Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison
Abstract
1. Introduction
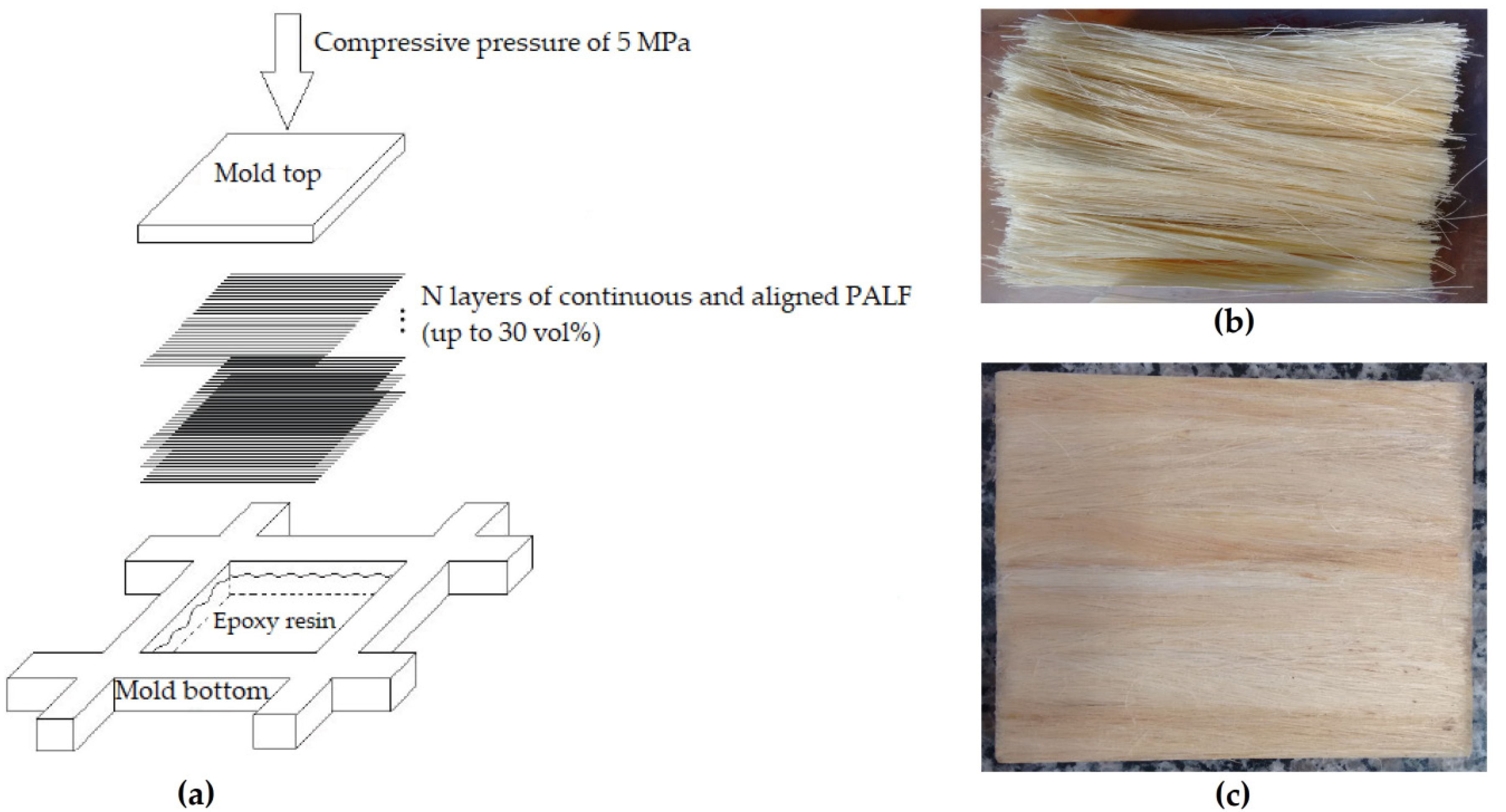
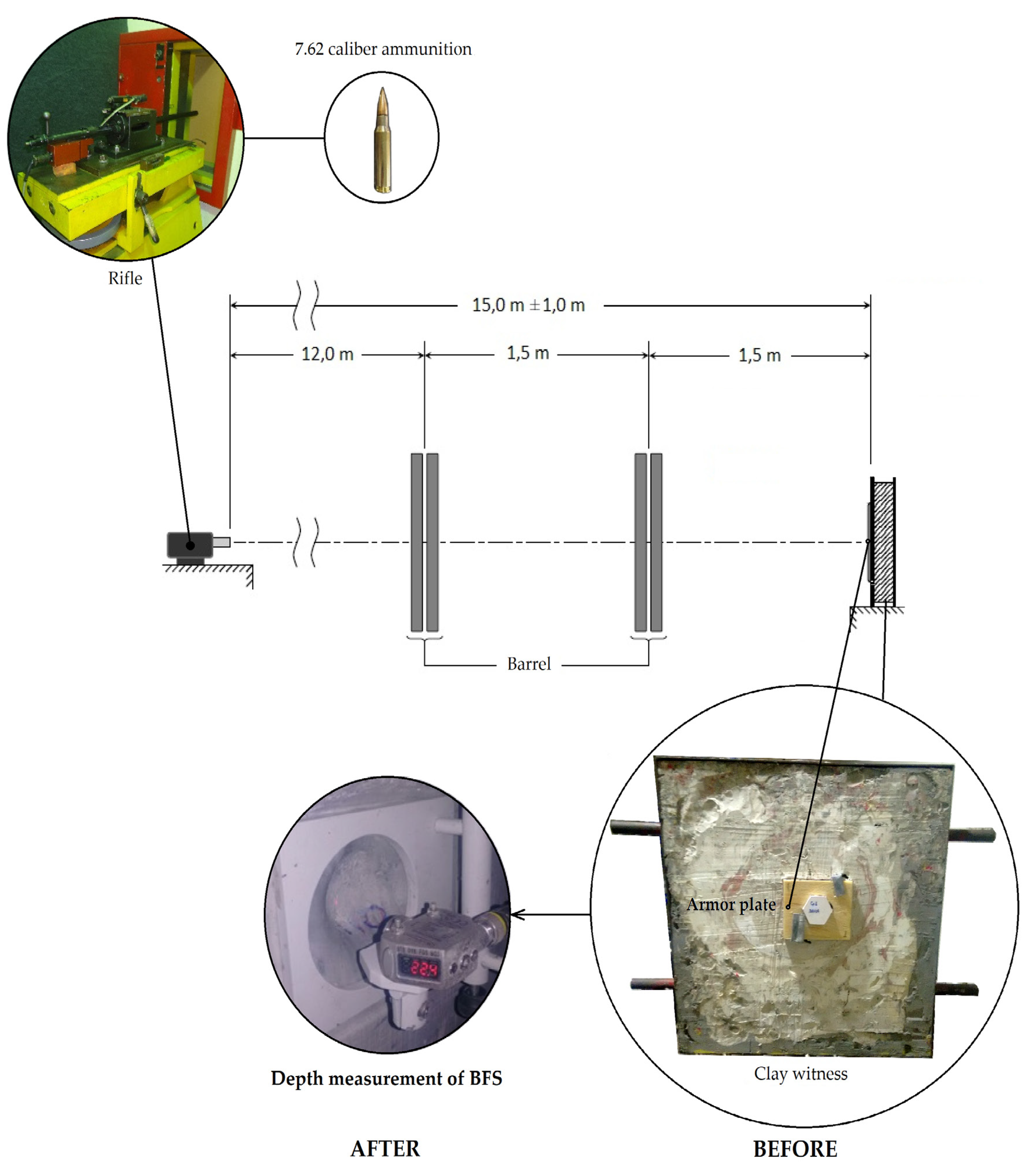
2. Materials and Methods
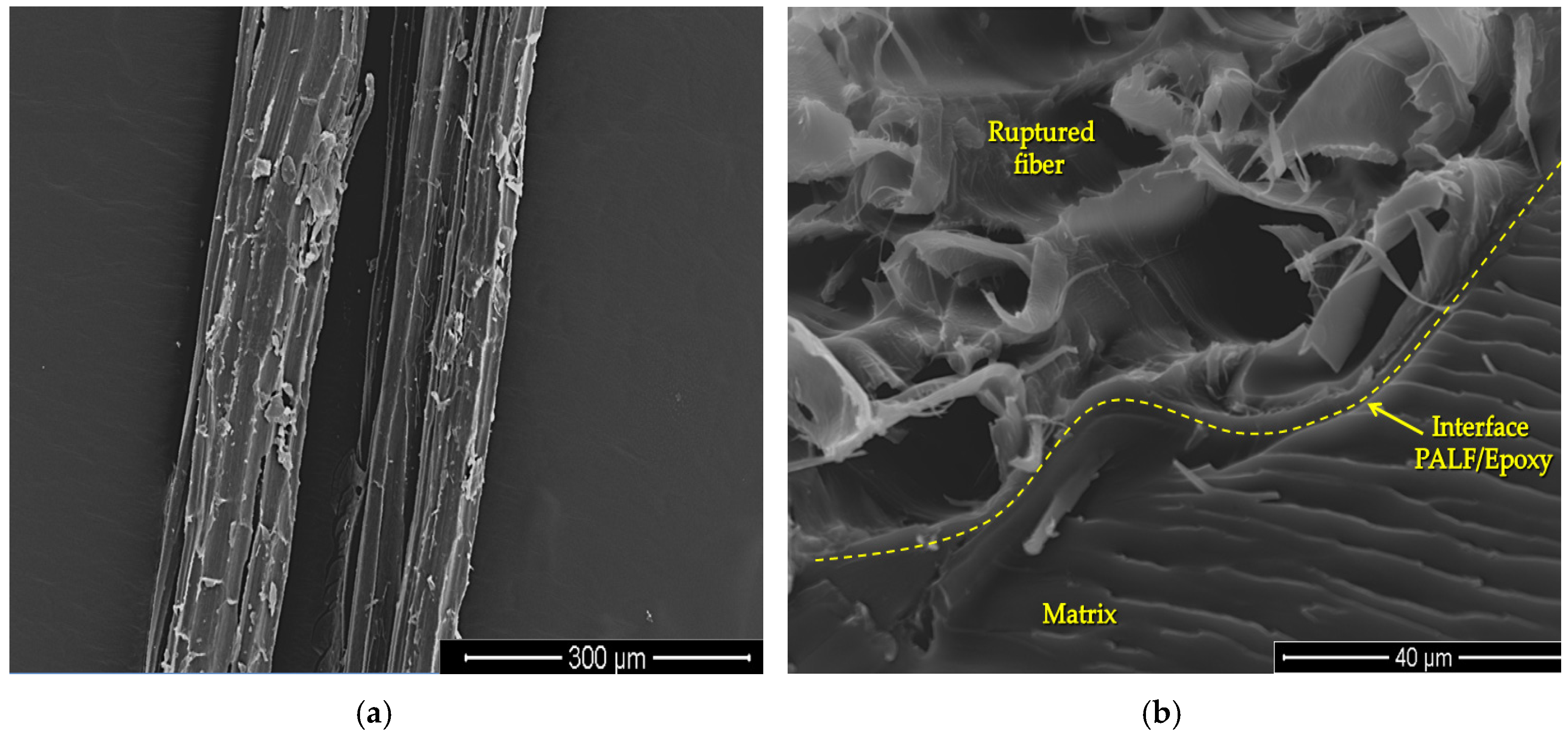
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
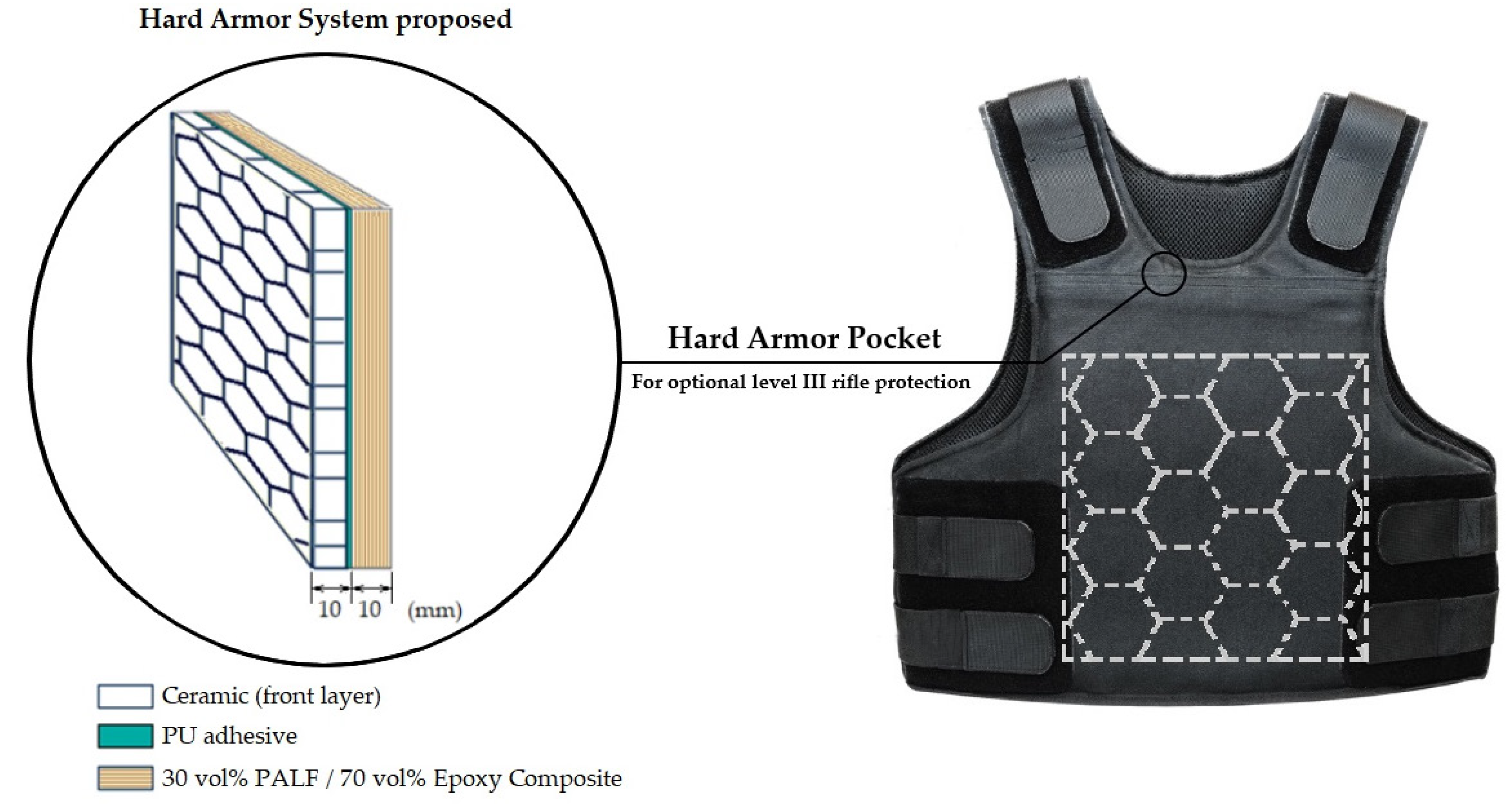
- A comparison between the ballistic performance of pineapple leaf fiber (PALF) epoxy composites and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (Dyneema) backing the front ceramic of multilayered armor systems revealed that no perforation of the target occurred in all armor plates.
- All the armor plates (single-layer ceramic tested targets, Dyneema, and the ceramic/PALF composite) met the NIJ standard. However, the Dyneema, a material conventionally used in bulletproof vests, tested as a 25 mm thick hard armor plate, exhibited a back-face signature (BFS) depth (41.5 mm) that was close to the NIJ standard limit (44 mm) and performed significantly worse than the ceramic/PALF composite.
- The hard armor system with the ceramic front layer followed by the epoxy composite incorporated with 30 vol % of pineapple leaf fibers (PALF) exhibited a BFS depth of 26.6 mm, which meets the NIJ standard for ballistic protection against a rifle with 7.62 mm caliber ammunition. Tests using single-layer ceramic as an armor plate presented a 35% higher BFS depth, but the depth was still below the 44 mm required by the standard criterion.
- Therefore, these results indicate the possibility of optimizing the thickness of this armor plate. They also highlight the potential of using the PALF composite in a hard armor system in order to transform a ballistic vest from level IIIA to level III. However, further experimental work in an enlarged armor plate with six-shot testing is needed to validate the application of this composite in a hard, multilayered armor system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, P.; Strano, M.S. Towards ambient armor: Can new materials change longstanding Concepts of Projectile Protection? Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børvik, T.; Dey, S.; Clausen, A.H. Perforation resistance of five different high-strength steel plates subjected to small-arms projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 948–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, S. Impact on Composite Structures. Ed. Revised; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedovski, E. Lightweight ceramic composite armour system. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2006, 105, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemirci, A.; Tunusoglu, G.; Güden, M. The effect of the interlayer on the ballistic performance of ceramic/composite armors: Experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Wetzel, E.D.; Wagner, N.J. The Ballistic Impact Characteristic of Kevlar Woven Fabrics Impregnated with a Colloidal Shear Thickening Fluid. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.J.N.; Dindenen, J.L.J.V. Ballistic protection mechanisms in personal armour. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morye, S.S.; Hine, P.J.; Duckett, R.A.; Carr, D.J.; Ward, I.M. Modelling of the energy absorption by polymer composites upon ballistic impact. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 2631–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, P. Armour: Materials, Theory, and Design; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Benzait, S.; Trabzon, L. A review of recent research on materials used in polymer–matrix composites for body armor application. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 3241–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Criminal Justice Reference Service. US Department of Justice, & National Institute of Justice. NIJ 0101.04. Ballistic Resistance of Body Armor. 2000. Available online: https://nij.ojp.gov/library/publications/ballistic-resistance-personal-body-armor-nij-standard-010104 (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Rohen, L.A.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F.; de Araujo, B.M.; Lima, E.S. Ballistic efficiency of an individual epoxy composite reinforced with sisal fibers in multilayered armor. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L.; Trindade, W.; Elias, C.N.; Ferreira, C.L.; de Sousa Lima, E.; Weber, R.P.; Suarez, J.C.M.; da Silva Figueiredo, A.B.-H.; Pinheiro, W.A.; et al. Natural curaua fiber-reinforced composites in multilayered ballistic armor. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4567–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Gomes, A.V.; Lima, É.P., Jr.; Marçal, R.L.S.B. Ballistic performance in multilayer armor with epoxy composite reinforced with mallow fibers. In Proceedings of the 3rd Pan American Materials Congress; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.S.; Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.S.; Júnior, É.P.L. Ballistic application of coir fiber reinforced epoxy composite in multilayered armor. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Milanezi, T.L.; Louro, L.H.L.; Lima, É.P., Jr.; Braga, F.O.; Gomes, A.V.; Drelich, J.W. Novel ballistic ramie fabric composite competing with KevlarTM fabric in multilayered armor. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.S.; Lima, É.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N. Ballistic test of multilayered armor with intermediate epoxy composite reinforced with jute fabric. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Luz, F.S. Mallow Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites in Multilayered Armor for Personal Ballistic Protection. JOM 2017, 69, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.B.; Lima, É.P., Jr.; Monteiro, S.; Louro, L. Giant bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy composite in multilayered ballistic armor. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Candido, V.S.; Braga, F.O.; Bolzan, L.T.; Weber, R.P.; Drelich, J.W. Sugarcane bagasse waste in composites for multilayered armor. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 78, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Braga, F.O.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Drelich, J.W. Promising curaua fiber-reinforced polyester composite for high-impact ballistic multilayered armor. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Bolzan, L.T.; Luz, F.S.; Lopes, R.H.L.M.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Monteiro, S.N. High energy ballistic and fracture comparison between multilayered armor systems using non-woven curaua fabric composites and aramid laminates. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Bolzan, L.T.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Monteiro, S. Performance of natural curaua fiber-reinforced polyester composites under 7.62 mm bullet impact as a standalone ballistic armor. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Drelich, J.W.; Lopera, H.A.C.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; da Luz, F.S.; da Silva, L.C.; dos Santos, J.L.; Garcia Filho, F.C.; de Assis, F.S.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; et al. Natural Fibers Reinforced Polymer Composites Applied in Ballistic Multilayered Armor for Personal Protection—An Overview. In Green Materials Engineering; Ikhmayies, S., Li, J., Vieira, C.M.F., Margem, J.I., de Oliviera, F.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia Filho, F.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Piassava fiber as an epoxy matrix composite reinforcement for ballistic armor applications. JOM 2019, 71, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Garcia Filho, F.C.; Pereira, A.C.; Nunes, L.F.; Luz, F.S.; Braga, F.O.; Colorado, H.A.; Monteiro, S.N. Ballistic performance and statistical evaluation of multilayered armor with epoxy-fique fabric composites using the Weibull analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5899–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.S.; Ramos, F.J.H.T.V.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Figueiredo, A.B.H.S.; Monteiro, S.N. Critical length and interfacial strength of PALF and coir fiber incorporated in epoxy resin matrix. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Milanezi, T.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L.; Gomes, A.V.; Lima, E.P., Jr. Ballistic comparison between epoxy-ramie and epoxy-aramid composites in Multilayered Armor Systems. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Bolzan, L.T.; Ramos, F.J.H.T.V.; Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.P., Jr. Ballistic Efficiency of Multilayered Armor Systems with Sisal Fiber Polyester Composites. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. 2018, 20, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, F.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Garcia Filho, F.C.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Monteiro, S.N.; Weber, R.P. Performance of jute non-woven mat reinforced polyester matrix composite in multilayered armor. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Pereira, A.C.; Ferreira, C.; Lima, E.P., Jr. Performance of Plain Woven Jute Fabric-Reinforced Polyester Matrix Composite in Multilayered Ballistic System. Polymers 2018, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Lopes, P.H.L.M.; Oliveira, M.S.; Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.P., Jr. Thickness assessment and statistical optimization of a 3-layered armor system with ceramic front and curaua fabric composite/aluminum alloy backing. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 166, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.Y.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shenoy, S.B.; Kini, C.R.; Samant, R.; Shah, A.U.M.; Amuthakkannan, P. Potential of Natural Fibers in Composites for Ballistic Applications—A Review. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, J.; Jawaid, M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Yahaya, R. Evaluation of ballistic performance of hybrid Kevlar®/Cocos nucifera sheath reinforced epoxy composites. J. Text. Inst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambari, S.; Yahya, M.Y.; Abdulah, M.R.; Jawaid, M. Woven Kenaf/Kevlar hybrid yarn as potential fiber reinforced for anti-ballistic composite material. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaahaya, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Zainudin, E.S. Investigating ballistic impact properties of woven Kenaf-aramid hybrid composites. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radif, Z.S.; Ali, A.; Abdan, K. Development of a green combat armour from ramie-Kevlar®-polyester composite. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 19, 339–348. [Google Scholar]
- Risby, M.S.; Wong, S.V.; Hamouda, M.A.S.; Khairul, A.R.; Elsadig, M. Ballistic performance of coconut shell powder/twaron fabric against non-armour piercing projectiles. Defence Sci. J. 2008, 58, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijo, D. The use of UHMWPE films in ballistic protection (in Portuguese). Polímeros 2002, 12, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, K.L.; Efendy, M.G.A.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, O.; Monteiro, S.N.; Moura, E.A.B.; Drelich, J.W. Re-emerging field of lignocellulosic fiber—Polymer composites and ionizing radiation technology in their formulation. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 702–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K.; Gupta, R.K. Review: Raw natural fibers based polymer composites. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1555–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, J. Natural materials innovative natural composites. Mater. Technol. 2008, 2–3, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.G.; Arizaga, G.C.; Wypych, F. Biodegradable composites based on lignocellulosic fibers—An overview. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 982–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louro, L.H.L.; Gomes, A.V.; Costa, C.R.C. Dynamic fragmentation of alumina with additions of niobia and silica under impact. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium of Ballistics, Interlaken, Switzerland, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 1361–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, S.; Kaith, B.S.; Kaur, I. Pretreatments of natural fibers and their application as reinforcing material in polymer composites: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.S.D.; Monteiro, S.N.; Tommasini, F.J. Evaluation of dynamic mechanical properties of PALF and coir fiber reinforcing epoxy composites. Mater. Res. 2018, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, F.; Potluri, P.; Afroj, S.; Koncherry, V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Karim, N. Ultrahigh Performance of Nanoengineered Graphene-Based Natural Jute Fiber Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019, 11, 21166–21176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, D.C.O.; Ferreira, A.S.; Monteiro, S.N.; Aquino, R.C.M.; Kestur, S.G. Studies on the characterization of piassava fibers and their epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Lima, E.P., Jr.; Louro, L.H.L.; Silva, L.C.; Drelich, J.W. Unlocking function of aramid fibers in multilayered ballistic armor. Mettal. Mat. Trans. A 2014, 46, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
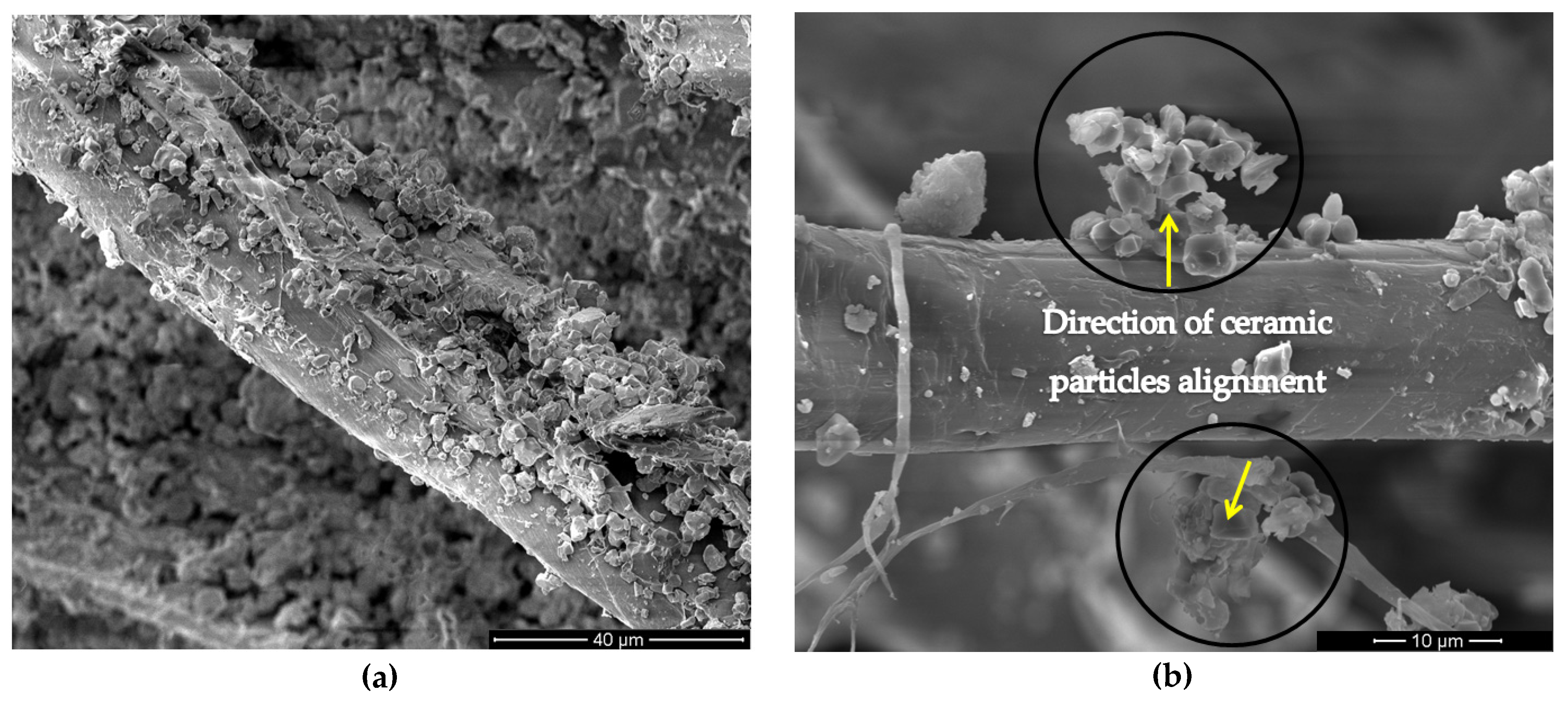





| Source | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean of Squares | F (Calculated) | p-Value | F Critical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 799 | 2 | 399 | 74 | 2 × 10−9 | 3.6 |
| Residual | 97 | 18 | 5 | |||
| Total | 896 | 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luz, F.S.d.; Garcia Filho, F.d.C.; Oliveira, M.S.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison. Polymers 2020, 12, 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091920
Luz FSd, Garcia Filho FdC, Oliveira MS, Nascimento LFC, Monteiro SN. Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuz, Fernanda Santos da, Fabio da Costa Garcia Filho, Michelle Souza Oliveira, Lucio Fabio Cassiano Nascimento, and Sergio Neves Monteiro. 2020. "Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091920
APA StyleLuz, F. S. d., Garcia Filho, F. d. C., Oliveira, M. S., Nascimento, L. F. C., & Monteiro, S. N. (2020). Composites with Natural Fibers and Conventional Materials Applied in a Hard Armor: A Comparison. Polymers, 12(9), 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091920









