A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
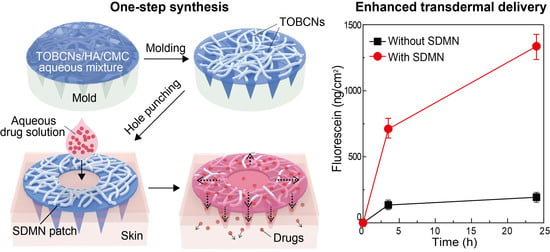
2.2. Preparation of SDMN Patch
2.3. Morphological and Mechanical Characterization of SDMN Patch
2.4. Skin Distribution Analysis of Model Drug
2.5. In Vitro Skin Permeation Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SDMN Preparation and Characterization
3.2. Distribution Analysis of Model Drugs
3.3. In Vitro Skin Permeation Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Gill, H.S. Coating solid dispersions on microneedles via a molten dip-coating method: Development and in vitro evaluation for transdermal delivery of a water-insoluble drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vora, L.K.; Vavia, P.R.; Larrañeta, E.; Bell, S.E.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Novel nanosuspension-based dissolving microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of a hydrophobic drug. J. Interdiscip. Nanomed. 2018, 3, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Erdos, G.; Huang, S.; Kenniston, T.W.; Balmert, S.C.; Carey, C.D.; Raj, V.S.; Epperly, M.W.; Klimstra, W.B.; Haagmans, B.L.; et al. Microneedle array delivered recombinant coronavirus vaccines: Immunogenicity and rapid translational development. EBioMedicine 2020, 55, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, R.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chiang, W.-H.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Hu, S.-H. Transdermal Composite Microneedle Composed of Mesoporous Iron Oxide Nanoraspberry and PVA for Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.J.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F.; Montesinos, M.C.; Garrigues, T.M.; Melero, A. Microneedle-Based Delivery: An Overview of Current Applications and Trends. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated microneedles: A novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, M.; Johnson, B.; Ameri, M.; Nyam, K.; Libiran, L.; Zhang, D.D.; Daddona, P. Transdermal delivery of desmopressin using a coated microneedle array patch system. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated microneedles for gene and drug delivery. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 289–313. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, A.M.; Simone, C.; O’Leary, M.D. Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Eom, Y.A.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.; Jung, S.U.; Park, Y.O.; Lee, S.E.; Jung, H. Skin barrier restoration and moisturization using horse oil-loaded dissolving microneedle patches. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, K.M.; Jeong, K.H.; Yang, H.; Kim, M.; Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.W. Nanostructured lipid carrier-loaded hyaluronic acid microneedles for controlled dermal delivery of a lipophilic molecule. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Limcharoen, B.; Toprangkobsin, P.; Kröger, M.; Darvin, M.E.; Sansureerungsikul, T.; Rutwaree, T.; Wanichwecharungruang, S.; Banlunara, W.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A. Microneedle-Facilitated Intradermal Proretinal Nanoparticle Delivery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Dangol, M.; Kang, G.; Lahiji, S.F.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.; Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, C.H.; et al. Enhanced transdermal delivery by combined application of dissolving microneedle patch on serum-treated skin. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Kim, S.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.; Chiang, L.; Baek, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Choi, G.W.; Jung, H. Combinatorial application of dissolving microneedle patch and cream for improvement of skin wrinkles, dermal density, elasticity, and hydration. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Kim, S.; Jang, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Eom, Y.A.; Kang, G.; Chiang, L.; Baek, J.H.; et al. Two-phase delivery using a horse oil and adenosine-loaded dissolving microneedle patch for skin barrier restoration, moisturization, and wrinkle improvement. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick, W.J.; Hallett, J.P.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Abeer, M.M.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I.; Martin, C. A review of bacterial cellulose-based drug delivery systems: Their biochemistry, current approaches and future prospects. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, D.; Letchford, K.; Jackson, J.; Burt, H. A review of nanocellulose as a novel vehicle for drug delivery. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2014, 29, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Adnan, A.S.; Yahya, E.B.; Olaiya, N.G.; Safrida, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Abdullah, C.K.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; et al. A Review on Plant Cellulose Nanofibre-Based Aerogels for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaikit, T.; Chusuit, T.; Raknam, P.; Boonme, P. Effects of a cellulose mask synthesized by a bacterium on facial skin characteristics and user satisfaction. Med. Devices (Auckl) 2011, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, G.; de Mello, C.V.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Isaac, V.L.B.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Pecoraro, É.; Trovatti, E. Bacterial cellulose skin masks-Properties and sensory tests. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Wei, T.; Li, J.; Fan, Z. Nanocellulose: A promising nanomaterial for advanced electrochemical energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2837–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-M.; Lee, C.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jung, U.-W.; Chung, G.; Jung, H. Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Painless Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahara, N.; Tabuchi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Yano, H.; MoRinaga, Y.; Yoshinaga, F. Degree of polymerization of cellulose from Acetobacter xylinum BPR2001 decreased by cellulase produced by the strain. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi, T.; Kouda, T.; Yano, H.; Yoshinaga, F. Effect of lactate on bacterial cellulose production from fructose in continuous culture. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 85, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Deng, F.; Yeomans, W.G.; Allen, A.L.; Gross, R.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Direct incorporation of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine into exopolymers by Gluconacetobacter xylinus (=Acetobacter xylinum) ATCC 10245: Production of chitosan-cellulose and chitin-cellulose exopolymers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, A.; Nicklasson, E.; Harrah, T.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Brittberg, M.; Gatenholm, P. Bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for tissue engineering of cartilage. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 419–431. [Google Scholar]
- Pasaribu, K.M.; Gea, S.; Ilyas, S.; Tamrin, T.; Sarumaha, A.A.; Sembiring, A.; Radecka, I. Fabrication and in-Vivo Study of Micro-Colloidal Zanthoxylum acanthopodium-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose as a Burn Wound Dressing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, R.M.; Abdel-Magied, A.F.; Wu, Q.; Olsson, R.T.; Forsberg, K. Green Synthesis of Metal-Organic Framework Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites for Separation Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Kang, N.-K. Physical properties of TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers on the skin surface. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5267–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Kang, N.-G. One-pot method of synthesizing TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers using immobilized TEMPO for skincare applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAllister, D.V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.-H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.Y.; Ren, L.; Chen, Z.P.; Pan, C.F.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, L.L. Fabrication of micro-needle electrodes for bio-signal recording by a magnetization-induced self-assembly method. Sensors 2016, 16, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. Highly porous silk fibroin scaffold packed in PEGDA/sucrose microneedles for controllable transdermal drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J.; Joo, K., II; Kim, K.H.; Lim, G.; Cha, H.J. Bio-inspired swellable hydrogel-forming double-layered adhesive microneedle protein patch for regenerative internal/external surgical closure. Biomaterials 2019, 222, 119439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Ankrum, J.A.; Guo, D.; Chester, S.A.; Yang, S.Y.; Kashyap, A.; Campbell, G.A.; Wood, R.J.; Rijal, R.K.; Karnik, R.; et al. Microstructured barbs on the North American porcupine quill enable easy tissue penetration and difficult removal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21289–21294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, P.; Luongo, K.; Strom, J.A.; Bhansali, S. Sharpening of hollow silicon microneedles to reduce skin penetration force. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 45011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Moore, J.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; González-Vázquez, P.; Lutton, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, P.J.; Kuijt, N.; Kaya, M.; Rol, S.; van der Maaden, K. Nanoporous microneedle arrays seamlessly connected to a drug reservoir for tunable transdermal delivery of memantine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105331. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Mahmood, T.M.T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; O’Neill, S.; O’Mahony, C.; Armstrong, K.; McLoone, N.; Kole, P.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays exhibit antimicrobial properties: Potential for enhanced patient safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 451, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearney, M.-C.; McKenna, P.E.; Quinn, H.L.; Courtenay, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Development of Liquid Drug Reservoirs for Microneedle Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drug Molecules. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellemère, G.; Stamatas, G.N.; Bruère, V.; Bertin, C.; Issachar, N.; Oddos, T. Antiaging Action of Retinol: From Molecular to Clinical. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 22, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Oh, S.-G.; Moon, S.-K.; Bae, S.-Y. Preparation of silica particles encapsulating retinol using O/W/O multiple emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 240, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Jee, J.-P.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, C.-K. Stabilization of all-trans retinol by loading lipophilic antioxidants in solid lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandar, N.G.; Simovic, S.; Prestidge, C.A. Chemical stability and phase distribution of all-trans-retinol in nanoparticle-coated emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 376, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, Y.; Hirobe, S.; Iioka, H.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Asada, H.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Development of a novel therapeutic approach using a retinoic acid-loaded microneedle patch for seborrheic keratosis treatment and safety study in humans. J. Control. Release 2013, 171, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.; Cui, Y.; Fisher, G.J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Schneider, L.M.; Majmudar, G. A comparative study of the effects of retinol and retinoic acid on histological, molecular, and clinical properties of human skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.E.; Jun, S.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Kang, N.-G. A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2020, 12, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091873
Song JE, Jun S-H, Park S-G, Kang N-G. A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091873
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ji Eun, Seung-Hyun Jun, Sun-Gyoo Park, and Nae-Gyu Kang. 2020. "A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091873
APA StyleSong, J. E., Jun, S.-H., Park, S.-G., & Kang, N.-G. (2020). A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Polymers, 12(9), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091873