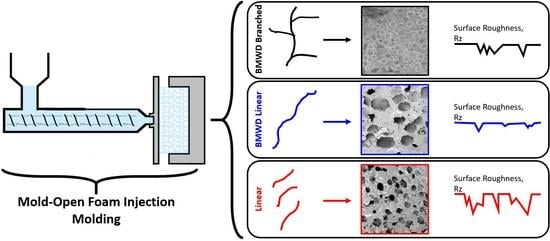
Improved Cell Morphology and Surface Roughness in High-Temperature Foam Injection Molding Using a Long-Chain Branched Polypropylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparations
2.2. Foam Injection Molding and Processing Conditions
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.4. Rheological Characterization
2.5. Surface Roughness Characterization
2.6. Cell Morphology Characterization
2.7. Mechanical Property Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crystallization and Melting Temperatures
3.2. Shear and Extensional Rheology
3.3. Cell Morphology
3.4. Surface Roughness
3.5. Flexural Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, J.-B.; Nyantaki, A., Jr.; Weng, G.-S.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.-W.; Hu, G.-H. Tensile and impact properties of microcellular isotactic polypropylene (PP) foams obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 111, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.W.; Park, C.P.; Maurer, M.J.; Tusim, M.H.; De Genova, R.; Broos, R.; Sophiea, D.P. Lightweight cellular plastics. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, H.E.; Park, C.B.; Reichelt, N. Fundamental foaming mechanisms governing the volume expansion of extruded polypropylene foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaversuch, R.D. Enhanced PP resins offer a wide balance of properties. Mod. Plast. 1996, 26, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.B.; Cheung, L.K. A study of nell nucleation in the extrusion of polypropylene foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1997, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ishihara, S.; Ando, M.; Minato, A.; Hikima, Y.; Ohshima, M. Fabrication of high expansion microcellular injection-molded polypropylene foams by adding long-chain branches. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11970–11982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Dong, J.; He, J. Cell coalescence suppressed by crosslinking structure in polypropylene microcellular foaming. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudiani, S.; Park, C.B.; Kortschot, M.T. Processing and characterization of microcellular foamed high-density polyethylene/isotactic polypropylene blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-X.; Wang, J.-K.; Sun, X.-H. Improving of cell structure of microcellular foams based on polypropylene/high-density polyethylene blends. J. Cell Plast. 2008, 44, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitael, P.; Macosko, C.W. Strain hardening in polypropylenes and its role in extrusion foaming. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsis, A.D.; Zeevenhoven, B.L.F.; Tsenoglou, C. Effect of long branches on the rheology of polypropylene. J. Rheol. 2004, 48, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, J.; Münstedt, H. Rheological properties and foaming behavior of polypropylenes with different molecular structures. J. Rheol. 2006, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Diez, S.; Kweon, M.S.; Kim, E.S.; Gupta, A.; Yan, X.; Pehlert, G.; Park, C.B.; Lee, P.C. In situ visualization of crystal nucleation and growth behaviors of linear and long chain branched polypropylene under shear and CO2 pressure. Polymer 2021, 213, 123215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kweon, M.S.; Romero-Diez, S.; Gupta, A.; Yan, X.; Spofford, C.; Pehlert, G.; Lee, P.C. Effects of pressure drop rate and CO2 content on the foaming behavior of newly developed high-melt-strength polypropylene in continuous extrusion. J. Cell. Plast. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-L.; Zhao, G.-Q.; Wang, J.-C.; Zhang, L. Research on formation mechanisms and control of external and inner bubble morphology in microcellular injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 807–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Turng, L.-S.; Dougherty, E.; Gordon, P. A novel method for improving the surface quality of microcellular injection molded parts. Polymer 2011, 52, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Mu, Y.; Park, C.B. Lightweight and tough nanocellular PP/PTFE nanocomposite foams with defect-free surfaces obtained using in situ nanofibrillation and nanocellular injection molding. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASME B46.1-2019 Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness, and Lay); ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 6.
- Wang, X.; Tzoganakis, C.; Rempel, G.L. Chemical modification of polypropylene with peroxide/pentaerythritol triacrylate by reactive extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, H.E.; Park, C.B.; Song, S.-W. Effect of supercritical gas on crystallization of linear and branched polypropylene resins with foaming additives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6685–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, Q. The molecular structure characteristics of long chain branched polypropylene and its effects on non-isothermal crystallization and mechanical properties. Polymer 2013, 54, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.H.; Carreau, P.J.; Ajji, A. Rheological and thermal properties of blends of a long-chain branched polypropylene and different linear polypropylenes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 22, 4719–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-L.; Liu, T.; Xu, Z.-M.; Zhao, L.; Hu, G.-H.; Yuan, W.-K. Effects of crystal structure on the foaming of isotactic polypropylene using supercritical carbon dioxide as a foaming agent. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 2, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsby, P.R.; Russel, D.A.M. Spherulitic morphology in polypropylene structural foam mouldings. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1984, 3, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Tanigaki, M.; Ohshima, M. Effects of CO2 on crystallization kinetics of polypropylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 41, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, W.-K. Determination of CO2 solubility in isotactic polypropylene melts with different polydispersities using magnetic suspension balance combined with swelling correction. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 530, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, T.; Pillon, C.; Carrot, C.; Ruiz, J.A.R.; Vincent, M.; Billon, N. Polypropylene structural foams: Measurements of the core, skin, and overall mechanical properties with evaluation of predictive models. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Designation | Material | Mw 1 (g/mol) | Mw/Mn 1 (g/mol) | MFR 2 (g/10 min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Linear | 182,000 | 3.7 | 37 |
| B | BMWD Linear | 303,000 | 18 | 30 |
| C | BMWD Branched | 292,000 | 19 | 40 |
| Designation | Material | Gas | Decomposition Ranges (°C) | Weight Loss (%) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AV | ITP-817A | CO2 | 161–175 | 211–229 | 13.5 |
| UC | ACBA35-450EN | CO2 | 157–175 | 193–215 | 9.9 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Injection Speed (cm3/s) | 100 |
| Mold Temperature (°C) | 80 |
| Shot Size (cm3) | 60 |
| Screw Speed (rpm) | 500 |
| Barrel Pressure (MPa) | 15 |
| Packing Pressure (MPa) | 20 |
| Packing Time (s) | 0.5, 5, 10, 20 |
| Mold Opening Distance (mm) | 0.5 |
| Mold Opening Speed (mm/s) | 50 |
| Cooling Time (s) | 60 s |
| CBA | Zone 1 (Hopper) | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | Zone 5 | Zone 6 (Nozzle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UC | 50 | 200 | 230 | 210 | 190 | 190 |
| AV | 50 | 200 | 215 | 200 | 190 | 190 |
| Resin | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Χc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 115 | 160 | 103 | 49 |
| B | 120 | 163 | 111 | 54 |
| C | 129 | 163 | 110 | 53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Cedeno, S.; Kweon, M.S.; Newby, S.; Shivokhin, M.; Pehlert, G.; Lee, P.C. Improved Cell Morphology and Surface Roughness in High-Temperature Foam Injection Molding Using a Long-Chain Branched Polypropylene. Polymers 2021, 13, 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152404
Mendoza-Cedeno S, Kweon MS, Newby S, Shivokhin M, Pehlert G, Lee PC. Improved Cell Morphology and Surface Roughness in High-Temperature Foam Injection Molding Using a Long-Chain Branched Polypropylene. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152404
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Cedeno, Steven, Mu Sung Kweon, Sarah Newby, Maksim Shivokhin, George Pehlert, and Patrick C. Lee. 2021. "Improved Cell Morphology and Surface Roughness in High-Temperature Foam Injection Molding Using a Long-Chain Branched Polypropylene" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152404
APA StyleMendoza-Cedeno, S., Kweon, M. S., Newby, S., Shivokhin, M., Pehlert, G., & Lee, P. C. (2021). Improved Cell Morphology and Surface Roughness in High-Temperature Foam Injection Molding Using a Long-Chain Branched Polypropylene. Polymers, 13(15), 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152404