Strength of Flocs Formed by the Complexation of Lysozyme with Leonardite Humic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leonardite Humic Acid and Lysozyme
2.2. Electrophoretic Mobility
2.3. Observation of Aggregation and Dispersion
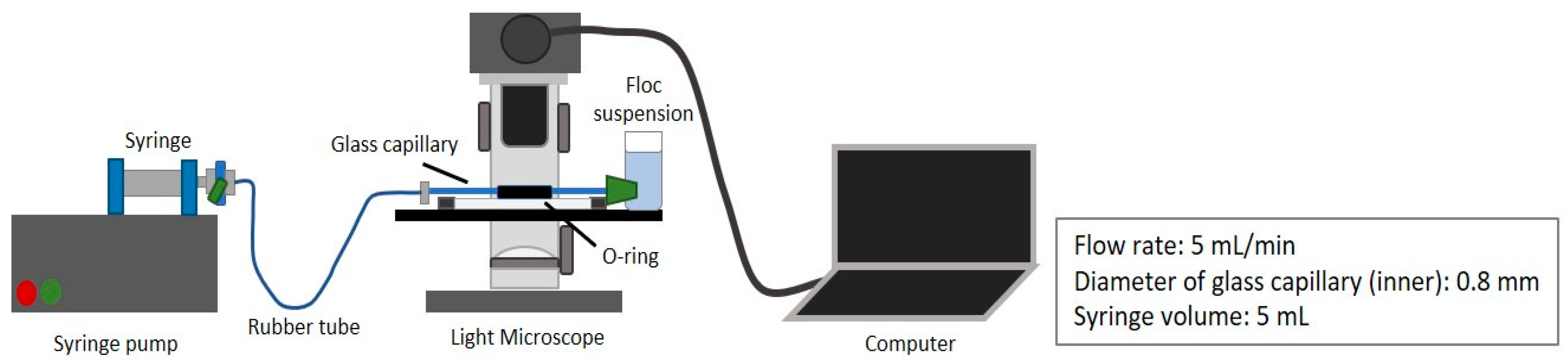
2.4. Floc Breakage and Strength
3. Results and Discussion
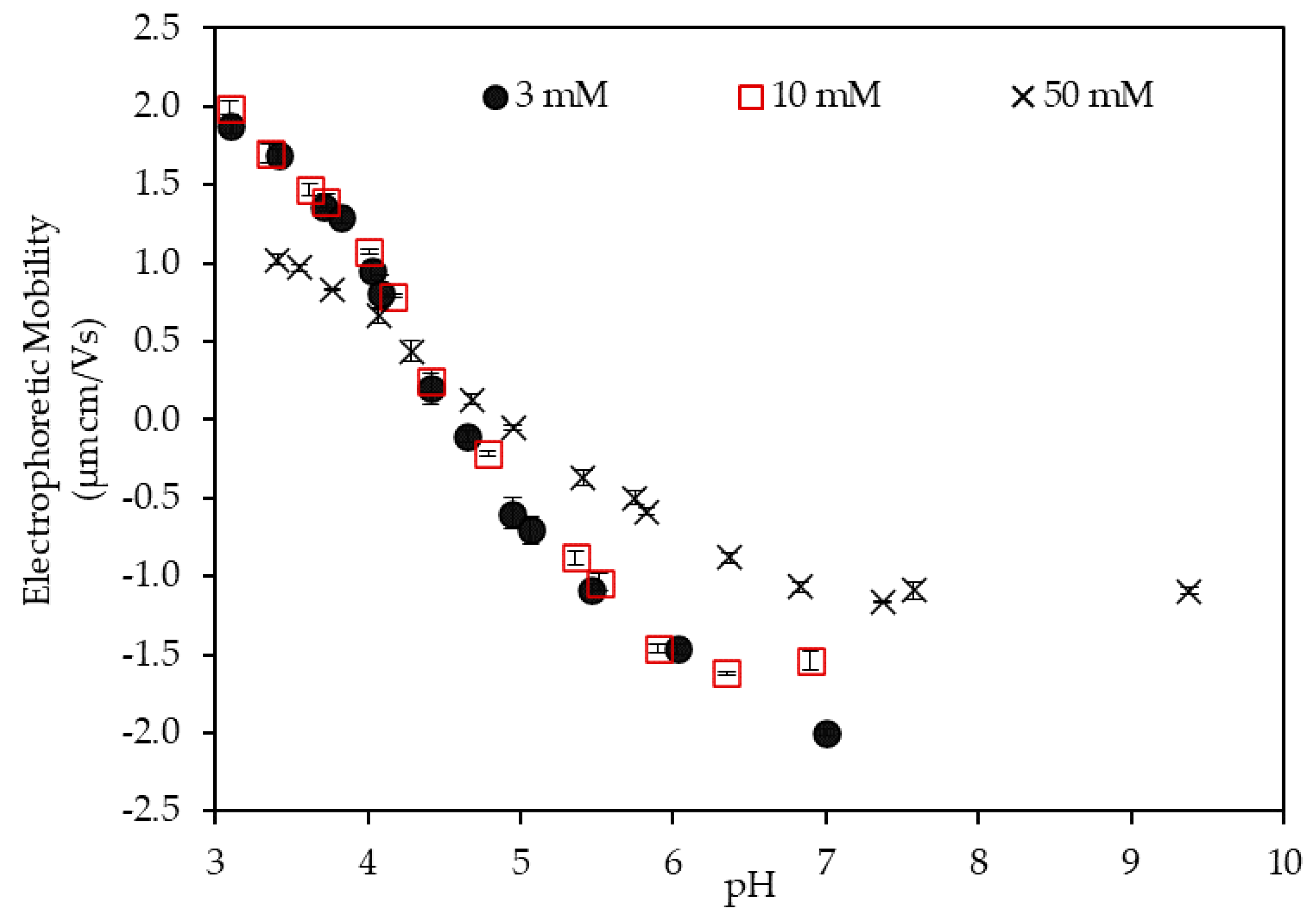
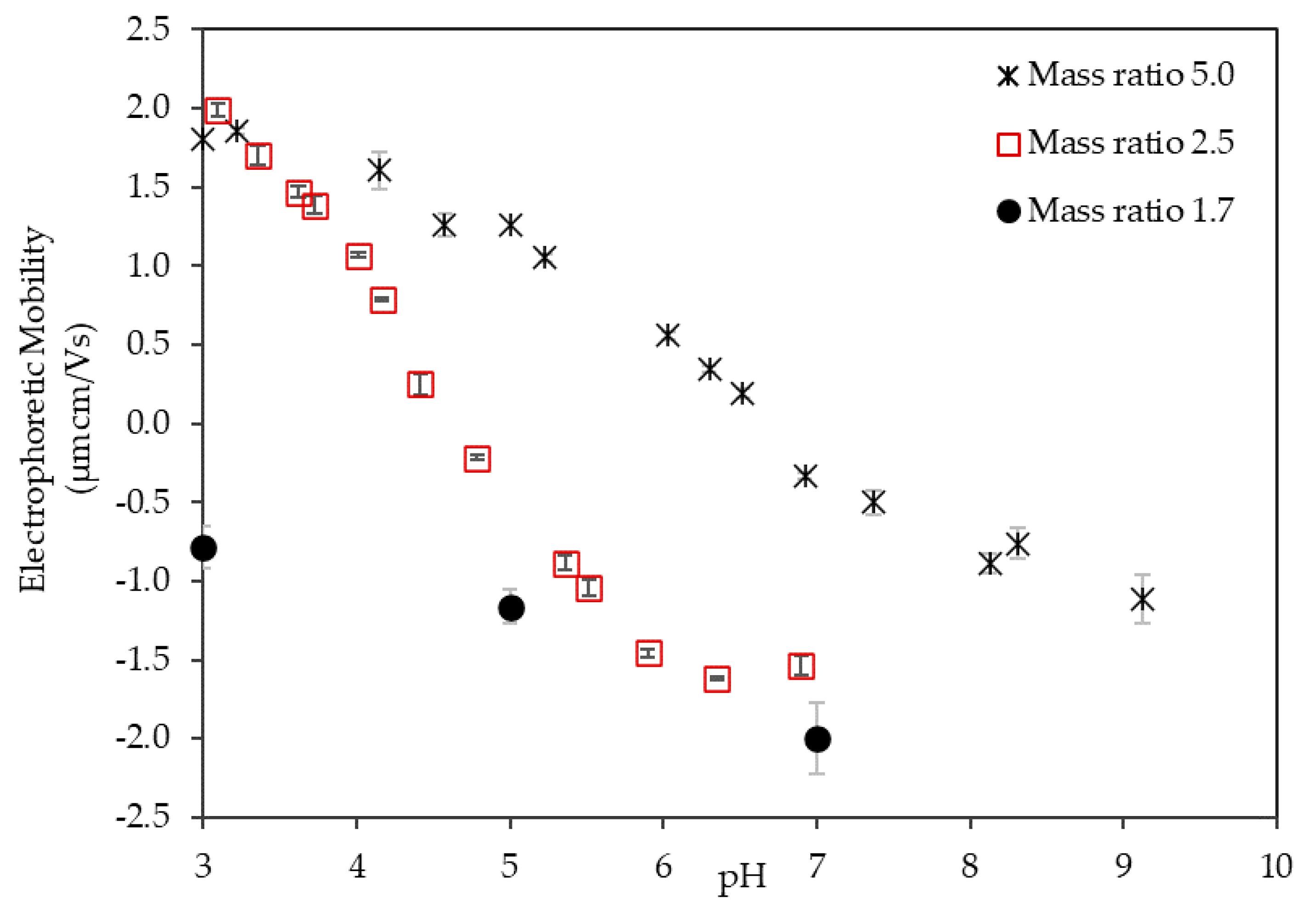
3.1. Electrophoretic Mobility of the LSZ–LHA Complex
3.1.1. Effect of the KCl Concentration
3.1.2. Effect of the Mass Ratio
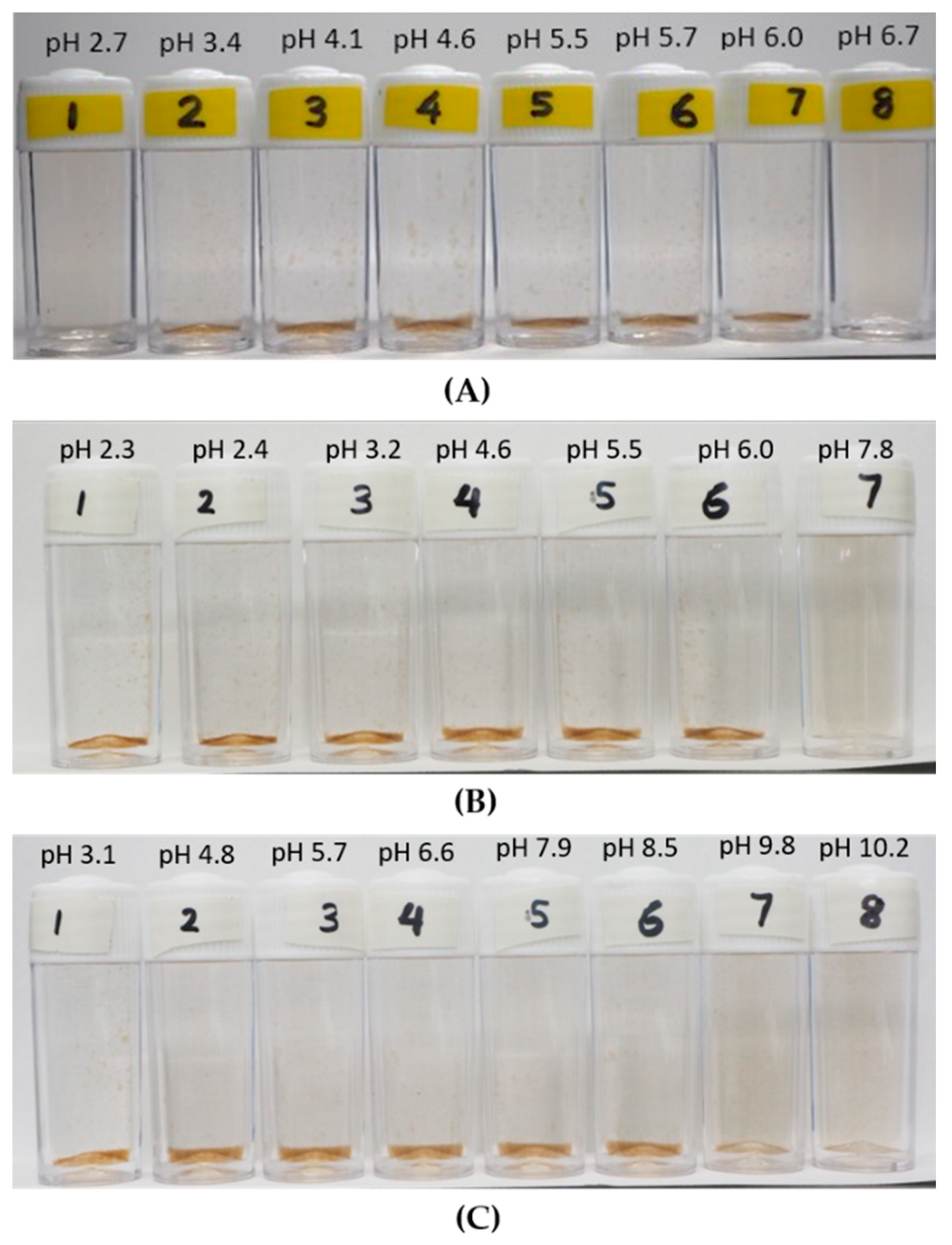
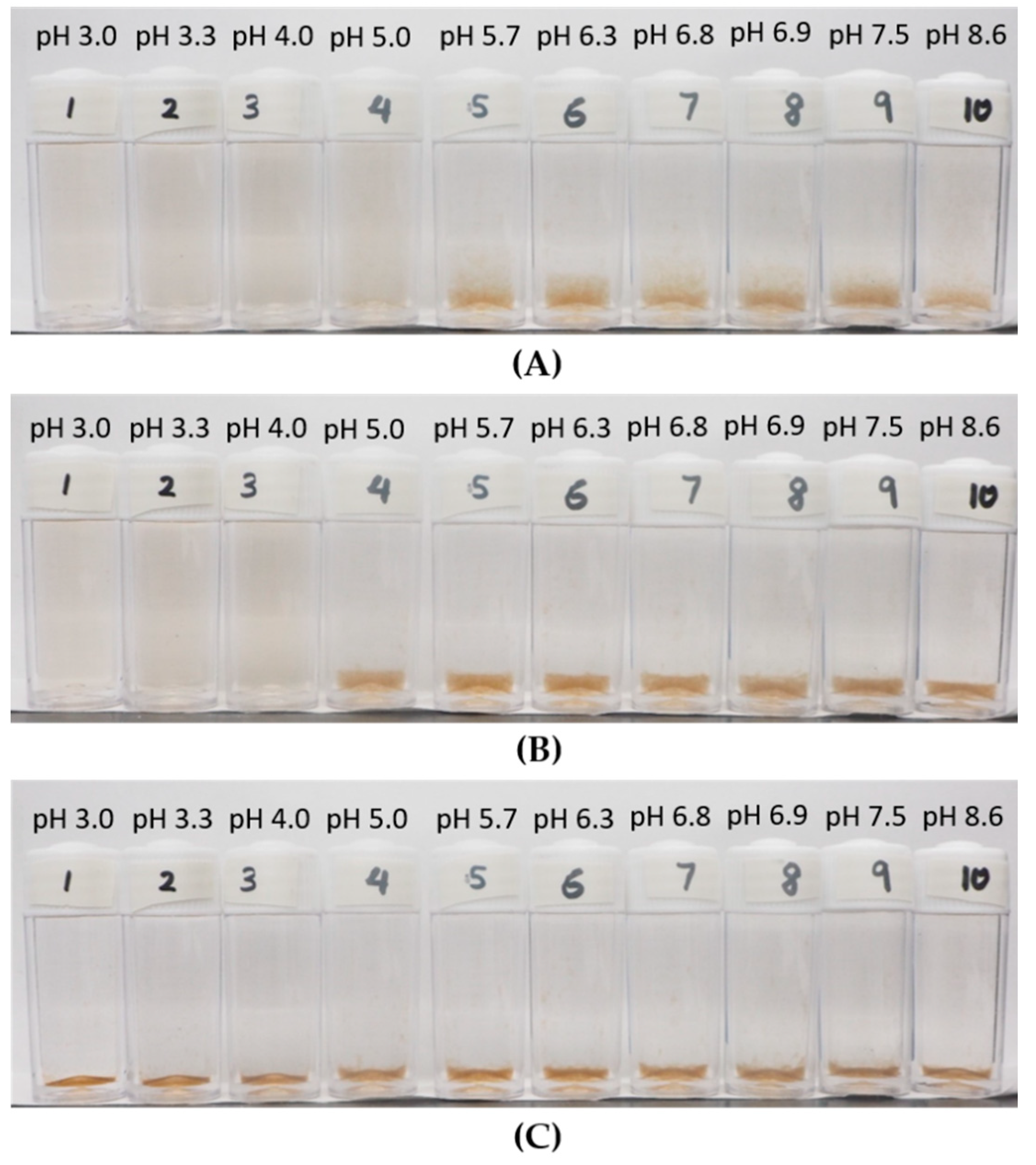
3.2. Observation on the Aggregation Behavior of the LSZ–LHA Complex
3.2.1. Effect of KCl Concentration
3.2.2. Effect of the Mass Ratio
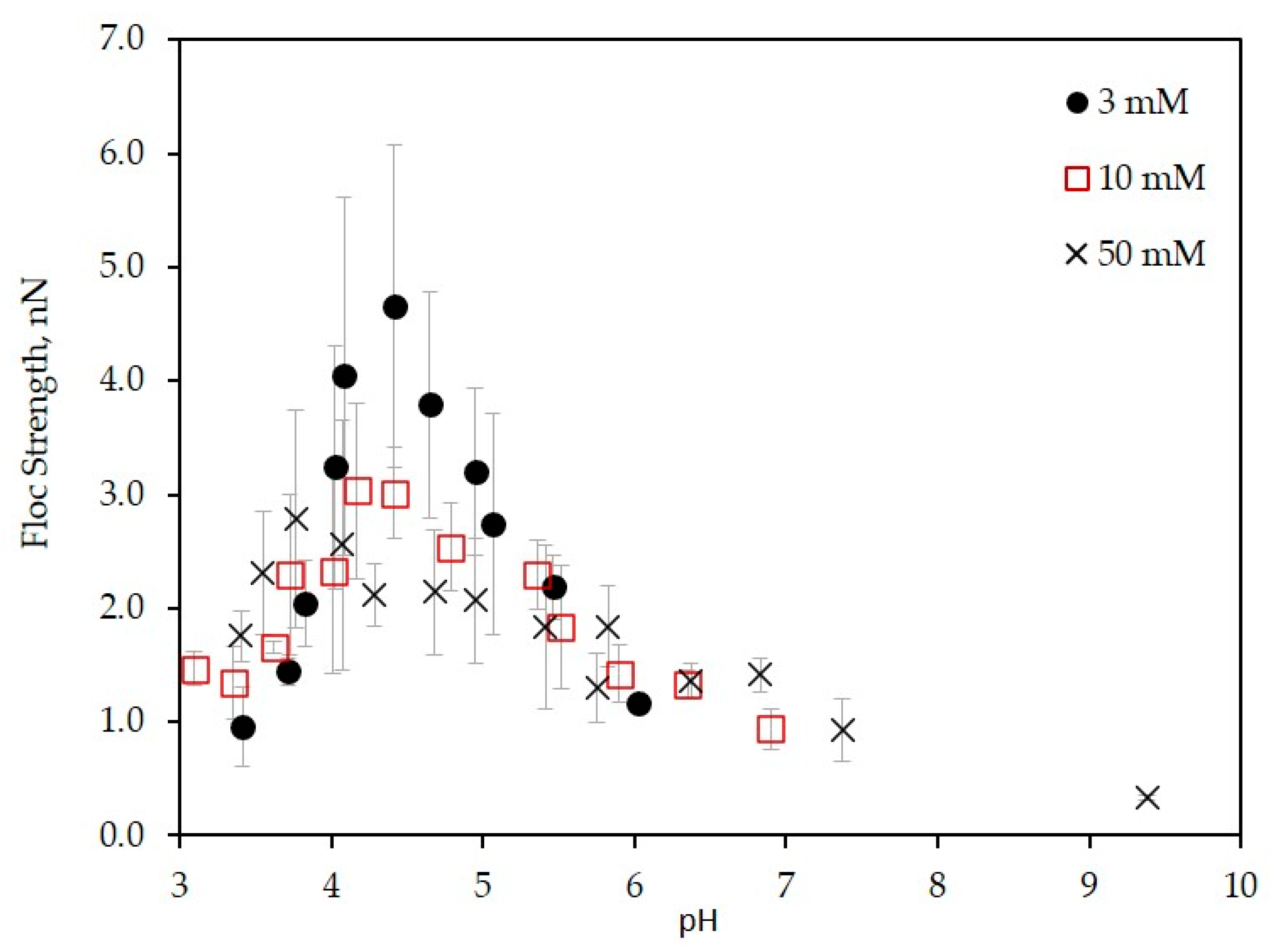
3.3. Floc Strength of the LSZ–LHA Complex
3.3.1. Effect of KCl Concentration
3.3.2. Effect of the Mass Ratio
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kobayashi, M. Strength of Natural Soil Flocs. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3273–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trefalt, G.; Borkovec, M. Overview of DLVO Theory. Laboratory of Colloid and Surface Chemistry; University of Geneva: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Verwey, E.J.W. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1947, 51, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y.; Ooi, S. Breakup of Fractal Flocs in a Turbulent Flow. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4351–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M. Breakup and Strength of Polystyrene Latex Flocs Subjected to a Converging Flow. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 235, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, M. Strength of Humic Acid Aggregates: Effects of Divalent Cations and Solution PH. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8559–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Gregory, J.; Parsons, S.A. A Review of Floc Strength and Breakage. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashitani, K.; Iimura, K.; Vakarelski, I.U. Fundamentals of Breakage of Aggregates in Fluids. KONA Powder Part. J. 2000, 18, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil Quality—A Critical Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, J.E.; Madliger, M.; Pedersen, J.A.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Adsorption of Insecticidal Cry1Ab Protein to Humic Substances. 2. Influence of Humic and Fulvic Acid Charge and Polarity Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9932–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, J.E.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Protein Encapsulation by Humic Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6003–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Koopal, L.K.; Xiong, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, C.; Tan, W. Influence of Humic Acid on Transport, Deposition and Activity of Lysozyme in Quartz Sand. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madliger, M.; Gasser, C.A.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Adsorption of Transgenic Insecticidal Cry1Ab Protein to Silica Particles. Effects on Transport and Bioactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4377–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M.; Madliger, M.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. Adsorption of Transgenic Insecticidal Cry1Ab Protein to SiO2. 1. Forces Driving Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8870–8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.B.; Booth, C.J.; Pedersen, J.A. Fate of Prions in Soil: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giachin, G.; Narkiewicz, J.; Scaini, D.; Ngoc, A.T.; Margon, A.; Sequi, P.; Leita, L.; Legname, G. Prion Protein Interaction with Soil Humic Substances: Environmental Implications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rigou, P.; Rezaei, H.; Grosclaude, J.; Staunton, S.; Quiquampoix, H. Fate of Prions in Soil: Adsorption and Extraction by Electroelution of Recombinant Ovine Prion Protein from Montmorillonite and Natural Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, W.F.; Wang, M.X.; Liu, F.; Weng, L.P.; Norde, W.; Koopal, L.K. Influence of Lysozyme Complexation with Purified Aldrich Humic Acid on Lysozyme Activity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.S.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G.; Teixeira, J.A.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Nogueira, R. Interaction of Moringa Oleifera Seed Lectin with Humic Acid. Chem. Pap. 2011, 65, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.F.; Koopal, L.K.; Norde, W. Interaction between Humic Acid and Lysozyme, Studied by Dynamic Light Scattering and Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.F.; Koopal, L.K.; Weng, L.P.; van Riemsdijk, W.H.; Norde, W. Humic Acid Protein Complexation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosen-runge, F. Salt Effects in Protein Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Eberhard Karls University Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Tan, W.; Koopal, L.K.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Norde, W. Influence of Soil Humic and Fulvic Acid on the Activity and Stability of Lysozyme and Urease. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5050–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, A.; Kobayashi, M. Charging, Aggregation, and Aggregate Strength of Humic Substances in the Presence of Cationic Surfactants: Effects of Humic Substances Hydrophobicity and Surfactant Tail Length. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena, M.J.; Wilkinson, K.J. Disaggregation Kinetics of a Peat Humic Acid: Mechanism and PH Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5100–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigante, M.; Zanini, G.; Avena, M. Effect of PH, Anions and Cations on the Dissolution Kinetics of Humic Acid Particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 347, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, S. Flocs in Shear and Strain Flows. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 225, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambo, N.; Hozumi, H. Physical Characteristics of Flocs-II. Strength of Floc. Water Res. 1979, 13, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Kobayashi, M. Aggregation and Charge Reversal of Humic Substances in the Presence of Hydrophobic Monovalent Counter-Ions: Effect of Hydrophobicity of Humic Substances. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 540, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Kobayashi, M. Quantitative Evaluation of Shift of Slipping Plane and Counterion Binding to Lysozyme by Electrophoresis Method. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Pham, T.D.; Kobayashi, M. Charging and Aggregation Behavior of Silica Particles in the Presence of Lysozymes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuehner, D.E.; Engmann, J.; Fergg, F.; Wernick, M.; Blanch, H.W.; Prausnitz, J.M. Lysozyme Net Charge and Ion Binding in Concentrated Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norde, W.; Gonzalez, F.G.; Haynes, C.A. Protein Adsorption on Polystyrene Latex Particles. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1995, 6, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Norde, W.; Koopal, L.K. Interaction between Lysozyme and Humic Acid in Layer-by-Layer Assemblies: Effects of PH and Ionic Strength. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, S. Break-up of Flocs in Contraction and Swirling Flows. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 166, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, S. Mathematical Formulas (Sugaku Koshikishu); Iwanami Shoten: Tokyo, Japan, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, T.; Nishiya, M.; Kobayashi, M. Electrophoretic Mobility of Carboxyl Latex Particles: Effects of Hydrophobic Monovalent Counter-Ions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahill, B.P.; Papastavrou, G.; Koper, G.J.M.; Borkovec, M. Adsorption of Poly(Amido Amine) (PAMAM) Dendrimers on Silica: Importance of Electrostatic Three-Body Attraction. Langmuir 2008, 24, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pota, G.; Venezia, V.; Vitiello, G.; Di Donato, P.; Mollo, V.; Costantini, A.; Avossa, J.; Nuzzo, A.; Piccolo, A.; Silvestri, B.; et al. Tuning Functional Behavior of Humic Acids through Interactions with Stöber Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szilagyi, I.; Polomska, A.; Citherlet, D.; Sadeghpour, A.; Borkovec, M. Charging and Aggregation of Negatively Charged Colloidal Latex Particles in the Presence of Multivalent Oligoamine Cations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 392, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.L.; Bouyer, F.; Borkovec, M. Polystyrene Sulfate Latex Particles in the Presence of Poly(Vinylamine): Absolute Aggregation Rate Constants and Charging Behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 241, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Kobayashi, M.; Skarba, M.; Mu, C.; Galletto, P.; Borkovec, M. Heteroaggregation in Binary Mixtures of Oppositely Charged Colloidal Particles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Galletto, P.; Borkovec, M. Charging and Aggregation of Latex Particles by Oppositely Charged Dendrimers. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7465–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Vu, T.N.; Nguyen, H.L.; Le, P.H.P.; Hoang, T.S. Adsorptive Removal of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Solution Using Protein-Modified Nanosilica. Polymers 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gassenschmidt, U.; Jany, K.D.; Tauscher, B.; Niebergall, H. Isolation and Characterization of a Flocculating Protein from Moringa Oleifera Lam. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1243, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, F.; Robben, A.; Yu, W.L.; Borkovec, M. Aggregation of Colloidal Particles in the Presence of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolytes: Effect of Surface Charge Heterogeneities. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5225–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Ji, Z. Enhanced Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cellulose from Waste Paper Fibers by Cationic Polymers Addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi, I.; Trefalt, G.; Tiraferri, A.; Maroni, P.; Borkovec, M. Polyelectrolyte Adsorption, Interparticle Forces, and Colloidal Aggregation. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2479–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nanaumi, H.; Muto, Y. Initial Deposition Rate of Latex Particles in the Packed Bed of Zirconia Beads. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 347, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Feng, L.; Kobayashi, M. Kinetics of Flocculation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in the Mixing Flow Induced with High Charge Density Polycation near the Isoelectric Point. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 471, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Kinetics of Turbulent Hetero-Coagulation of Oppositely Charged Colloidal Particles. Theor. Appl. Mech. Jpn. 2015, 63, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan Abdul Khodir, W.K.; Hakim, A.; Kobayashi, M. Strength of Flocs Formed by the Complexation of Lysozyme with Leonardite Humic Acid. Polymers 2020, 12, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081770
Wan Abdul Khodir WK, Hakim A, Kobayashi M. Strength of Flocs Formed by the Complexation of Lysozyme with Leonardite Humic Acid. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081770
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan Abdul Khodir, Wan Khairunnisa, Azizul Hakim, and Motoyoshi Kobayashi. 2020. "Strength of Flocs Formed by the Complexation of Lysozyme with Leonardite Humic Acid" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081770
APA StyleWan Abdul Khodir, W. K., Hakim, A., & Kobayashi, M. (2020). Strength of Flocs Formed by the Complexation of Lysozyme with Leonardite Humic Acid. Polymers, 12(8), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081770







