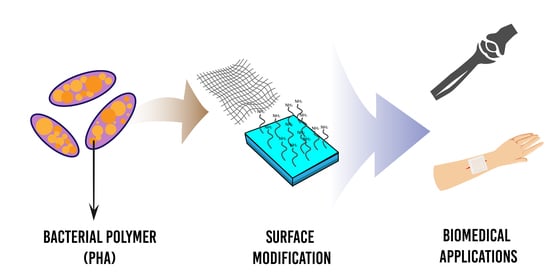
Surface-Modified Highly Biocompatible Bacterial-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate): A Review on the Promising Next-Generation Biomaterial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs)
2.1. Properties of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs)
2.2. P(3HB-co-4HB) Producing Bacteria
3. Synthesis of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) [P(3HB-co-4HB)]
3.1. Physical and Mechanical Properties of P(3HB-co-4HB)
3.2. Biodegradability of P(3HB-co-4HB)
3.3. Biocompatibility of P(3HB-co-4HB)
4. Surface Functionalisation of P(3HB-co-4HB)
4.1. Electrospinning
4.2. Aminolysis
4.3. Biomolecule Immobilisation
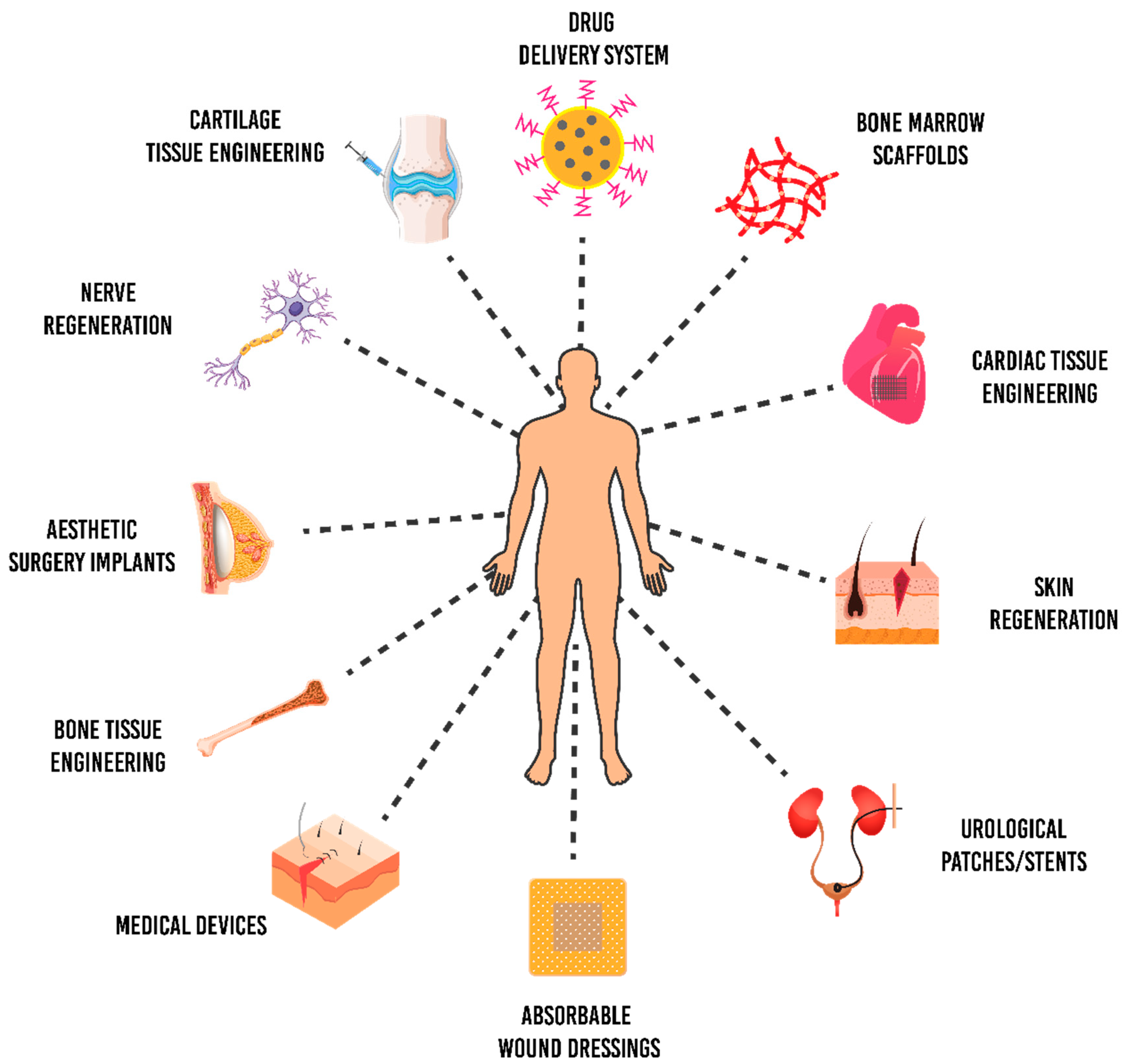
5. Biomedical Applications of P(3HB-co-4HB)
5.1. Cardiac Patch
5.2. Bone Grafts
5.3. Nerve Regeneration
5.4. Skin Grafts
5.5. Antimicrobial Scaffolds
5.6. Drug-Delivery System
6. Challenges and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, P.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roy, I. Novel cardiac patch development using natural biopolymers. ACS Symp. Ser. 2014, 1175, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hung, S.; Chou, E.; Wu, H.S. Review of polyhydroxyalkanoates materials and other biopolymers for medical applications. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2018, 15, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarali, S.; Marlinghaus, L.; Viebahn, R.; Lewis, H.; Ryadnov, M.G.; Groll, J.; Salber, J.; Roy, I. Activated polyhydroxyalkanoate meshes prevent bacterial adhesion and biofilm development in regenerative medicine applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, J.; Gupta, S. Bioplastics: Need for the future. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Alcântara, J.M.G.; Distante, F.; Storti, G.; Moscatelli, D.; Morbidelli, M.; Sponchioni, M. Current trends in the production of biodegradable bioplastics: The case of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 42, 107582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Salvador, A.; Alves, M.M.; Vicente, A.A. Factors affecting polyhydroxyalkanoates biodegradation in soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 182, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga-Valderrama, L.R.; Panchal, B.; Thomas, C.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roy, I. Biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates. In Biomaterials from Nature for Advanced Devices and Therapies; Reis, R.L., Neves, N., Eds.; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 337–383. [Google Scholar]
- Prados, E.; Maicas, S. Bacterial production of hydroxyalkanoates (PHA). Univ. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 4, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rathour, R.; Singh, R.; Sun, Y.; Pandey, A.; Gnansounou, E.; Lin, K.T.A.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Thakur, I.S. Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates: Opportunities, challenges, and prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, C.; Devaraj, S.; Meixner, K.; Anburajand, P.; Kathirvele, P.; Ravikumar, Y.; Zabeda, H.M.; Qi, X. Recent developments in polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production—A review. Biores. Technol. 2020, 306, 123132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Presti, D.; Montiell-Jarillo, G.; Carrera, J.; Suarez-Ojeda, M.E. Recovery of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from wastewater: A review. Biores. Technol. 2020, 297, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, K.; Perez-Zabaleta, M.; Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Cetecioglu, Z. Waste to bioplastics: How close are we to sustainable polyhydroxyalkanoates production? Waste Manag. 2021, 119, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, G. Engineering biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) for diversity and cost reduction. Metabol. Eng. 2020, 58, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigore, M.E.; Grigorescu, R.M.; Iancu, L.; Ion, R.-M.; Zaharia, C.; Andrei, E.R. Methods of synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates: A review. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.F.; Rizk, S.; Martin, D.P. Poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB): A new generation of resorbable medical devices for tissue repair and regeneration. Biomedizinische Technik 2013, 58, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanprateep, S.; Buasri, K.; Muangwong, A.; Utiswannakul, P. Biosynthesis and biocompatibility of biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, R.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Living cardiac patch: The elixir for cardiac regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoušková, O. Synthetic polymer scaffolds for soft tissue engineering. Physiol. Res. 2018, 67, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Slamovich, E.B.; Webster, T.J. Less harmful acidic degradation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) bone tissue engineering scaffolds through titania nanoparticle addition. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankaran, K.K.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Axially aligned 3D nanofibrous grafts of PLA–PCL for small diameter cardiovascular applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 1791–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, D.P.; Aguilar, L.E.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. A review on properties of natural and synthetic based electrospun fibrous materials for bone tissue engineering. Membranes 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathuriya, A.S.; Yakhmi, J.V. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biodegradable plastics and their applications. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L., Kharissova, O., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Jamil, N. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Current applications in the medical field. Front. Biol. 2016, 11, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Możejko-Ciesielska, J.; Kiewisz, R. Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates: Still fabulous? Microbiol. Res. 2016, 192, 217–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M. Biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Auspicious microbial macromolecules for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Contreras, A. Recent advances in the use of polyhydroyalkanoates in biomedicine. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinn, M.; Witholt, B.; Egli, T. Occurrence, synthesis and medical application of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2001, 53, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.A. From oil to bioplastics, a dream come true? J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griebel, R.; Smith, Z.; Merrick, J.M. Metabolism of poly-P-hydroxybutyrate. I. Purification, composition, and properties of native poly-P-hydroxybutyrate granules from Bacillus megaterium. Biochemistry 1968, 7, 3676–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.A.; Abid, S.; Banat, I.M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Characteristics, production, recent developments and applications. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, J.K.; Chandel, A.K.; Sharma, L.; Mallick, N.; Singh, S.P. Biomedical applications of microbially engineered polyhydroxyalkanoates: An insight into recent advances, bottlenecks, and solutions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2007–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, C.Y.; Sudesh, K. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Bio-based microbial plastics and their properties. Malay. Polym. J. 2007, 2, 31–57. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammadi; Shabina; Afzal, M.; Hameed, S. Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates-eco-friendly next generation plastic: Production, biocompatibility, biodegradation, physical properties and applications. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2015, 8, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallen, L.L.; Rohwedder, W.K. Poly-β-hydroxyalkanoate from activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1974, 8, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbuchel, A.; Schubert, P.; Timm, A.; Pries, A. Genetic and molecular analysis of the alcaligenes eutrophus polyhydroxyalkanoate-biosynthetic genes and accumulation of PHA in recombinant bacteria. In Novel Biodegradable Microbial Polymers; Dawes, E.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.J.; Dawes, E.A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 54, 450–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y. Plastic bacteria? Progress and prospects for polyhydroxyalkanoate production in bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Recent advances in microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Proc. Biochem. 2005, 40, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlawat, G.; Kumari, P.; Bhagat, N.R. Technological advances in the production of polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymers. Curr. Sust. Renew. Energy Rep. 2020, 7, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.P.; Nandy, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Pramanik, N. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Microbial synthesis and applications. In Encyclopedia of Biomedical Polymers and Polymeric Biomaterials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 11, p. 10444. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuge, T. Metabolic improvements and use of inexpensive carbon sources in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 94, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of synthesis, characteristics, processing and potential applications in packaging. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneswari, S.; Gurusamy, T.P.; Khalil, H.P.S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Amirul, A.A.A. Elucidation of antimicrobial silver sulfadiazine (SSD) blend/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) immobilised with collagen peptide as potential biomaterial. Polymers 2020, 12, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chu, T.L. Property analysis of biodegradable material P(3HB-co-4HB). Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 380, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlinden, R.A.J.; Hill, D.J.; Kenward, M.A.; Williams, C.D.; Radecka, I. Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Side-chain effect of second monomer units on crystalline morphology, thermal properties, and enzymatic degradability for random copolyesters of (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid with (R)-3-hydroxyalkanoic acids. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Tappel, R.C.; Nomura, C.T. Mini-review: Biosynthesis of poly(hydroxyalkanoates). Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, B.S.; Grewal, A.; Kumar, P. Biotechnological production of polyhydroxyalkanoates: A review on trends and latest developments. Chin. J. Biol. 2014, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciesielski, S.; Górniak, D.; Mozejko, J.; Świątecki, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Zdanowski, M. The diversity of bacteria isolated from Antarctic freshwater reservoirs possessing the ability to produce polyhydroxyalkanoates. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, G.Y.A.; Chen, C.L.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Razaad, I.M.N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. Start a research on biopolymer polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghul, S.S. Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Accumulating Vibrios from Marine Benthic Environments and Production Studies of Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Vibrio sp. BTKB33. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kerala, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.H.; Azizan, M.N.M.; Sudesh, K. Effects of culture conditions on the composition of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) synthesized by Comamonas acidovorans. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 84, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, U.; Kumar, R.; Balaji, S.; Sehgal, P.K. A novel biocompatible poly(3-hydroxy-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) blend as a potential biomaterial for tissue engineering. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2010, 25, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhafini, H.; Thinagaran, L.; Shantini, K.; Huong, K.H.; Syafiq, I.M.; Bhubalan, K.; Amirul, A.A. Synthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) with high 4HB composition and PHA content using 1,4-butanediol and 1,6-hexanediol for medical application. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanprateep, S.; Katakura, Y.; Visetkoop, S.; Shimizu, H.; Kulpreecha, S.; Shioya, S. Characterization of new isolated Ralstonia eutropha strain A-04 and kinetic study of biodegradable copolyester poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Ohura, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ikarashi, T. Effective biosynthesis of poly(3-hydoxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) with high 4-hydroxybutyrate fractions by Wautersia eutropha in the presence of α-amino acids. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.M.; Sadasivam, M.; Vigneswari, S. Isolation and identification of P(3HB-co-4HB) producing bacteria from various locations in Kuala Terengganu. Malay. Appl. Biol. 2019, 48, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, T.H.; Ishii, D.; Mahara, A.; Murakami, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Sudesh, K.; Samian, R.; Fujita, M.; Maeda, M.; Iwata, T.; et al. Scaffolds from electrospun polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers: Fabrication, characterization, bioabsorption and tissue response. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswari, S.; Murugaiyah, V.; Kaur, G.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Amirul, A.A. Simultaneous dual syringe electrospinning system using benign solvent to fabricate nanofibrous P(3HB-co-4HB)/collagen peptides construct as potential leave-on wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 66, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Kunioka, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Soga, K. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on unusual bacterial copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 4-hydroxybutyrate. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunioka, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Doi, Y. Production of biodegradable copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 4-hydroxybutyrate by Alcaligenes europhus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1989, 30, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirul, A.A.; Yahya, A.R.M.; Sudesh, K.; Azizan, M.N.M.; Majid, M.I.A. Biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) copolymer by Cupriavidus sp. USMAA1020 isolated from Lake Kulim, Malaysia. Biores. Technol. 2008, 99, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirul, A.A.; Yahya, A.R.M.; Sudesh, K.; Azizan, M.N.M.; Majid, M.I.A. Microbial synthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) by Cupriavidus sp. USMAA1020 isolated from Malaysian environment. In Innovations in Chemical Biology; Şener, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, K.H.; Azuraini, M.J.; Aziz, N.A.; Amirul, A.A. Pilot scale production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) biopolymers with high molecular weight and elastomeric properties. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbüchel, A.; Lütke-Eversloh, T. Metabolic engineering and pathway construction for biotechnological production of relevant polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 16, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswari, S.; Majid, M.I.A.; Amirul, A.A. Tailoring the surface architecture of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 124, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.; Goncharov, D.; Sukovatyi, A.; Shabanov, A.; Nikolaeva, E.; Shishatskaya, E. Electrospinning of polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds: Effects on electrospinning parameters on structure and properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 25, 370–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswari, S.; Amirul, A.A. Biodegradability and cellular compatibility of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) via subcutaneous implantation in rat model. Malay. Appl. Biol. 2017, 46, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abedalwafa, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Biodegradable poly-epsilon-caprolactone (PCL) for tissue engineering applications: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2013, 34, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, K.; Dasgupta, S.; Pramanik, K.; Bissoyi, A. Preparation and evaluation of gelatin-chitosan-nanobioglass 3D porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biomater. 2016, 2016, 9825659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brigham, C.J.; Sinskey, A.J. Applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates in the medical industry. Int J. Biotechnol. Well. Ind. 2012, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, F.J. Biomaterials and scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Niu, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Bo, P.; Wang, Y. Examination of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) biological materials for myocardial patch. J. Histotechnol. 2015, 38, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, M.; Wu, G. Surface modification of polyhydroxyalkanoates toward enhancing cell compatibility and antibacterial activity. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepicka, P.; Styblova, S.; Kasalkova, N.S.; Rimpelova, S.; Svorcik, V. Cytocompatibility of polyhydroxybutyrate modified by plasma discharge. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Kasuya, K.; Takemura, A.; Isogai, A.; Iwata, T. Properties and enzymatic degradation of poly(acrylic acid) grafted polyhydroxyalkanoate films by plasma-initiated polymerization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswari, S.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Amirul, A.A. Designing of collagen based poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds for tissue engineering. Int J. Polym, Sci. 2015, 2015, 731690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roseti, L.; Parisi, V.; Petretta, M.; Cavallo, C.; Desando, G.; Bartolotti, I.; Grigolo, B. Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1246–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswari, S.; Chai, J.M.; Shantini, K.; Bhubalan, K.; Amirul, A.A. Designing novel interfaces via surface functionalization of short-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2019, 2019, 3831251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.F.; Amirul, A.A. Preparation and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoates macroporous scaffold through enzyme-mediated modifications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurusu, R.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Surface modification to control the water wettability of electrospun mats. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 64, 249–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassas-Galià, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Micaux, F.; Gaillard, V.; Piantini, U.; Schintke, S.; Zinn, M.; Mathieu, M. Chemical modification of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) for the preparation of hybrid biomaterials. Chimia 2015, 69, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rošic, R.; Kocbek, P.; Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Baumgartner, S. Nanofibers and their biomedical use. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Zhu, M.L.; Leach, M.K.; Naim, Y.I.; Corey, J.M.; Feng, Z.Q.; Jiang, Q. Electrospun fibers and tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotech. 2012, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. Applications of electrospun nanofibers in the biomedical field. SURG J. 5 2012, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, N.G.; Shin, C.S.; Shin, H. Current approaches to electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 014102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingavle, G.C.; Leach, J.K. Advancements in electrospinning of polymeric nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Tiss. Eng. Part B Rev. 2014, 20, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabafrooz, V.; Mozafari, M.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. Electrospun nanofibers: From filtration membranes to highly specialized tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2014, 14, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Truckenmüller, R.; Blitterswijk, C.V.; Moroni, L. Fabrication of nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. In Nanomaterials in Tissue Engineering: Fabrication and Applications; Gaharwar, A.K., Sant, S., Hancock, M.J., Hacking, S.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 158–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sanhueza, C.; Acevedo, F.; Rocha, S.; Villegas, P.; Seeger, M.; Navia, R. Polyhydroxyalkanoates as biomaterial for electrospun scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Y. Rheological, thermal, and mechanical properties of P (3HB-co-4HB) and P (3HB-co-4HB)/EVA blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Thomas, L.; Fusco, A.; Kalaoglu-Altan, O.I.; Basnett, P.; Cinelli, P.; De Clerck, K.; Roy, I.; Donnarumma, G.; Coltelli, M.B.; et al. Electrosprayed chitin nanofibril/electrospun polyhydroxyalkanoate fiber mesh as functional nonwoven for skin application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimcuka, J.; Obata, A.; Sampson, W.W.; Blanc, R.; Gao, C.; Withers, P.J.; Tsigkou, O.; Kasuga, T.; Lee, P.D.; Poologasundarampillai, G. X-ray tomographic imaging of tensile deformation modes of electrospun biodegradable polyester fibers. Front. Mater. 2017, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhijiang, C.; Qin, Z.; Xianyou, S.; Yuanpei, L. Zein/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) electrospun blend fiber scaffolds—Preparation, characterization and cytocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Sridewei, N.; Ramanathan, S.; Sudesh, K. The influence of electrospinning parameters and drug loading on polyhydroxyalkanoate (pha) nanofibers for drug delivery. Int. J. Biotech. Well. Ind. 2017, 4, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lan, P. Surface glycosylation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) membrane for selective adsorption of low-density lipoprotein. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 2094–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrahi, R.; Fathi, Z.; Seydibeyoğlu, M.O.; Doustkhah, E.; Khataee, A. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): From production to nanoarchitecture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 596–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, D.; Ramier, J.; Versace, D.L.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Design of functionalized biodegradable PHA-based electrospun scaffolds meant for tissue engineering applications. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswari, S.; Chai, J.M.; Kamarudin, K.H.; Amirul, A.A.; Focarete, M.L.; Ramakrishna, S. Elucidating the surface functionality of biomimetic rgd peptides immobilized on nano-p(3hb-co-4hb) for h9c2 myoblast cell proliferation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 567693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C. Aminolysis-based surface modification of polyesters for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettikiriarachchi, J.T.S.; Parish, C.L.; Nisbet, D.R.; Forsythe, J.S. Architectural and surface modification of nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Nanomat. Life. Sci. 2012, 10, 397–427. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneswari, S.; Murugaiyah, V.; Kaur, G.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Amirul, A.A. Biomacromolecule immobilization: Grafting of fish-scale collagen peptides onto aminolyzed P(3HB-co-4HB) scaffolds as a potential wound dressing. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.M.; Wei, D.X.; Yao, H.; Wu, L.P.; Chen, G.Q. Synthesis, characterization and application of thermoresponsive polyhydroxyalkanoate-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wei, D.; Che, X.; Cai, L.; Tao, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Chen, G.Q. Comb-like temperature-responsive polyhydroxyalkanoate-graft-poly(2-dimethylamino-ethylmethacrylate) for controllable protein adsorption. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, V.G.; Seifalian, A.M.; Antonova, L.V.; Velikanova, E.A.; Sergeeva, E.A.; Krivkina, E.O.; Glushkova, T.V.; Kudryavtseva, Y.A.; Barbarash, O.L.; Barbarash, L.S.; et al. Biofunctionalization of polycaprolactone scaffolds with RGD peptides for the better cells integration. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1760, 020048. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Hollister, S. Comparison of bone marrow stromal cell behaviors on poly(caprolactone) with or without surface modification: Studies on cell adhesion, survival and proliferation. J. Biomater. Sci. 2009, 20, 1975–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Bianchi, A. Click chemistry for the synthesis of RGD-containing integrin ligands. Molecules 2010, 15, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goddard, J.M.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Polymer surface modification for the attachment of bioactive compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 698–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.P.; Cui, F.Z. Surface modification of polyester biomaterials for tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2007, 2, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuraini, M.J.; Huong, K.-H.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Amirul, A.A. Fabrication and characterization of P(3HB-co-4HB)/gelatine biomimetic nanofibrous scaffold for tissue engineering application. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijiang, C.; Chengwei, H.; Guang, Y. Poly(3-hydroxubutyrate-co-4-hydroxubutyrate)/bacterial cellulose composite porous scaffold: Preparation, characterization and biocompatibility evaluation. Carb. Polym. 2012, 87, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennukka, M.; Amirul, A.A. Fabrication of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/chitosan blend material: Synergistic effects on physical, chemical, thermal and biological properties. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 1937–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tathe, A.; Ghodke, M.; Nikalje, A.P. A brief review: Biomaterials and their application. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaramurthi, D.M.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Electrospun nanofibers as scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 348–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Zagho, M.M.; Elzatahry, A.A. Polymer-based electrospun nanofibers for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.W.; Dalgliesh, A.J.; López, J.E.; Griffiths, L.G. Cardiac extracellular matrix proteomics: Challenges, techniques, and clinical implications. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rienks, M.; Papageorgiou, A.P.; Frangogiannis, N.G.; Heymans, S. Myocardial extracellular matrix: An ever-changing and diverse entity. Circul. Res. 2014, 114, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, D.A.; Sampaio, L.C.; Gobin, A. Building new hearts: A review of trends in cardiac tissue engineering. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 2448–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GORE-TEX® Cardiovascular Patch. Available online: https://www.goremedical.com/resource/AT0904-EN2 (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Cardiovascular Patches—ePTFE. Available online: https://www.crbard.com/Peripheral-Vascular/en-US/Products/Cardiovascular-Patches-ePTFE (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Lam, M.T.; Wu, J.C. Biomaterial applications in cardiovascular tissue repair and regeneration. Expert Rev. Cardio. Ther. 2012, 10, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Fan, K.; Ou, W.; Chen, K.C.; Xu, K. Synthesis, characterizations, and biocompatibility of block poly(ester-urethane)s based on biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) (P3/4HB) and poly(ε-caprolactone). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 101, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Mu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Bo, P.; Wang, Y. Comparative study of three types of polymer materials co-cultured with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for use as a myocardial patch in cardiomyocyte regeneration. J. Mat. Sci. 2013, 24, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, R.; Cui, W. ECM decorated electrospun nanofiber for improving bone tissue regeneration. Polymers 2018, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, N.; Meng, Z.; Jiao, T.; Luo, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Sui, L.; Cai, X. P34HB electrospun fibres promote bone regeneration in vivo. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, 12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo-Nava, J.; Führmann, T.; Klinkhammer, K.; Seiler, N.; Mey, J.; Klee, D.; Möller, M.; Dalton, P.D.; Brook, G.A. Human neural cell interactions with orientated electrospun nanofibers in vitro. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Li, X.T.; Peng, S.W.; Xiao, J.F.; Liu, C.; Fang, G.; Chen, K.C.; Chen, G.Q. The behaviour of neural stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishatskaya, E.I.; Nikolaeva, E.D.; Vinogradova, O.N.; Volova, T.G. Experimental wound dressings of degradable PHA for skin defect repair. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 27, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, L.; Shivakumar, S. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)—Applications in wound treatment and as precursors for oral drugs. In Biotechnological Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Kalia, V.C., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 227–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Li, G.; Lin, S.; Tian, T.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, S.; Xue, C.; Ma, W.; Cai, X.; et al. Electrospun poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/graphene oxide scaffold: Enhanced properties and promoted in vivo bone repair in rats. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42589–42600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, K.; Jiang, X.; Xie, J.; Cai, P.; Li, F.; Zheng, L. Electrospun poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/octacalcium phosphate nanofibrous membranes for effective guided bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishatskaya, E.I. Investigation of toxicological properties of p (3hb-co-4hb) electrospun membranes as an experimental wound dressings. J. Siber. Fed. Univ. 2017, 10, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatullin, R.; Thomas, P.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Puthussery, H.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of natural polymers, and their applications in drug delivery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotech. 2015, 90, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, E.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Skouras, A.; Tiboni, M.; Casettari, L.; Guarino, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisalina, A.F.; Sonvico, F.; Colombo, P.; Abdullah, A.A.A.; Wahab, H.A.; Majid, M.I.A. Docetaxel-loaded poly (3hb-co-4hb) biodegradable nanoparticles: Impact of co-polymer composition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Property | P(3HB) | P(3HB-co-4HB) |
|---|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature, Tg | 2–4 °C | −48–4 °C |
| Melting temperature, Tm | 160–175 °C | 50–175 °C |
| Tensile strength, σ | 15–40 MPa | 17–104 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 1–2 GPa | 0.07–1.5 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 1–15% | 14–1320% |
| Crystallinity | 50–80% | 34–60% |
| Common physical form | Film, microfiber, microparticle | Film, microfibre, microparticle |
| Bacteria | PHA Composition | Authors and Numbers in Reference List | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comamonas acidovorans | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Lee, Azizan and Sudesh [52] | 2004 |
| Cupriavidus necator | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Rao, Kumar, Balaji, and Sehgal [53] | 2010 |
| Transformant Cupriavidus sp. USMAA1020 | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Norhafini, Thinagaran, Shantini, Huong, Syafiq, Bhubalan and Amirul [54] | 2017 |
| Ralstonia eutropha strain A-04 | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Chanprateep, Katakura, Visetkoop, Shimizu, Kulpreecha and Shioya [55] | 2008 |
| Wautersia eutropha H16 | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Kimura, Ohura, Matsumoto and Ikarashi [56] | 2008 |
| Cupriavidus sp. TMT 11 | P(3HB-co-4HB) | Chai, Sadasivam and Vigneswari [57] | 2019 |
| Biomolecules on P(3HB-co-4HB) | Potential Applications | Enhanced Properties | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen | Fibroblast cells (L929) adhesion and proliferation | Hydrophilicity of P(3HB-co-4HB)/collagen blend scaffolds increased as the collagen concentration increased and the cell adhesion and growth of L929 culture enhanced. | [43,77] |
| Gelatin | Fibroblast cells (L929), mesenchymal stromal culture adhesion and proliferation | Addition of gelatin improved the surface wettability of the scaffolds as well as biological properties; cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation | [98,110] |
| Zein | NIH3T3 fibroblast cells and MG-63 osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation | Improvement in tensile strength and increase in elongation at break as well as improved cytocompatibility | [94] |
| Bacterial cellulose | Chinese Hamster Lung (CHL) fibroblast cells attachment and proliferation | The biocompatibility and cell adhesion of CHL cells of the composite scaffold was enhanced | [111] |
| Chitosan | Wound healing | The hydrophobic nature of the P(3HB-co-4HB) copolymer was modified with chitosan. Water-absorption capacity and solubility increased | [112] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, J.M.; Amelia, T.S.M.; Mouriya, G.K.; Bhubalan, K.; Amirul, A.-A.A.; Vigneswari, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Surface-Modified Highly Biocompatible Bacterial-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate): A Review on the Promising Next-Generation Biomaterial. Polymers 2021, 13, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010051
Chai JM, Amelia TSM, Mouriya GK, Bhubalan K, Amirul A-AA, Vigneswari S, Ramakrishna S. Surface-Modified Highly Biocompatible Bacterial-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate): A Review on the Promising Next-Generation Biomaterial. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Jun Meng, Tan Suet May Amelia, Govindan Kothandaraman Mouriya, Kesaven Bhubalan, Al-Ashraf Abdullah Amirul, Sevakumaran Vigneswari, and Seeram Ramakrishna. 2021. "Surface-Modified Highly Biocompatible Bacterial-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate): A Review on the Promising Next-Generation Biomaterial" Polymers 13, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010051
APA StyleChai, J. M., Amelia, T. S. M., Mouriya, G. K., Bhubalan, K., Amirul, A.-A. A., Vigneswari, S., & Ramakrishna, S. (2021). Surface-Modified Highly Biocompatible Bacterial-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate): A Review on the Promising Next-Generation Biomaterial. Polymers, 13(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010051