Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IPN Based Epoxy Systems with Thermoplastic Tougheners
2.1. Effect of Toughener Content
2.2. Effect of Other Parameters

3. IPN Based Epoxy Systems with Thermosetting Tougheners
The Toughening of Bio-Based Epoxy (BE) Resin Has Been Performed by Using Epoxidized Soybean
4. IPN in Aerospace Applications
Case Study: PEI as a Thermoplastics Toughener
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| DGEBA | Diglycidyl ether of biphenol A |
| DDM | 4,4′-Diaminodiphenyl methane |
| PBHDDP | poly[4,4′-bis(6-hydroxyhexyloxy)biphenyl 9,10-dihydro-10-[2,3-di(hydroxycarbonyl) propyl]-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide] |
| TGAP | Triglycidyl p-aminophenol |
| DDS | 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl sulfone |
| Poly(p-BAB/PBP) | Poly(p-1,4-bis(azidomethyl)benzene/4,4′-bis(2-propynyloxy)benzophenone) |
| Poly(p-BAB/SPB) | Poly(p-1,4-bis(azidomethyl)benzene/4,4′-sulfonylbis(propynyloxy)benzene) |
| Poly(m-BAB/SPB) | Poly(p-1,3-bis(azidomethyl)benzene/4,4′-sulfonylbis(propynyloxy)benzene) |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| D-230 | Poly(propylene glycol) bis (2-aminopropyl ether) |
| BADCy | bisphenol A dicyanate |
| BMI | 4,4′-bismaleimidodiphenylmethane |
| PPO | polyphenylene ether |
| MHHPA | Methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride |
| FCBHBP | Flexible chain blocking hyperbranched polyester |
| MABS | Methyl methacrylate acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
| PEEK-PR | PEEK oligomer with terminal propargyl groups |
| PEEK-TOH | Hydroxyl terminated PEEK |
| PPG | Polypropylene glycol |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| MDI | 4,4′-Diphenylmethane diisocyanate |
| TMHDA | 2,2,4-trimethylhexane-1,6-diamine |
| 9G | Poly(ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) |
| CDGE | Cardanol diglycidyl ether |
| IPD | Isophorone diamine |
| Poly(EDBz) | Polybenzoxazine |
| DMPA | 2,2-dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone |
| INN | Triethylenetetramine |
| TDI | Toluene diisocyanate |
| TETA | Triethylene tetramine |
| PUP | Polyurethane prepolymer |
| PAMAM | Polyamidoamine |
| HBP-PU | Hyperbranched polyester-Polyurethane |
| RTA | Polyurethane active toughening agent |
| STU | Silane terminated urethane |
| MOCA | 3,3′-dichloro-4,4′-diamino diphenyl methane |
| H-957 | Ciba–Geigy two-pack hardener |
| DADPE | Diaminodiphenyl ether |
| DADPS | Diaminodiphenyl sulfone |
| SiMPU | Hydroxy-terminated silicon-modified polyurethane |
| NMA | Nadic methyl anhydride |
| PDCPD | Polydicyclopentadiene |
| UVR | 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl 3′,4′-epoxycyclohexane carboxylate |
| TMPTMA | Trimethylol-1,1,1-propane trimethacrylate |
| OMMTs | Organic montmorillonties |
| SLFs | Scrap leather fibers |
| ECH | 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl 3,4-epoxycyclohexanecarboxylate |
| BPAEDA | Bisphenol A ethoxylate dimethacrylate |
| FETI | Fluorinated ethynyl-terminated imide oligomers |
| UP | Orthophtaleic acid based resin |
| CF | Carbon fibre |
| GF | Glass fibre |
| HTTE | Hyperbranched poly(trimellitic anhydride-triethylene glycol) ester epoxy |
| ESO | Epoxidized soybean oil |
| PFA | Poly(furfuryl alcohol) |
| DGEBS | Diglycidyl ether of bisphenol S |
| TGDDM | Tetraglycidyl-4,4-diaminodiphenylmethane |
| HPT | N,N,N′,N′-tetraglycidyl-α,α′-bis-(4-aminophenyl)-p-diisopropylbenzene |
| DGEAC | Diglycidylester of aliphatic cyclo epoxy |
| HBP | Hyperbranched polyesters |
| HMDI | Hexamethylene diisocyanate |
| PEN | Poly(arylene ether nitrile) |
| BA-ph | Phthalonitrile containing benzoxazine |
| PMSQ | Polymethylsilsesquioxane |
References
- Paul, S. Manufacture of Organic Compounds Containing Basic Substituents. Google Patents US2131120A, 27 September 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Castan, P. Process for the manufacture of thermosetting synthetic resins by the polymerization of alkylene oxide derivatives. Google Patents US2444333A, 29 June 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Yahyaie, H.; Ebrahimi, M.; Tahami, H.V.; Mafi, E.R. Toughening mechanisms of rubber modified thin film epoxy resins. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-F.; Jeng, R.-J. Carbon black containing IPNs based on unsaturated polyester/epoxy. I. Dynamic mechanical properties, thermal analysis, and morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AJ, K.; Young, R. Fracture Behavior of Polymers; Applied Science Publishers: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sue, H.J.; Puckett, P.M.; Bertram, J.L.; Walker, L.L. The Network Structure of Epoxy Systems and Its Relationship to Toughness and Toughenability. In Toughening of Plastics; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 759, pp. 171–197. [Google Scholar]
- Harani, H.; Fellahi, S.; Bakar, M. Toughening of epoxy resin using synthesized polyurethane prepolymer based on hydroxyl-terminated polyesters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 2603–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 5045-95. Standard Test Methods for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness and Strain Energy Release Rate of Plastic Materials. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.; Beier, U.; Wolff-Fabris, F.; Altstädt, V. Toughened high performance epoxy resin system for aerospace applications. Sci. Eng. Comp. Mater. 2011, 18, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Weng, L.; Liu, L. Low dielectric constant and high toughness epoxy resin based on hyperbranched polyester grafted by flexible chain modified. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 5936–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuniya, S.; Adhikari, B. Toughening of epoxy resins by hydroxy-terminated, silicon-modified polyurethane oligomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hu, N.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.Q. Synthesis and research of epoxy resin toughening agent. Springerplus 2016, 5, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula Dhevi, D.; Jaisankar, S.N.; Pathak, M. Effect of new hyperbranched polyester of varying generations on toughening of epoxy resin through interpenetrating polymer networks using urethane linkages. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubeldia, A.; Larrañaga, M.; Remiro, P.; Mondragon, I. Fracture toughening of epoxy matrices with blends of resins of different molecular weights and other modifiers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3920–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Kinloch, A.J.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. The mechanisms and mechanics of the toughening of epoxy polymers modified with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2010, 51, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Ning, R.; Kong, J. Self-toughening of epoxy resin through controlling topology of cross-linked networks. Polymer 2016, 99, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, X.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y. Synthesis and characterization of trifluoromethyl-containing polyimide-modified epoxy resins. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10833–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiravand, F.; Ascione, L.; Persico, P.; Carfagna, C.; Brocks, T.; Cioffi, M.O.H.; Puglisi, C.; Samperi, F.; Ambrogi, V. A novel hybrid linear–hyperbranched poly(butylene adipate) copolymer as an epoxy resin modifier with toughening effect. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohseni, A.; Zavareh, S. Epoxy/acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer/clay ternary nanocomposite as impact toughened epoxy. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Song, X.; Cai, Y. Mechanical Properties and Morphologies of Carboxyl-Terminated Butadiene Acrylonitrile Liquid Rubber/Epoxy Blends Compatibilized by Pre-Crosslinking. Materials 2016, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, A.; Kaynak, C.; Tincer, T. Effects of liquid rubber modification on the behaviour of epoxy resin. Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Chiba, T.; Inoue, T. Morphology development via reaction-induced phase separation in epoxy/poly(ether sulfone) blends: Morphology control using poly(ether sulfone) with functional end-groups. Polymer 1995, 36, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.S.; Farris, R.J.; Thompson, S.A. Amine-terminated poly(aryl ether ketone)-epoxy/amine resin systems as tough high performance materials. Polymer 1991, 32, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Chu, F.; Cui, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Enhanced flexibility of conductive layer with inkjet-imprinted microstructure surface. Mater. Lett. 2020, 266, 127461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Jian, X. Introduction to Epoxy/Thermoplastic Blends. In Handbook of Epoxy Blends; Parameswaranpillai, J., Hameed, N., Pionteck, J., Woo, E.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 429–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.R. Interpenetrating polymer networks. Styrene–divinylbenzene copolymers with two and three interpenetrating networks, and their sulphonates. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Jeong, D. Basic Principles and Practical Applications of the Cahn–Hilliard Equation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9532608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, A.; Cherukattu, J.; Anand, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Thermoplastic-Toughened High-Temperature Cyanate Esters and Their Application in Advanced Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4479–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, L.H. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks: An Overview. In Interpenetrating Polymer Networks; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 239, pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Harismendy, I.; Del Río, M.; Eceiza, A.; Gavalda, J.; Gómez, C.M.; Mondragon, I. Morphology and thermal behavior of dicyanate ester-polyetherimide semi-IPNS cured at different conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, J.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Thomas, D.A.; Sperling, L.H. Effect of morphology, crosslink density, and miscibility on interpenetrating polymer network damping effectiveness. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1991, 31, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Min, H.-S.; Kim, S.-C. Polyetherimide/dicyanate semi-interpenetrating polymer networks having a morphology spectrum. Macromol. Res. 2002, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harismendy, I.; Del Río, M.; Marieta, C.; Gavalda, J.; Mondragon, I. Dicyanate ester–polyetherimide semi-interpenetrating polymer networks. II. Effects of morphology on the fracture toughness and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, L.H. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks and Related Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, W.B.; Yang, H.S.; Moon, D.S.; Lee, M.W.; Ko, N.Y.; Kwak, N.H.; Lee, B.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, R. Epoxy resins toughened with in situ azide–alkyne polymerized polysulfones. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Jeong, E.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Lee, Y.-S. Improvement of the mechanical and thermal properties of polyethersulfone-modified epoxy composites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turmel, D.J.P.; Partridge, I.K. Heterogeneous phase separation around fibres in epoxy/PEI blends and its effect on composite delamination resistance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1997, 57, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Mathew, D.; Robert, T.M. Poly(ether ether ketone)-bischromenes: Synthesis, characterization, and influence on thermal, mechanical, and thermo mechanical properties of epoxy resin. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, J.; Winkler, K.; Joseph, K.; Anas, S.; Thomas, S. Epoxy/methyl methacrylate acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (MABS) copolymer blends: Reaction-induced viscoelastic phase separation, morphology development and mechanical properties. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 9216–9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S. Damping, thermal, and mechanical performances of a novel semi-interpenetrating polymer networks based on polyimide/epoxy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolghadr, M.; Shakeri, A.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Salimi, A. Self-healing semi-IPN materials from epoxy resin by solvent-free furan–maleimide Diels–Alder polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, W.; Lu, G.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based on Cyanate Ester and Highly Soluble Thermoplastic Polyimide. Polymers 2019, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangermano, M.; Roppolo, I.; Ortiz, R.A.; Tovar, A.G.N.; Valdez, A.E.G.; Duarte, M.L.B. Interpenetrated hybrid thiol-ene/epoxy UV-cured network with enhanced impact resistance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yuan, L.; Gu, A.; Liang, G. Fabrication of In Situ Nanofiber-Reinforced Molecular Composites by Nonequilibrium Self-Assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39293–39306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.P.; Rai, S.K. Studies on the Mechanical Performance of PMMA Toughened Epoxy–Silk and PC Toughened Epoxy–Silk Fabric Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, S.; Sarmah, A.; Sarkar, C.; Dolui, S.K. In situ development of bio-based polyurethane-blend-epoxy hybrid materials and their nanocomposites with modified graphene oxide via non-isocyanate route. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białkowsk, A.; Bakar, M.; Przybyłek, M. Effect of Nonisocyanate Polyurethane and Nanoclay on the Mechanical Properties of an Epoxy Resin. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2018, 54, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Interpenetrating polymer network and nanocomposite IPN of polyurethane/epoxy: A review on fundamentals and advancements. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 58, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Kausar, A.; Muhammad, B. Advances in Shape Memory Polyurethanes and Composites: A Review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, F.; Chen, S.; Dmitriev, A.I.; Zhang, G. Regulating microstructures of interpenetrating polyurethane-epoxy networks towards high-performance water-lubricated bearing materials. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, L.; Lu, X.; Jiang, L.; Cao, T. Preparation and Properties of Toluene-Diisocyanate-Trimer-Modified Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2019, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.A.; Inglis, H.; Ng WeiLong, E.; McKinley, C.; Lewis, D.A. Morphology Control in a Dual-Cure System for Potential Applications in Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2019, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchot, L.; Verge, P.; Peralta, S.; Habibi, Y.; Vancaeyzeele, C.; Vidal, F. Elaboration of bio-epoxy/benzoxazine interpenetrating polymer networks: A composition-to-morphology mapping. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, İ. Investigation of Wear Properties of Toughened Epoxy Resin using Silane Terminated Urethane. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2019, 135, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Pan, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, F. Development of cold-mix high-toughness resin and experimental research into its performance in a steel deck pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, B.M.; Mendez, R.B.; Auad, M.L.; Tippur, H.V. Quasi-static and dynamic mechanical behavior of transparent graft-interpenetrating polymer networks (graft-IPNs). Polym. Test. 2018, 70, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C.; Roy, P.K. Graft-interpenetrating polymer networks of epoxy with polyurethanes derived from poly(ethyleneterephthalate) waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.; Duk, R.; Przybyłek, M.; Kostrzewa, M. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Resin Modified with Polyurethane. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 28, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, H. Preparation and properties of polyurethane-modified epoxy cured in different simulated gravity environments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Ko, N.Y.; Kwak, N.H.; Ying, W.B.; Lee, B. Toughening of semi-IPN structured epoxy using a new PEEK-type polymer via in situ azide–alkyne click polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, K.; Ito, H.; Fujioka, H. Improvement of thermal and mechanical properties by control of morphologies in PES-modified epoxy resins. Polymer 2000, 41, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.-G.; Hu, J.-M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Cao, C.-N. Improving the corrosion performance of epoxy coatings by chemical modification with silane monomers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4789–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, K.; Fan, R.; Li, X. Preparation and Properties Characterization of Interpenetrating Polymer Networks/Organically Modified Montmorillonite/Scrap Leather Fibers Composites. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-F.; Shi, L.-Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhong, Q.-D.; Zhang, D.-S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Morphology, toughness mechanism, and thermal properties of hyperbranched epoxy modified diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) interpenetrating polymer networks. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Delpouve, N.; Araujo, S.; Batteux, F.; Bobo, E.; Saiter, J.-M.; Tan, L.; Negahban, M. Controlling properties of acrylate/epoxy interpenetrating polymer networks by premature termination of radical polymerization of acrylate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Interpenetrating polymer networks based on cyanate ester and fluorinated ethynyl-terminated imide oligomers. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashouf Roudsari, G.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. A study of mechanical properties of biobased epoxy network: Effect of addition of epoxidized soybean oil and poly(furfuryl alcohol). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcsan, T.; Meszaros, L. Mechanical performance of hybrid thermoset composites: Effects of matrix and reinforcement hybridization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Rohde, B.J.; Krishnamoorti, R.; Robertson, M.L.; Dawood, M. Bond behavior of epoxy resin–polydicyclopentadiene phase separated interpenetrating networks for adhering carbon fiber reinforced polymer to steel. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, B.J.; Le, K.M.; Krishnamoorti, R.; Robertson, M.L. Thermoset Blends of an Epoxy Resin and Polydicyclopentadiene. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 8960–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Cicala, G.; Faro, C.L.; Recca, A. Development of a toughened DGEBS/DDS system toward improved thermal and mechanical properties by the addition of a tetrafunctional epoxy resin and a novel thermoplastic. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, M.; Liu, X. Designing and Preparation of Fiber-Reinforced Composites with Enhanced Interface Adhesion. Polymers 2018, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitha Alex, A.; Rajeev, R.S.; Ranjith, R.; Mohammad, F.; Gouri, C.; Sekkar, V. Short silica fiber composites with simultaneous interpenetrating polymer networks constituted by siloxane and phenolic systems. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 4010–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugnoni, J.; Amacher, R.; Kohler, S.; Brunner, J.; Kramer, E.; Dransfeld, C.; Smith, W.; Scobbie, K.; Sorensen, L.; Botsis, J. Towards aerospace grade thin-ply composites: Effect of ply thickness, fibre, matrix and interlayer toughening on strength and damage tolerance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzmann, M.T.; Hou, M.; Veidt, M.; Vandi, L.J.; Paton, R. Morphology of an Interface between Polyetherimide and Epoxy Prepreg. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 393, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Huson, M.; Slota, I.; Fox, B. Interphase study of thermoplastic modified epoxy matrix composites: Phase behaviour around a single fibre influenced by heating rate and surface treatment. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, M. Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Composites; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.; Shin, S. Toughness improvement of tetrafunctional epoxy resin by using hydrolysed poly(ether imide). Polymer 1995, 36, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.; Yu, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Zhuang, J. Studies on the Phase Separation of Poly(Ether Imide)-Modified Cyanate Ester Resin. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2003, 40, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhan, G.; Tang, X.; Li, S. Morphology and mechanical properties of poly(ether-imide)-modified polycyanurates. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2006, 284, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Yu, Y.; Tang, X.; Tao, Q.; Li, S. Further study of the viscoelastic phase separation of cyanate ester modified with poly(ether imide). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-C. Properties of Polyetherimide/Dicyanate Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Network Having the Morphology Spectrum. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wu, P. Effect of chemically modified graphene oxide on the phase separation behaviour and properties of an epoxy/polyetherimide binary system. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tao, Z.; Fan, L.; Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y. Effect of poly(etherimide) chemical structures on the properties of epoxy/poly(etherimide) blends and their carbon fiber-reinforced composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 3162–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, I.F.; van Moorleghem, R. Ultrasonic welding of carbon/epoxy and carbon/PEEK composites through a PEI thermoplastic coupling layer. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Epoxy | Toughener | Toughener Content | Morphology | Investigated Properties | Key Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGEBA/DDS/BMI | PPO | 10–25 wt % | Micron-sized fibrous structure |
|
| [44] |
| DGEBA/NMA/MHHPA | FCBHBP | 10–30 wt % | Ridge morphology |
|
| [10] |
| DGEBA/DDS | MABS | 4.76–16.6 wt % | Co-continuous morphology |
|
| [39] |
| DGEBA/DDS | PEEK-PR | 4.76–13 wt % | Inverted phase morphology |
|
| [38] |
| Bisphenol A type epoxy | Polymer prepared from PPG, PEG and MDI | 10–50 wt % | Two-phase structure |
|
| [12] |
| DGEBA/TMHDA | 9G | 25–75 wt % | Discrete morphology |
|
| [52] |
| CDGE/IPD | Poly(EDBz) | 20–80 wt % | Phase inversion |
|
| [53] |
| DGEBA/DMPA | Polysulfide prepared in-situ from thiol-ene system | 10–40 mol % | Micro-heterogeneous structure |
|
| [43] |
| Bisphenol A type epoxy | STU | 5–20 wt % | - |
|
| [54] |
| DGEBA/MOCA | PUP | 30–70 wt % | Dispersed or bi-continuous phases |
|
| [50] |
| Bisphenol A type epoxy/G1-G3 | RTA | 7.6–78 wt % | Sea-island structure |
|
| [55] |
| DGEBA/H-957/DADPE/DADPS | SiMPU | 4.8–28.6 wt % | - |
|
| [11] |
| Bisphenol A type epoxy/Polyamide | PUP | 9–23 wt % | Two-phase structure |
|
| [51] |
| DGEBA/DDM | PBHDDP | 0.99–11.11 wt % | Homogeneous distribution (i.e., no phase separation) |
|
| [24] |
| DGEBA/D-230 | Co-polyimide | 30–50 wt % | Micro heterogeneous morphology |
|
| [40] |
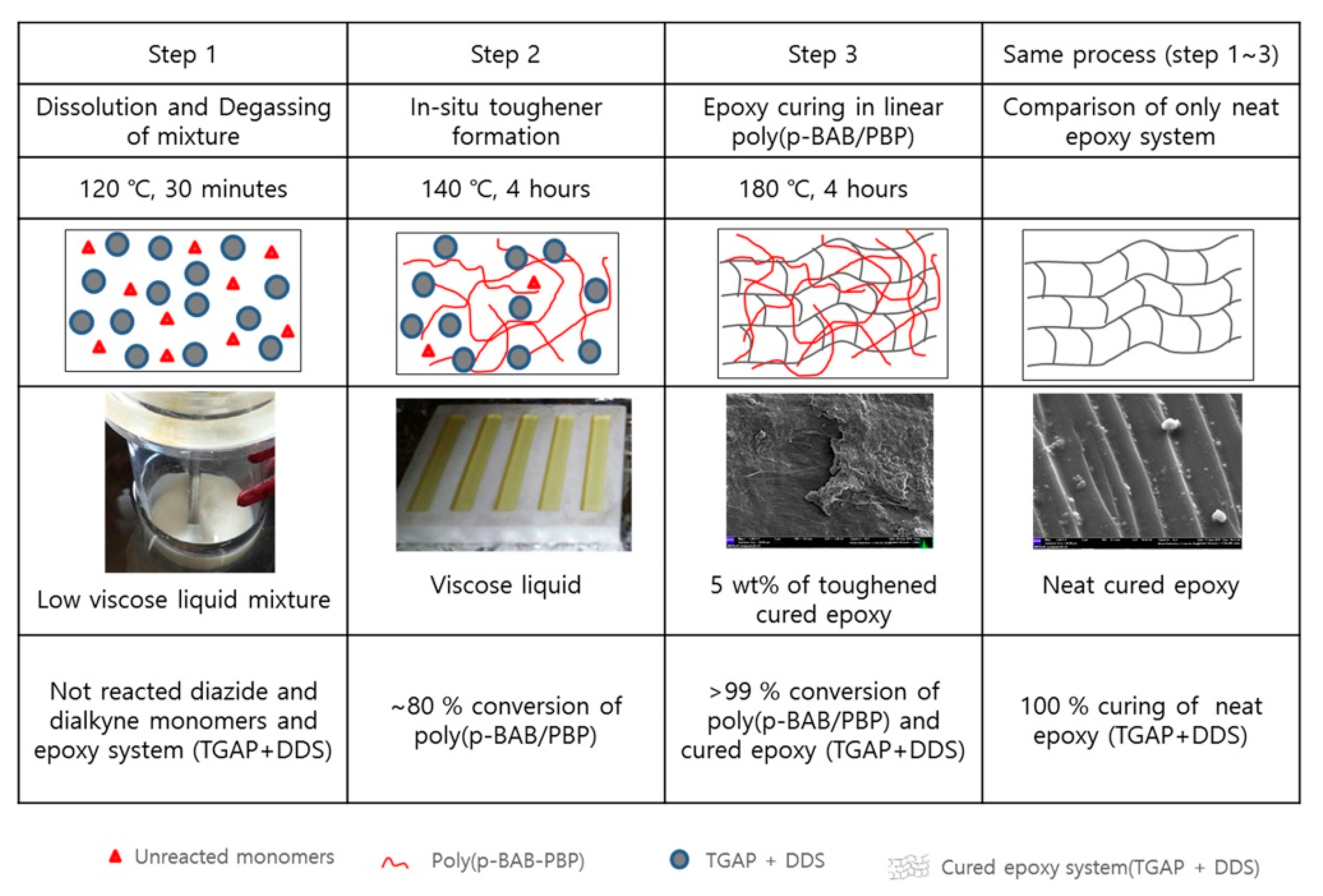
| TGAP/DDS | Poly(p-BAB/SPB), Poly(m-BAB/SPB) | 5–15 wt % | Simultaneous existence of co-continuous and spherical domains |
|
| [35] |
| TGAP/DDS | PES | 4.76–16.67 wt % | Co-continuous domains |
|
| [36] |
| BADCy | Polyimide | 3–20 wt % | Co-continuous domains | impact strength of semi-IPN was 47–320% greater than that of polycyanurate.
|
| [42] |
| Epoxy | Toughener | Morphology | Objective | Investigated Properties | Key Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGEBA/INN | Polyurethane obtained from TDI and Desmophen 1200 | No phase separation | To investigate the effect of isocyanate content |
|
| [58] |
| DGEBA/TETA | Polyurethane derived from PET waste by glycolysis | Homogeneous morphology | To analyze the influence of molecular weight ofpolyethylene glycol (600–1500 g·mol−1) |
|
| [57] |
| DGEBA/modified amine | PUP | Sea-island structure | To understand the influence of different gravity accelerations of 0, 1, and 2 g |
|
| [59] |
| DGEBA/PAMAM | HBP-PU | Two-phase morphology | To study the impact of different generations (G) of HBPs (G1–G4) |
|
| [13] |
| Bisphenol A type epoxy | RTA | Sea-island structure | To examine the effect of different curing agents (G1–G3) |
|
| [55] |
| DGEBA | SiMPU | - | To assess the influence of different curing agents (H-957, DADPE and DADPS) |
|
| [11] |
| Epoxy | Toughener | Morphology | Investigated Properties | Key Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGEBA/NMA | PDCPD | Co-continuous phase-separated structures |
|
| [69,70] |
| ECH | BPAEDA | - |
|
| [65] |
| BADCy | FETI | - |
|
| [66] |
| DGEBA/IPD | UP and VE CF and GF | Phase separation |
|
| [68] |
| DGEBA/DDM | HTTE | Sea-island morphology |
|
| [64] |
| Bio-based epoxy resin | ESO and PFA | Non-homogenous network |
|
| [67] |
| DGEBS/DDS | TGDDM | Homogeneous morphology |
|
| [71] |
| UVR/MHHPA | TMPTMA, OMMTs and SLFs | Two-phase morphology |
|
| [63] |
| Sample | Molecular Weight of PEI, Mn (g/mol) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | KIC (MPa·m1/2) | GIC (kJ/m2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BADCy | 63.7 | 2.27 | 4.14 | 0.62 | 0.100 | [33] | |
| BADCy/PEI = 90/10 | 12,000 | 75.6 | 2.38 | 4.66 | 1.35 | 0.495 | [33] |
| BADCy/PEI = 85/15 | 12,000 | 84.7 | 2.39 | 5.86 | 1.6 | 0.680 | [33] |
| BADCy/PEI = 80/20 | 12,000 | 73.4 | 2.00 | 5.50 | 3.1 | 2.480 | [33] |
| BADCy | 84.2 | 2.60 | 4.43 | - | 0.190 | [82] | |
| BADCy/PEI = 95/5 | 18,000 | 82.1 | 2.57 | 4.33 | - | 0.211 | [82] |
| BADCy/PEI = 90/10 | 18,000 | 83.4 | 2.54 | 4.50 | - | 0.202 | [82] |
| BADCy/PEI = 85/15 | 18,000 | 99.2 | 2.53 | 6.20 | - | 0.603 | [82] |
| BADCy/PEI = 80/20 | 18,000 | 108.4 | 2.54 | 7.33 | - | 1.207 | [82] |
| BADCy/PEI = 75/25 | 18,000 | 110.9 | 2.55 | 7.91 | - | 2.105 | [82] |
| HPT | - | - | - | 0.60 | - | [78] | |
| HPT/PEI = 95/5 | 20,000 | - | - | - | 1.18 | - | [78] |
| HPT/PEI = 90/10 | 20,000 | - | - | - | 1.22 | - | [78] |
| HPT/PEI = 85/15 | 20,000 | - | - | - | 1.35 | - | [78] |
| BADCy | - | - | - | - | 0.196 | [32] | |
| BADCy/PEI = 92.5/7.5 | 18,000 | - | - | - | - | 0.261 | [32] |
| DGEBA/PEI = 87/13 | 19,000 | 49.3 | 0.67 | 7.1 | - | - | [83] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC | 62.0 | 2.6 | 3.2 | - | - | [84] | |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 85/15 | 23,825 | 80.9 | 2.6 | 3.5 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 80/20 | 23,825 | 88.8 | 2.6 | 4.7 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 85/15 | 25,405 | 87.3 | 2.7 | 4.3 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 80/20 | 25,405 | 88.8 | 2.6 | 4.7 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 85/15 | 21,175 | 77.0 | 2.6 | 3.9 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 80/20 | 21,175 | 81.6 | 2.6 | 4.2 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 85/15 | 20,983 | 89.2 | 2.7 | 4.4 | - | - | [84] |
| TGDDM + DGEAC/PEI = 80/20 | 20,983 | 86.6 | 2.7 | 4.4 | - | - | [84] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farooq, U.; Teuwen, J.; Dransfeld, C. Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091908
Farooq U, Teuwen J, Dransfeld C. Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091908
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarooq, Ujala, Julie Teuwen, and Clemens Dransfeld. 2020. "Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091908
APA StyleFarooq, U., Teuwen, J., & Dransfeld, C. (2020). Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review. Polymers, 12(9), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091908





