Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Color Change Evaluation
2.3. Surface Roughness Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
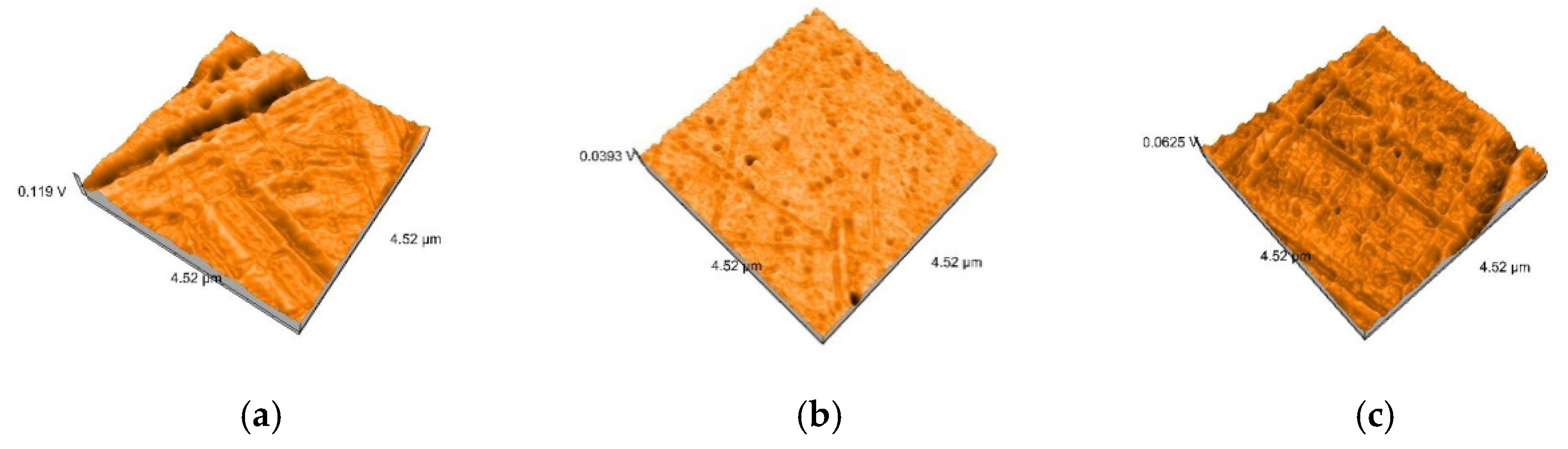
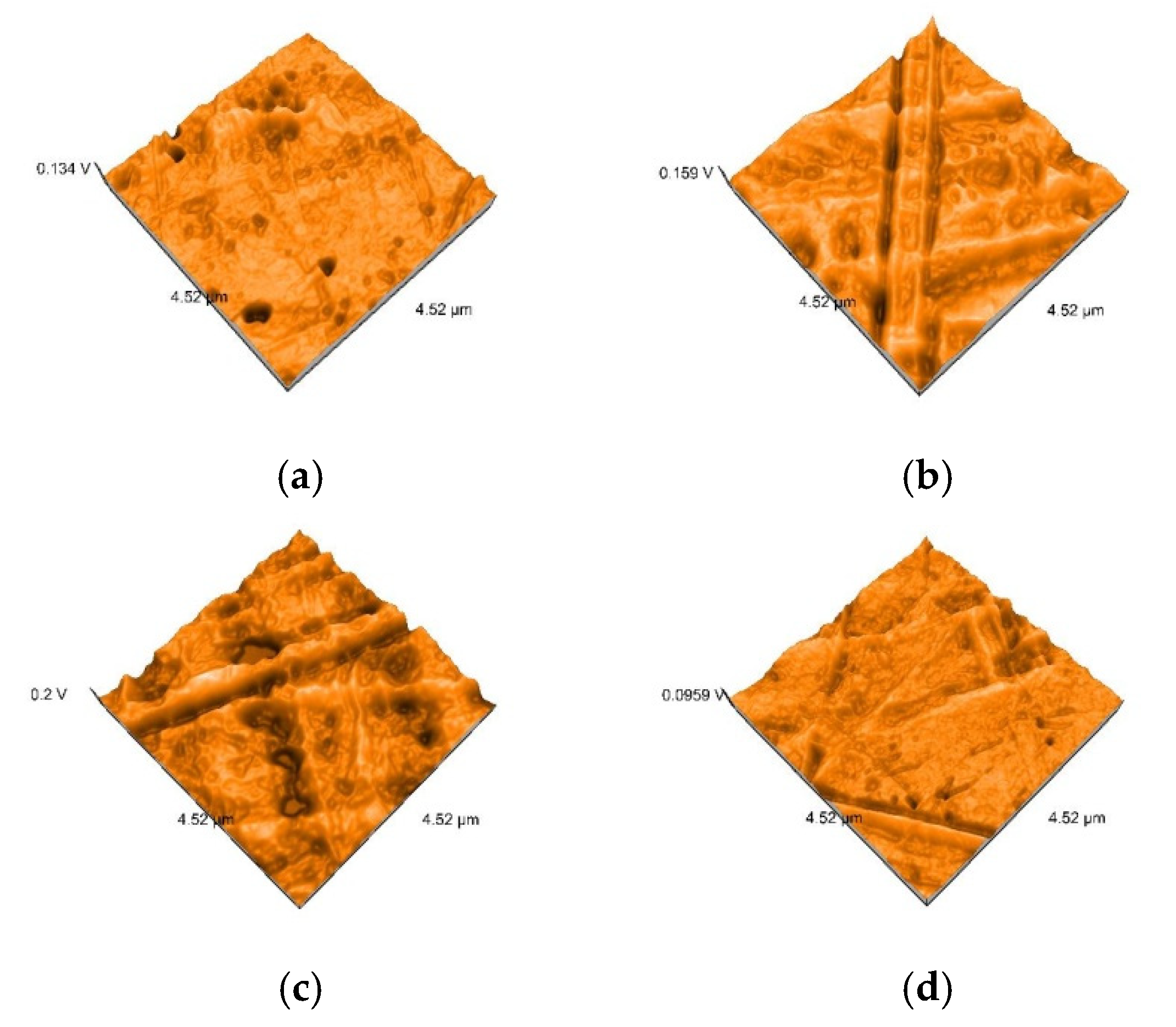
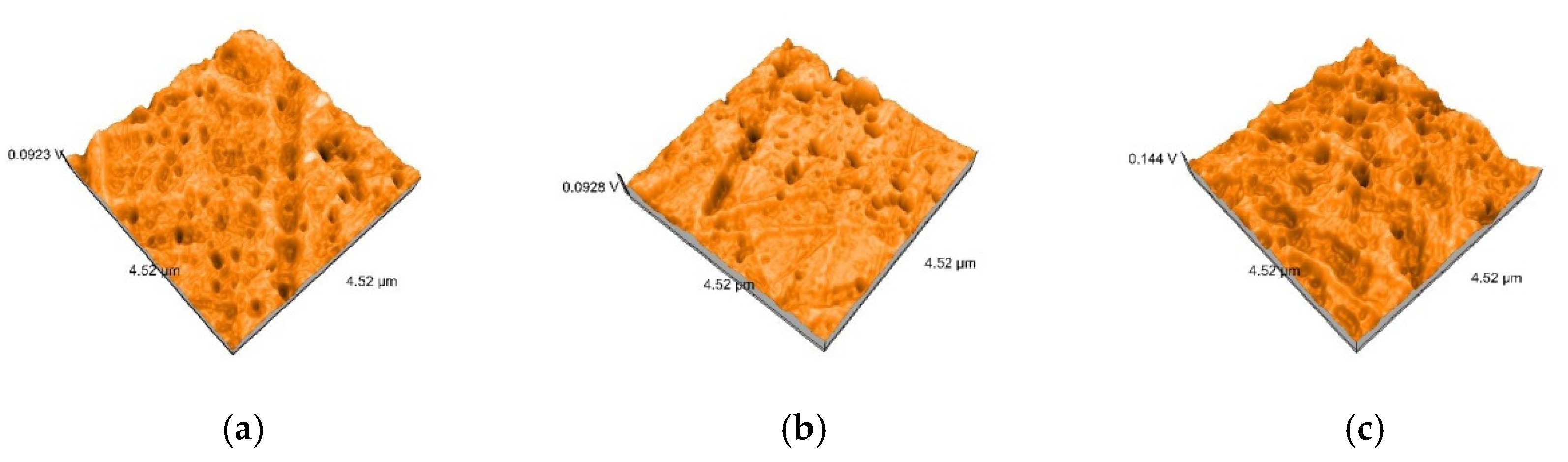
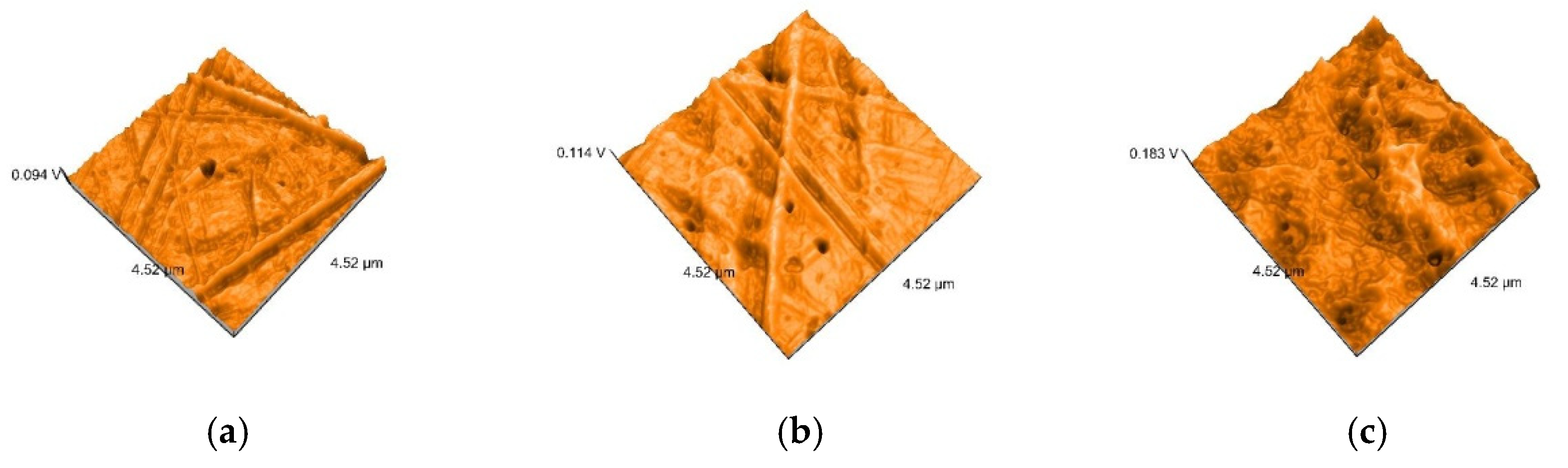
2.5. Nanosurface Topographic Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.6. Microstructure Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
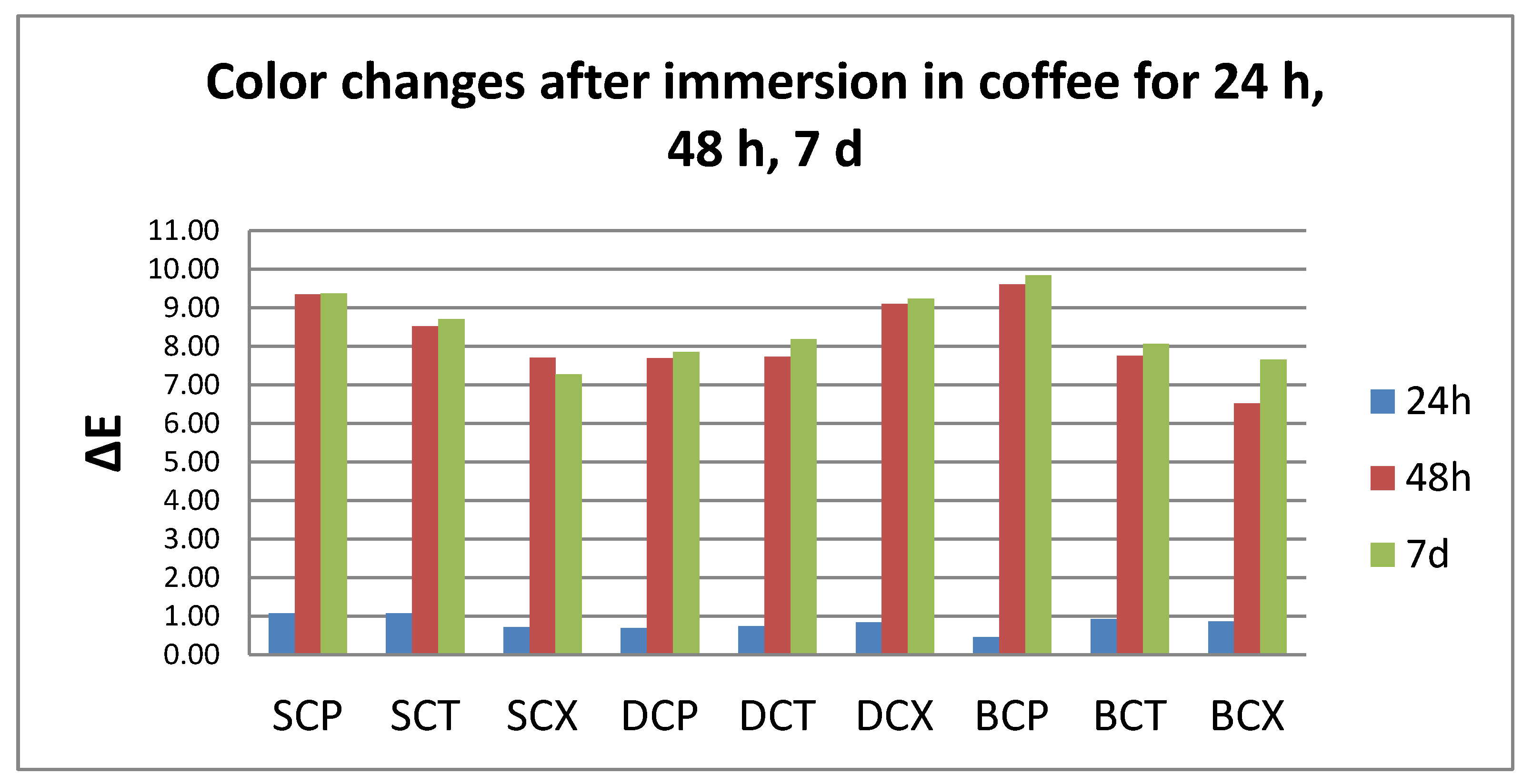
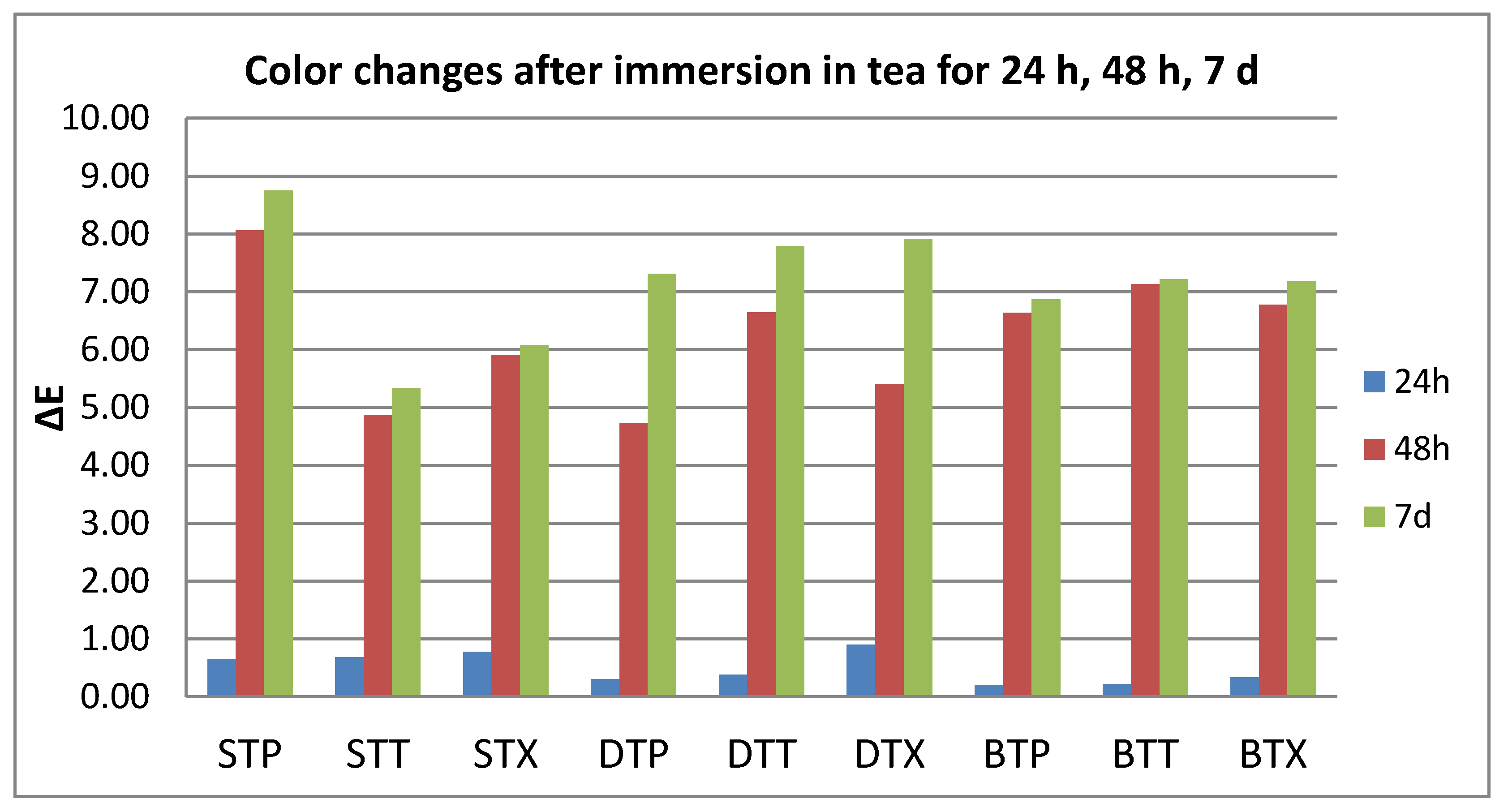
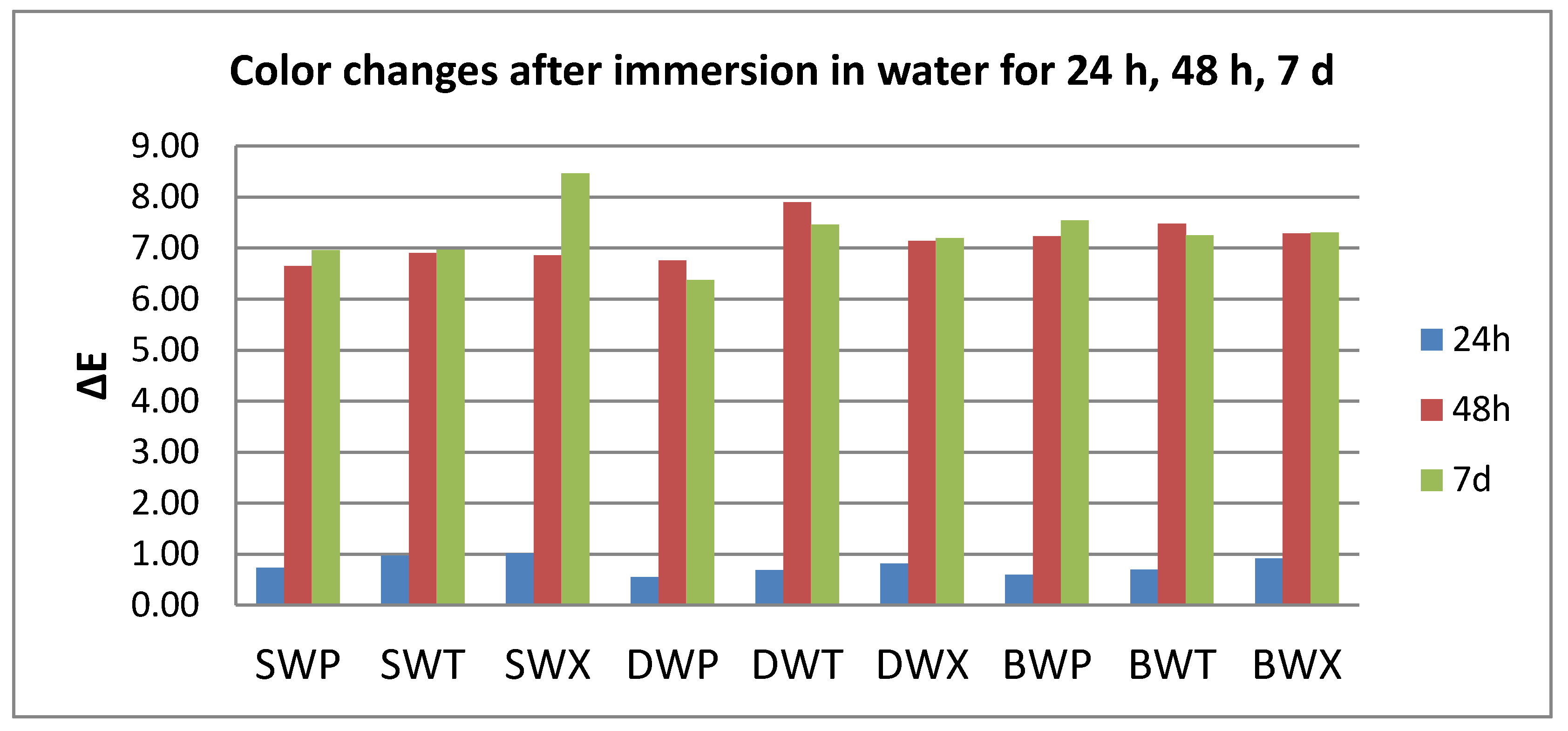
3.1. Color Evaluation
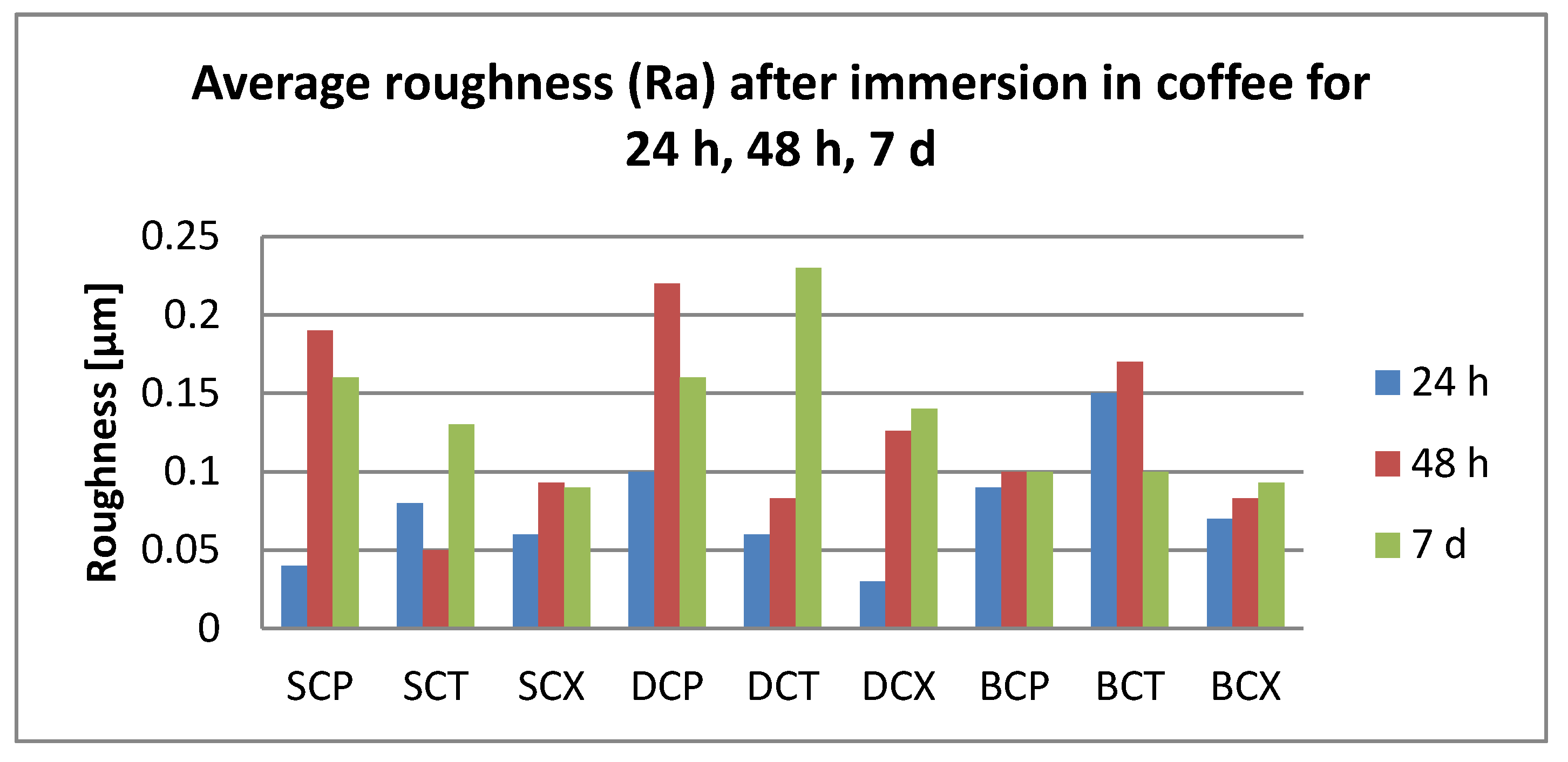
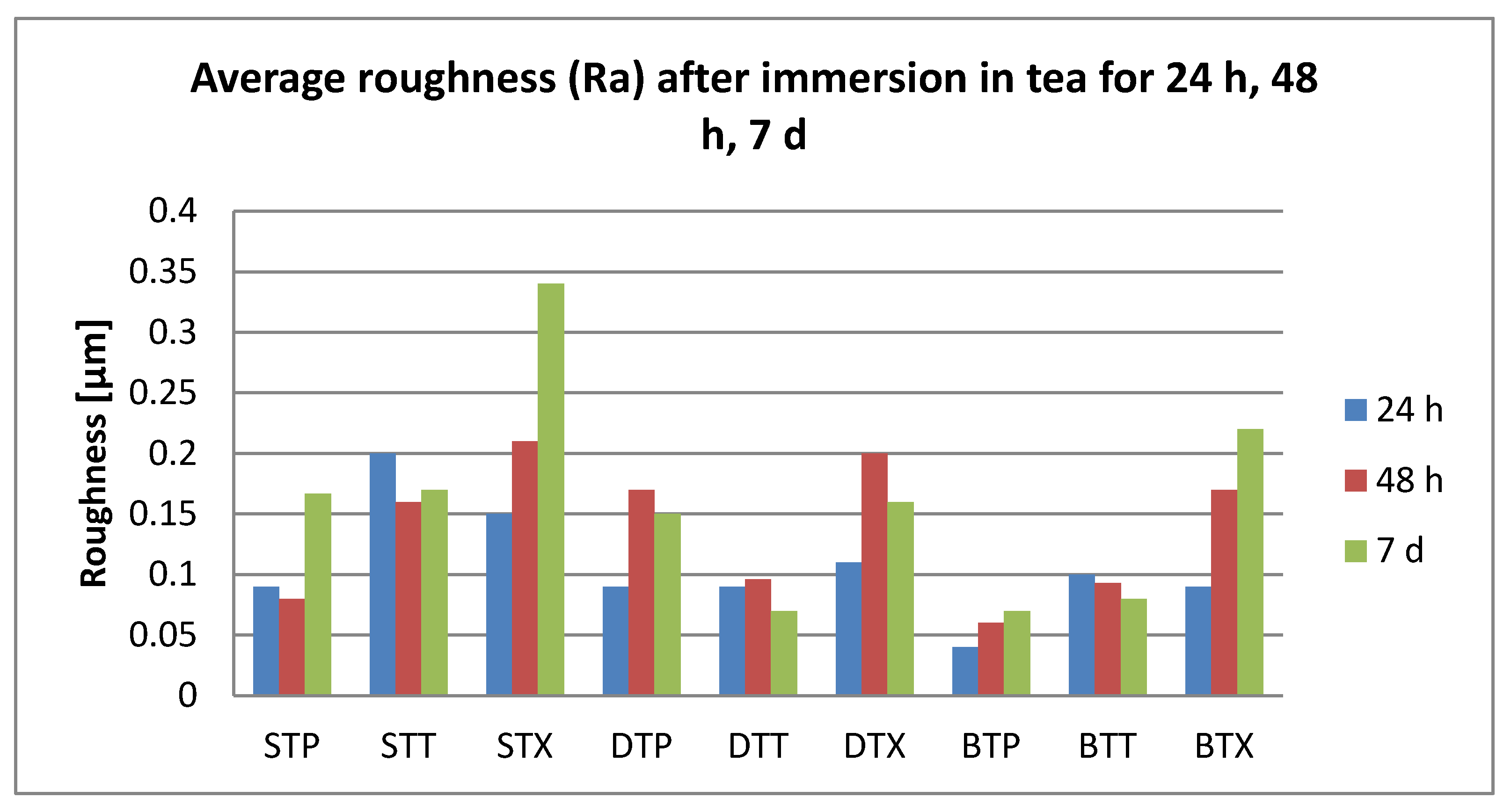
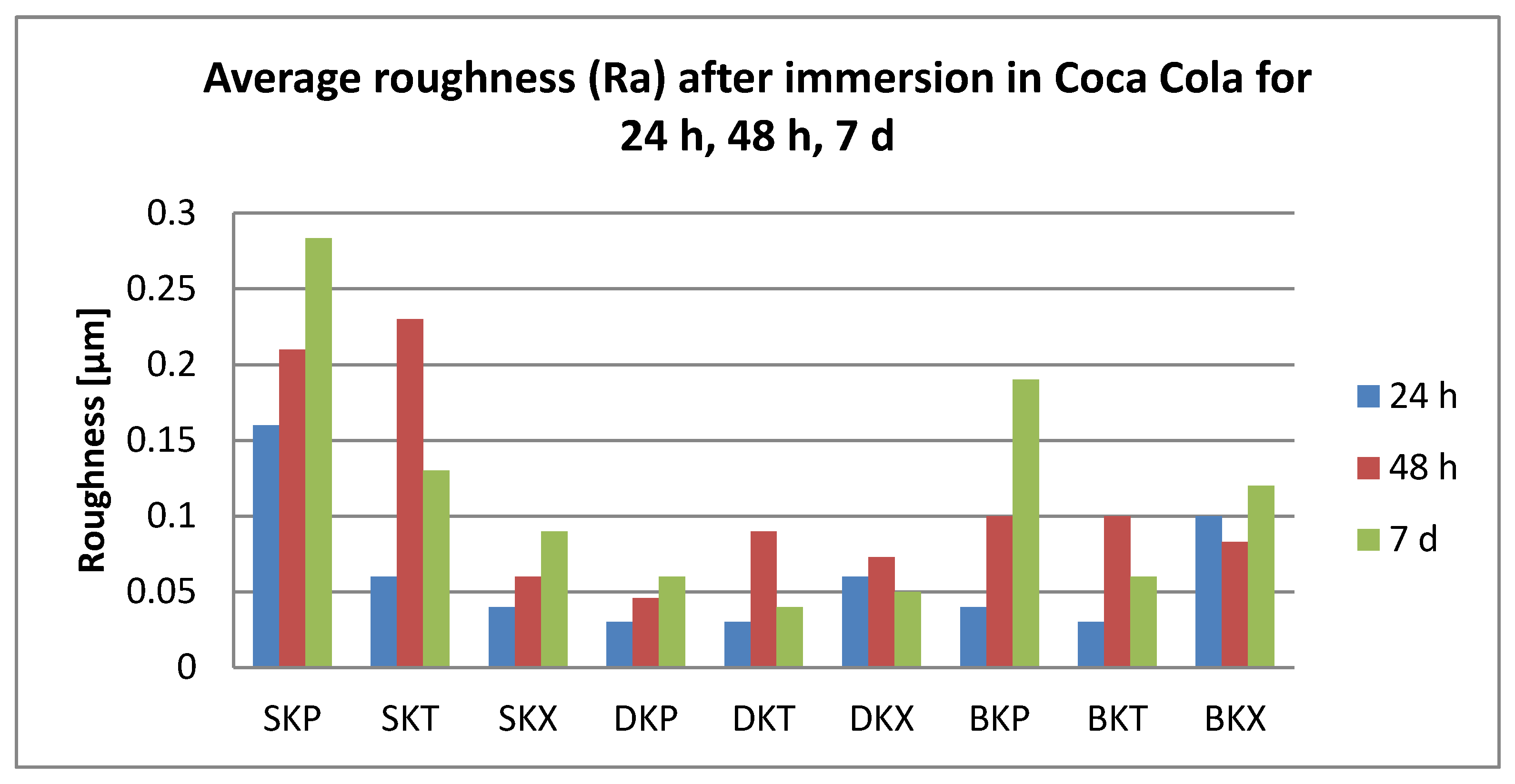
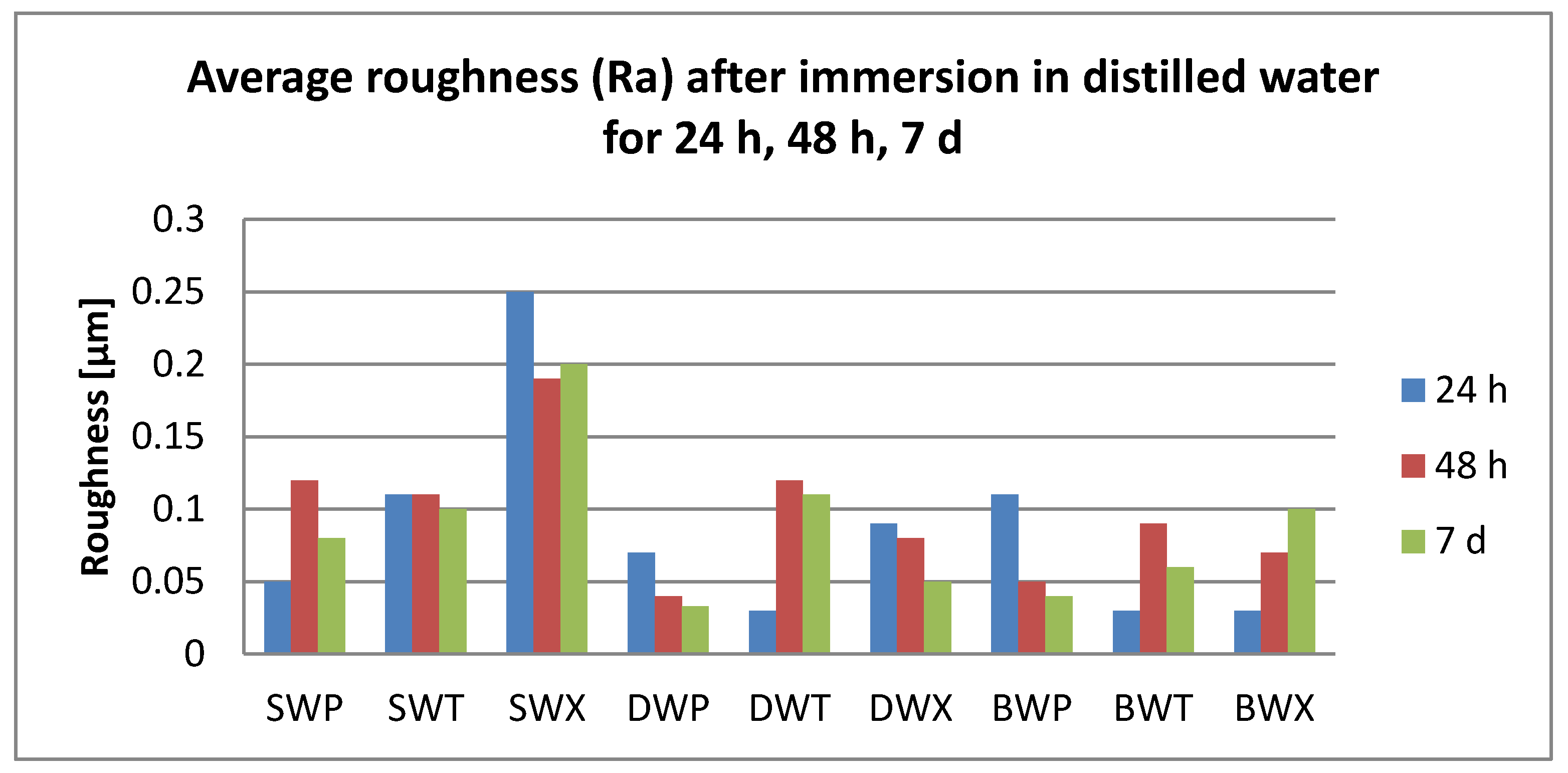
3.2. Surface Roughness Measurements
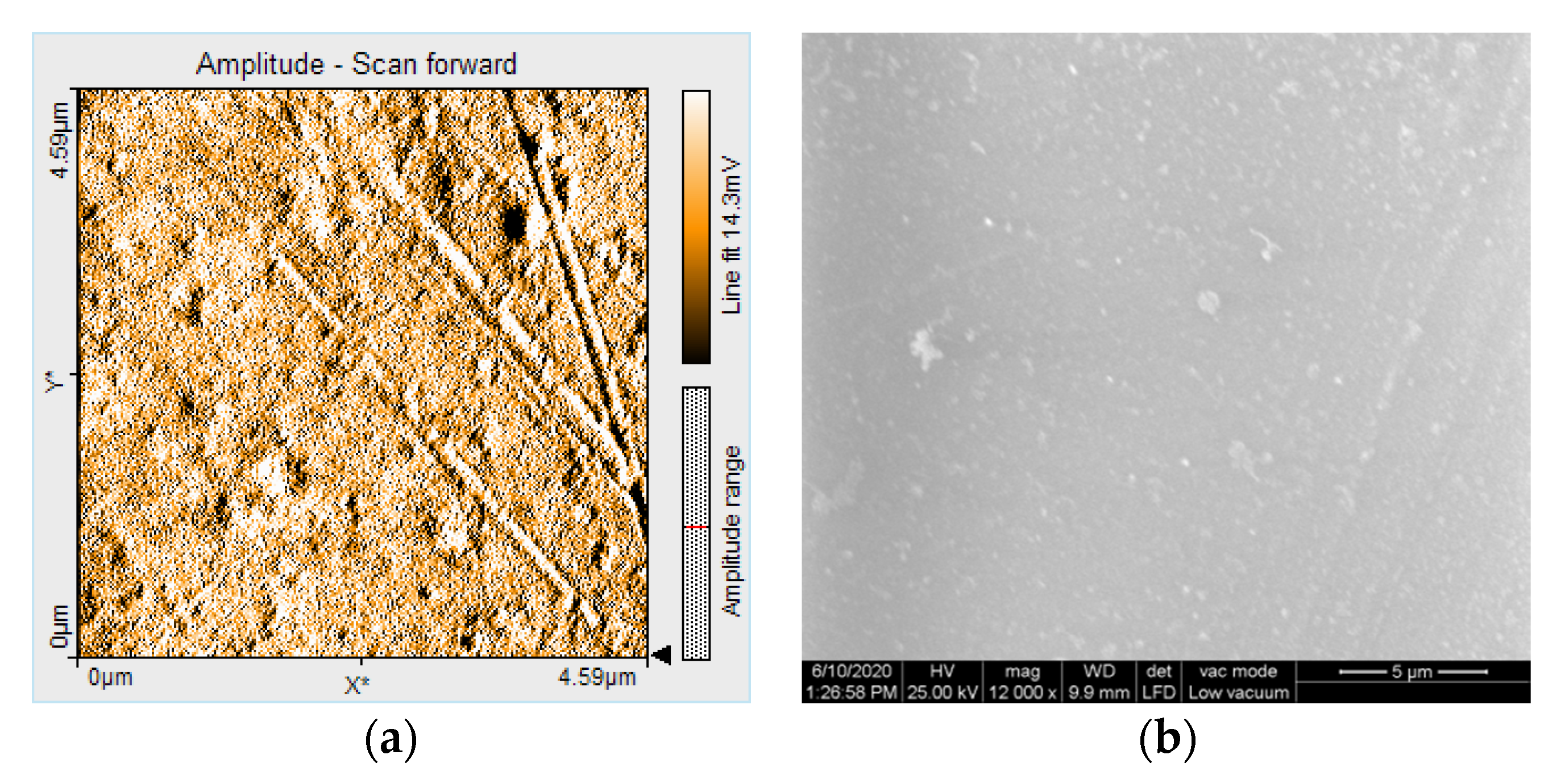
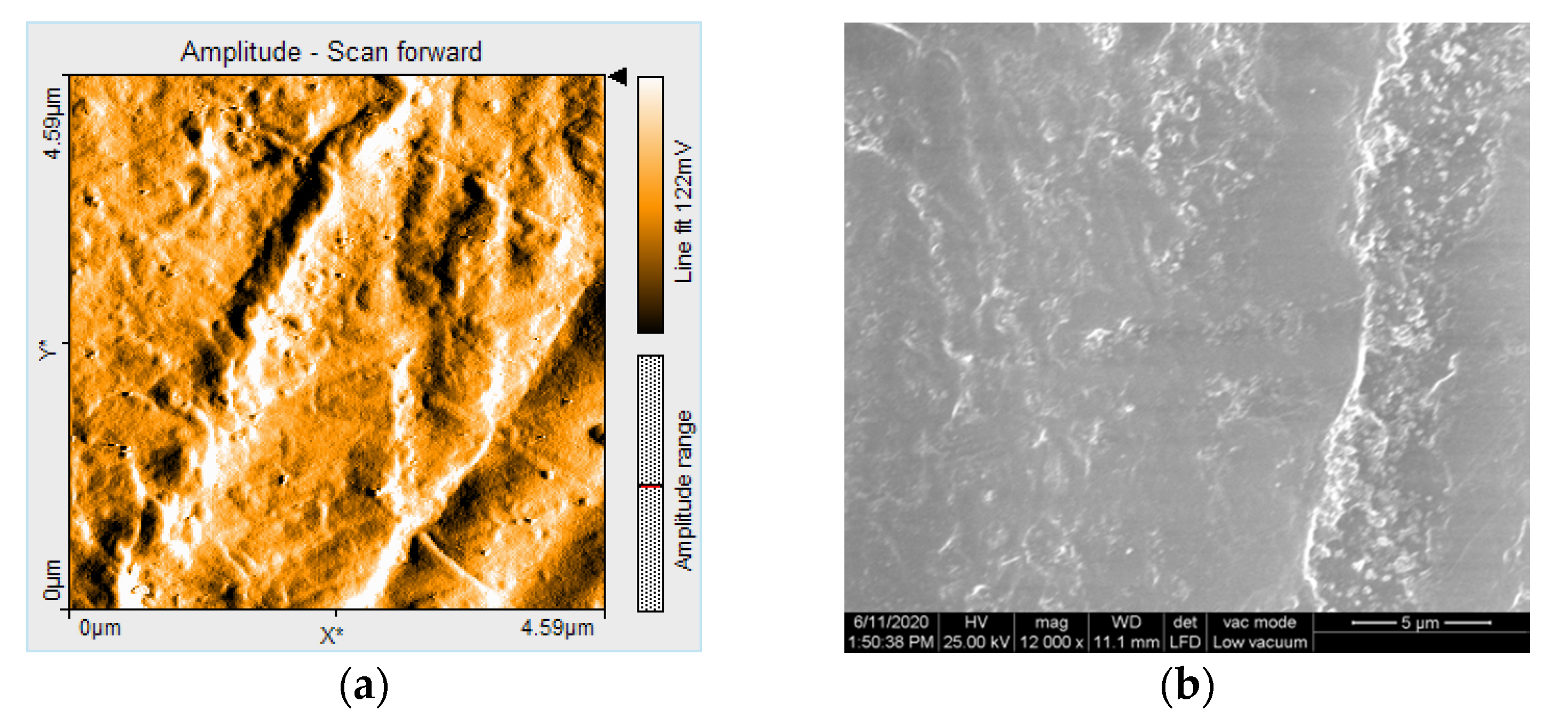
3.3. AFM and SEM Evaluations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Quantitative color change evaluations revealed a slight change in color after 24 h and an extremely marked change after 48 h, respective 7 days, for all tested specimens, regardless of the type of material, beverage, or cleaning method.
- Related to the microroughness, values are below the clinically acceptable limit of 0.20 µm for all samples, all the time during the investigations.
- Related to the type of material, color changes are insignificant, and roughness values registered some significant variations, but with the preservation of the values below the accepted limit.
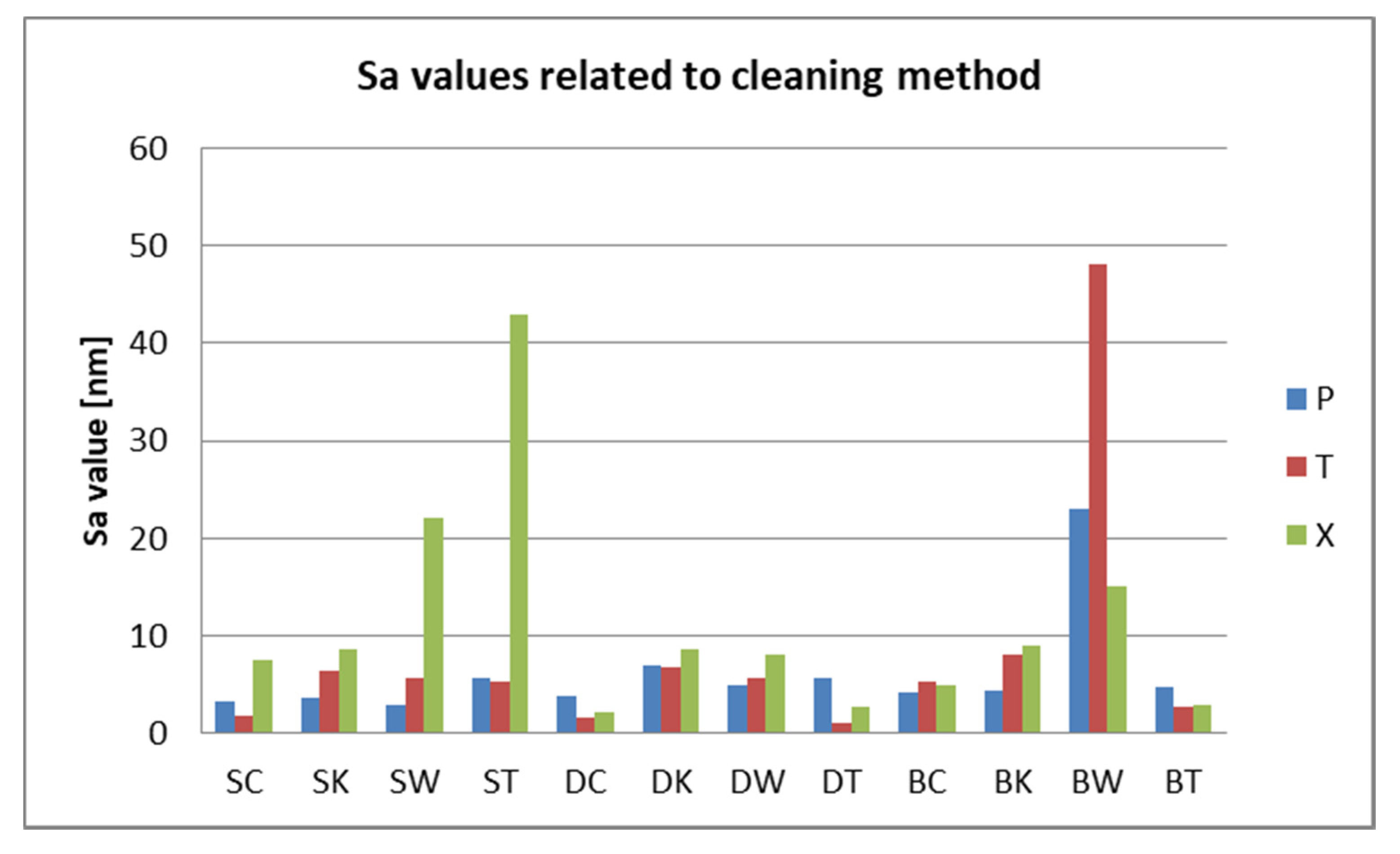
- Related to mean nanoroughness values Sa, and 3D evaluations of the surface quality, D samples have demonstrated the most constant behavior, while B samples are svisibly influenced by W. Related to the cleaning method, nanoroughness values support the 3D images, showing the influence of the mechanical cleaning method on S samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon, J.S.; Lee, Y.K. Force delivery properties of thermoplastic orthodontic materials. Am. J. Ortho Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condo’, R.; Pazzini, L. Mechanical properties of “two generations” of teeth aligners: Change analysis during oral permanence. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamburrino, F.; D’Antò, V. Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polymers for Aligner Manufacturing: In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L.; Sun, W.T.; Wen-Xin, W.L. Colour stabilities of three types of clear orthodontic aligners exposed to staining agents. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupaix, R.B.; Boyce, M.C. Finite strain behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) and poly(ethylene terephthalate)-glycol (PETG). Polymers 2005, 46, 4827–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, T.E.W. Orthodontic Applications of Biomaterials, A Clinical Guide; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sifakakis, I.; Zinelis, S. Aligners for orthodontic applications. Orthod. Appl. Biomater. 2017, 1, 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ryokawa, H.; Miyazaki, Y. The mechanical properties of dental thermoplastic materials in a simulated intraoral environment. Orthod. Waves 2006, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-S. Effects of thermoforming on the physical and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials for transparent orthodontic aligners. Korean. J. Orthod. 2006, 48, 316. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; Zhang, N.; Chen, H. Dynamic stress relaxation of orthodontic thermoplastic materials in a simulated oral environment. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, L.; Martines, E. Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-h in vitro study. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shpack, N.; Greenstein, R.B. Efficacy of three hygienic protocols in reducing biofilm adherence to the removable thermoplastic appliance. Angle Orthod. 2014, 84, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.S.; Fang, D.Y. Mechanical Properties of Orthodontic Thermoplastics PETG/PC2858 after Blending. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsomos, G.; Ludwig, B. Objective assessment of patient compliance with removable orthodontic appliances: A cross-sectional cohort study. Angle Orthod. 2014, 84, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, M.; Wible, E. Long-term effects of seven cleaning methods on light transmittance, surface roughness, and flexural modulus of polyurethane retainer material. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jindal, P.; Juneja, M. Mechanical, and geometric properties of thermoformed and 3D printed clear dental aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Tri, P.; Prud’homme, R.E. Nanoscale analysis of the photodegradation of Polyester fibers by AFM-IR. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 371, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, M. Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Composites, 3rd ed.; Detailed Accounts of Thermoplastic Resins; William Andrew, Kindlington: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 203–766. [Google Scholar]
- Inami, T.; Tanimoto, Y. Color stability of laboratory glass-fiber-reinforced plastics for esthetic orthodontic wires. Korean J. Orthod. 2015, 45, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, A.B.; Ruellas, A.C. Assessment of exogenous pigmentation in colorless elastic ligatures. J. Orthod. 2014, 41, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.S.; Billington, R.W. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2004, 196, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iijima, M.; Kohda, N.; Kawaguchi, K. Effects of temperature changes and stress loading on the mechanical and shape memory properties of thermoplastic materials with different glass transition behaviors and crystal structures. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.X.; Ding, X.J. Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic materials for invisible orthodontics. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, D.L.; Mattos, C.T. Color stability and fluorescence of different orthodontic esthetic archwires. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, G.; Rompré, P. Colorimetric and spectrophotometric measurements of orthodontic thermoplastic aligners exposed to various staining sources and cleaning methods. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegbola, A.; Aghachi, I.E.A.; Sadiku-Agboola, O. SEM and AFM microscopical characterization of rPAN fibre and PET blends. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan, M.; Dargent, E. Strain induced crystallization in uniaxially drawn PETG plates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.L.; Beeman, C.S. The Essential Work of Fracture of Thermoplastic Orthodontic Retainer Materials. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.W.; Ha, H.R. Effects of aging procedures on the molecular, biochemical, morphological, and mechanical properties of vacuum-formed retainers. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 51, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaboura, A.; Fragouli, M.; Rahiotis, C.; Silikas, N. Evaluation of surface characteristics of dental composites using profilometry, scanning electron, atomic force microscopy and gloss-meter. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Thiele, J.; Geisler, D.; Boening, K.; Wieckiewicz, M. Effect of Chemical Disinfection on Chitosan Coated PMMA and PETG Surfaces—An In Vitro Study. Polymers 2018, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alshahrani, I.; Asiry, M.A. Nanomechanical properties, surface topography, and color stability of fiber-reinforced composite orthodontic retainers. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2019, 27, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.P.; Lee, S.J. Surface characteristics of orthodontic materials and their effects on adhesion of mutans streptococci. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.; Carl’en, A. Adsorption of parotid saliva proteins and adhesion of Streptococcus mutans ATCC 21752 to dental fiber-reinforced composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 66, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, C.M.; Lambrechts, P. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, R.D.; Porojan, S.D.; Bîrdeanu, M.I.; Uțu, I.D.; Porojan, L. The Effect of Thermocycling and Surface Treatments on the Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Three Heat-Pressed Ceramics Systems. Crystal 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiliu, R.D.; Porojan, S.D.; Bîrdeanu, M.I.; Porojan, L. Effect of Thermocycling, Surface Treatments and Microstructure on the Optical Properties and Roughness of CAD-CAM and Heat-Pressed Glass Ceramics. Materials 2020, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramoglu, S.I.; Usumez, S. Accelerated aging effects on surface hardness and roughness of lingual retainer adhesives. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Bakr, N.; Han, L.; Okamoto, A.; Iwaku, M. Evaluation of the Surface Roughness of Compomer by Laser Scanning Microscopy. Dent. Mater. J. 2001, 20, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigo, L.; Rizzi, M.; La Torre, G.; Rumi, G. 3-D Surface Profile Analysis: Different Finishing Methods for Resin Composites. Oper. Dent. 2001, 26, 562–568. [Google Scholar]
- Tański, T.; Staszuk, M.; Ziębowicz, B. Atomic-Force Microscopy and Its Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gopferich, A. Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Ullah, R.; Qamar, Z. Properties of dental biomaterials. Adv. Dent. Biomater. 2019, 1, 7–35. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, A.K.; Cantele, A.; Polychronis, G.; Zinelis, S. Changes in Roughness and Mechanical Properties of Invisalign® Appliances after One- and Two-Weeks Use. Materials 2019, 12, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
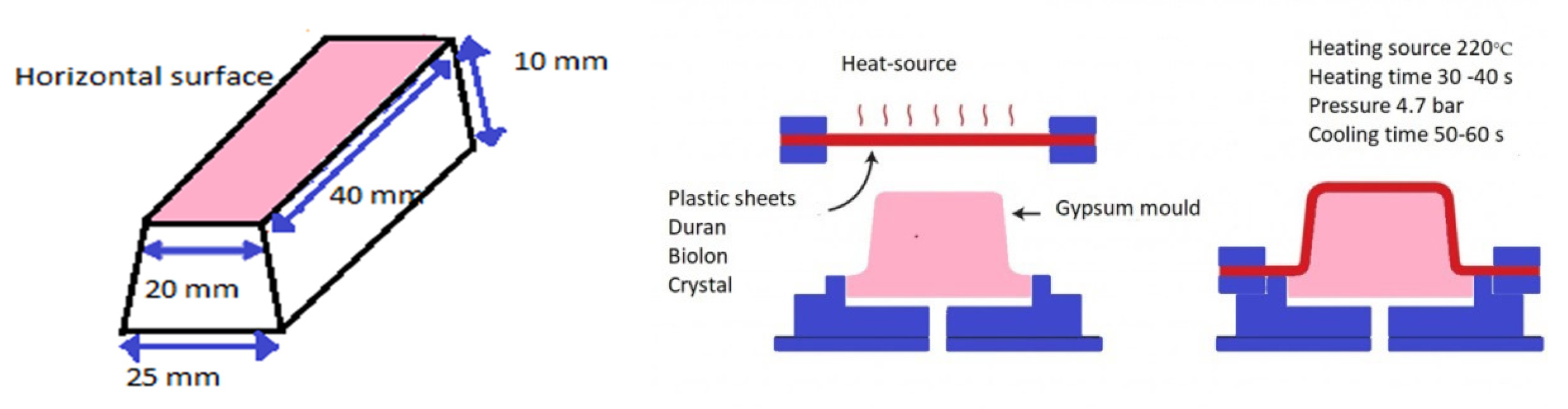




| Material | Pressure (Bar) | Heating Time (Seconds) | Cooling Time (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duran (Scheu-Dental GmbH, Iserlohn, Germany) | 4.7 | 30 | 60 |
| Biolon (Dreve Dentamid GmbH, Unna, Germany) | 4.7 | 40 | 50 |
| Crystal (Bio Art Dental Equipment, Sao Carlos, Brazil) | 4.7 | 30 | 60 |
| No. | Material/Beverage/Cleaning Method | Abbreviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | material | Duran (Scheu-Dental GmbH, Iserlohn, Germany) | S |
| Biolon (Dreve Dentamid GmbH, Unna, Germany) | D | ||
| Crystal (Bio Art Dental Equipment, Sao Carlos, Brazil) | B | ||
| 2. | beverage | Coffee | C |
| Tea | T | ||
| Coca-cola | K | ||
| distilled water | W | ||
| 3. | cleaning method | Centron Cleaning Powder (Scheu, Iserlohn, Germany) | P |
| Corega Cleanser Tablets (Stafford-Miller, Dungarvan, Ireland) | T | ||
| Brushing | X | ||
| NBS Units | Color Changes |
|---|---|
| 0.0–0.5 | extremely slight change |
| 0.5–1.5 | slight change |
| 1.5–3.0 | perceivable |
| 3.0–6.0 | marked change |
| 6.0–12.0 | extremely marked change |
| 12.0 or more | change to another color |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porojan, L.; Vasiliu, R.-D.; Porojan, S.-D.; Bîrdeanu, M.-I. Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents. Polymers 2020, 12, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081736
Porojan L, Vasiliu R-D, Porojan S-D, Bîrdeanu M-I. Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081736
Chicago/Turabian StylePorojan, Liliana, Roxana-Diana Vasiliu, Sorin-Daniel Porojan, and Mihaela-Ionela Bîrdeanu. 2020. "Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081736
APA StylePorojan, L., Vasiliu, R.-D., Porojan, S.-D., & Bîrdeanu, M.-I. (2020). Surface Quality Evaluation of Removable Thermoplastic Dental Appliances Related to Staining Beverages and Cleaning Agents. Polymers, 12(8), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081736





