Mechanical and Antimicrobial Polyethylene Composites with CaO Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CaO Nanoparticles
2.2.1. Nanoparticles of CaO ca. 55 nm
2.2.2. Nanoparticles of CaO ca. 25 nm
2.2.3. Organic Modification of CaO Nanoparticles (Mod-CaO)
2.3. Preparation of LDPE Nanocomposites with the Incorporation of CaO and Modified CaO Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Characterization of CaO Nanoparticles and the LDPE /CaO Nanocomposite
CaO Nanoparticles and their Organic Modification Characterization
LDPE /CaO and LDPE /Mod-CaO Nanocomposite Characterization
3. Results
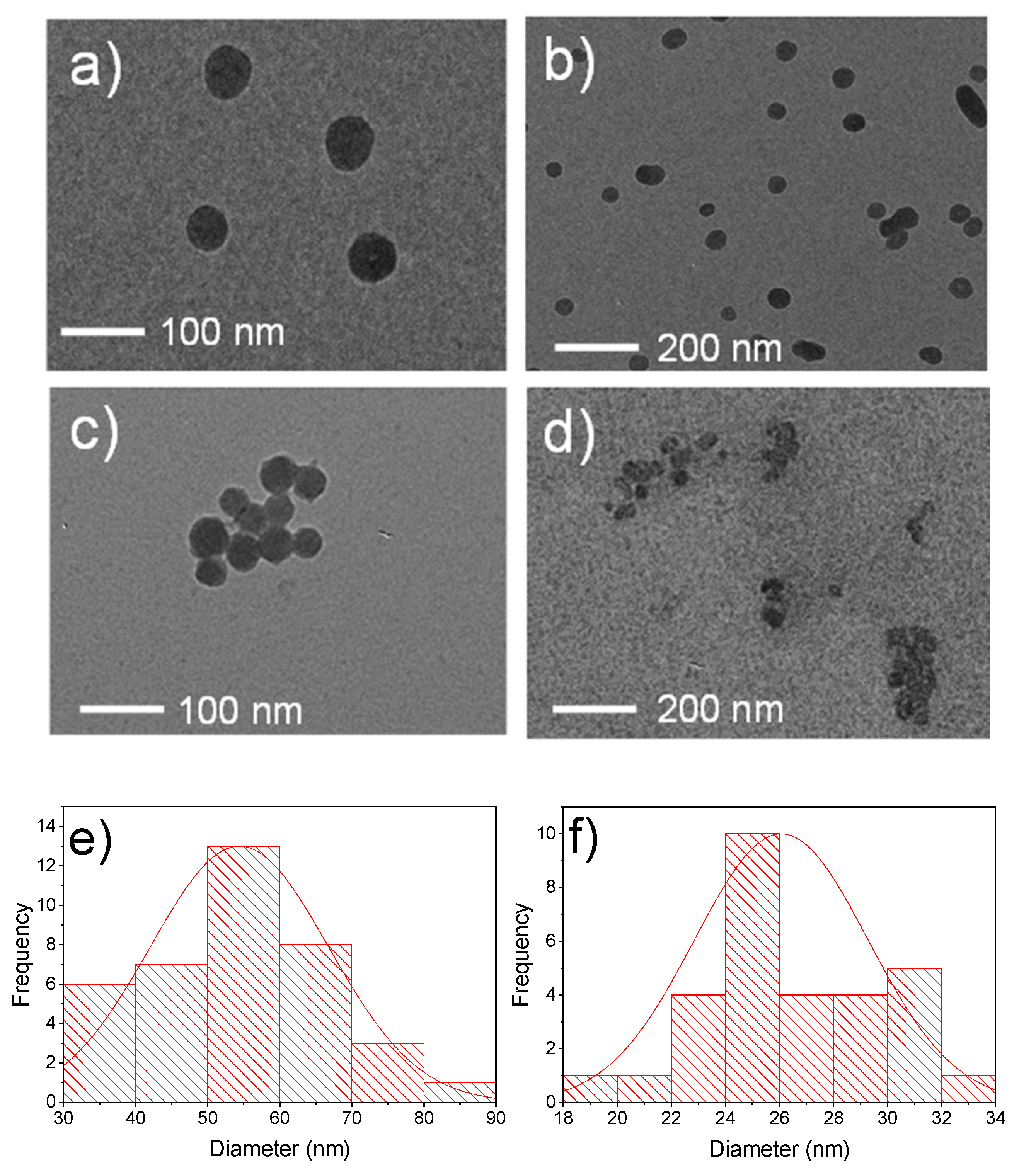
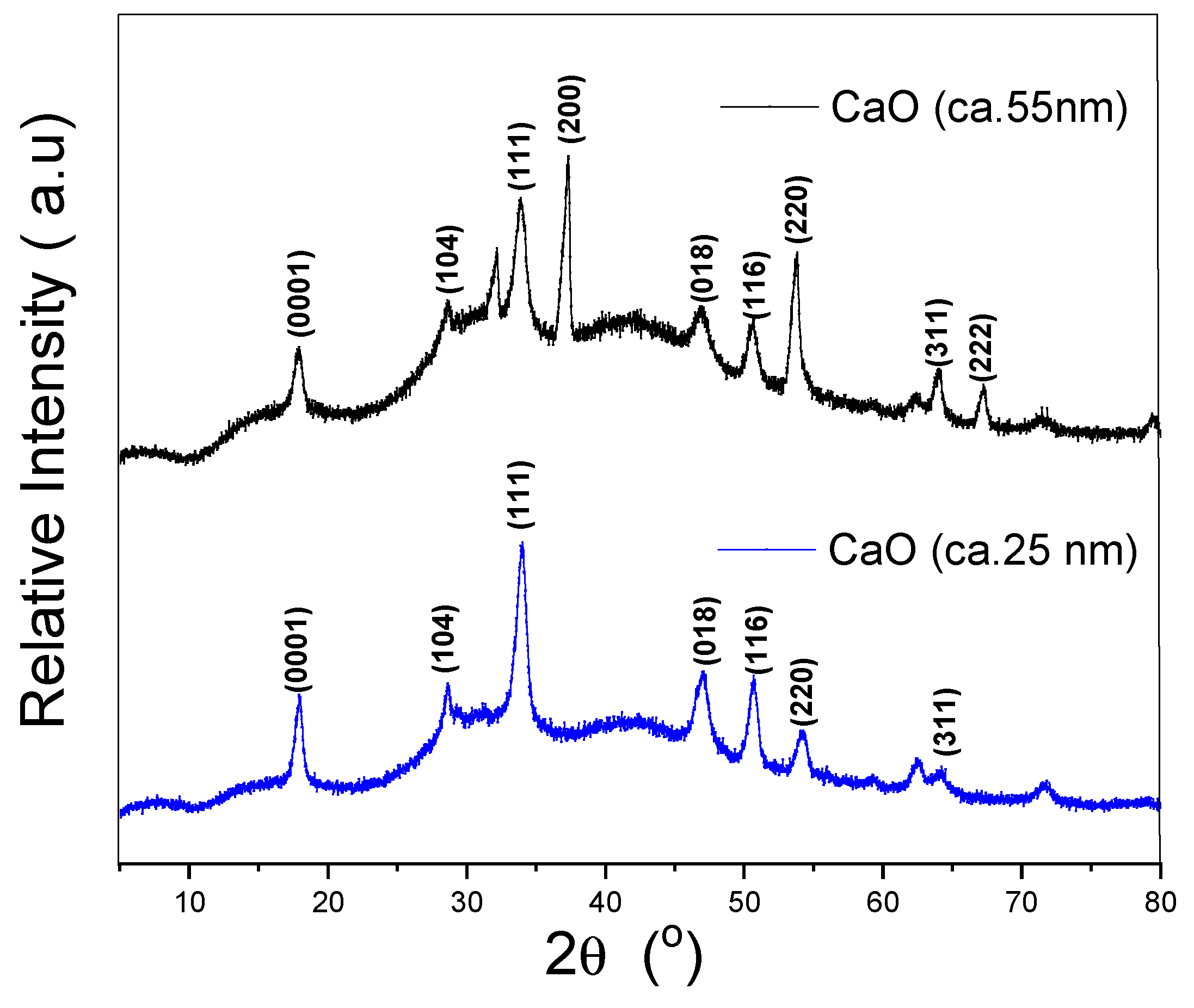
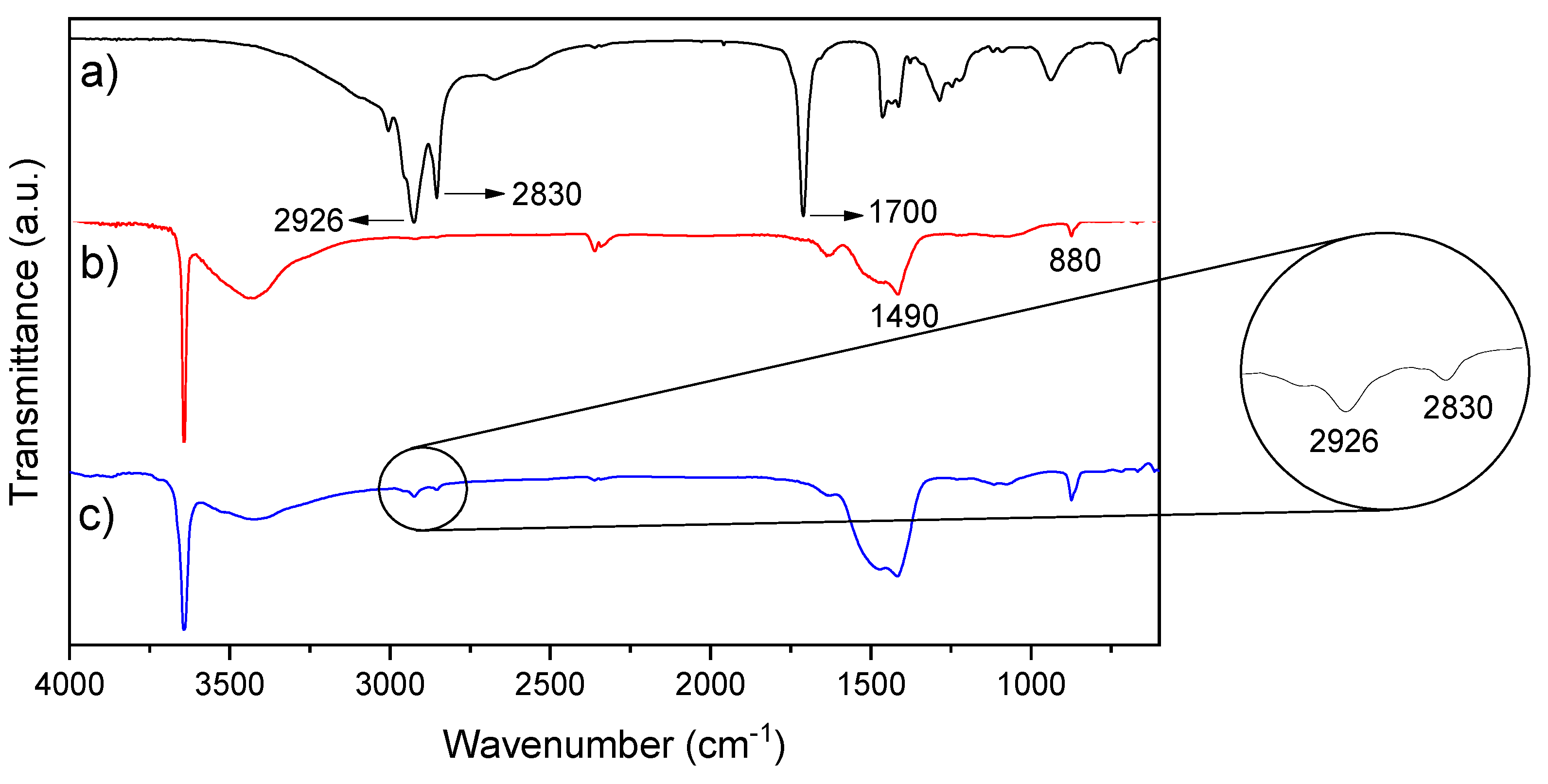
3.1. Characterization of Calcium Oxide Nanoparticles
3.2. Characterization of Polymer Nanocomposites
3.2.1. Thermal Properties
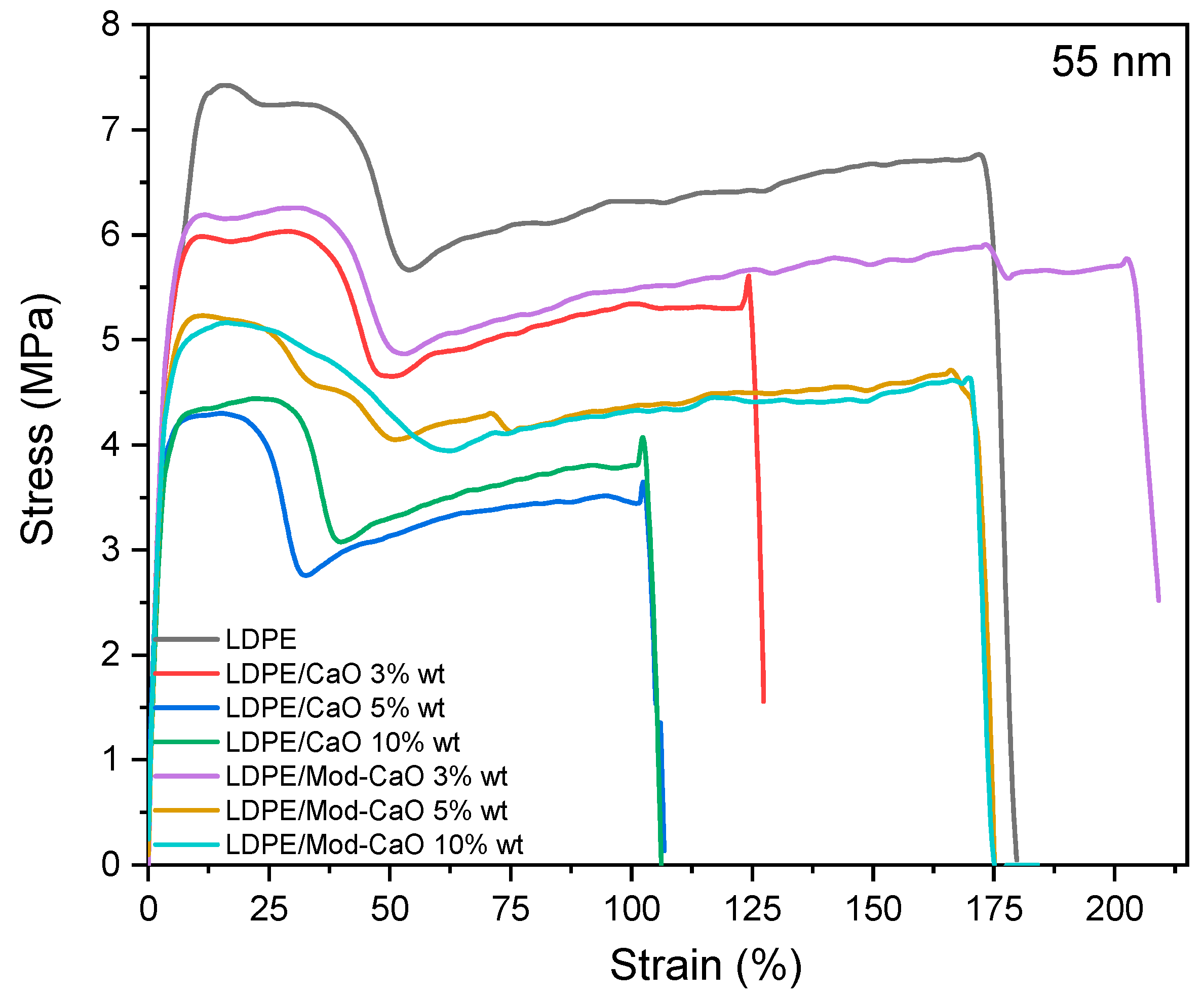
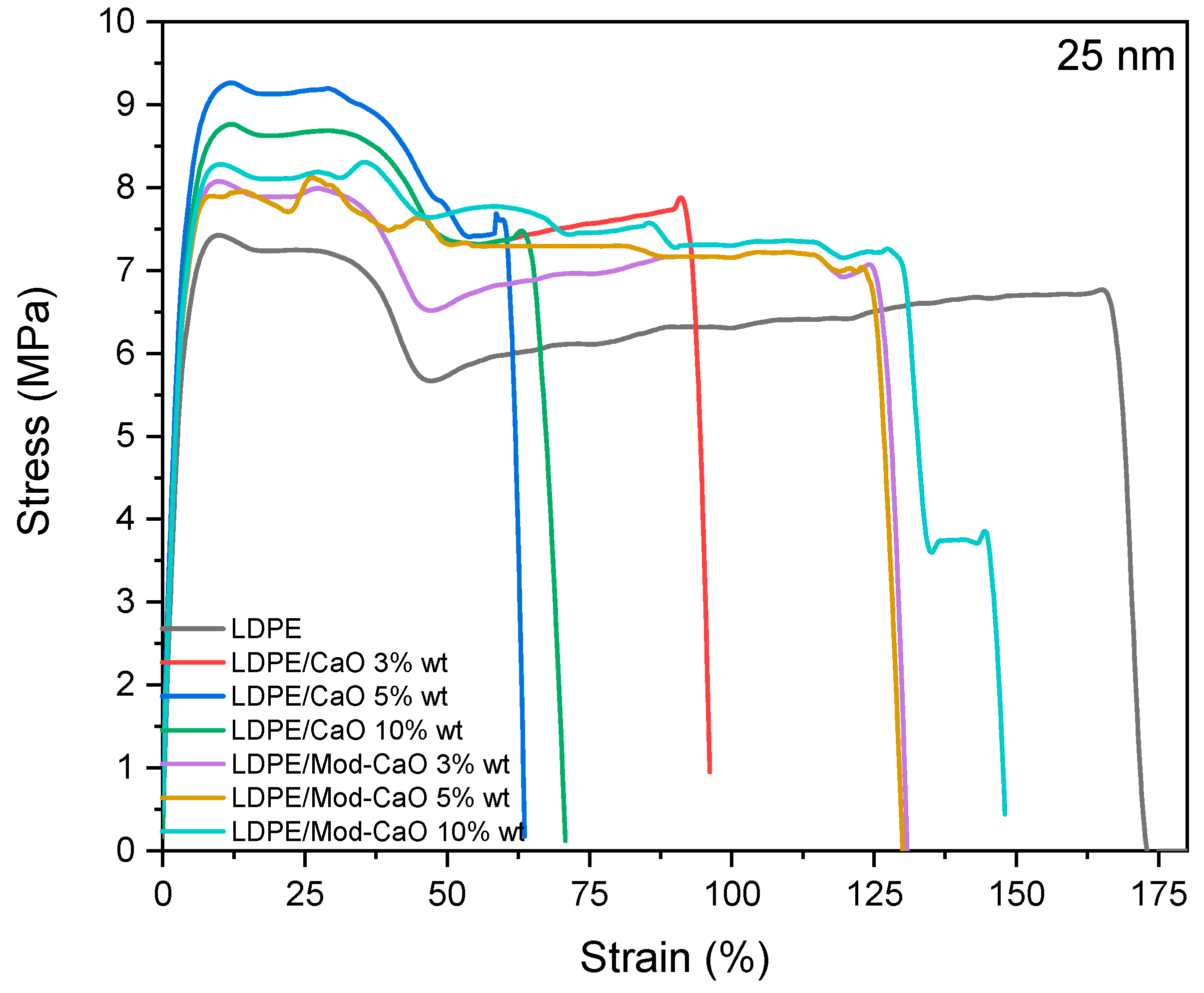
3.2.2. Mechanical Properties
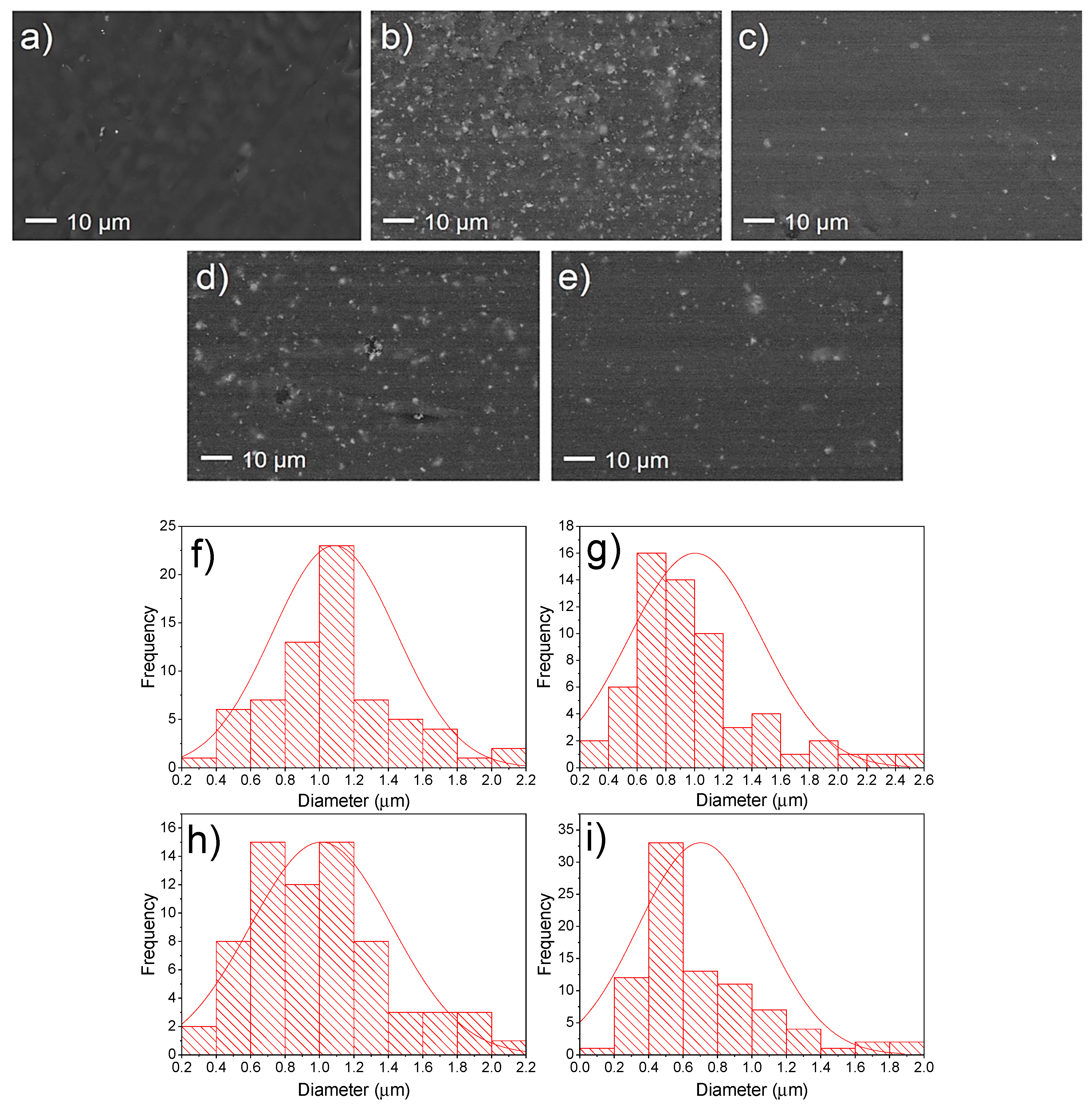
3.2.3. Biocidal Properties
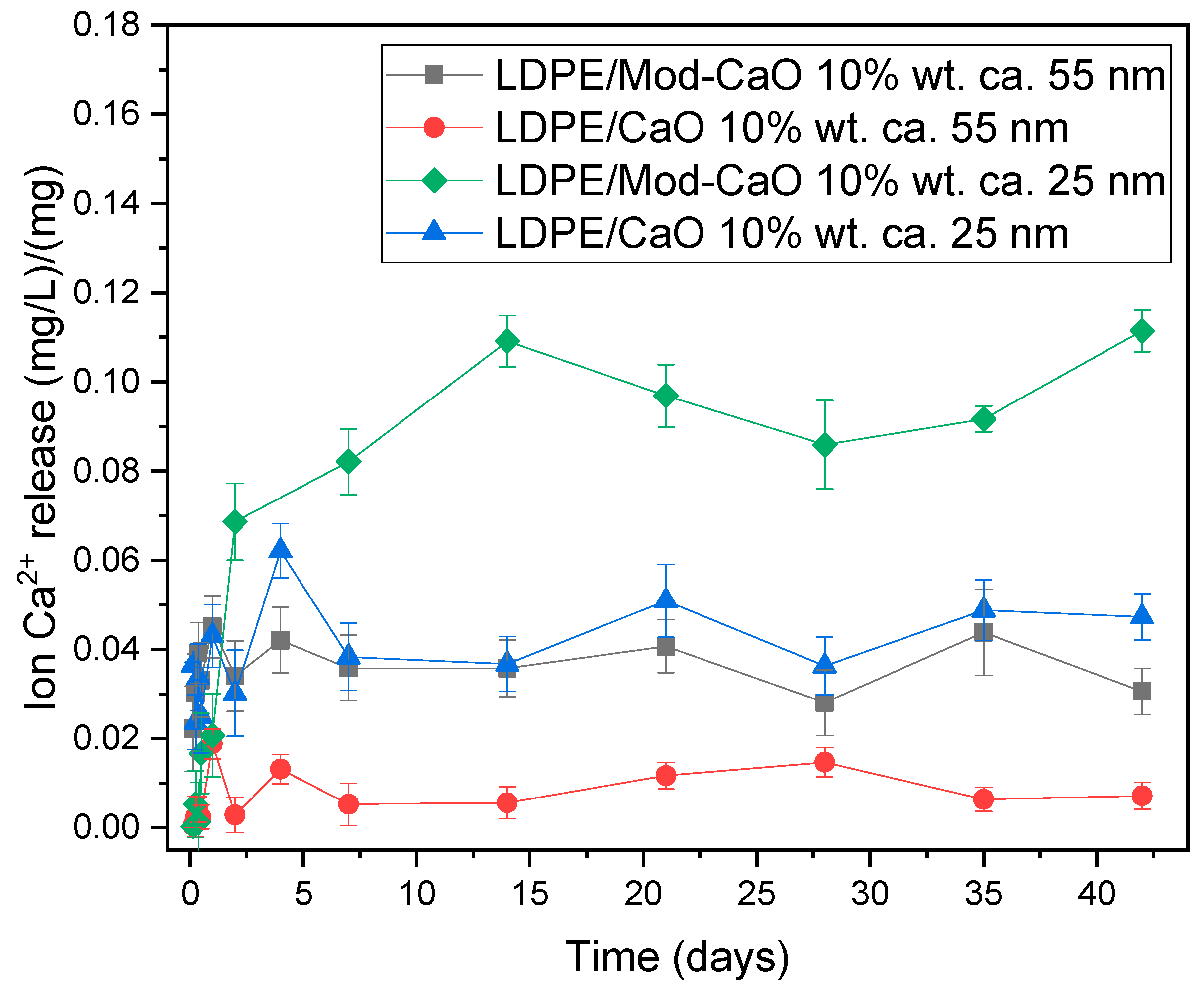
3.2.4. Ion Release from LDPE Matrix
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Song, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, L. Nanoscopic confinement effects on ethylene polymerization by intercalated silicate with metallocene catalyst. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2004, 42, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwu, J.; Jiang, G. Preparation and characterization of polypropylene-montmorillonite nanocomposites generated by in situ metallocene catalyst polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.B.; Morales, A.R.; Valenzuela Díaz, F.R. Organoclays: Properties, preparation and applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Quijada, R.; Covarrubias, C.; Moncada, E.; Retuert, J. Catalytic activity during the preparation of PE/clay nanocomposites by in situ polymerization with metallocene catalysts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2368–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, S.; Papaspyrides, C.D. A review on polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1119–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tayyar, N.A.; Youssef, A.M.; Al-Hindi, R.R. Antimicrobial packaging efficiency of ZnO-SiO2 nanocomposites infused into PVA/CS film for enhancing the shelf life of food products. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 25, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomate, G.B.; Dandi, B.; Mishra, S. Development of antimicrobial LDPE/Cu nanocomposite food packaging film for extended shelf life of peda. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 16, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Tamayo, L.; Páez, M.; Cerda, E.; Azócar, I.; Rabagliati, F.M. Nanocomposites based on polyethylene and nanosilver particles produced by metallocenic “in situ” polymerization: Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial behavior. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palza, H.; Gutiérrez, S.; Salazar, O.; Fuenzalida, V.; Avila, J.I.; Figueroa, G.; Quijada, R. Toward tailor-made biocide materials based on poly(propylene)/copper nanoparticles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Palza, H.; Rabagliati, F.M. Novel antimicrobial polyethylene composites prepared by metallocenic in situ polymerization with TiO2-based nanoparticles. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, K.; Canales, D.; Amigo, N.; Montoille, L.; Cament, A.; Rivas, L.; Gil-Castell, O.; Reyes, P.; Ulloa, M.T.; Ribes-Greus, A.; et al. Effective antimicrobial materials based on Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Compos. Part-B Eng. 2019, 172, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Palza, H. Polyethylene-based bio-and nanocomposite for packaging aplications. In Polyethylene-Based Biocomposites and Bionanocomposites; Lüftl, P.M., Visakh, S., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 69–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saee, G.; Aman, A.; Balaprasad, A. A review on antimicrobial properties of metal nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2020, 20, 3303–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghiasi, Z.; Bakhtiari, F.; Darezereshki, E.; Esmaeilzadeh, E. Preparation and characterization of CaO nanoparticles from Ca(OH)2 by direct thermal decomposition method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Yeon, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Do, H.S. Bactericidal effects of CaO (scallop-shell powder) on foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ro, E.Y.; Ko, Y.M.; Yoon, K.S. Survival of pathogenic enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) and control with calcium oxide in frozen meat products. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.S.; Park, J.S.; Song, S.H.; Jang, S.B. Characterization of antibacterial nanoparticles from the scallop, Ptinopecten yessoensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2242–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; He, Y. Antibacterial activities of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 6877–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O.; Ohira, T.; Alvarez, K.; Fukuda, M. Antibacterial characteristics of CaCO3-MgO composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2010, 173, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhluf, S.; Dror, R.; Nitzan, Y.; Abramovich, Y.; Jelinek, R.; Gedanken, A. Microwave-assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline MgO and its use as a bacteriocide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Kawada, E.; Kanou, F.; Igarashi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Kokugan, T.; Shimizu, M. Detection of active oxygen generated from ceramic powders having antibacterial activity. J. Chem. Eng. JPN 1996, 29, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, C.J.; Bellara, S.R.; Andreani, A.; Nebe-von-Caron, G.; McFarlane, C.M. An evaluation of the anti-bacterial action of ceramic slurries using multi-parameter flow cytometry. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedda, G.; Pandey, S.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, H.F. Antibacterial effect of calcium oxide nano-plates fabricated from shrimp shells. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3276–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenov, P.K.; Klinger, R.L.; Marchin, G.L.; Klabunde, K.J. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6679–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münchow, E.A.; Pankajakshan, D.; Albuquerque, M.T.P.; Kamocki, K.; Piva, E.; Gregory, R.L.; Bottino, M.C. Synthesis and characterization of CaO-loaded electrospun matrices for bone tissue engineering. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2016, 20, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirimali, H.D.; Chaudhari, B.C.; Khanderay, J.C.; Joshi, S.A.; Singh, V.; Patil, A.M.; Gite, V.V. Waste eggshell-derived calcium oxide and nanohydroxyapatite biomaterials for the preparation of LLDPE polymer nanocomposite and their thermomechanical study. Polym-Plast Technol. 2017, 57, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, S. Impact of nano-CaCO3-LDPE packaging on quality of fresh-cut sugarcane. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M.; Scaffaro, R.; Tulone, S. Rheological and mechanical behavior of LDPE/calcium carbonate nanocomposites and microcomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapčík, L.; Maňas, D.; Vašina, M.; Lapčíková, B.; Řezníček, M.; Zádrapa, P. High density poly(ethylene)/CaCO3 hollow spheres composites for technical applications. Compos. Part-B Eng. 2017, 113, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Palza, H.; Díaz, B.; Armijo, A.; Sepúlveda, F.; Ortiz, J.A.; Ramírez, M.P.; Oyarzún, C. Effect of CaCO3 nanoparticles on the mechanical and photo-degradation properties of LDPE. Molecules 2019, 24, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pan, Q.Q.; Shi, L.E. Sonication-assisted preparation of CaO nanoparticles for antibacterial agents. Quim. Nova 2013, 36, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sängerlaub, S.; Kucukpinar, E.; Kiese, S.; Bauer, D.K.; Müller, K. Desiccant films made of low-density polyethylene with dispersed calcium oxide: Water vapor absorption, permeation and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 136, 47460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrano, F.H.C.; das Chagas, T.F.; de Melo, P.M.A.; da Silva, L.B. Characterization of the particulate composites of high density polyethylene/mollusk shell powder. Revista Matéria 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebarjad, S.M.; Sajjadi, S.A. On the strain rate sensitivity of HDPE/CaCO3 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 475, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y. Surface-modification of SiO2 nanoparticles with oleic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 211, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez, D.; Guerrero, S.; Lieberwirth, I.; Ulloa, M.T.; Gomez, T.; Rabagliati, F.M.; Zapata, P.A. Photocatalytic inhibition of bacteria by TiO2 nanotubes-doped polyethylene composites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 489, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo, N.; Palza, H.; Canales, D.; Sepúlveda, F.; Vasco, D.A.; Sepúlveda, F.; Zapata, P.A. Effect of starch nanoparticles on the crystallization kinetics and photodegradation of high density polyethylene. Compos. Part-B Eng. 2019, 174, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Quijada, R.; Benavente, R. In situ formation of nanocomposites based on polyethylene and silica nanospheres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno, A.; Guerrero, S.; Ulloa, M.T.; Palza, H.; Zapata, P.A. Effect of hydrothermally synthesized titanium nanotubes on the behaviour of polypropylene for antimicrobial applications. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, I.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, H. Effect of orientation of CaO plate-like particle on CO2 adsorption property. Powder Technol. 2017, 315, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.K.; Tallapragada, R.M.; Branton, A.; Trivedi, D.; Nayak, G.; Latiyal, O.; Mishra, R.K.; Jana, S. Physicochemical characterization of biofield energy treated calcium carbonate powder. Am. J. Health Res. 2015, 3, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Yang, S.T.; Ahn, W.S. Calcium oxide as high temperature CO2 sorbent: Effect of textural properties. Mater. Lett. 2012, 75, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.T.; Alfonsín, C.; Chambel, A.J.S.; Fernandes, A.; Soares Dias, A.P.; Pinheiro, C.I.C.; Ribeiro, M.F. Investigation of a stable synthetic sol-gel CaO sorbent for CO2 capture. Fuel 2012, 94, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, G.D.; Lajolo, F.M. FT-IR spectroscopy as a tool for measuring degree of methyl esterification in pectins isolated from ripening papaya fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.M.; Catalano, E.A.; Andrews, B.A.K. FT-IR Determination of degree of esterification in polycarboxylic acid cross-link finishing of cotton. Cellulose 1995, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Ochoa, A.; Ulloa, M.T.; Alvarez, E.; Canales, D.; Zapata, P.A. Poly(lactic acid)/TiO2 nanocomposites as alternative biocidal and antifungal materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashantha, K.; Lacrampe, M.F.; Krawczak, P. Processing and characterization of halloysite nanotubes filled polypropylene nanocomposites based on a masterbatch route: Effect of halloysites treatment on structural and mechanical properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, M.; Królikowski, Z. Application of dsc to study crystallization kinetics of polypropylene containing fillers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 74, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, A.; Sun, C.T.; Mahfuz, H. A molecular dynamics simulation study to investigate the effect of filler size on elastic properties of polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, N.; Mahfuz, H.; Rangari, V.K.; Ashfaq, A.; Jeelani, S. Fabrication and mechanical characterization of carbon/SiC-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Struct. 2005, 67, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lam, Y.C.; Tam, K.C.; Chua, T.H.; Sim, G.W.; Ang, L.S. Strengthening acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) with nano-sized and micron-sized calcium carbonate. Polymer 2005, 46, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, D.; Vazquez, G.E.; Díaz, M.F. Prediction of elongation at break for linear polymers. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2014, 139, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, E.; Niaounakis. Thermo-mechanical properties of LLDPE/SiO2 nanocomposites. Polymer 2006, 47, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Wong, M.T.; Chan, C.M.; Guo, M.Y.; Ng, Y.H.; Djurišić, A.B.; et al. Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of MgO: Non-ros mediated toxicity of MgO nanoparticles towards Escherichia coli. Small 2014, 10, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, A.; Serrano, C.; Ferrer, M.; Lunsdorf, H.; Bielecki, P.; Cerrada, M.L.; Fernández-García, M.; Fernández-García, M. High-performance dual-action polymer-TiO2 nanocomposite films via melting processing. NANO Lett. 2007, 7, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Yoshikawa, T. Quantitative evaluation of antifungal activity of metallic oxide powders (MgO, CaO and ZnO) by an indirect conductimetric assay. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radheshkumar, C.; Münstedt, H. Antimicrobial polymers from polypropylene/silver composites-Ag+ release measured by anode stripping voltammetry. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
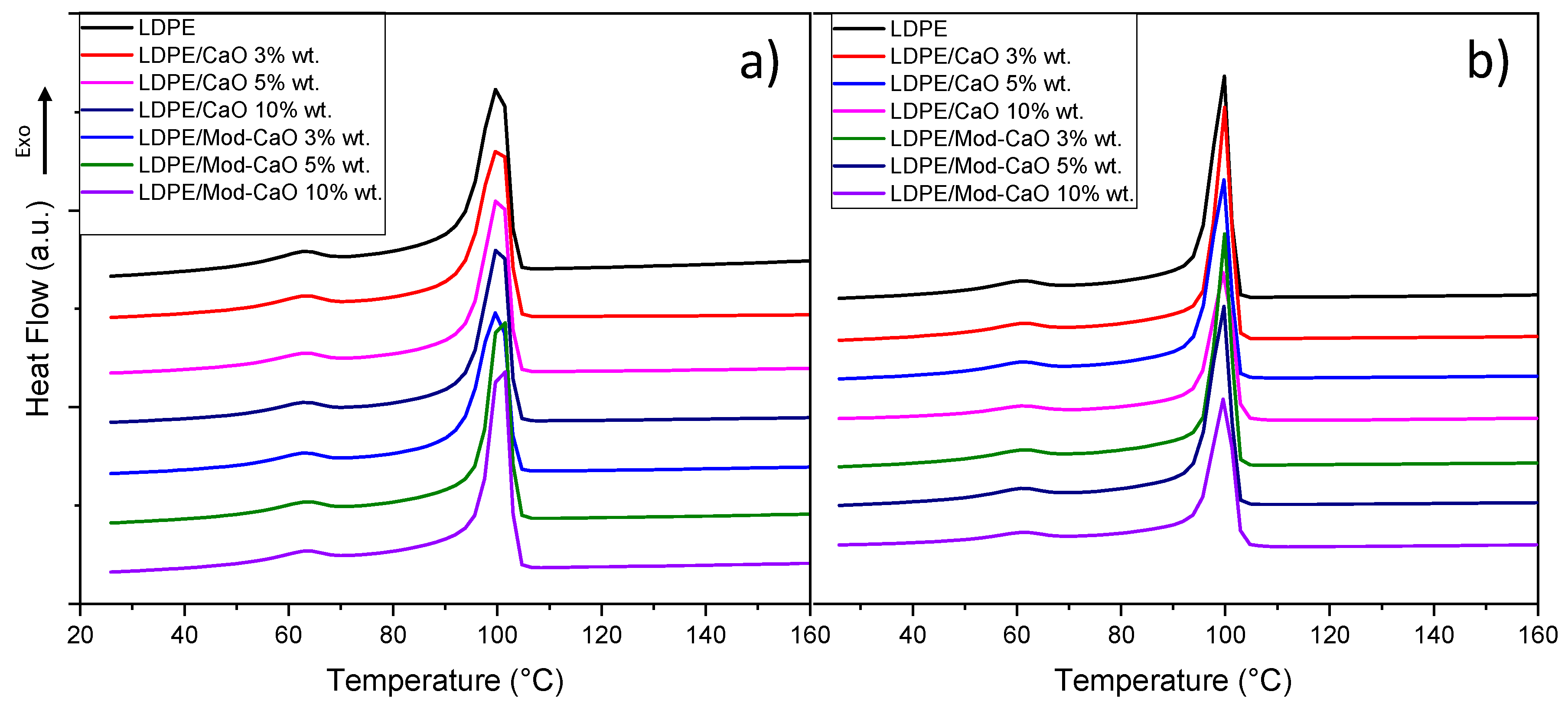

| Nanoparticle Size | 55 nm | 25 nm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Weight (%) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) |
| LDPE | 0 | 100 | 113 | 40 | 100 | 113 | 40 |
| LDPE/CaO | 3 | 101 | 113 | 41 | 100 | 111 | 40 |
| 5 | 101 | 112 | 39 | 100 | 112 | 39 | |
| 10 | 100 | 113 | 40 | 100 | 112 | 39 | |
| LDPE/Mod-CaO | 3 | 100 | 113 | 37 | 100 | 113 | 52 |
| 5 | 101 | 112 | 39 | 100 | 113 | 47 | |
| 10 | 102 | 113 | 39 | 100 | 113 | 45 | |
| Nanoparticle Size | 55 nm | 25 nm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | CaO Weight (%) | E (Mpa) | Σy (Mpa) | Ee% | E (Mpa) | Σy (Mpa) | Ee % |
| LDPE | 0 | 150 ± 5 | 7.7 ± 0.7 | 169 ± 4 | 150 ± 5 | 7.7 ± 0.7 | 169 ± 4 |
| LDPE/CaO | 3 | 175 ± 16 | 5.2 ± 0.6 | 124 ± 4 | 154 ± 120 | 8.7 ± 0.6 | 96 ± 3 |
| 5 | 165 ± 6 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 104 ± 1 | 162 ± 24 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 62 ± 2 | |
| 10 | 190 ± 18 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 104 ± 1 | 193 ± 11 | 8.8 ± 0.4 | 70 ± 2 | |
| LDPE/Mod-CaO | 3 | 180 ± 12 | 5.1 ± 0.7 | 200 ± 14 | 170 ± 17 | 8.1 ± 1.1 | 130 ± 7 |
| 5 | 195 ± 14 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 164 ± 11 | 197 ± 12 | 8.1 ± 0.7 | 116 ± 2 | |
| 10 | 203 ± 17 | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 167 ± 23 | 205 ± 14 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 147 ± 4 | |
| Nanoparticle Size | 55 nm | 25 nm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Weight (wt%) | % Reduction | % Reduction |
| LDPE/CaO | 3 | 12.4 | 61.8 |
| 5 | 20.2 | 64.2 | |
| 10 | 30.6 | 81.4 | |
| LDPE/Mod-CaO | 3 | 20.5 | 80.8 |
| 5 | 32.2 | 87.3 | |
| 10 | 53.0 | 99.9 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, C.; Bobillier, F.; Canales, D.; Antonella Sepúlveda, F.; Cament, A.; Amigo, N.; Rivas, L.M.; Ulloa, M.T.; Reyes, P.; Ortiz, J.A.; et al. Mechanical and Antimicrobial Polyethylene Composites with CaO Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092132
Silva C, Bobillier F, Canales D, Antonella Sepúlveda F, Cament A, Amigo N, Rivas LM, Ulloa MT, Reyes P, Ortiz JA, et al. Mechanical and Antimicrobial Polyethylene Composites with CaO Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092132
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Cristián, Felipe Bobillier, Daniel Canales, Francesca Antonella Sepúlveda, Alejandro Cament, Nicolás Amigo, Lina M. Rivas, María T. Ulloa, Pablo Reyes, J. Andrés Ortiz, and et al. 2020. "Mechanical and Antimicrobial Polyethylene Composites with CaO Nanoparticles" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092132
APA StyleSilva, C., Bobillier, F., Canales, D., Antonella Sepúlveda, F., Cament, A., Amigo, N., Rivas, L. M., Ulloa, M. T., Reyes, P., Ortiz, J. A., Gómez, T., Loyo, C., & Zapata, P. A. (2020). Mechanical and Antimicrobial Polyethylene Composites with CaO Nanoparticles. Polymers, 12(9), 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092132






