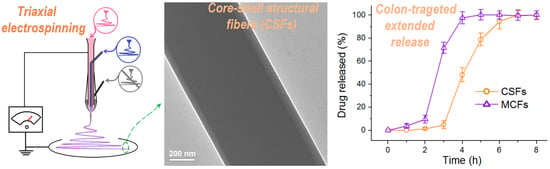
Core–Shell Eudragit S100 Nanofibers Prepared via Triaxial Electrospinning to Provide a Colon-Targeted Extended Drug Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modified Triaxial Electrospinning
2.3. The Morphologies and Inner Structures of the MCFS and CSFs
2.4. Aspirin Physical State and its Compatibility with ES100
2.5. Functional Performances of the Colon-Targeted Extended Release of Aspirin
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Triaxial Electrospinning
3.2. The Morphologies and Inner Structures of the MCFs and CSFs
3.3. The Physical State of Aspirin and Its Compatibility with ES100
3.4. The Functional Performances of Aspirin Colon-Targeted Extended-Release Profiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakielski, P.; Kowalczyk, T.; Zembrzycki, K.; Kowalewski, T.A. Experimental and numerical evaluation of drug release from nanofiber mats to brain tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 103, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, P.; Bi, H.; Zhao, G.; Han, Y.; Wickramaratne, M.N.; Dai, H.; Wang, X. Electrospun preparation and biological properties in vitro of polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/nano-hydroxyapatite composite fiber membrane. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chen, M.; Dou, Y.; Ding, J.; Yue, H.; Yin, G.; Chen, X.; Cui, Y. Electrospun silver nanoparticles-embedded feather keratin/poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(ethylene oxide) antibacterial composite nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Zhang, B.; Dou, Y.; Yin, G.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.-J. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun feather keratin/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9854–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, D.-G. Preparing composite nanoparticles for immediate drug release by modifying electrohydrodynamic interfaces during electrospraying. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.A.; Adnan, A.; Yahya, E.; Olaiya, N.; Safrida, S.; Hossain, M.; Balakrishnan, V.; Gopakumar, D.; Abdullah, C.; Oyekanmi, A.; et al. A Review on plant cellulose nanofibre-based aerogels for biomedical applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, A.; Re, I.L.; Clasen, C.; Mooter, G.V.D. Fixed dose combinations for cardiovascular treatment via coaxial electrospraying: Coated amorphous solid dispersion particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 118949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.F.; Nuge, T.; Andriyana, A.; Ang, B.C.; Muhamad, F. Core–Shell Fibers: Design, roles, and controllable release strategies in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Li, C.-J.; Cao, R.; Du, X. High-performance electronic cloth for facilitating the rehabilitation of human joints. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 22722–22729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.-J. Functional fibrous compositions: Applications and perspectives. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile platform for enzyme mimicking and their sensing applications. Compos. Commun. 2019, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.P. Performance of masks and discussion of the inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Eng. Sci. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.T.; Goepp, M.; Rossi, A.G.; Yao, C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins and COVID-19. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 368, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT04365309. Protective Effect of Aspirin on COVID-19 Patients. Available online: https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Show/NCT04365309 (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, B.; Balogh, A.; Cselkó, R.; Molnár, K.; Farkas, A.; Nagy, Z.K.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Corona alternating current electrospinning: A combined approach for increasing the productivity of electrospinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, P.; Hirsch, E.; Kóczián, R.; Démuth, B.; Farkas, A.; Fehér, C.; Szabó, E.; Németh, Á.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; et al. Scaled-up production and tableting of grindable electrospun fibers containing a protein-type drug. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.; Haj-Ahmad, R.; Rasekh, M.; Arshad, M.S.; Smith, A.; Van Der Merwe, S.M.; Li, X.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z. Pharmaceutical and biomaterial engineering via electrohydrodynamic atomization technologies. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, H.; Khorashadizadeh, M.; Haseloer, A.; Klein, A. Characterization and release behavior of a thiosemicarbazone from electrospun polyvinyl alcohol core‒shell nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.I.; Lee, J.Y.; Son, B.C.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Bi-layered nanofibers membrane loaded with titanium oxide and tetracycline as controlled drug delivery system for wound dressing applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipos, E.; Kósa, N.; Kazsoki, A.; Szabó, Z.-I.; Zelkó, R. Formulation and characterization of aceclofenac-loaded nanofiber based orally dissolving webs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin functional nanofibers for drug delivery applications. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Rath, G.; Singh, R.; Goyal, A.K. Nanofibers: An effective tool for controlled and sustained drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelkó, R.; Lamprou, D.A.; Sebe, I. Recent development of electrospinning for drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlachou, M.; Kikionis, S.; Siamidi, A.; Tragou, K.; Kapoti, S.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V.; Tsotinis, A. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers for the Modified Release of the Chronobiotic Hormone Melatonin. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.J.T.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M.; Medina, A.S.; Pérez-González, G.L.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J. A summary of electrospun nanofibers as drug delivery system: Drugs loaded and biopolymers used as matrices. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.-F.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colon-specific delayed drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.S.; Bachu, R.D.; Boddu, S.H.; Bhaduri, S.B. Biomedical applications of electrospun nanofibers: Drug and nanoparticle delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, B. Targeting delivery system for Lactobacillus Plantarum based on functionalized electrospun nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuysinuan, P.; Pengsuk, C.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Techasakul, S.; Svasti, J.; Nooeaid, P. Enhanced structural stability and controlled drug release of hydrophilic antibiotic-loaded alginate/soy protein isolate core-sheath fibers for tissue engineering applications. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Weih, Y. One-dimensional composite nanomaterials: Synthesis by electrospinning and their applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, R. Cost-effectiveness of rivaroxaban plus aspirin (dual pathway inhibition) for prevention of ischaemic events in patients with cardiovascular disease: On top optimisation of secondary prevention medication in the context of COVID-19 pandemia. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Crighton, A.J.; McCann, C.T.; Todd, E.J.; Brown, A.J. Safe use of paracetamol and high-dose NSAID analgesia in dentistry during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br. Dent. J. 2020, 229, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavillet, M.; Rolnik, D.L.; Hoffman, M.K.; Panchaud, A.; Bau, D. Should we stop aspirin prophylaxis in pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19? Ultrasound Obst. Gyn. 2020, 55, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.; Aliae, A.R.; Aly, K.M.E.; Ibrahim, M.A.A. Should aspirin be used for prophylaxis of COVID-19-induced coagulopathy? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ge, J. Clinical use of aspirin in treatment and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Thrombosis 2011, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byron, C.; Kenneth, W.M. Gastrointestinal ulcers, role of aspirin, and clinical outcomes: Pathobiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2014, 7, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Haastrup, P.F.; Grønlykke, T.; Jarbøl, D. Enteric Coating Can Lead to Reduced antiplatelet effect of low-dose acetylsalicylic acid. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 116, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Huang, Y.-W.; Oshima, K.; Yearsley, M.M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Arnold, M.; Wang, L. Could aspirin and diets high in fiber act synergistically to reduce the risk of colon cancer in humans? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.-G.; Shen, H. Sheath-separate-core nanocomposites fabricated using a trifluid electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-K.; Zhang, K.; Gong, Q.; Yu, D.-G.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Quan, H. Ethylcellulose-based drug nano depots fabricated using a modified triaxial electrospinning. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2020, 152, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. A nanofiber-based drug depot with high drug loading for sustained release. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.-G.; Wan, F.; Bligh, S.A. Comparative study of electrospun crystal-based and composite-based drug nano depots. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G. From Taylor cone to solid nanofiber in tri-axial electrospinning: Size relationships. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, S.; Bai, Y.; Du, Y.; Yu, D.G. Discrete drug distributions within electrospun tri-layer core-shell nanofibers for accurate dual-stage release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun environment remediation nanofibers using unspinnable liquids as the sheath fluids: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Yu, D.-G.; Li, X.; Williams, G.R. The development and bio-applications of multifluid electrospinning. Mater. Highlights 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.D.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.-L.; Huang, J.X.; Zuo, X.-H.; Lu, X.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Yu, D.G. Electrosprayed ultra-thin coating of ethyl cellulose on drug nanoparticles for improved sustained release. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Feng, T.; Li, B.; Han, Y. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison study of electrospun PLA and PLA/PVA/SA fiber membranes for wound healing. Polymers 2020, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vass, P.; Szabó, E.; Domokos, A.; Hirsch, E.; Galata, D.; Farkas, B.; Démuth, B.; Andersen, S.K.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; et al. Scale-up of electrospinning technology: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2019, 12, e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, W.; Liu, S.; Yao, K.; Zhao, L.; Cao, L.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. Ultrafine hollow TiO2 nanofibers from core-shell composite fibers and their photocatalytic properties. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Wan, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D.G. Dual-stage release of ketoprofen from electrosprayed core-shell hybrid polyvinyl pyrrolidone/ethyl cellulose nanoparticles. Mater. Highlight 2020, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hai, T.; Feng, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Bligh, S.A. The relationships between the working fluids, process characteristics and products from the modified coaxial electrospinning of zein. Polymers 2019, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Drug delivery applications of core-sheath nanofibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning: A review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.-S.; Lee, B.-S.; Yu, W.-R. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: New parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupka, V.; Dvořáková, E.; Manakhov, A.; Michlíček, M.; Petrus, J.; Vojtova, L.; Zajíčková, L. Well-blended PCL/PEO electrospun nanofibers with functional properties enhanced by plasma processing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, S.; Timofeeva, V.; Permyakova, E.; Ershov, S.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V.; Dvořáková, E.; Shtansky, D.; Zajíčková, L.; Solovieva, A.O.; Manakhov, A.; et al. Plasma-coated polycaprolactone nanofibers with covalently bonded platelet-rich plasma enhance adhesion and growth of human fibroblasts. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michlíček, M.; Manakhov, A.; Dvořáková, E.; Zajíčková, L. Homogeneity and penetration depth of atmospheric pressure plasma polymerization onto electrospun nanofibrous mats. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, W.J.; He, M.; Zhou, X.Y.; Yin, G.D. Vapor-assisted cross-linking of a FK/PVA/PEO nanofiber membrane. Polymers 2018, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Kowalczyk, T. Functional micro- and nanofibers obtained by nonwoven post-modification. Polymers 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Hasegawa, Y.; An, S.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Thiol-functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes for the effective adsorption of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, H. Recent Advances on nanofiber fabrications: Unconventional state-of-the-art spinning techniques. Polymers 2020, 12, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Cho, S.; Nam, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. X-ray-based spectroscopic techniques for characterization of polymer nanocomposite materials at a molecular level. Polymers 2020, 12, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.-M.; Bligh, S.W.A. Multifluid electrospinning for the generation of complex nanostructures. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.Z. Electrospun Janus zein–PVP nanofibers provide a two-stage controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mater. Des. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.-G.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable drug release from nanofibers coated with blansk cellulose acetate layers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neault, J.F.; Naoui, M.; Manfait, M.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Aspirin-dna interaction studied by FTIR and laser Raman difference spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1996, 382, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, P.J.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, B.H.; Nam, R.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Chang, H.; Jung, H.C.; et al. Comparison of indomethacin, diclofenac and aspirin-induced gastric damage according to age in rats. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Narasimhan, B. Mathematical models in drug delivery: How modeling has shaped the way we design new drug delivery systems. J. Control Release 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| No.a | Electro-Spinning | Voltage (kV) | Flow Rate of Fluid (mL/h) | Morphology/ Structure | Drug Loading (wt. %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer | Middle | Inner | |||||
| MCFs | Single-fluid | 13 | 2.0 | Linear/Monolithic | 25.0% | ||
| CSFs | Triaxial | 15 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.4 | Linear/Core–shell | 19.4% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Dou, C.; Chang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J. Core–Shell Eudragit S100 Nanofibers Prepared via Triaxial Electrospinning to Provide a Colon-Targeted Extended Drug Release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092034
Ding Y, Dou C, Chang S, Xie Z, Yu D-G, Liu Y, Shao J. Core–Shell Eudragit S100 Nanofibers Prepared via Triaxial Electrospinning to Provide a Colon-Targeted Extended Drug Release. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092034
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yanfei, Cheng Dou, Shuyue Chang, Zhengming Xie, Deng-Guang Yu, Yanan Liu, and Jun Shao. 2020. "Core–Shell Eudragit S100 Nanofibers Prepared via Triaxial Electrospinning to Provide a Colon-Targeted Extended Drug Release" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092034
APA StyleDing, Y., Dou, C., Chang, S., Xie, Z., Yu, D.-G., Liu, Y., & Shao, J. (2020). Core–Shell Eudragit S100 Nanofibers Prepared via Triaxial Electrospinning to Provide a Colon-Targeted Extended Drug Release. Polymers, 12(9), 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092034