Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review
Abstract
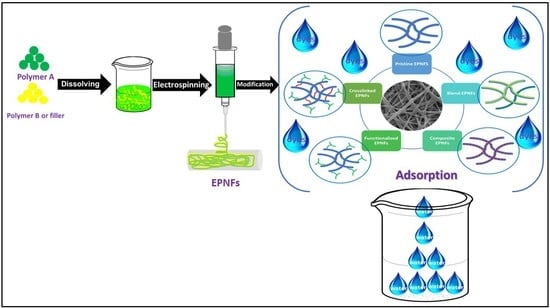
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of EPNFs
3. Modification of Polymer Nanofibers
3.1. One-Step Modification
3.1.1. Blending with Other Polymers
3.1.2. Incorporating Nanomaterials
3.2. Post-Treatment Methods
3.2.1. Wet Chemistry
3.2.2. Surface Grafting
3.2.3. Surface Coating
3.2.4. Plasma
4. Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Nanofibers for the Adsorption of Dyes
4.1. Effect of Physio-Chemical Properties of Nanofibers
4.1.1. Functional Groups
4.1.2. Surface Area and Porosity
4.1.3. Hydrophilicity/Hydrophobicity of Nanofibers
4.2. Effect of Dye Nature
4.3. Effect of Operating Conditions of Adsorption
4.3.1. pH Effect
4.3.2. Nanofibers Dosage
4.3.3. Contact Time
4.3.4. Initial Dye Concentration
4.3.5. Temperature
5. Adsorption Mechanism of Dyes onto Nanofiber Mats
6. Types of EPNFs as Adsorbent for the Removal of Dyes
6.1. Homopolymers-Based-EPNFs as Adsorbent for Dyes Removal
6.2. EPNFs Blends as Adsorbent for Dyes Removal
6.3. Crosslinked EPNFs as Adsorbent for Dyes Removal
6.4. Functionalized EPNFs as Adsorbent for Dyes Removal
6.5. EPNFs Based on Composites Polymers as an Adsorbent for Dye Removal
6.5.1. EPNFs/Clay Nanocomposites
6.5.2. EPNFs/Carbon Nanomaterials Nanocomposites
6.5.3. EPNFs/Silica Nanocomposites
6.5.4. EPNFs/Metal Oxides Nanocomposites
6.5.5. EPNFs/MOFs Nanocomposites
6.5.6. EPNFs/Microorganisms Composite for Dyes Removal
7. EPNFs-Based Carbon Nanofibers as Adsorbents for Dyes Removal
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nomenclature | Abbreviation |
| Acetic acid | AcOH |
| Acid blue 113 | AB-113 |
| Acid blue 117 | AB-117 |
| Acid blue 41 | AB-41 |
| Acid red 252 | AR-252 |
| Alternating current | AC |
| Amaranth | AM |
| Amidoximated polyacrilonitrile | APAN |
| Amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile | AOPAN |
| Azobisisobutyronitrile | AIBN |
| Basic blue 41 | BB-41 |
| Basic fuschin | BF |
| Basic violet 14 | BV-14 |
| Benzoxazine | P(BA-a) |
| Beta-cyclodextrin | β-CD |
| Brilliant blue | Bb |
| Calcium alginate | Ca-Alg |
| Carboxymethyl-b-cyclodextrin | CM-β-CD |
| Chitosan | CA |
| Chitosan | CS |
| Chitosan/Poly (vinyl alcohol) | CA/PVA |
| Congo red | CR |
| Crystal violet | CV |
| Deacetylated cellulose acetate | DCA |
| Dichloromethane | DCM |
| Diethylenetriamine | DETA |
| Diethylenetriamine | DETA |
| Dimethyl formamide | DMF |
| Direct current | DC |
| Direct red 23 | DR-23 |
| Direct red 80 | DR-80 |
| Electrospun polymer nanofibers | EPNFs |
| Epichlorohydrin | EPI |
| Ethanol | EtOH |
| Ethylene diamine | EDA |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic | EDTA |
| Fast green fcf | FG FCF |
| Flow rate | F. R |
| Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy | FTIR |
| Freundlich model | F |
| Gelatin | Gel |
| Glutaraldehyde | GA |
| Graphene | Gr |
| Graphene oxide | GO |
| Hinokitiol | HT |
| Humic acid | HA |
| Hyperbranched polyethylenimine | HPEI |
| Indigo carmine | IC |
| Intraparticle diffusion | IPD |
| Langmuir model | L |
| Layered double hydroxide | LDH |
| Malachite green | MG |
| Maximum adsorption capacity | Qmax |
| Mercaptopropionic acid | MPA |
| Metal-organic-frameworks | MOFs |
| Methyl orange | MO |
| Methylene blue | MB |
| Methyltrichlorosilane | MTS |
| Molybdenum disulfide | MoS2 |
| Nanoparticles | NPs |
| Nylone 6 | N-6 |
| Oxidized chitosan | OCS |
| Oxidized multiwall carbon nanotubes | MWCNTs-COOH |
| Oxime | OX |
| Poly ((butylene succinate-co-terephthalate)-co-serinolTerephthalate) | PBSST |
| Poly ([2- (methacryloyloxy)-ethyl] trimethyl ammonium chloride) | PMETAC |
| Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) | PLGA |
| Poly (l-lactic acid) | PLLA |
| Poly (N-Isopropyl acrylamide-co-Methacrylic acid) | P(NIAPM-co-MAA) |
| Poly (N-Isopropyl acrylamide-co-β-cyclodextrin) | P(NIPAM-co-βCD) |
| Poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile) | Poly(St-co-AN) |
| Poly (vinyl alcohol) | PVA |
| Poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) | PDMAEMA |
| Poly(amidoamine) | PAMAM |
| Poly(arylene ether nitrile)(PEN) | PAEN |
| Poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) | PBST |
| Poly(hexamethylene guanidine) | PHMG |
| Poly(hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin) | P(HPβCD) |
| Poly(methacrylic acid) | PMAA |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) | P(MMA-co-AA) |
| Poly(propylene imine) | PPI |
| Poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) | PBGL |
| Polyacrylamide | PAM |
| Polyacrylonitrile | PAN |
| Polyamide | PA |
| Polyamide 6 | PA6 |
| Polyaniline | PANI |
| Polycaprolactone | PCL |
| Polydopamine | PDA |
| Polyether sulfone | PES |
| Polyethylene oxide | PEO |
| Polyethylene terephthalate | PET |
| Polyethyleneimine | PEI |
| Polymer of intrinsic microporosity | PIM-1 |
| Polymethyl methacrylate | PMMA |
| Polypyrrole | PPy |
| Polystyrene | PS |
| Polyurethane | PU |
| Polyvinyl acetate | PVAc |
| Polyvinyl chloride | PVC |
| Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | PVP |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | PVDF |
| Ponceau 4R | P4R |
| Ponceau s | P-s |
| Pseudo first order model | PFO |
| Pseudo second order model | PSO |
| P-toluenesulfonic acid | pTSA |
| Pullulan | Pu |
| Reactive black 5 | RB-5 |
| Reactive blue 180 | RR-180 |
| Reactive red | RR |
| Redlich-Peterson model | R-P |
| Reduced graphene oxide | rGO |
| Rhodamine B | RhB |
| Safranin T | ST |
| Sericin | SS |
| Sodium alginate | Na-Alg |
| Sodium styrene sulfonate | SSNa |
| Sulfonated polysulfone | SPES |
| Sunset yellow fcf | SY FCF |
| Tectomer | TM |
| Tetraethyl orthosilicate | TEOS |
| Thiol-functionalized polyvinyl alcohol | PVA-SH |
| Tip-collector-distance | TCD |
| Titanium dioxide | TiO2 |
| Triethylenetetramine | TETA |
| Volatage | V |
| X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy | XPS |
| Zeolite | Zeo |
| Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks | ZIF |
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Dong, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, N.; Liu, J. Sulfonated halloysite nanotubes/polyethersulfone nanocomposite membrane for efficient dye purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrelkas, F.; Azizi, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Benhammou, A.; Pons, M.N. Treatment of textile dye effluents using coagulation-flocculation coupled with membrane processes or adsorption on powdered activated carbon. Desalination 2009, 235, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chen, M.L. Treatment of textile wastewater by-chemical methods for reuse. Water Res. 1997, 31, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Ng, H.Y.; You, S.; Teixeira, J.A. Microbial degradation of dyes: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehorek, A.; Tauber, M.; Gübitz, G. Application of power ultrasound for azo dye degradation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayodhya, D.; Veerabhadram, G. A review on recent advances in photodegradation of dyes using doped and heterojunction based semiconductor metal sulfide nanostructures for environmental protection. Mater. Today Energy. 2018, 9, 83–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Jegal, J. Treatment of dye aqueous solutions using nanofiltration polyamide composite membranes for the dye wastewater reuse. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 76, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z. i. H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.S.; Li, C.W.; Nguyen, N.C.; Nguyen, H.T. A comprehensive review: Electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85495–85514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Yap, C.C.; He, J.; Chen, C.; Wong, S.Y.; Li, X. Electrospinning: A facile technique for fabricating functional nanofibers for environmental applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. Nanocomposite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Environmental Remediation. Materials 2014, 7, 1017–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R. Structural design and environmental applications of electrospun nanofibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 137, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Frey, M.W. Electrospun Nanofibers for Chemical Separation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereao, O.K.; Bode-Aluko, C.; Ndayambaje, G.; Fatoba, O.; Petrik, L.F. Electrospinning: Polymer Nanofibre Adsorbent Applications for Metal Ion Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jian, S.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, S.; Fang, H.; Song, Y.; Duan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H. Nanofibers with diameter below one nanometer from electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4794–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleny, J. The role of surface instability in electrical discharges from drops of alcohol and water in air at atmospheric pressure. J. Franklin Inst. 1935, 219, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2012, 7, 155892501200700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental investigation of the governing parameters in the electrospinning of polymer solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.D.; Li, M.M.; Duvail, J.L.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yin, H.L. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Al-Zeghayer, Y.; Ahmed Ali, F.A.; Haider, A.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Imran, M.; Aijaz, M.O. Highly aligned narrow diameter chitosan electrospun nanofibers. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SalehHudin, H.S.; Mohamad, E.N.; Mahadi, W.N.L.; Muhammad Afifi, A. Multiple-jet electrospinning methods for nanofiber processing: A review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardick, O.; Stevens, B.; Bracewell, D.G. Nanofibre fabrication in a temperature and humidity controlled environment for improved fibre consistency. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrostat. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning of nanofibers with a conical wire coil. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varesano, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Mazzuchetti, G.; Tonin, C.; Comotto, R. Multi-jet nozzle electrospinning on textile substrates: Observations on process and nanofibre mat deposition. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, I.C.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Okamoto, A.; Chu, B. Electro-spinning and electro-blowing of hyaluronic acid. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Jing, X. Preparation of core-sheath composite nanofibers by emulsion electrospinning. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L. Coaxial electrospinning and emulsion electrospinning of core-shell fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Xin, B.; Xu, Y. Roles of Coaxial Spinneret in Taylor Cone and Morphology of Core-Shell Fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 17310–17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ni, C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Preparation of multilayer biodegradable nanofibers by triaxial electrospinning. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Triaxial electrospun nanofiber membranes for controlled dual release of functional molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8241–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkasaby, M.; Hegab, H.A.; Mohany, A.; Rizvi, G.M. Modeling and optimization of electrospinning of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabadi, S.M.S.; Kheradmand, A.; Montazeri, V.; Ziaee, H. Effects of process and ambient parameters on diameter and morphology of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2015, 57, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, I.H.; Bea, G.N. Optimization of the electrospinning conditions for preparation of nanofibers from polyvinylacetate (PVAc) in ethanol solvent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasouri, K.; Shoushtari, A.M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M. Evaluation of effective electrospinning parameters controlling polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers surface morphology via response surface methodology. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, M. Optimization of Electrospinning Parameters to Fabricate Aligned Nanofibers for Neural Tissue Engineering—CORE Reader. Master’s Thesis, National Institute of Technology Rourkela, Rourkela, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: Processing optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. Alignment and optimization of nylon 6 nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, T.; Anandhan, S. Electrospinning of non-woven poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) nanofibrous webs for corrosive chemical filtration: Process evaluation and optimization by Taguchi and multiple regression analyses. J. Electrostat. 2015, 73, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlou, H.M.; Sadollah, A.; Ang, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Talebian, S.; Ghadimi, A. Prediction and optimization of electrospinning parameters for polymethyl methacrylate nanofiber fabrication using response surface methodology and artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi Abdolmaleki, A.; Zilouei, H.; Nouri Khorasani, S.; Abdolmaleki, A. Optimization and characterization of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers as a phenol adsorbent via response surface methodology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; Agend, F.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Sharifi-Sanjani, N.; Madani, M. Prediction of nanofiber diameter and optimization of electrospinning process via response surface methodology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, S.; Balme, S.; Narayana Kalkura, S.; Miele, P.; Bohatier, C.P.; Bechelany, M. Various Techniques to Functionalize Nanofibers. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 347–372. [Google Scholar]
- Kurusu, R.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Surface modification to control the water wettability of electrospun mats. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 249–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Kolahchi, A.; Ajji, A.; Carreau, P.J. Enhancing hydrophilicity of polyethylene terephthalate surface through melt blending. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F. fang; Zhang, D.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. Polydopamine-assisted deposition of polypyrrole on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers for bidirectional removal of cation and anion dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiquette, D.; Pellerin, C. Miscible and core-sheath PS/PVME fibers by electrospinning. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, M.; Shi, Y.; Cao, D. Super hydrophilic poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) composite fibrous mats with improved mechanical properties prepared via electrospinning process. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.T.; Zhu, X.Y.; Liu, Q.Q. In Vitro Degradation of Electrospun Fiber Membranes of PCL/PVP Blends. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 332, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Functionalized polyethersulfone nanofibrous membranes with ultra-high adsorption capacity for organic dyes by one-step electrospinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, M.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Arami, M.; Takhtkuse, N.; Rezaei, B. Fabrication of electrospun polyamide-6/chitosan nanofibrous membrane toward anionic dyes removal. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, H.; He, A.; Jia, B.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Q.; Han, C.C. A novel carrier of radionuclide based on surface modified poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanofibrous membrane. Polymer 2010, 51, 3344–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nie, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, Y. Bilayer porous scaffold based on poly-(ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous membrane and gelatin sponge for favoring cell proliferation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakamada, Y.; Ohgushi, N.; Fujimura-Kondo, N.; Matsuda, T. Electrospun poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) and its alkali-treated meshes: Their water wettability and cell-adhesion potential. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Hota, G. Synthesis of novel surface functionalized electrospun PAN nanofibers matrix for efficient adsorption of anionic CR dye from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5301–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horzum, N.; Shahwan, T.; Parlak, O.; Demir, M.M. Synthesis of amidoximated polyacrylonitrile fibers and its application for sorption of aqueous uranyl ions under continuous flow. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasreen, S.A.A.N.; Sundarrajan, S.; Nizar, S.A.S.; Balamurugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Advancement in electrospun nanofibrous membranes modification and their application in water treatment. Membranes 2013, 3, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.; Gopal, R.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Plasma-induced graft copolymerization of poly(methacrylic acid) on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber membrane. Langmuir 2007, 23, 13085–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Fan, T. Hydrophilic surface modification of DPVC nanofibrous membrane by free-radical graft polymerization. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Olya, M.E.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Zarinabadi, E. Grafting of polyamidoamine dendrimer on polyacrylonitrile nanofiber surface: Synthesis and optimization of anionic dye removal process by response surface methodology method. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 147, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, T.; Yan, X.; Wang, X. Chitosan coated polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous mat for dye adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrini, K.; Rahimi, A.A.; Alihosseini, F.; Fashandi, H. Highly efficient dye adsorbent based on polyaniline-coated nylon-6 nanofibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, J.; Wang, R.; Jiao, T.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Q. Facile preparation of self-assembled polydopamine-modified electrospun fibers for highly effective removal of organic dyes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C. In situ synthesis of MnO2 coated cellulose nanofibers hybrid for effective removal of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Pinho, E.D.; Faria, S.; Pashkuleva, I.; Marques, A.P.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Surface modification of electrospun polycaprolactone nanofiber meshes by plasma treatment to enhance biological performance. Small 2009, 5, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Jia, L.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Plasma-etched electrospun nanofiber membrane as adsorbent for dye removal. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 132, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Botelho, G.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Ribelles, J.L.G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Influence of oxygen plasma treatment parameters on poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun fiber mats wettability. Prog. Org. Coatings 2015, 85, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, S.; Binagag, F.F.; Haider, A.; Mahmood, A.; Shah, N.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Khan, S.U.D.; Ramay, S.M. Adsorption kinetic and isotherm of methylene blue, safranin T and rhodamine B onto electrospun ethylenediamine-grafted-polyacrylonitrile nanofibers membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Binagag, F.F.; Haider, A.; Al-Masry, W.A. Electrospun oxime-grafted-polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane and its application to the adsorption of dyes. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, L.; Bao, J.; He, C.; Zhao, W.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. Positively-charged polyethersulfone nanofibrous membranes for bacteria and anionic dyes removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Shi, Z.; Ji, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. One-step electrospinning of negatively-charged polyethersulfone nanofibrous membranes for selective removal of cationic dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Montazerghaem, L.; Olya, M.E. Preparation of Porous Nanofibers from Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile/Polyvinylidene Fluoride Composite Nanofibers by Inexpensive Salt Using for Dye Adsorption. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3550–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wang, R.; Yin, J.; Jiao, T.; Huang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Q. Fabrication and highly efficient dye removal characterization of beta-cyclodextrin-based composite polymer fibers by electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Lou, T.; Yan, X.; Long, Y. ze; Cui, G.; Wang, X. Fabrication of pure chitosan nanofibrous membranes as effective absorbent for dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, F. Fabrication of eco-friendly nanofibrous membranes functionalized with carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin for efficient removal of methylene blue with good recyclability. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37715–37723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Zhan, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Turng, L.S. Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from an Aqueous Solution Using Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Membranes Modified by Polydopamine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Shen, L.; Hong, G.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hsiao, B.S. Micro-nano structure poly(ether sulfones)/poly(ethyleneimine) nanofibrous affinity membranes for adsorption of anionic dyes and heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Y.E.; Satilmis, B.; Uyar, T. Crosslinked PolyCyclodextrin/PolyBenzoxazine electrospun microfibers for selective removal of methylene blue from an aqueous system. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 119, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Guan, X.; Ren, E.; Lin, S.; Lan, J. Fabrication of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 functional polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous mats for dye removal. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Adsorption of anionic MO or cationic MB from MO/MB mixture using polyacrylonitrile fiber hydrothermally treated with hyperbranched polyethylenimine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Deuber, F.; Petrozzi, S.; Federer, L.; Aliabadi, M.; Shahraki, F.; Adlhart, C. Efficient dye adsorption by highly porous nanofiber aerogels. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 547, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Oveisi, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M. Synthesis of pearl necklace-like ZIF-8@chitosan/PVA nanofiber with synergistic effect for recycling aqueous dye removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasian, A.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Olya, M.E. Tectomer grafted nanofiber: Synthesis, characterization and dye removal ability from multicomponent system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi Mohammad Soltan, F.; Hajiani, M.; Haji, A. Nylon-6/poly(propylene imine) dendrimer hybrid nanofibers: An effective adsorbent for the removal of anionic dyes. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Qi, S.; Huan, C.; Zhan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Xu, G. Petal-like molybdenum disulfide loaded nanofibers membrane with superhydrophilic property for dye adsorption. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, N.O.; Celebioglu, A.; Tümtaş, Y.; Uyar, T.; Tekinay, T. Reusable bacteria immobilized electrospun nanofibrous webs for decolorization of methylene blue dye in wastewater treatment. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32249–32255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Ju, J.; Tan, Y.; Hao, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Sui, K. Controlled synthesis of sodium alginate electrospun nanofiber membranes for multi-occasion adsorption and separation of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuyue, J.; Dongyan, T.; Jing, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhaojie, S. Crosslinked electrospinning fibers with tunable swelling behaviors: A novel and effective adsorbent for Methylene Blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Tonetti, C.; Jannoke, L. Study of Methylene Blue adsorption on keratin nanofibrous membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Song, Y. Environmentally friendly gelatin/β-cyclodextrin composite fiber adsorbents for the efficient removal of dyes from wastewater. Molecules 2018, 23, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Tang, D.; Peng, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, X. β-Cyclodextrin modified electrospinning fibers with good regeneration for efficient temperature-enhanced adsorption of crystal violet. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaúque, E.F.C.; Dlamini, L.N.; Adelodun, A.A.; Greyling, C.J.; Ngila, J.C. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers functionalized with EDTA for adsorption of ionic dyes. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 100, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Ghane-Karade, A. Dye removal from wastewater by the cross-linked blend nanofiber and homogenous surface diffusion modeling. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Abdi, J. Preparation of mesoporous polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/silica composite nanofiber and dye removal from wastewater. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, S100–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.; Atassi, Y. Adsorption of methylene blue onto electrospun nanofibrous membranes of polylactic acid and polyacrylonitrile coated with chloride doped polyaniline. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahalkeh, F.; Habibi juybari, M.; Zafar Mehrabian, R.; Ebadi, M. Removal of Brilliant Red dye (Brilliant Red E-4BA) from wastewater using novel Chitosan/SBA-15 nanofiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.T.M.; Chai, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiu, C.Y.; Tsai, S.L.; Chang, Y.K. Removal of cationic dye waste by nanofiber membrane immobilized with waste proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3873–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, J.T.; Orlando, R.M.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Pinzón-García, A.D.; Rodrigues, G.D. Polymer-bixin nanofibers: A promising environmentally friendly material for the removal of dyes from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.F.; Ma, T.Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Li, J.Q.; Yu, Y.; Chu, L. ling 3D superhydrophilic polypyrrole nanofiber mat for highly efficient adsorption of anionic azo dyes. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Ibupoto, A.S.; Khatri, M.; Mahar, F.K.; Brohi, R.Z.; Kim, I.S. Highly efficient and robust electrospun nanofibers for selective removal of acid dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 244, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qassar Bani Al-Marjeh, R.; Atassi, Y.; Mohammad, N.; Badour, Y. Adsorption of methyl orange onto electrospun nanofiber membranes of PLLA coated with pTSA-PANI. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 37282–37295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wiener, J.; Zhu, G. Langmuir isotherm models applied to the sorption of acid dyes from effluent onto polyamide nanofibers. Autex Res. J. 2013, 13, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J. Preparation and Properties of Electrospun Polyethersulfone Membranes with its Sulfonated Derivative. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2013, 52, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Venkateswaran, S.; Hsiao, B.S. Ultra-fine electrospun nanofibrous membranes for multicomponent wastewater treatment: Filtration and adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Khatri, M.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun Zein Nanofiber as a Green and Recyclable Adsorbent for the Removal of Reactive Black 5 from the Aqueous Phase. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4340–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De A., B.; Barbosa, J.; dos Santos, M.R.; de Oliveira, H.P. Electrospun Fibers of Copolymers for the Removal of Ionic Dyes: The Influence of Processing Variables. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, O.; Guven, I.; Özcan, F.; Ertul, S.; Bayrakci, M. Humic-makeup approach for simultaneous functionalization of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers during electrospinning process, and dye adsorption study. Soft Mater. 2016, 14, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Olya, M.E.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Preparation and adsorption behavior of diethylenetriamine/polyacrylonitrile composite nanofibers for a direct dye removal. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.M.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Hashem, F.S.; Moussa, N.A. Surface Modified of Cellulose Acetate Electrospun Nanofibers by Polyaniline/β-cyclodextrin Composite for Removal of Cationic Dye from Aqueous Medium. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2057–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.L.; Wei, Y.M. Preparation of PAN/PAMAM blend nanofiber mats as efficient adsorbent for dye removal. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sellaoui, L.; Dotto, G.L.; Lamine, A. Ben; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Hanafy, H.; Belmabrouk, H.; Netto, M.S.; Erto, A. Interpretation of the adsorption mechanism of Reactive Black 5 and Ponceau 4R dyes on chitosan/polyamide nanofibers via advanced statistical physics model. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Santos, J.M.N.; Tanabe, E.H.; Bertuol, D.A.; Foletto, E.L.; Lima, E.C.; Pavan, F.A. Chitosan/polyamide nanofibers prepared by Forcespinning® technology: A new adsorbent to remove anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Yu, M.; Li, L.; Li, J. Polyethylenimine nanofibrous adsorbent for highly effective removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Sci. China Mater. 2016, 59, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Bao, J.; Xie, Y.; He, M.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; He, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Nanofibrous membranes with surface migration of functional groups for ultrafast wastewater remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13359–13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, B.L.; Urbano, B.F.; Sánchez, J. Water-soluble and insoluble polymers, nanoparticles, nanocomposites and hybrids with ability to remove Hazardous inorganic pollutants in water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miraftab, M.; Saifullah, A.N.; Çay, A. Physical stabilisation of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibres: Comparative study on methanol and heat-based crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1943–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, Y.; Ullah, A.; Boluk, Y.; Wu, J. Preparation and characterization of thermally crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/feather keratin nanofiber scaffolds. Mater. Des. 2017, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, K.C.S.; Alves, T.L.M.; Borges, C.P. Poly(vinyl alcohol) films crosslinked by glutaraldehyde under mild conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destaye, A.G.; Lin, C.K.; Lee, C.K. Glutaraldehyde vapor cross-linked nanofibrous PVA mat with in situ formed silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4745–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paipitak, K.; Pornpra, T.; Mongkontalang, P.; Techitdheer, W.; Pecharapa, W. Characterization of PVA-chitosan nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Eng. Proc. 2011, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Gu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, C. Electrospun starch nanofibers: Recent advances, challenges, and strategies for potential pharmaceutical applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiturong, P.; Sirithunyalug, B.; Eitsayeam, S.; Asawahame, C.; Tipduangta, P.; Sirithunyalug, J. Preparation of glutinous rice starch/polyvinyl alcohol copolymer electrospun fibers for using as a drug delivery carrier. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.S.; Behzad, T.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Bagheri, R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Pierini, F. Theoretical and experimental study of the stiffness of electrospun composites of poly(vinyl alcohol), cellulose nanofibers, and nanohydroxy apatite. Cellulose 2018, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Aytac, Z.; Umu, O.C.O.; Dana, A.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. One-step synthesis of size-tunable Ag nanoparticles incorporated in electrospun PVA/cyclodextrin nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costoya, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Electrospun fibers of cyclodextrins and poly(cyclodextrins). Molecules 2017, 22, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Runjun, S.; Yan, F.; Honghong, W.; Hao, D.; Chengkun, L. Preparation, characterization and kinetics study of chitosan/PVA electrospun nanofiber membranes for the adsorption of dye from water. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, E.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Mehrani, Z.; Asgharinezhad, A.A. The efficient removal of methylene blue from water samples using three-dimensional poly (vinyl alcohol)/starch nanofiber membrane as a green nanosorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35071–35081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, F.; Lu, G.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Q. Preparation of PEI nanofiber membrane based on in situ and solution crosslinking technology and their adsorption properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.; He, X.; Qi, B.; Zeng, G.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Cui, F. Ultrahigh adsorption capacity of anionic dyes with sharp selectivity through the cationic charged hybrid nanofibrous membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qi, P.; Ju, J.; Wang, Q.; Hao, L.; Wang, R.; Sui, K.; Tan, Y. Gelatin/alginate composite nanofiber membranes for effective and even adsorption of cationic dyes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z. Modified poly(vinyl alcohol)-triethylenetetramine nanofiber by glutaraldehyde: Preparation and dye removal ability from wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 20076–20083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Preparation of molecularly imprinted sericin/poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun fibers for selective removal of methylene blue. Chem. Res. Chinese Univ. 2017, 33, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, C. Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin-based electrospun nanofiber membranes for highly efficient adsorption and separation of methylene blue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26649–26657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C. Water-insoluble sericin/β-cyclodextrin/PVA composite electrospun nanofibers as effective adsorbents towards methylene blue. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Talebian, S.; Lee, J.J.L.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Effect of deacetylation on property of electrospun chitosan/PVA nanofibrous membrane and removal of methyl orange, Fe(III) and Cr(VI) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Peng, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Lou, T. Electrospun cellulose acetate/P(DMDAAC-AM) nanofibrous membranes for dye adsorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GHANI, M.; REZAEI, B.; GHARE AGHAJI, A.; ARAMI, M. Novel Cross-linked Superfine Alginate-Based Nanofibers: Fabrication, Characterization, and Their Use in the Adsorption of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 35, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Wen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y. Electrospinning preparation of β-cyclodextrin/glutaraldehyde crosslinked PVP nanofibrous membranes to adsorb dye in aqueous solution. Chem. Res. Chinese Univ. 2014, 30, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z. Preparation of PVA-chitosan blend nanofiber and its dye removal ability from colored wastewater. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, M.; El-Aassar, M.; Hassan, H. Adsorption Profile of Basic Dye onto Novel Fabricated Carboxylated Functionalized Co-Polymer Nanofibers. Polymers 2016, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Lu, G.; Song, Y.; Li, Y. Preparation of amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous adsorbents for the extraction of copper(II) and lead(II) ions and dye from aqueous media. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Chizari Fard, G.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Mirjalili, M.; Mokhtari Shourijeh, Z. Surface modification of electrospun PAN nanofibers by amine compounds for adsorption of anionic dyes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10333–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hota, G. Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye by functionalized electrospun PAN nanofibers membrane. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z. Preparation of aminated nanoporous nanofiber by solvent casting/porogen leaching technique and dye adsorption modeling. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 65, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Langari, S.; Montazerghaem, L.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of porous aminated PAN/PVDF composite nanofibers by electrospinning: Characterization and Direct Red 23 removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Olya, M.E.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of polyacrylonitrile/polyamidoamine composite nanofibers using electrospinning technique and their dye removal capacity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, C.; Hou, T.; Cai, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, M. Polyhexamethylene guanidine functionalized chitosan nanofiber membrane with superior adsorption and antibacterial performances. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 145, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, D.; Li, F. Rapid, Selective Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Durable Nanofibrous Membranes. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Yu, J.; Li, F. Biodegradable poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) nanofibrous membranes functionalized with cyclodextrin polymer for effective methylene blue adsorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108240–108246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satilmis, B.; Budd, P.M.; Uyar, T. Systematic hydrolysis of PIM-1 and electrospinning of hydrolyzed PIM-1 ultrafine fibers for an efficient removal of dye from water. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 121, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, L.; Belchinskaya, L. Adsorption of Industrial Pollutants by Natural and Modified Aluminosilicates. In Clays, Clay Minerals and Ceramic Materials Based on Clay Minerals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Vossoughi, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Sadrzadeh, M. Clay-based electrospun nanofibrous membranes for colored wastewater treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.L.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Shariful, M.I.; Amalina, M.A. Fabrication of PMMA/zeolite nanofibrous membrane through electrospinning and its adsorption behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Li Lee, J.J.; Joo, T.C.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Adsorption study of methyl orange by chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 191, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaran, S.P.; Reshmi, C.R.; Sagitha, P.; Manaf, O.; Sujith, A. Multifunctional graphene oxide loaded nanofibrous membrane for removal of dyes and coliform from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, K. Preparation and dye filtration property of electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate–calcium alginate/carbon nanotubes composite nanofibrous filtration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F. fang; Zhang, D.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Ultrasonication-assisted deposition of graphene oxide on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane and the adsorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.M.; Locilento, D.A.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Solution blow spun PMMA nanofibers wrapped with reduced graphene oxide as an efficient dye adsorbent. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9087–9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Wan, X.; He, S.; Yang, Q.; He, Y. Design of durable and efficient poly(arylene ether nitrile)/bioinspired polydopamine coated graphene oxide nanofibrous composite membrane for anionic dyes separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z. Preparation of nanofibrous metal-organic framework filter for rapid adsorption and selective separation of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, O.F.; Keskin, N.O.S.; Celebioglu, A.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Bacteria encapsulated electrospun nanofibrous webs for remediation of methylene blue dye in water. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, R.; Wang, W.; Jiao, T.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, W.; Qiu, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Q. Bioinspired Polydopamine Sheathed Nanofibers Containing Carboxylate Graphene Oxide Nanosheet for High-Efficient Dyes Scavenger. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4948–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailek, N.; Daranarong, D.; Punyodom, W.; Molloy, R.; Worajittiphon, P. Crosslinking assisted fabrication of ultrafine poly(vinyl alcohol)/functionalized graphene electrospun nanofibers for crystal violet adsorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Imayathamizhan, N.; Muthumanickkam, A. Kinetic and isotherm studies on adsorption of methylene blue using polyacrylonitrile/hydroxyl group functionalized multiwall carbon nanotube multilayered nanofibrous composite. J. Elastomers Plast. 2020, 009524431989728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzain, A.A.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Hashem, F.S.; Mohamed, F.M.; Ali, A.S.M. Removal of methylene dye using composites of poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile) nanofibers impregnated with adsorbent materials. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Li, F.; Zhi, P. Adsorption of hazardous dyes indigo carmine and acid red on nanofiber membranes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Taha, A.A. Electrospun cyclodextrin-functionalized mesoporous polyvinyl alcohol/SiO2 nanofiber membranes as a highly efficient adsorbent for indigo carmine dye. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 385, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizari Fard, G.; Mirjalili, M.; Najafi, F. Hydroxylated α-Fe2O3 nanofiber: Optimization of synthesis conditions, anionic dyes adsorption kinetic, isotherm and error analysis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.N.; Rebia, R.A.; Saito, Y.; Kharaghani, D.; Khatri, M.; Tanaka, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, I.S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles attached to polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with hinokitiol as gluing agent for synergistic antibacterial activities and effective dye removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, C.; Jin, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, Q.; Gu, J.; Ou, M.; Xu, X. Development of a novel mixed titanium, silver oxide polyacrylonitrile nanofiber as a superior adsorbent and its application for MB removal in wastewater treatment. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. The pervasive chemistry of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, L.; Jiang, H.L. Metal–organic framework-derived porous materials for catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 362, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmi, H.W.; Ren, J.; North, B.; Mathe, M.; Bessarabov, D. Hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks: A review. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 128, 368–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Abney, C.; Lin, W. Enantioselective catalysis with homochiral metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, H.L.; Sun, L.B. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Basic Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8129–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, A.H.; Ahmad, N.; Younus, H.A.; Laypkov, A.; Verpoort, F. Metal-organic frameworks: Versatile heterogeneous catalysts for efficient catalytic organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6804–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrasheedy, A.; Nady, N.; Bassyouni, M.; El-Shazly, A. Metal Organic Framework Based Polymer Mixed Matrix Membranes: Review on Applications in Water Purification. Membranes 2019, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Meng, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. A new MOFs/polymer hybrid membrane: MIL-68(Al)/PVDF, fabrication and application in high-efficient removal of p-nitrophenol and methylene blue. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, B. Novel one step preparation of a 3D alginate based MOF hydrogel for water treatment. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 7202–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.T.; Peng, L.; Reeder, W.S.; Moosavi, S.M.; Tiana, D.; Britt, D.K.; Oveisi, E.; Queen, W.L. Rapid, Selective Heavy Metal Removal from Water by a Metal-Organic Framework/Polydopamine Composite. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Dong, M. Electrospinning Synthesis of ZIF-67/PAN Fibrous Membrane with High-capacity Adsorption for Malachite Green. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Sorption of malachite green on vinyl-modified mesoporous poly(acrylic acid)/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 149, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.G.; Ivanic, M.; Mohamed, A.; Uheida, A. Surface modified composite nanofibers for the removal of indigo carmine dye from polluted water. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24588–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadasivam, R.K.; Mohiyuddin, S.; Packirisamy, G. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Templated 2D Nanofibrous Mats: A platform toward practical applications for dye removal and bacterial disinfection. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6556–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Lv, W.; Du, M.; Zheng, Q. Morphological control of poly(vinylidene fluoride)@layered double hydroxide composite fibers using metal salt anions and their enhanced performance for dye removal. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46576–46588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chizari Fard, G.; Mirjalili, M.; Almasian, A.; Najafi, F. PAMAM grafted α-Fe2O3 nanofiber: Preparation and dye removal ability from binary system. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Yuan, W. A superhydrophobic poly(lactic acid) electrospun nanofibrous membrane surface-functionalized with TiO2 nanoparticles and methyltrichlorosilane for oil/water separation and dye adsorption. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 15823–15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZabihiSahebi, A.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Pishnamazi, M.; Askari, A.; Khosravi, R.; Irani, M. Synthesis of cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers for the removal of Cr(VI), As(V), Methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, E.; Agarwal, V.; Bradshaw, M.; Chen, X.; Smith, S.M.; Raston, C.L.; Swaminathan Iyer, K. Nitrate removal from liquid effluents using microalgae immobilized on chitosan nanofiber mats. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2682–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Kuhn, J.; Avrahami, R.; Tarre, S.; Beliavski, M.; Green, M.; Zussman, E. Encapsulation of bacterial cells in electrospun microtubes. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouabidi, Z.B.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zhang, Z. Immobilization of microbial cells for the biotreatment of wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, O.F.; Celebioglu, A.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Bacteria-immobilized electrospun fibrous polymeric webs for hexavalent chromium remediation in water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Keskin, N.O.; Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T.; Tekinay, T. Microalgae immobilized by nanofibrous web for removal of reactive dyes from wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5802–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamel, D.; Hassanin, A.H.; Ellethy, R.; Singer, G.; Abdelmoneim, A. Novel Bacteria-Immobilized Cellulose Acetate/Poly(ethylene oxide) Nanofibrous Membrane for Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- San Keskin, N.O.; Celebioglu, A.; Sarioglu, O.F.; Uyar, T.; Tekinay, T. Encapsulation of living bacteria in electrospun cyclodextrin ultrathin fibers for bioremediation of heavy metals and reactive dye from wastewater. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarioglu, O.F.; San Keskin, N.O.; Celebioglu, A.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Bacteria immobilized electrospun polycaprolactone and polylactic acid fibrous webs for remediation of textile dyes in water. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M.H. Fabrication of functionalized electrospun carbon nanofibers for enhancing lead-ion adsorption from aqueous solutions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.H. Functionalized electrospun carbon nanofibers for removal of cationic dye. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Newehy, M.H. Effective adsorption of Coomassie brilliant blue dye using poly(phenylene diamine)grafted electrospun carbon nanofibers as a novel adsorbent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 234, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Singh, M.; Bansal, V.; El-Newehy, M.H. Alkali-activated electrospun carbon nanofibers as an efficient bifunctional adsorbent for cationic and anionic dyes. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M.H. Synthesis of aminated electrospun carbon nanofibers and their application in removal of cationic dye. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 132, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A., M.; El-Newehy, M.H. In Situ Preparation of Novel Porous Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Polluted Water. Polymers 2020, 12, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Polymer | Avg. Mw (g/mol) | Concn (w/w%) | Solvent | Optimum Conditions for Fabricating Bead-Free Nanofibers | Avg. Diameter (nm) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | 130k | 7 | H2O | V = 25 kv, TCD = 5 cm, F. R = 0.1 mL/h | 510 | [44] |
| PAN | 100k | 10 | DMF | V = 25 kv, TCD = 20 cm, F. R = 1 mL/h | 88 | [45] |
| PVAc | 140k | 15 | EtOH | V = 15 kv, TCD = 10 cm, F. R = 0.06 mL/h | 700 | [46] |
| PVP | 360k | 13 | DMF | V = 15 kv, TCD = 20 cm, F. R = 0.25 mL/h | 172 | [47] |
| PCL | 80k | 10 | DCM/DMF 3:1 | V = 12 kv, TCD = 10 cm, F. R = 1 mL/h | 455 | [48] |
| Chitosan | 294k | 7 | AcOH | V = 17 kv, TCD = 16 cm, F. R = 1.6 mL/h | 250 | [49] |
| Nylon 6 | − | 20 | Formic acid | V = 15 kv, TCD = 8 cm, F. R = 0.2 mL/h | 800 | [50] |
| Poly (St-co-AN) | 2460k | 25 | n-Butanone | V = 12 kv, TCD = 23 cm, F. R = 0.2 mL/h | 880 | [51] |
| PMMA | 120k | 15 | DMF | V = 12 kv, TCD = 11.4cm, F. R = 2.36 mL/h | 177 | [52] |
| CA/PVA | 120k | 50/50 | AcOH | V = 22.5 kv, TCD = 15 cm, F. R = 1.99 mL/h | 11 | [53] |
| PA6 | 17k | 20 | Formic acid | V = 19 kv, TCD = 10 cm, F. R = 0.9 mL/h | 141 | [54] |
| Adsorbent | Dye Class | Dye Name | Temperature Range (K) | Process Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(NIPAM-co-βCD)/P(NIAPM-co-MAA) | Cationic | MB | 298–328 | Endothermic | [101] |
| P(NIPAM-co-MAA)/β-CD | Cationic | CV | 298–333 | Endothermic | [104] |
| DCA/PDA | Cationic | MB | 288–323 | Endothermic | [89] |
| PMETAC/PES | Anionic | CR | 298–318 | Endothermic | [83] |
| PAN-EDA | Anionic | CR | 303–323 | Endothermic | [67] |
| EDTA-EDA-PAN | Anionic | MO | 298–318 | Endothermic | [105] |
| Anionic | RR | Exothermic | |||
| sodium alginate | Cationic | MB | 288–218 | Exothermic | [100] |
| PES/PEI | Anionic | SY FCF | 278–323 | Endothermic | [90] |
| Keratin | Cationic | MB | 293–323 | Exothermic | [102] |
| gelatin/β-CD | Cationic | MB | 298–333 | Exothermic | [103] |
| PVA/CS/DETA/EDA | Anionic | DR-23 | 298–333 | Endothermic | [106] |
| PVA/CA/SiO2 | Anionic | DR-80 | 298–333 | Endothermic | [107] |
| Adsorbent | Dye | Adsorption Conditions | Qmax(mg/g) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T (°C) | Dosage (g/L) | Range conc (mg/L) | ||||||
| PMAA-co-PMMA | MV | 6 | 25 | − | 5–200 | 135.37 | PSO | L | [119] |
| Zein | RB5 | 2–6 | 25 | 8 | 20–200 | 18.18 | PSO | L | [118] |
| Chitosan | AB-113 | – | – | 0.66 | 50–250 | 1377 | PSO | L | [87] |
| Nylone-6 | AB-117 | 5.5 | 25 | 4 | 25–400 | 58.8 | PSO | F | [113] |
| polyamide 6 | AB-41 | − | 20 | 0.1 | 10 | 43.9 | – | L | [115] |
| PLLA | MB | – | – | 3.33 | 4–200 | 8.73 | PSO | L | [79] |
| Keratin | MB | 6 | 20 | 1 | 50–250 | 170 | PSO | L | [102] |
| SPES | MB | 6.8 | RT | 1 | 6 | 6.6 | PSO | L | [117] |
| pTSA-@PANIPLLA | MO | 6 | 25 | 1 | 50–600 | 377 | PFO | L | [114] |
| CS@PAN | AB-113 | – | 25 | – | 50–250 | 1708 | PSO | L | [73] |
| CS/PA | RB5 | 1 | 25 | 0.2 | 0–150 | 456.9 | PSO | L | [126] |
| P4R | 502.4 | ELV | |||||||
| P(β-CD)/PCL | MB | – | RT | 0.1 | – | 10.5 | PSO | – | [86] |
| P(MMA-AA)/PES | MB | 9 | – | 0.25 | 100–3000 μmol | 2257.8 | PSO | L | [62] |
| PANI@N-6 | MO | 1 | RT | – | – | 370 | – | – | [74] |
| PDA@CA | MB | 6.5 | 25 | 0.5 | 30–100 | 88.2 | PSO | L | [89] |
| HA@PAN | CV | 7 | 25 | 0.025 | 1–7.5 μmol | 81.6 | – | L | [121] |
| CS/PA | RB5 | 1 | 25 | 0.2 | 0–150 | 198.6 | – | L–F | [125] |
| P4R | 222.4 | ||||||||
| P(MMA-co-SSNa)@PES | MB | 3–10 | RT | 0.2 | 100–500 μmol | 625 | PSO | L | [128] |
| PPI-N6 | AR-252 | 4 | 25 | 0.6 | 12.5–100 | 158.73 | PSO | L | [97] |
| PPy@PVDF/PDA | MB | 13 | – | – | 30–200 | 370.4 | PSO | L | [58] |
| CR | 1 | 384.6 | |||||||
| m-PEI/PVDF | MO | 7 | 25 | 0.5 | 200–1000 | 633.3 | PSO | L | [127] |
| DETA@PAN | DR-80 | 2.1 | – | 0.044 | 20–100 | 1250 | PSO | L | [122] |
| PAN/PAMAM | MO | – | 30 | 3.33 | – | 120.77 | PSO | L | [124] |
| PAN/PVDF | BB-41 | 6 | 25 | 0.66 | 10–40 | 166.6 | PSO | L | [85] |
| CA-PANI/β-CD | MB | 8 | 25 | 0.64 | 50–70 | 49.51 | PSO | L | [123] |
| Adsorbent | Crosslinked Type | Dye | Adsorption Conditions | Qmax (mg/g) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T (°C) | Dos. (g/L) | Range conc (mg/L) | |||||||
| Na-Alg | CaCl2 | MB | 6 | 25 | 0.4 | 200–1500 | 2230 | PSO | L | [100] |
| P(NIPAM-co-β-CD)/P(NIAPM-co-MAA) | thermally | MB | 9 | 55 | 0.35 | 50–1400 | 1834.9 | PSO | L | [101] |
| P(HPβCD)/PBA-a | thermally | MB | − | − | 1 | 10–100 | 46.08 | PSO | L | [91] |
| P(NIPAM-co-MAA)/β-CD | thermally | CV | 9 | 55 | 0.35 | 50-900 | 1253.7 | PSO | L | [104] |
| PVA/CS/DETA/EDA | GA | DR-23 | 2.1 | 25 | 0.1 | 40–100 | 526.31 | PSO | L | [106] |
| Pu/PVA/PAA | thermally | MB | 11 | 25 | 1.33 | − | 383 | PSO | L | [94] |
| β-CD/PVP | GA | MO | 7 | 25 | 2.5 | 10–150 | 39.82 | − | L | [152] |
| Gel/β-CD | GA | MB | 8 | 25 | 1.25 | 5–100 | 47.4 | PSO | L | [103] |
| Gel/Ca-Alg | CaCl2 | MB | 6 | 25 | 0.4 | 50–900 | 1937 | PSO | L | [144] |
| PES/PEI | GA | SY FCF | 1 | 30 | 0.8 | 100-2000 | 1000 | PSO | L | [90] |
| FG FCF | 344.83 | |||||||||
| AM | 454.55 | |||||||||
| PVA–TETA | GA | DR-80 | 2.1 | 25 | 0.06 | 20–50 | 128.2 | PSO | L | [145] |
| DR-81 | 178.6 | |||||||||
| RR-180 | 181.8 | |||||||||
| Alg/PEO | CaCl2 | AR-14 | 1 | 25 | 4 | − | 17.9 | − | L | [151] |
| BB-41 | 9 | 17.3 | ||||||||
| PSSNa/PAA@PES | MBA | MB | 11 | − | 50–250 μmol | 119.65 | PSO | F | [84] | |
| PMETAC@PES | MBA | CR | 3 | 25 | − | 50-800μmol | 208 | − | L | [83] |
| SS/PVA | GA | MB | 7 | − | − | 40–450 | 223.21 | PSO | L | [146] |
| PEI/EPI/PAN | thermally | MO | − | 30 | - | - | 636.94 | − | L | [142] |
| PVA-CS | GA | DR-80 | 2.1 | 25 | 0.06 | 20-80 | 151 | PSO | L | [153] |
| DR-81 | 95 | |||||||||
| RR-180 | 114 | |||||||||
| PVA-CS | GA | CR | 6 | 25 | 6 | − | 358 | PSO | L | [140] |
| β-CD/PAA/citric acid | thermally | MB | 9 | 20 | 0.175 | 80–800 | 826.45 | PSO | L | [147] |
| PVA-ST | thermally | MB | 8.5 | 25 | 0.083 | 25–400 | 400 | PSO | L | [141] |
| SS/β-CD/PVA | thermally | MB | 8 | 20 | 0.175 | 20–200 | 187.97 | PSO | L | [148] |
| PVA-CS | GA | MO | − | − | 5 | 200–1000 | 183 | − | L | [149] |
| CA/P(DMDAAC-AM) | MBA | AB-172 | 25 | 0.1 | 20-120 | 192 | PSO | L | [150] | |
| PDA/PEI@PVA/PEI | GA | P-s | 7 | 25 | 0.5 | 50–1200 | 1180 | PSO | L | [143] |
| MB | 1290 | |||||||||
| Adsorbent | Dye | Adsorption Conditions | Qmax (mg/g) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | Ref | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T (°C) | Dosage (g/L) | Range Conc (mg/L) | |||||||
| EDA-g-PAN | MB | − | 25 | − | − | 94.07 | PSO | L | [81] | |
| ST | 110.62 | |||||||||
| RB | 138.69 | |||||||||
| OX-g-PAN | MB | − | 25 | − | − | 102.15 | PSO | L | [82] | |
| ST | 118.34 | |||||||||
| RB | 221.24 | |||||||||
| PAN-g-HPEI | MB | 10 | 25 | 1.66 | − | 161 | PSO | L | [93] | |
| MO | 5 | 194 | ||||||||
| Carboxylated poly(AN-co-St) | BV-14 | 6.2 | 25 | 2 | 0–100 | 67.11 | PSO | L | [154] | |
| PAN-COOH | MG | 5 | 35 | 0.5 | 100–500 | 1038 | PSO | L | [157] | |
| PCD-f-PBST | MB | − | 30 | 1.25 | 5–100 | 90.9 | PSO | L | [163] | |
| EDTA-PAN | MO | 7 | 25 | 2 | 10–300 | 90.15 | PSO | F | [105] | |
| 110 | ||||||||||
| RB | ||||||||||
| CM-β-CD-g-PBSST | MB | 9 | RT | − | 5–200 | 543.48 | PSO | L | [88] | |
| PAMAM-g-PAN-DETA | DR-80 | 3.5 | RT | 0.02 | 40–100 | 3333 | PSO | L | [72] | |
| DR-23 | 2500 | |||||||||
| PHMG-OCS-PVA | CR | − | 30 | 1 | − | 289 | PSO | F | [161] | |
| AOPAN | MO | 3 | 30 | − | 10–100 | 68.07 | PFO | L | [155] | |
| TETA-PPAN | DB-78 | 2.1 | 25 | 0.06 | 80–140 | 2500 | PSO | L | [158] | |
| TETA-PAN | DR-80 | 2.1 | RT | 0.012 | 40–100 | 5000 | PSO | L | [156] | |
| 5000 | ||||||||||
| DR-23 | ||||||||||
| EDA-PAN | CR | 3 | 30 | 0.5 | 10–70 | 130 | PSO | L | [67] | |
| DETA-PAN/PVDF | DR-23 | 2 | − | 0.044 | 20–50 | 685.63 | IPD | L | [159] | |
| PIM-1 | MB | − | − | 0.25 | 50–500 | 157 | − | L | [164] | |
| TM-PAN | DR-80 | 3.5 | RT | 0.033 | 40–100 | 1250 | PSO | L | [96] | |
| DR23 | 1111 | |||||||||
| PDA@PCL/PEO | MB | − | 25 | 0.3 | − | 14.8 | PSO | − | [75] | |
| MO | 60.2 | |||||||||
| PAN/PAMAM | DR80 | 2.1 | 25 | 0.033 | 40–100 | 1666.6 | PSO | L | [160] | |
| DR23 | 2000 | |||||||||
| Adsorbent | Dye | Adsorption Conditions | Qmax (mg/g) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ph | T (°C) | Dosage (g/L) | Range Conc (mg/L) | ||||||
| PMMA/zeo | MO | − | − | 10 | 30–100 | 95.33 | PSO | L | [167] |
| CS/PVA/Zeo | MO | 4 | − | − | 100–500 | 153 | PSO | F | [168] |
| PU/GO | MB | 12 | 30 | − | − | 109.88 | PSO | L | [169] |
| RB | 10 | 77.15 | |||||||
| PHB CaAlg/CMWCNT | Bb | − | 25 | 1 | 5–50 | 24.09 | PSO | F | [170] |
| PVDF/GO | MB | − | 30 | 0.1 | 30–200 | 621.1 | PSO | F | [171] |
| PMMA-rGO | MB | − | RT25 | 0.3 | − | 698.51 | PSO | L | [172] |
| PVA/PAA/GO-COOH@PDA | MB | − | 25 | 0.3 | 10 | 34.05 | PSO | − | [176] |
| PVA/Gr | CV | − | 25 | − | 1–10 | 10.96 | PSO | L | [177] |
| PAN/MWCNT-OH | MB | 10 | 1 | 10–30 | 8 | PSO | F | [178] | |
| P(St-co-AN)/CNTs | MB | 8 | − | − | 5–60 | 23.55 | PSO | L | [179] |
| Adsorbent | Dye | Adsorption Conditions | Qmax (mg/g) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T (°C) | Dosage (g/L) | Range Conc (mg/L) | ||||||
| PVA-SH/SiO2 | IC | 2 | 25 | 1 | 10–500 | 246.88 | PSO | R-P | [180] |
| AR-1 | 81.72 | PFO | |||||||
| PAN-Ti/Ag | MB | 8 | 25 | 1 | 5–210 | 155.4 | PSO | L | [184] |
| APAN/Fe3O4@3-MPA | IC | 5 | 23 | 1 | 5–100 | 154.5 | PFO | L | [199] |
| PVA/CS/SiO2 | DR-80 | 2 | RT | 0.06 | 15–30 | 322 | PSO | L | [107] |
| ZIF-67/PAN | MG | − | RT | 0.5 | 100–600 | 1305 | PSO | F | [197] |
| SiO2@PVA-CD | IC | 5.2 | RT | 1 | 90–720 | 495 | PSO | L | [181] |
| PAN/PEI-Fe | CR | − | RT | 1 | 20–60 | 77.51 | PSO | L | [200] |
| ZIF-8/PAN | MB | 11 | 30 | 0.25 | 15–100 | 120.48 | PSO | L | [92] |
| MG | 5 | 15–700 | 1666.6 | ||||||
| PVAc-TEOS@α-Fe2O3 | BR-46 | 8.5 | − | 0.035 | 20–60 | 946.28 | PSO | L | [182] |
| PVDF@CoAl-LDH | MO | 7 | 30 | 0.4 | 20–500 | 621.17 | PSO | L | [201] |
| PAMAM/α-Fe2O3 | DR-80 | 3 | − | 0.032 | 40–70 | 1428.5 | PSO | L | [202] |
| AR-18 | 1250 | ||||||||
| PAN-MoS2 | RhB | − | − | 3 | 20–1000 | 75.41 | PSO | L | [98] |
| PAA/SiO2 | MG | − | 30 | 1 | 5–300 | 220.49 | PSO | R-P | [198] |
| PLA@TiO2@MTS | MB | − | RT | − | 10–40 | 236.25 | − | − | [203] |
| CA/CS/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 | MB | 3 | − | 0.5 | − | 97.6 | PSO | L | [204] |
| CR | 74.2 | ||||||||
| ZIF-8@CS/PVA | MG | 7 | 25 | 0.03 | 10–40 | 1000 | PSO | L | [95] |
| ZnO-HT-PAN | RB-19 | − | 25 | 0.66 | 10–400 | 267.37 | PFO | L | [183] |
| RR-195 | 245.76 | ||||||||
| Polymer Nanofibers | Microorganisms | Dye | Dye Concentration (ppm) | Removal Efficiency (%) | Time | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polysulfone | Lysinibacillus sp. | RB-5 | 30 | 99.7 | 24 h | [208] |
| CA | Aeromonas eucrenophila, | MB | 20 | 95 | 24 h | [99] |
| polysulfone | microalgae | RB-5 | 10 | 72.97 | 14 day | [209] |
| RB-221 | 10 | 30.2 | ||||
| PVA | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | MB | 25 | 68 | 48 h | [175] |
| PEO | 25 | 69 | ||||
| CA/PEO | Bacillus paramycoides | MB | 20 | 87.39 | 48 h | [210] |
| CD | Lysinibacillus sp. NOSK | RB-5 | 30 | 82 | 24 h | [211] |
| PCL | Clavibacter michiganensis | STB G | 200 | 93.18 | 48 h | [212] |
| PLA | 200 | 93.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thamer, B.M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Moydeen A, M.; Rahaman, M.; El-Newehy, M.H. Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010020
Thamer BM, Aldalbahi A, Moydeen A M, Rahaman M, El-Newehy MH. Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleThamer, Badr M., Ali Aldalbahi, Meera Moydeen A, Mostafizur Rahaman, and Mohamed H. El-Newehy. 2021. "Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review" Polymers 13, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010020
APA StyleThamer, B. M., Aldalbahi, A., Moydeen A, M., Rahaman, M., & El-Newehy, M. H. (2021). Modified Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers and Their Nanocomposites as Nanoadsorbents for Toxic Dye Removal from Contaminated Waters: A Review. Polymers, 13(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010020