.29 | 34.29 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Ji, C.; Zha, D.; Ding, Y.; Wu, D.; Yu, Q. Surface Modification of Carbon Microspheres with Guanidine Phosphate and Its Application as a Flame Retardant in PET. Polymers 2020, 12, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081689
Jiang S, Ji C, Zha D, Ding Y, Wu D, Yu Q. Surface Modification of Carbon Microspheres with Guanidine Phosphate and Its Application as a Flame Retardant in PET. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081689
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shan, Cheng Ji, Dan Zha, Yonghong Ding, Dun Wu, and Qiang Yu. 2020. "Surface Modification of Carbon Microspheres with Guanidine Phosphate and Its Application as a Flame Retardant in PET" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081689
APA StyleJiang, S., Ji, C., Zha, D., Ding, Y., Wu, D., & Yu, Q. (2020). Surface Modification of Carbon Microspheres with Guanidine Phosphate and Its Application as a Flame Retardant in PET. Polymers, 12(8), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081689