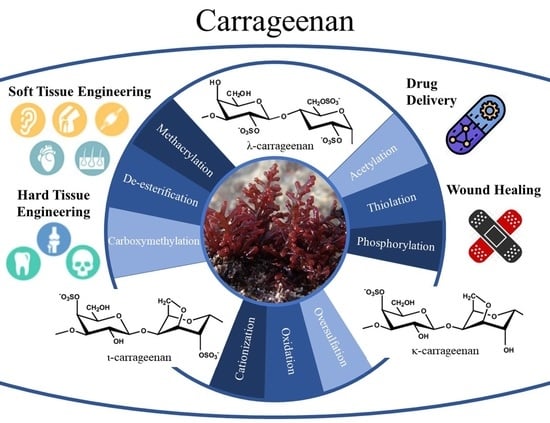
Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Carrageenan Properties for Biomedical Applications
3. Chemical Modification of Carrageenan
4. Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms and Its Application
4.1. Hybrid Carrageenan Based Platforms for Tissue Engineering
4.1.1. Hard Tissue
4.1.2. Soft Tissue
4.2. Hybrid Carrageenan Based Platforms for Wound Healing
4.3. Hybrid Carrageenan Based Platforms for Drug Delivery
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelco, C. Genu® Carrageenan Book; CP Kelco ApS: Lille Skensved, Denmark, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; da Silva, D.B., Jr.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis–A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Nasif, M.; Sultan, N.; Aslam, N.; Noreen, A.; Zuber, M. A review on synthesis, properties and applications of natural polymer based carrageenan blends and composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ruiter, G.A.; Rudolph, B. Carrageenan biotechnology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A review. Vet. Med. 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarı, Ö.; Kara, S.; Pekcan, Ö. Critical Exponents of Kappa Carrageenan in the Coil-Helix and Helix-Coil Hysteresis Loops. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2009, 48, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavli, M.; Baumgartner, S.; Kos, P.; Kogej, K. Doxazosin–carrageenan interactions: A novel approach for studying drug–polymer interactions and relation to controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, S. Algal Polysaccharides, Novel Applications and Outlook, Carbohydrates-Comprehensive Studies on Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Amirthalingam, S.; Jayakumar, R. Carrageenan based hydrogels for drug delivery, tissue engineering and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Kim, G.J.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.; Zhang, X.; Kang, M.G.; Seo, J.W.; Cha, J.M.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.-Y.; et al. Kappa-Carrageenan-Based Dual Crosslinkable Bioink for Extrusion Type Bioprinting. Polymers 2020, 12, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaila, S.M.; Gaharwar, A.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P.; Gomes, M.E.; Khademhosseini, A. PhotocrosslinkableKappa-Carrageenan Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Peak, C.W.; Carrow, J.K.; Gentry, J.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. Injectable shear-thinning nanoengineered hydrogels for stem cell delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12362–12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhtari, H.; Kharaziha, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Tavakoli, S. An injectable mechanically robust hydrogel of Kappa-carrageenan-dopamine functionalized graphene oxide for promoting cell growth. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Kermanpur, A.; Mokhtari, H. Sprayable and injectable visible-light Kappa-carrageenan hydrogel for in-situ soft tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Nemati, S.; Kalateh, A. Nanocomposite hydrogel based on carrageenan-coated starch/cellulose nanofibers as a hemorrhage control material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, S.; Klar, A. Advanced Hydrogels as Wound Dressings. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett-Catton, E.; Ross, M.; Asuri, P. Multifunctional Hydrogel Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.W.; Fowler, E.F. Carrageenan: A review of its effects on the immune system. Agents Actions 1981, 11, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.K.; Saba, A.U.; Nawazish, S.; Akhtar, F.; Rashid, R.; Mir, S.; Nasir, B.; Iqbal, F.; Afzal, S.; Pervaiz, F.; et al. Carrageenan Based Bionanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tool with Special Emphasis on the Influence of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Review for carrageenan-based pharmaceutical biomaterials: Favourable physical features versus adverse biological effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacman, J.K. Review of harmful gastrointestinal effects of carrageenan in animal experiments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sf-Tischer, P.C.; Talarico, L.B.; Noseda, M.D.; Guimarães, S.M.P.B.; Damonte, E.B.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure and antiviral activity of carrageenans from Meristiella gelidium against herpes simplex and dengue virus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Castro, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Moenne, A. Seaweed Polysaccharides and Derived Oligosaccharides Stimulate Defense Responses and Protection against Pathogens in Plants. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Dai, J. Immunomodulation and antitumor activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides. Cancer Lett. 2006, 243, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Tao, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X. Degradation and antioxidant activity of κ-carrageenans. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciuttolo, M.A.; Trinh, L.; Lumpkin, J.A.; Rao, G. Hyperoxia induces DNA damage in mammalian cells. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 14, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhou, D.; Xie, J.; Mao, F. Preparation of chitosan oligomers and their antioxidant activity. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Rupérez, P. Bioactivity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible red seaweed Mastocarpus stellatus. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2014, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buck, C.; Thompson, C.D.; Roberts, J.N.; Müller, M.; Lowy, D.R.; Schiller, J.T. Carrageenan Is a Potent Inhibitor of Papillomavirus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassauer, A.; Weinmuellner, R.; Meier, C.; Pretsch, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E.; Unger, H. Iota-Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of rhinovirus infection. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, A.; Lu, Z.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Yin, J. Overview on the antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides from seaweeds. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 453–454, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.J.; Pujol, C.A.; Ciancia, M.; Noseda, M.D.; Matulewicz, M.C.; Damonte, E.B.; Cerezo, A.S. Antiherpetic and anticoagulant properties of carrageenans from the red seaweed Gigartina skottsbergii and their cyclized derivatives: Correlation between structure and biological activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1997, 20, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Quito, E.-M.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Veiga, M.-D. Carrageenan: Drug Delivery Systems and Other Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Shimizu, M. In vitro Bacteriostatic Effects on Dietary Polysaccharides. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2001, 7, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, C.; Ramezanpour, M.; Cooksley, C.; Vreugde, S.; Psaltis, A.J. Kappa-carrageenan sinus rinses reduce inflammation and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus infection in airway epithelial cells. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Mao, X.; Peng, X.; Tang, S. Effects of sulfate group in red seaweed polysaccharides on anticoagulant activity and cytotoxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, K.O.A.L.; Bezerra, D.; Alves, A.P.N.N.; Alencar, N.M.N.; Lima, M.W.; Torres, V.M.; Farias, W.R.L.; Pessoa, C.; De Moraes, M.O.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Antitumor properties of a sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Champia feldmannii (Diaz-Pifferer). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. The antitumor activity of a red alga polysaccharide complexes carrying 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, Y.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z. In vivo antitumor and immunomodulation activities of different molecular weight lambda-carrageenans from Chondrus ocellatus. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 50, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijin, M.; Xiaolu, J.; Huashi, G. A κ-carrageenan derived oligosaccharide prepared by enzymatic degradation containing anti-tumor activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhan, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X. Anti-Cancer Activity of Porphyran and Carrageenan from Red Seaweeds. Molecules 2019, 24, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yermak, I.M.; Barabanova, A.O.; Aminin, D.L.; Davydova, V.N.; Sokolova, E.V.; Solov’Eva, T.F.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, K.S. Effects of structural peculiarities of carrageenans on their immunomodulatory and anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, C.M.P.G.; Alves, M.G.C.F.; Will, L.S.E.P.; Costa, T.G.; Sabry, D.A.; Rêgo, L.A.R.D.S.; Accardo, C.M.; Rocha, H.A.; Filgueira, L.G.A.; Leite, E.L. A sulfated polysaccharide, fucans, isolated from brown algae Sargassum vulgare with anticoagulant, antithrombotic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Kam, E.L.; De Vry, J.; Schiene, K.; Tzschentke, T.M. Differential effects of morphine on the affective and the sensory component of carrageenan-induced nociception in the rat. Pain 2008, 136, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, A. Advance on safety evaluation of carrageenan. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 512–514. [Google Scholar]
- Halasa, A.; Massie, J.M.; Ceresa, R. The Chemical Modification of Polymers. Sci. Technol. Rubber 2005, 2005, 497–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlhan, G.T.; Irmak, G.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Microwave assisted methacrylation of Kappa carrageenan: A bioink for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3523–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, S.; Mokhtari, H.; Kharaziha, M.; Kermanpur, A.; Talebi, A.; Moshtaghian, J. A multifunctional nanocomposite spray dressing of Kappa-carrageenan-polydopamine modified ZnO/L-glutamic acid for diabetic wounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Correia, S.; Gonçalves, C.; Reis, R.; Oliveira, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Biocompatible Methacrylated Kefiran Hydrogels: Towards Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, R.L.; Iovu, H.; Ghitman, J.; Serafim, A.; Stavarache, C.; Marin, M.-M.; Ianchis, R. 3D-Printed Gelatin Methacryloyl-Based Scaffolds with Potential Application in Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, L.; Mawad, D.; Dokos, S.; Koshy, P.; Martens, P.J.; Sorrell, C.C. Fucoidan- and carrageenan-based biosynthetic poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for controlled permeation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, L.M.; Shah, K.; Palani, S.; Peak, C.W.; Gaharwar, A.K. Gradient nanocomposite hydrogels for interface tissue engineering. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Li, C.Y.; Du, M.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Improved Toughness and Stability of κ-Carrageenan/Polyacrylamide Double-Network Hydrogels by Dual Cross-Linking of the First Network. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, L.; Van Damme, L.; Arevalo, M.D.P.O.; Declercq, H.; Thienpont, H.; Ottevaere, H.; Blondeel, P.; Dubruel, P.; Van Vlierberghe, S. Extrusion-based 3D printing of photo-crosslinkable gelatin and κ-carrageenan hydrogel blends for adipose tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peppas, N.A.; Hilt, J.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Langer, R. Hydrogels in Biology and Medicine: From Molecular Principles to Bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadi, I.; Hong, S.; Sullivan, K.E.; Sani, E.S.; Lara, R.P.; Tamayol, A.; Shin, S.R.; Gao, A.E.; Stoppel, W.L.; Iii, L.D.B.; et al. In vitro and in vivo analysis of visible light crosslinkable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Zang, L.; Luo, J. In situ synthesis of poly (methyl methacrylate)/SiO2 hybrid nanocomposites via “grafting onto” strategy based on UV irradiation in the presence of iron aqueous solution. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 217412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, L.; Vagenende, M.; Declercq, H.; Martins, J.; Thienpont, H.; Ottevaere, H.; Dubruel, P.; Van Vlierberghe, S. Synergistic effect of κ-carrageenan and gelatin blends towards adipose tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinelli, N.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S.; Bouza, R.; Barral, L.; Feijoo-Bandín, S.; Lago, F. Carrageenan-based physically crosslinked injectable hydrogel for wound healing and tissue repairing applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watase, M.; Nishinari, K. Effect of de-esterification on the rheological properties of κ-carrageenan gels. J. Texture Stud. 1981, 12, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, L.Y.; Sabino, R.M.; Santos, E.C.; Popat, K.C.; Balaban, R.D.C.; Kipper, M.J. Carboxymethyl-kappa-carrageenan: A study of biocompatibility, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, P.; Leong, K.H.; Nyamathulla, S.; Onuki, Y.; Takayama, K.; Chung, L.Y. Optimization of pH-responsive carboxymethylated iota-carrageenan/chitosan nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery using response surface methodology. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 119, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, V.; Melge, A.R.; Rajan, V.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R.; Mohan, C.G. Carboxymethylated ι-carrageenan conjugated amphotericin B loaded gelatin nanoparticles for treating intracellular Candida glabrata infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchaoin, W.; Bonengel, S.; Hussain, S.; Huck, C.; Ma, B.N.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Thiolated Carrageenan. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, F.; Li, F. Preparation and potential in vivo anti-influenza virus activity of low molecular-weight κ-carrageenans and their derivatives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praphakar, R.A.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Munusamy, M.A.; Dusthackeer, V.N.A.; Subbiah, S.K.; Rajan, M. Phosphorylated κ-Carrageenan-Facilitated Chitosan Nanovehicle for Sustainable Anti-Tuberculosis Multi Drug Delivery. Chem. Sel. 2017, 2, 7100–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ge, L.; Lyu, Y.; Zi, Y.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Mu, C. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity of oxidized κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos-Fidencio, G.C.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Noseda, M.D.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Ducatti, D.R. Effects of carboxyl group on the anticoagulant activity of oxidized carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, T.; Prado, H.J.; Bonelli, P.R.; Cukierman, A.L.; Fissore, E.L.; Gerschenson, L.N.; Matulewicz, M.C. Cationization of kappa- and iota-carrageenan—Characterization and properties of amphoteric polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 126, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, N.; Rana, D.; Sani, E.S.; Lara, R.P.; Gifford, J.L.; Fares, M.M.; Mithieux, S.M.; Weiss, A.S. Engineering a sprayable and elastic hydrogel adhesive with antimicrobial properties for wound healing. Biomaterials 2017, 139, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palareti, G.; Legnani, C.; Cosmi, B.; Antonucci, E.; Erba, N.; Poli, D.; Testa, S.; Tosetto, A.; De Micheli, V.; Ghirarduzzi, A.; et al. Comparison between different D - D imer cutoff values to assess the individual risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism: Analysis of results obtained in the DULCIS study. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyik, G.; Işıklan, N. Synthesis, characterization and swelling performance of a temperature/pH-sensitive κ-carrageenan graft copolymer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Boppana, R.; Mohan, G.K.; Mutalik, S.; Kalyane, N.V. pH-responsive interpenetrating network hydrogel beads of poly (acrylamide)-g-carrageenan and sodium alginate for intestinal targeted drug delivery: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Barzegar, S.; Zeidabadi, F. Synthesis and properties of biodegradable hydrogels of κ-carrageenan grafted acrylic acid-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid as candidates for drug delivery systems. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, S. Synthesis and characterization of thermo- and pH-sensitive kappa-carrageenan-g-poly(methacrylic acid)/poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide) semi-IPN hydrogel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Rubbery Chitosan/Carrageenan Hydrogels Constructed through an Electroneutrality System and Their Potential Application as Cartilage Scaffolds. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Zhang, H.; Ren, K.-F.; Ying, Z.; Zhu, F.; Qian, J.; Ji, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Ultrathin κ-Carrageenan/Chitosan Hydrogel Films with High Toughness and Antiadhesion Property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9002–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, J.V.; Davidenko, N.; Danner, M.; Cameron, R.E.; Best, S.M. Novel porous scaffolds of pH responsive chitosan/carrageenan-based polyelectrolyte complexes for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, M.P.; Angulski, A.B.B.; Gomes, F.A.; Da Silva, M.M.; Jeremias, T.D.S.; De Carvalho, R.G.; Vieira, D.G.I.; Oliveira, L.F.C.; Maia, L.; Trentin, A.G.; et al. Carrageenan hydrogel as a scaffold for skin-derived multipotent stromal cells delivery. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Jung, W.-K.; Oh, J.; Nam, S.Y. Enhanced rheological behaviors of alginate hydrogels with carrageenan for extrusion-based bioprinting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 98, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami-Hasan-Kohal, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, F.; Nikzad, B. Development of reinforced aldehyde-modified kappa-carrageenan/gelatin film by incorporation of halloysite nanotubes for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlowska, J.; Pauter, K.; Sionkowska, A. Carrageenan-based hydrogels: Effect of sorbitol and glycerin on the stability, swelling and mechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, Y.J.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Oppositely Charged Hydrogels with Super Strong Interface Bonding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11164–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashe, S.; Behera, S.; Dash, P.; Nayak, D.; Nayak, B. Gelatin carrageenan sericin hydrogel composites improves cell viability of cryopreserved SaOS-2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Amirthalingam, S.; Mohandas, A.; Hwang, N.S.; Jayakumar, R. Injectable angiogenic and osteogenic carrageenan nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Karimi, M.H.; Soltaniniya, M.; Massoumi, B. In vitro evaluation of sustained ciprofloxacin release from κ-carrageenan-crosslinked chitosan/hydroxyapatite hydrogel nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Doroudian, M.; Ahadpour, A.; Azari, S. Injectable chitosan/κ-carrageenan hydrogel designed with au nanoparticles: A conductive scaffold for tissue engineering demands. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Gao, X.; Xie, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Weir, M.D.; Reynolds, M.A.; et al. Advanced smart biomaterials and constructs for hard tissue engineering and regeneration. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.Y.; Iwatsuki, R.; Kikuta, K.; Morita, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Ohtsuki, C. Thermoreversible behavior of κ-carrageenan and its apatite-forming ability in simulated body fluid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanitakis, J. Anatomy, histology and immunohistochemistry of normal human skin. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2002, 12, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, S.; Klar, A. Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: Advances and Future Trends. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound Healing Dressings and Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aduba, D.C.; Yang, H. Polysaccharide fabrication platforms and biocompatibility assessment as candidate wound dressing materials. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisenbud, D.; Hunter, H.; Kessler, L.; Zulkowski, K. Hydrogel wound dressings: Where do we stand in 2003? Ostomy Wound Manag. 2003, 49, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.V.; Raman, M.; Doble, M. Cyclic β-(1→ 3)(1→ 6) glucan/carrageenan hydrogels for wound healing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 98545–98553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmi, F.A.; Zailani, M.A.; Abu Bakar, A.J.; Amin, K.A.M. Kinetic Release of Acetaminophen from Cross-Linked Carrageenan Hydrogel for Wound Dressing Application. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Andryukov, B.G.; Besednova, N.N.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kalinin, A.V. Marine Algae Polysaccharides as Basis for Wound Dressings, Drug Delivery, and Tissue Engineering: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, J.S.; Ravichandran, S.; Prithiviraj, K.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Sulfated macroalgal polysaccharides λ-carrageenan and ι-carrageenan differentially alter Arabidopsis thaliana resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 75, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusdin, A.; Thomas, N.; Tulsyahra, M.; Wathoni, N.; Kuswandi, A. Accelerated wound healing ability of Jatropha sap by iota carrageenan-poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel film. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2020, 11, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Kumari, L. Smart Nanopolysaccharides for the Delivery of Bioactives. In Nanoarchitectonics for Smart Delivery and Drug Targeting; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 67–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lokhande, G.; Carrow, J.K.; Thakur, T.; Xavier, J.R.; Parani, M.; Bayless, K.J.; Gaharwar, A.K. Nanoengineered injectable hydrogels for wound healing application. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boateng, J.S.; Pawar, H.V.; Tetteh, J. Polyox and carrageenan based composite film dressing containing anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory drugs for effective wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fawal, G.F.; Yassin, A.M.; El-Deeb, N.M. The Novelty in Fabrication of Poly Vinyl Alcohol/κ-Carrageenan Hydrogel with Lactobacillus bulgaricus Extract as Anti-inflammatory Wound Dressing Agent. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugapriya, K.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.W. A new alternative insight of nanoemulsion conjugated with κ-carrageenan for wound healing study in diabetic mice: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 133, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthuswamy, S.; Viswanathan, A.; Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Vasudevan, A.K.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R. Antistaphylococcal and Neutrophil Chemotactic Injectable κ-Carrageenan Hydrogel for Infectious Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 2, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, L.; Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Carrageenan-based functional hydrogel film reinforced with sulfur nanoparticles and grapefruit seed extract for wound healing application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepon, K.M.; Martins, M.M.; Marques, M.S.; Heckler, J.M.; Morisso, F.D.P.; Moreira, M.G.; Ziulkoski, A.L.; Kanis, L.A. Smart wound dressing based on κ–carrageenan/locust bean gum/cranberry extract for monitoring bacterial infections. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, A.; Mohanbhai, S.J.; Kushwaha, A.C.; Sood, A.; Sardoiwala, M.N.; Choudhury, S.R.; Karmakar, S. κ-carrageenan-C-phycocyanin based smart injectable hydrogels for accelerated wound recovery and real-time monitoring. Acta Biomater. 2020, 109, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, T.G.; Duman, O.; Tunç, S. Agar/κ-carrageenan/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, S.S.; Madiwale, P.V.; Patankar, K.C.; Chhabra, R.; Bangde, P.; Dandekar, P.; Adivarekar, R.V. Cytotoxicity and hemostatic activity of chitosan/carrageenan composite wound healing dressing for traumatic hemorrhage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Dong, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhong, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, Q.-Q.; Lei, M. Fabrication of Ag–ZnO@ carboxymethyl cellulose/K-carrageenan/graphene oxide/konjac glucomannan hydrogel for effective wound dressing in nursing care for diabetic foot ulcers. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Mao, X.; Tang, S. κ/β-Carrageenan oligosaccharides promoting polarization of LPS-activated macrophage and their potential in diabetes wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Aly, A.A.; Sayed, S.M.; Abou-Okeil, A. К-carrageenan/Na-alginate wound dressing with sustainable drug delivery properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kiarostami, K.; Khatir, N.M.; Rezania, S.; Muhamad, I.I. Green Synthesis of Mg0. 99 Zn0. 01O Nanoparticles for the Fabrication of κ-Carrageenan/NaCMC Hydrogel in order to Deliver Catechin. Polymers 2020, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croitoru, C.; Roata, I.C.; Pascu, A.; Stanciu, E.M. Diffusion and Controlled Release in Physically Crosslinked Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Iota-Carrageenan Hydrogel Blends. Polymers 2020, 12, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanaki, S.; Karavas, E.; Kalantzi, L.; Bikiaris, D. Miscibility study of carrageenan blends and evaluation of their effectiveness as sustained release carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, A.V.; Sato, T. Encapsulation of glucose oxidase (GOD) in polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan–carrageenan. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Villanueva, D.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Herrera-Ruiz, D.; Smyth, H.D.C. Design andIn VitroEvaluation of a New Nano-Microparticulate System for Enhanced Aqueous-Phase Solubility of Curcumin. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X. Studies on the physicochemical properties, gelling behavior and drug release performance of agar/κ-carrageenan mixed hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Egyed, A.; Koller, C.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E.; Morokutti-Kurz, M. Development of a nasal spray containing xylometazoline hydrochloride and iota-carrageenan for the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion caused by rhinitis and sinusitis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morokutti-Kurz, M.; König-Schuster, M.; Koller, C.; Graf, C.; Graf, P.; Kirchoff, N.; Reutterer, B.; Seifert, J.-M.; Unger, H.; Grassauer, A.; et al. The Intranasal Application of Zanamivir and Carrageenan Is Synergistically Active against Influenza A Virus in the Murine Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Chan, Y.-L.; Tsai, L.-W.; Li, T.-L.; Wu, C.-J. Prevention of human enterovirus 71 infection by kappa carrageenan. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, P.; Sun, J.; He, Z. Nanostructured lipid–carrageenan hybrid carriers (NLCCs) for controlled delivery of mitoxantrone hydrochloride to enhance anticancer activity bypassing the BCRP-mediated efflux. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothini, K.; Rajendran, N.K.; Munusamy, M.A.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Rajan, M. Development of biotin molecule targeted cancer cell drug delivery of doxorubicin loaded κ-carrageenan grafted graphene oxide nanocarrier. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Carrageenan Type | Chemical Modification | Target Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Cell–material platforms for TE | [11] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Bioink for cartilage TE | [49] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Sprayable hydrogel to cover skin injuries and heal soft tissue damages, bioadhesive hydrogels for chronic diabetic wound healing | [14,50] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Injectable shear-thinning and mechanically robust hydrogel for soft TE | [13] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Shear-thinning hydrogels can be used for cell delivery for cartilage tissue regeneration | [12] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Hydrogel for adipose TE, 3Dscaffolds for the differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells into the adipogenic lineage | [56,60] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Gradient scaffolds for mimicking tissue interfaces and cartilage tissue regeneration | [54] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Injectable delivery vehicle for wound healing and tissue repair | [61] |
| κ-carrageenan | Methacrylation | Bioink for soft TE | [10] |
| κ-carrageenan | De-esterification | Examine the effect of de-esterification on κ-carrageenan gels | [62] |
| κ-carrageenan | Carboxymethylation | Biomaterials for cell-contacting applications in wound dressings | [63] |
| ι- carrageenan | Carboxymethylation | Carrier for the oral delivery of insulin | [64] |
| ι- carrageenan | Carboxymethylation | Nanocarrier system for the treatment of intracellular C.glabrata infections | [65] |
| κ-carrageenan /ι- carrageenan | Thiolation | Characterize a thiolated carrageenan as a novel pharmaceutical excipient | [66] |
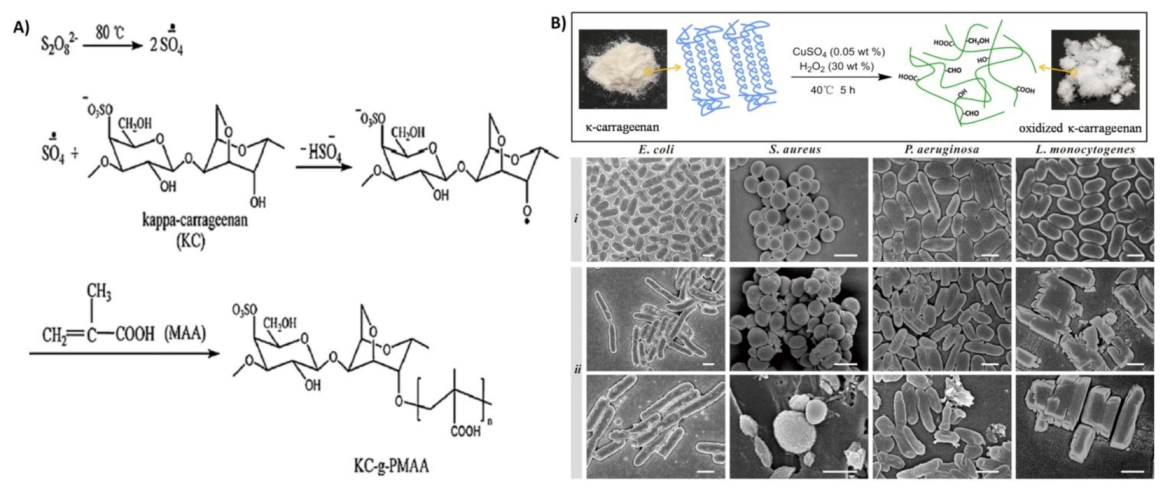
| κ-carrageenan | Acetylation | Biomaterials for potential applications as anti-influenza virus | [67] |
| κ-carrageenan | Phosphorylation | Nanoparticles are a pretty system for simultaneous release of rifampicin and isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculosis | [68] |
| κ-carrageenan | Oxidation | Antibacterial agent against Gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus and L. monocytogenes) and Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli and P. aeruginosa) | [69] |
| κ-carrageenan | Oxidation | Evaluate the effect of oxidation on the anticoagulant activity | [70] |
| κ-carrageenan /ι- carrageenan | Cationization | Cationic polysaccharides for various aplications | [71] |
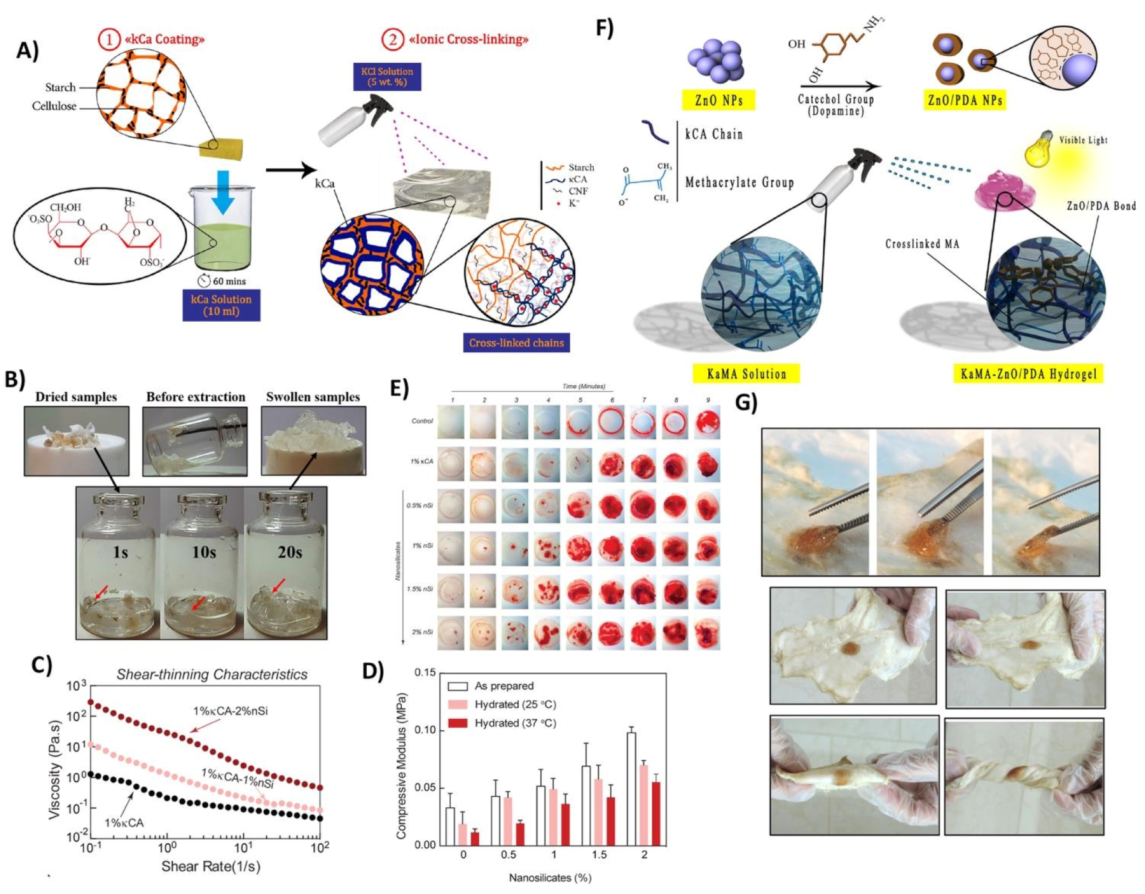
| Hydrogel | Nanoparticle | Crosslinking | Tissue | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KaMA | - | Chemical crosslinking | Cartilage | [49] |
| KaMA | 2D nanosilicates | Ionic and Chemical crosslinking | Cartilage | [12] |
| Gelatin methacryloyl/KaMA | 2D nanosilicates | Chemical crosslinking | Cartilage | [54] |
| κ-carrageenan/chitosan | - | Chemical crosslinking | Cartilage | [78] |
| κ-carrageenan/chitosan | - | Ionic crosslinking | Connective tissue | [79] |
| κ-carrageenan/chitosan | - | - | Soft tissue | [80] |
| KaMA | - | Ionic and Chemical crosslinking | Soft tissue | [10] |
| κ-carrageenan | - | Ionic crosslinking | Soft tissue (skin) | [81] |
| KaMA | - | Ionic and Chemical crosslinking | Soft tissue (skin) | [14] |
| KaMA | Dopamine functionalized graphene oxide | Ionic and Chemical crosslinking | Soft tissue | [13] |
| Methacrylamide- gelatin/KaMA | - | Chemical crosslinking | Soft tissue (adipose) | [56,60] |
| κ-carrageenan/alginate | - | Ionic crosslinking | Soft tissue | [82] |
| Aldehyde-modified κ-carrageenan/Gelatin | Halloysite nanotubes | - | Soft tissue | [83] |
| κ-carrageenan/sorbitol/glycerin | - | Ionic crosslinking | Soft tissue | [84] |
| κ-carrageenan/GelMA | Chemical crosslinking | Soft tissue | [85] | |
| ι- carrageenan/Gelatin/Silk | - | - | Bone | [86] |
| ι- carrageenan | Whitlockite nanoparticles | Ionic crosslinking | Bone | [87] |
| Chitosan/κ-carrageenan | Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles | Ionic crosslinking | Bone | [88] |
| Chitosan/κ-carrageenan | Gold nanoparticle | - | Bone | [89] |
| Major Material | Major Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene oxide + κ-carrageenan + streptomycin + diclofenac | Excellent transparency, protection of the wound, controlled release of both streptomycin and diclofenac, antibacterial activity | [104] |
| κ–carrageenan + poly vinyl alcohol + Lactobacillus bulgaricus extract | Anti-inflammatory ability, antibacterial activity, accelerate the healing process of the chronic wound | [105] |
| κ–carrageenan + nanosilicates + vascular endothelial growth factor | Injectable hydrogel, increase platelets binding and reduce blood clotting time, facilitate wound healing in vitro | [103] |
| κ–carrageenan + Skin-derived stromal cells | Reduce inflammatory process, fast initial recovery of wounded area, improved extracellular matrix deposition | [81] |
| Astaxanthin + alpha-tocopherol + κ-carrageenan nanoemulsion | Biocompatible in vitro and in vivo, reduce fasting blood glucose levels and improve glucose tolerance, accelerate wound closure | [106] |
| Octenidine dihydrochloride + Chitosan-treated serum + κ-carrageenan | Injectable hydrogel, biocompatible gel in vitro, induce migration of polymorphonuclear neutrophils and fibroblasts, antibacterial activity | [107] |
| κ-carrageenan + chitosan capped sulfur NPs + grapefruit seed | Strong antibacterial activity, ultraviolet barrier property, efficient wound healing in vivo, complete appearance of the healed epidermis | [108] |
| κ–carrageenan + locust bean gum + cranberry extract | Dose-dependent cytotoxicity against NIH 3T3 fibroblast cells Provide a visual system for monitoring bacterial wound infections | [109] |
| ι-carrageenans + κ-carrageenan + locust bean gum + gelatin | Injectable hydrogel, biocompatible with good cell adhesion in vitro, able to release encapsulated growth factor to promote cell migration | [61] |
| κ-carrageenan+ pigmented protein C-phycocyanin | Injectable hydrogel, enhance proliferation of dermal fibroblasts in vitro without inducing inflammation, reduce the blood clotting time | [110] |
| Aldehyde-modified κ–carrageenan + gelatin + halloysite nanotubes | Biodegradable and biocompatible | [83] |
| κ–carrageenan +Agar + montmorillonite | Control drug release, antibacterial activity | [111] |
| κ–carrageenan + chitosan | Promote thrombin formation and hemostasis, promote tissue growth | [112] |
| κ–carrageenan + Ag-ZnO@ carboxymethyl cellulose + graphene oxide | Improve epithelialization, advance fibroblast development, quicken wound recuperating | [113] |
| κ–carrageenan + Z/P + L-glutamic acid | Antibacterial activity, reduce clotting formation time, accelerate wound contraction | [50] |
| κ–carrageenan+ starch/CNF | Superabsorbent ability, reduce clotting formation time | [15] |
| κ/β-carrageenan | Promote the secretion of anti-inflammatory factors and accelerate polarization, accelerate the repair process of the full-thickness excisional wound, improve collagen deposition | [114] |
| κ–carrageenan + Na-alginate + silver NPs | Control drug release, antibacterial activity | [115] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokhtari, H.; Tavakoli, S.; Safarpour, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Berto, F. Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111744
Mokhtari H, Tavakoli S, Safarpour F, Kharaziha M, Bakhsheshi-Rad HR, Ramakrishna S, Berto F. Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111744
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokhtari, Hamidreza, Shima Tavakoli, Fereshteh Safarpour, Mahshid Kharaziha, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi-Rad, Seeram Ramakrishna, and Filippo Berto. 2021. "Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111744
APA StyleMokhtari, H., Tavakoli, S., Safarpour, F., Kharaziha, M., Bakhsheshi-Rad, H. R., Ramakrishna, S., & Berto, F. (2021). Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering. Polymers, 13(11), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111744