Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (RF) as a Novel Plasticizer for Starch-Based Solid Biopolymer Electrolyte
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Polymer Electrolyte
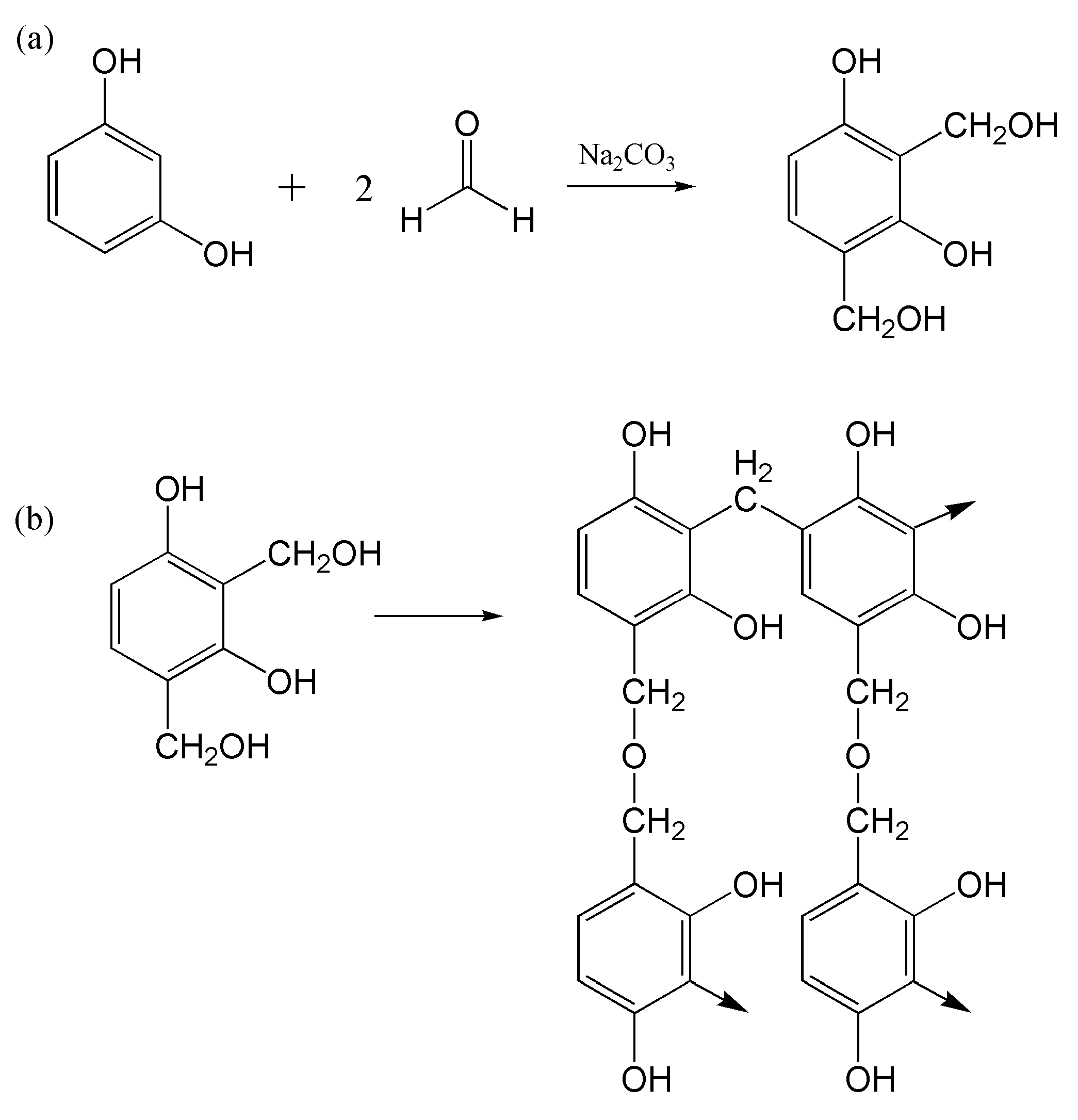
2.2.1. Preparation of RF Solution
2.2.2. Casting and Film Formation
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared-Attenuated Total Reflection (FTIR-ATR)
2.3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.2. Plasticization Mechanism
3.3. FTIR-ATR Analysis
3.4. XRD Analysis
3.5. Conductivity Studies
3.6. Equivalent Circuit Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K. Recent advances in additive-enhanced polymer electrolyte membrane properties in fuel cell applications: An overview. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 2756–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su’ait, M.S.; Rahman, M.Y.A.; Ahmad, A. Review on polymer electrolyte in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). Sol. Energy 2015, 115, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayung, M.; Aung, M.M.; Azhar, S.C.; Abdullah, L.C.; Su’ait, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M. Bio-Based Polymer Electrolytes for Electrochemical Devices: Insight into the Ionic Conductivity Performance. Materials 2020, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, O.V.; García, M.A.; Zaritzky, N.E. Film forming capacity of chemically modified corn starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvanathan, V.; Yahya, R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Alharthi, N.H.; Alharthi, Y.S.; Ruslan, M.H.; Amin, N.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. Organosoluble starch derivative as quasi-solid electrolytes in DSSC: Unravelling the synergy between electrolyte rheology and photovoltaic properties. Sol. Energy 2020, 197, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, V.; Yahya, R.; Ruslan, M.H.; Sopian, K.; Amin, N.; Nour, M.; Sindi, H.; Rawa, M.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. Organosoluble Starch-Cellulose Binary Polymer Blend as a Quasi-Solid Electrolyte in a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Polymers 2020, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, R.; Kyu, T. Effect of Plasticization on Ionic Conductivity Enhancement in Relation to Glass Transition Temperature of Crosslinked Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5637–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, M.P.; Bijaksana, S.; Abdullah, M. A General Formula for Ion Concentration-Dependent Electrical Conductivities in Polymer Electrolytes. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 9, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukur, M.F.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Hydrogen ion conducting starch-chitosan blend based electrolyte for application in electrochemical devices. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wei, C. In situ observation of crystallinity disruption patterns during starch gelatinization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, K.; Kaminski, D.; Kirwan, G.; Lascaris, E.; Shanks, R. Crystallinity and structure of starch using wide angle X-ray scattering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.H. Plasticization of Pea Starch Films with Monosaccharides and Polyols. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E253–E261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, R.-r.; Zhang, K.-r.; Cheng, F.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, P.-x. Effect of hyperbranched poly(citric polyethylene glycol) with various polyethylene glycol chain lengths on starch plasticization and retrogradation. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and Properties of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Organic and Carbon Gels. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J. Solid state electrochemistry. Edited by Peter G. Bruce, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1995, XVI, 344 pp., hardcover, £60.00, ISBN 0-521-40007-4. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Shanti, R.; Morris, E. Studies on the plasticization efficiency of deep eutectic solvent in suppressing the crystallinity of corn starch based polymer electrolytes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Miao, C.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced performance of P(VDF-HFP)-based composite polymer electrolytes doped with organic-inorganic hybrid particles PMMA-ZrO2 for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 382, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, C.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, P.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, M. Effect of different contents of organic-inorganic hybrid particles poly(methyl methacrylate)ZrO2 on the properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoroprolene)-based composite gel polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 272, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukur, M.F.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Majid, N.A.; Ithnin, R.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Electrical analysis of amorphous corn starch-based polymer electrolyte membranes doped with LiI. Phys. Scr. 2013, 88, 025601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwandt, N.W.; Gound, T.G. Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Resin “Russian Red” Endodontic Therapy. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambrel, M.G.; Hartwell, G.R.; Moon, P.C.; Cardon, J.W. The Effect of Endodontic Solutions on Resorcinol-Formalin Paste in Teeth. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T. The assignment of IR absorption bands due to free hydroxyl groups in cellulose. Cellulose 1997, 4, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, K.H.; Lim, C.-S.; Ramesh, S. Lithium ion conduction in corn starch based solid polymer electrolytes. Measurement 2014, 48, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Gao, W.; Pang, J.; Yu, J. Using X-ray diffractometry for identification of Fritillaria preparations according to geographical origin. Pharm. Chem. J. 2006, 40, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Watanabe, M. Highly conductive polymer electrolytes prepared by in situ polymerization of vinyl monomers in room temperature molten salts. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiar, A.S.A.; Arof, A.K. Conductivity studies of starch-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2010, 16, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmirzaei, M.H.; Ramesh, S. Studies on biodegradable polymer electrolyte rice starch (RS) complexed with lithium iodide. Ionics 2014, 20, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Wong, K. Conductivity, dielectric behaviour and thermal stability studies of lithium ion dissociation in poly (methyl methacrylate)-based gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2009, 15, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukur, M.F.; Ithnin, R.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Electrical characterization of corn starch-LiOAc electrolytes and application in electrochemical double layer capacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, C.-W.; Ramesh, S. Electrical, structural, thermal and electrochemical properties of corn starch-based biopolymer electrolytes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, K.H.; Lim, C.-S.; Liew, C.-W.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, S. Electric double-layer capacitors with corn starch-based biopolymer electrolytes incorporating silica as filler. Ionics 2015, 21, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azli, A.A.; Manan, N.S.A.; Aziz, S.B.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Structural, impedance and electrochemical double-layer capacitor characteristics of improved number density of charge carrier electrolytes employing potato starch blend polymers. Ionics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, H.; Dhapola, P.S.; Rahul; Sahoo, N.G.; Singh, V.; Singh, P.K. Ionic liquid (1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide)-incorporated biopolymer electrolyte for efficient supercapacitor. High Perform. Polym. 2020, 32, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, Y.N.; Selvakumar, M. Lithium perchlorate doped plasticized chitosan and starch blend as biodegradable polymer electrolyte for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 78, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.L.; Stuart, D.A. Calculation of Activation Energy of Ionic Conductivity in Silica Glasses by Classical Methods. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1954, 37, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Designation | Composition of RF Plasticizer (wt.%) | Composition of LiTf (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| SRF15 | 15 | 10 |
| SRF30 | 30 | 10 |
| SRF45 | 45 | 10 |
| SRF60-1 | 60 | 10 |
| SRF60-2 | 60 | 20 |
| SRF60-3 | 60 | 30 |
| Sample | Conductivity (S cm−1) |
|---|---|
| SRF15 | 1.70 × 10−6 |
| SRF30 | 2.61 × 10−6 |
| SRF45 | 2.33 × 10−5 |
| SRF60-1 | 7.23 × 10−5 |
| SRF60-2 | 4.29 × 10−4 |
| SRF60-3 | 9.45 × 10−6 |
| Type of Starch | Salt Species | Plasticizer | Ionic Conductivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | Lithium acetate (LiOAc) | Glycerol | 1.03 × 10−3 | [29] |
| Corn | Lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BmImPF6) | 1.47 × 10−4 | [30] |
| Corn | Lithium perchlorate salt (LiClO4) | Silica | 1.23 × 10−4 | [31] |
| Potato | Lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate (LiCF3SO3) | Graphene oxide (GO)/ 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([Bmim][Cl]) | 4.80 × 10−4 | [32] |
| Corn | Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide (HmIMI) | 3.40 × 10−4 | [33] |
| Potato | LiCF3SO3 | Resorcinol-formaldehyde | 4.29 × 10−4 | This work. |
| Sample | Rb (Ω) | C1 (F) | p1 | C2 (F) | p2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRF15 | 2620 | 2.36 × 10−8 | 0.64 | 1.63 × 10−6 | 0.64 |
| SRF30 | 1950 | 4.73 × 10−8 | 0.70 | 2.17 × 10−6 | 0.68 |
| SRF45 | 422 | 6.82 × 10−8 | 0.74 | 3.40 × 10−6 | 0.72 |
| Sample | Rb (Ω) | C (F) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRF60-1 | 202 | 2.58 × 10−6 | 0.68 |
| SRF60-2 | 15 | 6.19 × 10−6 | 0.78 |
| SRF60-3 | 350 | 4.97 × 10−7 | 0.61 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvanathan, V.; Ruslan, M.H.; Aminuzzaman, M.; Muhammad, G.; Amin, N.; Sopian, K.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (RF) as a Novel Plasticizer for Starch-Based Solid Biopolymer Electrolyte. Polymers 2020, 12, 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092170
Selvanathan V, Ruslan MH, Aminuzzaman M, Muhammad G, Amin N, Sopian K, Akhtaruzzaman M. Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (RF) as a Novel Plasticizer for Starch-Based Solid Biopolymer Electrolyte. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092170
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvanathan, Vidhya, Mohd Hafidz Ruslan, Mohammod Aminuzzaman, Ghulam Muhammad, N. Amin, Kamaruzzaman Sopian, and Md. Akhtaruzzaman. 2020. "Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (RF) as a Novel Plasticizer for Starch-Based Solid Biopolymer Electrolyte" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092170
APA StyleSelvanathan, V., Ruslan, M. H., Aminuzzaman, M., Muhammad, G., Amin, N., Sopian, K., & Akhtaruzzaman, M. (2020). Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (RF) as a Novel Plasticizer for Starch-Based Solid Biopolymer Electrolyte. Polymers, 12(9), 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092170









