Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Tensile Properties
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Vicat Softening Temperature
2.7. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
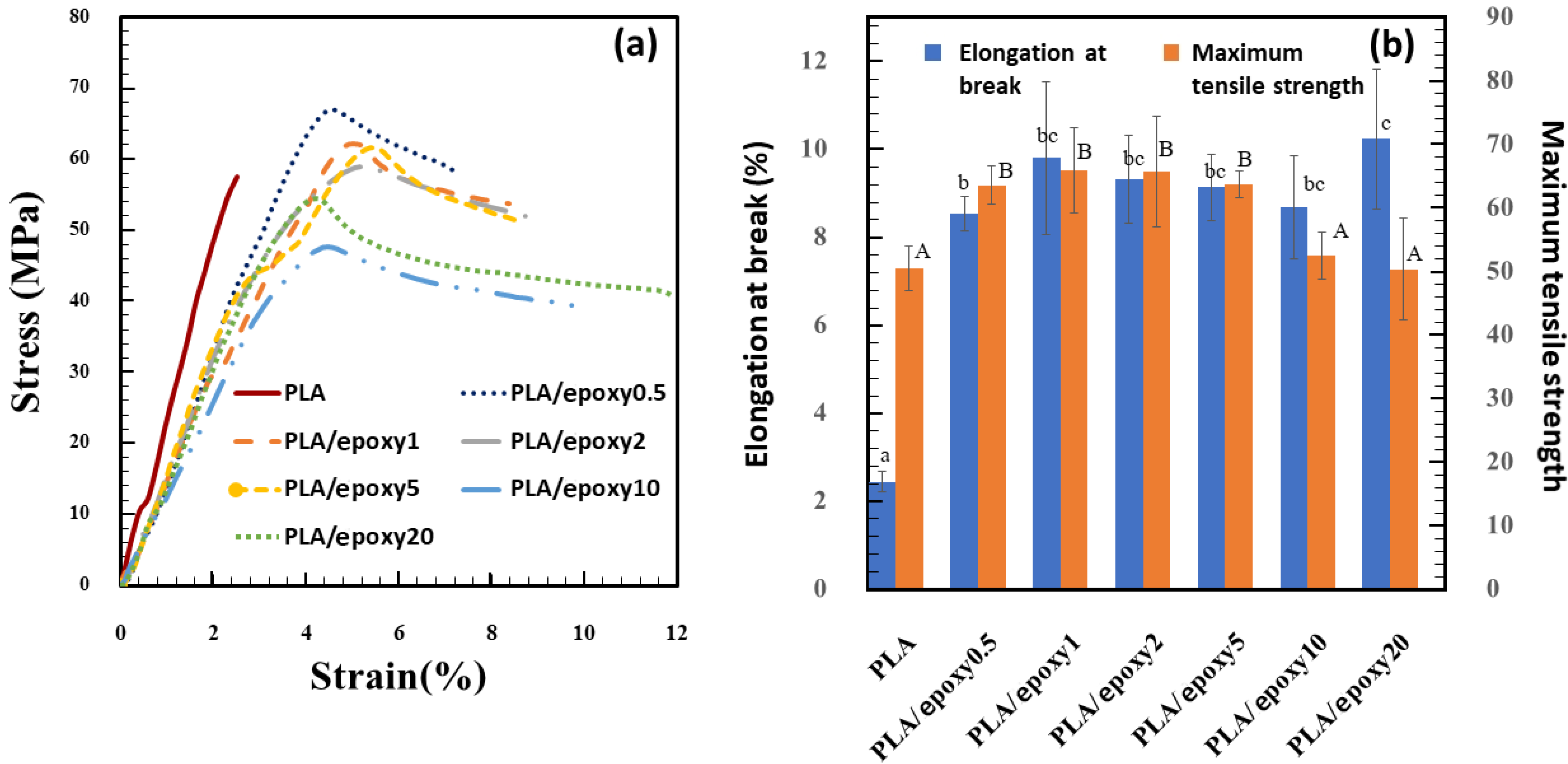
3.1. Mechanical Properties
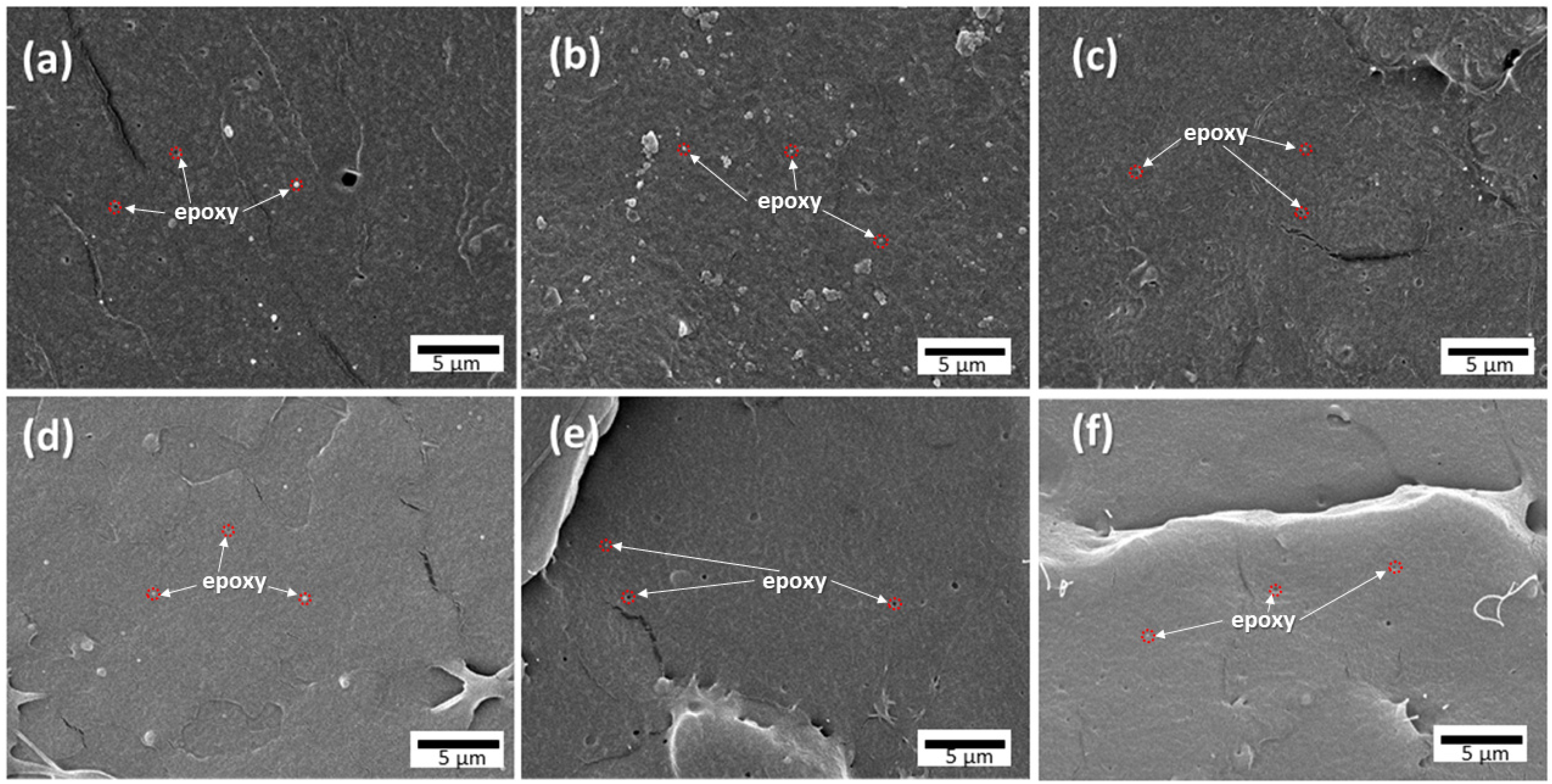
3.2. Morphology
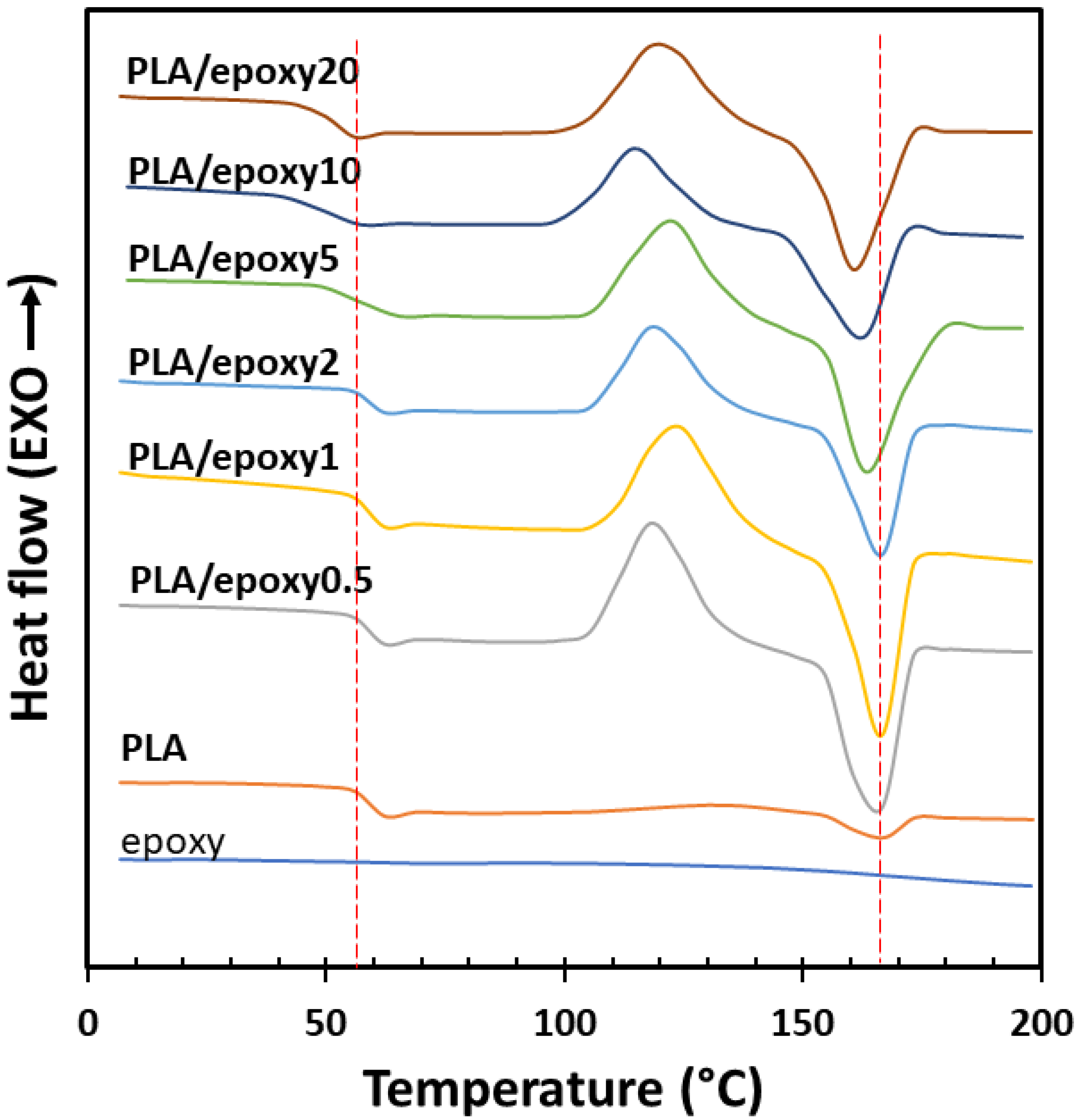
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
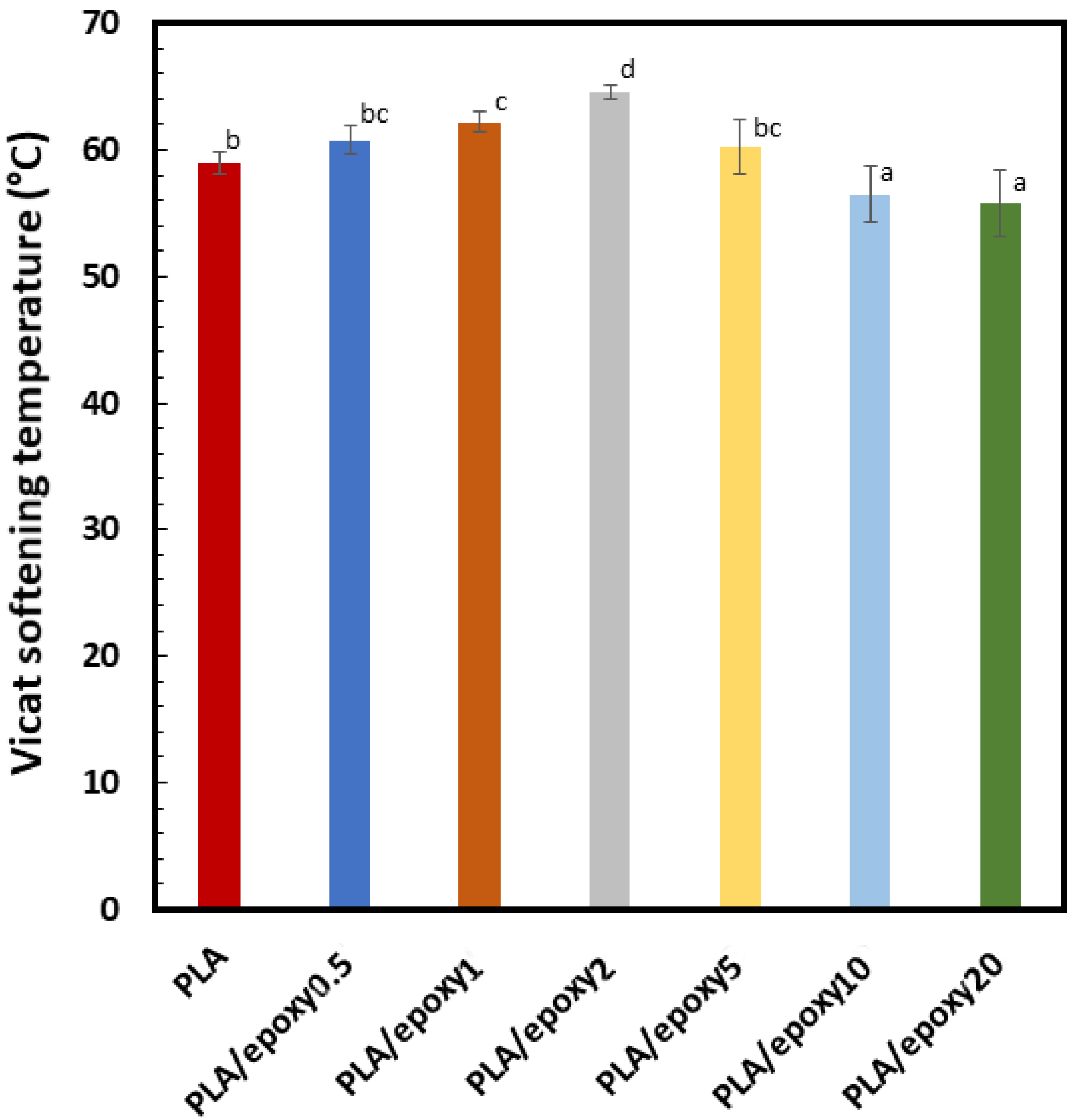
3.4. Vicat Softening Temperature (VST)
3.5. Reaction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLA | polylactic acid |
| PBS | polybutylene succinate |
| TPS | thermoplastic starch |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| Tm | melting temperature |
| Tg | glass transition temperature |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| CDCL3 | chloroform solvent |
References
- Gregor-Svetec, D.; Leskovšek, M.; Leskovar, B.; Elesini, U.S.; Leskovar, B.; Elesini, U.S.; Vrabič-Brodnjak, U. Analysis of PLA composite filaments reinforced with lignin and polymerised-lignin-treated NFC. Polymers 2021, 13, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rohindra, D.; Mori, K.; Kuboyama, K.; Ougizawa, T. Thermoplastic elastomer by reactive blending of poly(butylene succinate) with ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer and ethylene-1-butene rubbers. J. Elastomers Plast. 2015, 47, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaidin, R.; Diah, N.A.; IIyas, R.A.; Alamjuri, R.H.; Yusof, F.A.M. Processing and characterization of banana leaf fibre reinforced thermoplastic cassava starch composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszek, Z.; Lewandowicz, J.; Thanh-Blicharz, J.L.; Walkowiak, K.; Kowalczewski, P.L.; Baranowska, H.M. Water behavior of emulsions stabilized by modified potato starch. Polymers 2021, 13, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surin, S.; You, S.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Muangrat, R.; Wangtueai, S.; Jambrak, A.R.; Phongthai, S.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Chaiyaso, T.; Phimolsiripol, Y. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from purple glutinous rice bran (Oryza sativa L.) and their antioxidant activities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachtanapun, P.; Klunklin, W.; Jantrawut, P.; Leksawasdi, N.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Chaiyaso, T.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Phongthai, S.; et al. Effect of monochloroacetic acid on properties of carboxymethyl bacterial cellulose powder and film from nata de coco. Polymers 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, C.T.; Chen, C.L.; Nguyen, V.B.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Conversion of pectin-containing by-products to pectinases by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its applications on hydrolyzing banana pells for prebiotics production. Polymers 2021, 13, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkaew, M.; Sommano, S.R.; Tangpao, T.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K. Mango peel pectin by microwave-assisted extraction and its use as fat replacement in dried Chinese sausage. Foods 2020, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X. New advances in the biodegradation of Poly(lactic) acid. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 117, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Yumei, D.; Yuelong, H.; Le, Y.; Moldenaers, P.; Weimin, Y.; Czigany, T.; Thomas, S. Miscibility, morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties of a DGEBA based epoxy resin toughened with a liquid rubber. Polymer 2008, 49, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; McCarthy, S. Biodegradable poly(lactic acid) blends with chemically modified polyhydroxyoctanoate through chain extension. J. Polym. Environ. 2009, 17, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—Comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jantanasakulwong, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kuboyama, K.; Ougizawa, T. Thermoplastic vulcanizate based on poly(lactic acid) and acrylic rubber blended with ethylene ionomer. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. Part B 2016, 55, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P. Biodegradability and biodegradation of poly(lactide). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13316–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and its blends with poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): A brief review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavalitpanya, K.; Phattanarudee, S. Poly(lactic acid)/Polycaprolactone Blends Compatibilized with Block Copolymer. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jantanasakulwong, K.; Homsaard, N.; Phengchan, P.; Rachtanapun, P.; Leksawasdi, N.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Techapun, C.; Jantrawut, P. Effect of dip coating polymer solutions on properties of thermoplastic cassava starch. Polymers 2019, 11, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, C.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Akpan, E.D.; Quraishi, M.A.; Dagdag, O.; Gouri, M.E.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Epoxy resins as anticorrosive polymeric materials: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 156, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, C.B.; Gilbert, A.H. Toughening tetrafunctional epoxy resins using polyetherimide. Polymer 1989, 30, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourston, D.J.; Lane, J.M. The toughening of epoxy resins with thermoplastics: 1. Trifunctional epoxy resin-polyetherimide blends. Polymer 1992, 33, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, H.C. Thermal stability and toughening of epoxy resin with polysulfone resin. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.D.S.; Barros, J.J.P.; Albuquerque, A.; Jaques, N.G.; Fook, M.V.L.; Wellen, R.M.R. Insights into the curing kinetics of epoxy/PLA: Implications of the networking structure. Express Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 1180–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodsangma, A.; Homsaard, N.; Nadon, S.; Rachtanapun, P.; Leksawasdi, N.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Insomphun, C.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Chaiyaso, T.; Jantrawut, P.; et al. Effect of sodium benzoate and chlorhexidine gluconate on a biothermoplastic elastomer made from thermoplastic starch-chitosan blended with epoxidized natural rubber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Vuillaume, P.Y. Chapter 7—Reactive compatibilization of polymer blends by coupling agents and interchange catalysts. In Compatibilization of Polymer Blends, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 205–248. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Lim, S.; Kim, J.; Choe, C.R. Studies of an epoxy-compatibilized poly(phenylene sulfide)/polycarbonate blend. Polymer 1997, 38, 4401–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, K.C.; Chang, F.C. Reactive compatibilization of polyamide-6 (PA 6)/polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) blends by a multifunctional epoxy resin. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Weng, Y.-X.; Huang, Z.-G.; Wang, L.; Qiu, D.; Shao, S.-X. Effect of epoxy chain extender on the properties of polylactic acid. J. Appl. Mater. Sci. Eng. Res. 2019, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Limsukon, W.; Auras, R.; Selke, S. Hydrolytic degradation and lifetime prediction of poly(lactic acid) modified with a multifunctional epoxy-based chain extender. Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, S.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X. High-performance fully bio-based poly(lactic acid)/polyamide11 (PLA/PA11) blends by reactive blending with multi functionalized epoxy. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, Y.-M.; Duchet, J.; Reignier, J.; Maazouz, A. Melt strengthening of poly (lactic acid) through reactive extrusion with epoxy-functionalized chains. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, S.S.; Matuana, L.M. Extrusion blown films of poly(lactic acid) chain-extended with food grade multifunctional epoxies. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Yu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Fu, L. Morphology, crystallization and thermal behaviors of PLA-based composite: Wonderful effects of hybrid GO/PEG via Dynamic impregnating. Polymers 2017, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semba, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Ishiaku, U.S.; Hamada, H. The Effect of Crosslinking on the Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruhashi, Y.; Iida, S. Transparency of polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumnate, C.; Rudolph, N.; Sarmadi, M. Recycling of polypropylene/polyethylene blends: Effect of chain structure on the crystallization behaviors. Polymers 2019, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aid, S.; Eddhahak, A.; Ortega, Z.; Froelich, D.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Experimental study of the miscibility of ABS/PC polymer blends and investigation of the processing effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, M.; Borska, K.; Kubisa, P. Crosslinking of polylactide by high energy irradiation and photo-curing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simis, K.S.; Bistolfi, A.; Bellare, A.; Pruitt, L.A. The combined effects of crosslinking and high crystallinity on the microstructural and mechanical properties of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, M.; Monkenbusch, M.; Willner, L.; Wischnewski, A.; Farago, B.; Richter, D. Contour length fluctuations in polymer melts: A direct molecular proof. Europhys. Lett. 2005, 72, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Castaneda, C.; Benavides, R.; Martinez-Pardo, M.E.; Uribe, R.M.; Carrasco-Abrego, H.; Martinez, G. Crosslinking of rigid PVC by ionizing radiation to improve its thermal properties. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.X.; Zabihi, F.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhu, M.F. The Crystallization, Melting Behaviors and Thermal Stability of Cross-linked Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) by Octavinyloctasilasesquioxane. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Gupta, A.P.; Sharmin, E.; Alam, M.; Pandey, S.K. Synthesis, characterization and development of high performance siloxane-modified epoxy paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 54, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkajorn, J.; Tanrattanakul, V. The effect of epoxide content on compatibility of poly(lactic acid)/epoxidized natural rubber blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, W.J.; He, Z.A.; Picci, M. Catalysis of the epoxy-carboxyl reaction. J. Coat. Technol. 2002, 74, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morancho, J.M.; Ramis, X.; Fernandez-Francos, X.; Konuray, O.; Salla, J.M.; Serra, A. Dual curing of an epoxy resin with dicarboxylic acids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 142, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | PLA | Epoxy Resin |
|---|---|---|
| PLA | 100 | 0 |
| PLA/epoxy0.5 | 99.5 | 0.5 |
| PLA/epoxy1 | 99 | 1 |
| PLA/epoxy2 | 98 | 2 |
| PLA/epoxy5 | 95 | 5 |
| PLA/epoxy10 | 90 | 10 |
| PLA/epoxy20 | 80 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiattipornpithak, K.; Thajai, N.; Kanthiya, T.; Rachtanapun, P.; Leksawasdi, N.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Rohindra, D.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Sommano, S.R.; Jantanasakulwong, K. Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152429
Kiattipornpithak K, Thajai N, Kanthiya T, Rachtanapun P, Leksawasdi N, Phimolsiripol Y, Rohindra D, Ruksiriwanich W, Sommano SR, Jantanasakulwong K. Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152429
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiattipornpithak, Krittameth, Nanthicha Thajai, Thidarat Kanthiya, Pornchai Rachtanapun, Noppol Leksawasdi, Yuthana Phimolsiripol, David Rohindra, Warintorn Ruksiriwanich, Sarana Rose Sommano, and Kittisak Jantanasakulwong. 2021. "Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152429
APA StyleKiattipornpithak, K., Thajai, N., Kanthiya, T., Rachtanapun, P., Leksawasdi, N., Phimolsiripol, Y., Rohindra, D., Ruksiriwanich, W., Sommano, S. R., & Jantanasakulwong, K. (2021). Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin. Polymers, 13(15), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152429












