Application of Chitosan/Alginate Nanocomposite Incorporated with Phycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticles for Efficient Remediation of Chromium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Biological Samples Collection
2.3. Extraction of Marine Biopolymers
2.3.1. Chitosan (Cht)
2.3.2. Alginate (Alg)
2.4. Preparation of Biopolymers Nanoparticles
2.5. Iron Nanoparticle Phycosynthesis
2.6. Fabrication of Nano-Adsorbents
2.7. Characterization of Products and Nanomaterials
2.7.1. FTIR Analysis
2.7.2. Structural Analysis of Nanometals
2.7.3. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) Imaging
2.7.4. Particles’ Size and Charge
2.8. Batch Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium
3. Results and Discussion
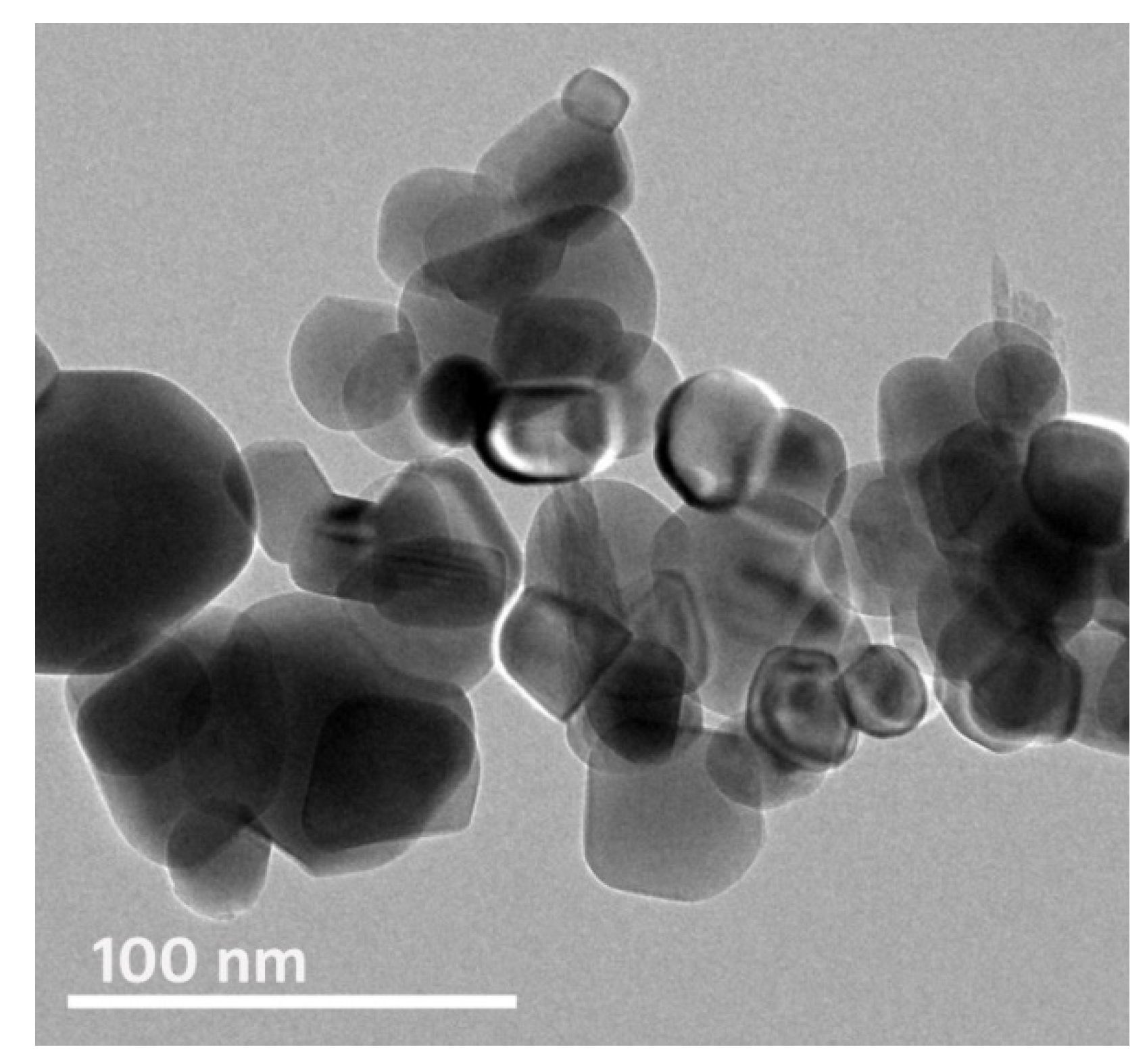
3.1. Phycosynthesis and Characterization of Fe-NPs Using Sargassum Linifolium Extract
3.2. Characterization of Biopolymers Nanocomposites
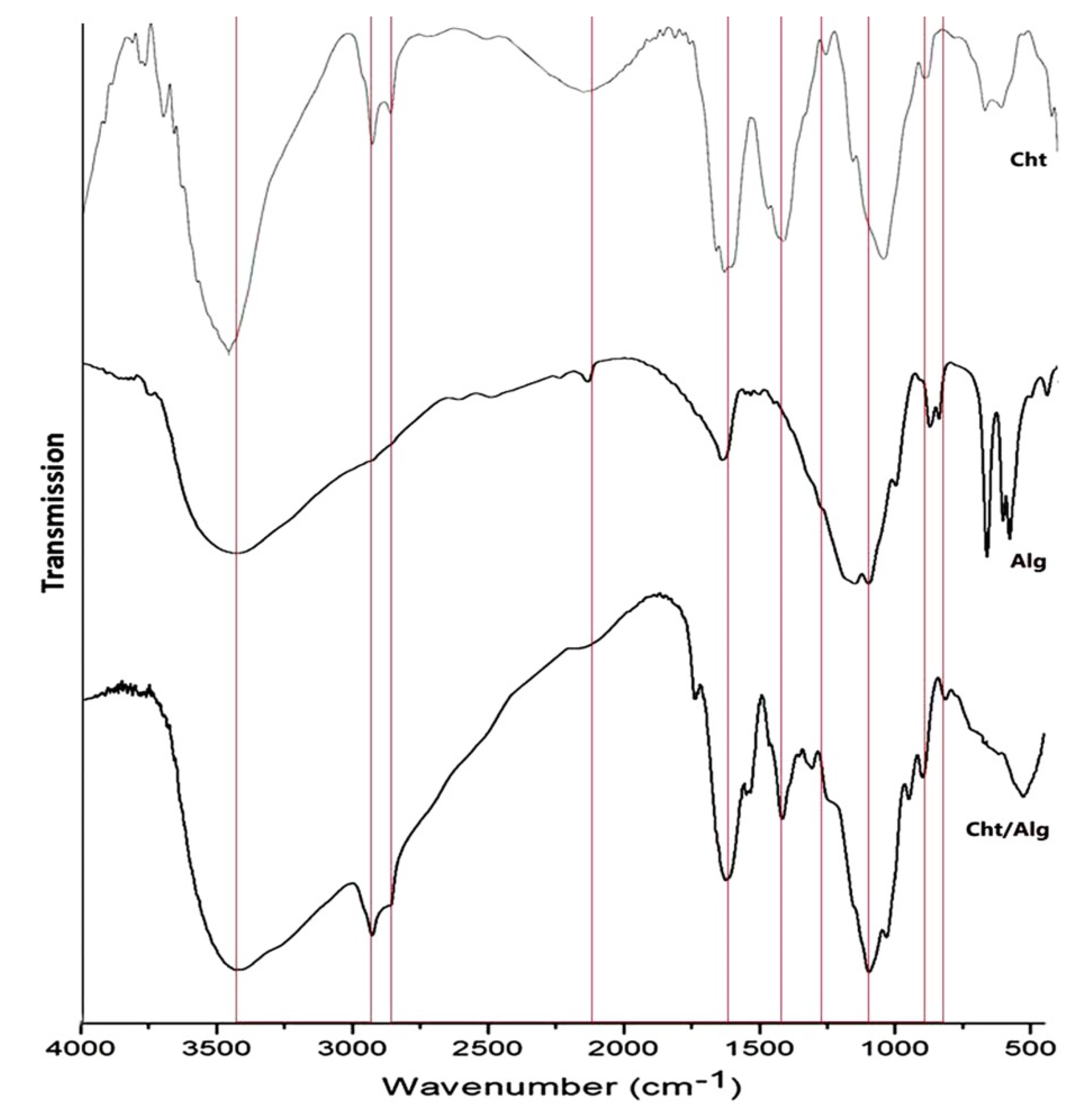
3.2.1. FTIR Analysis
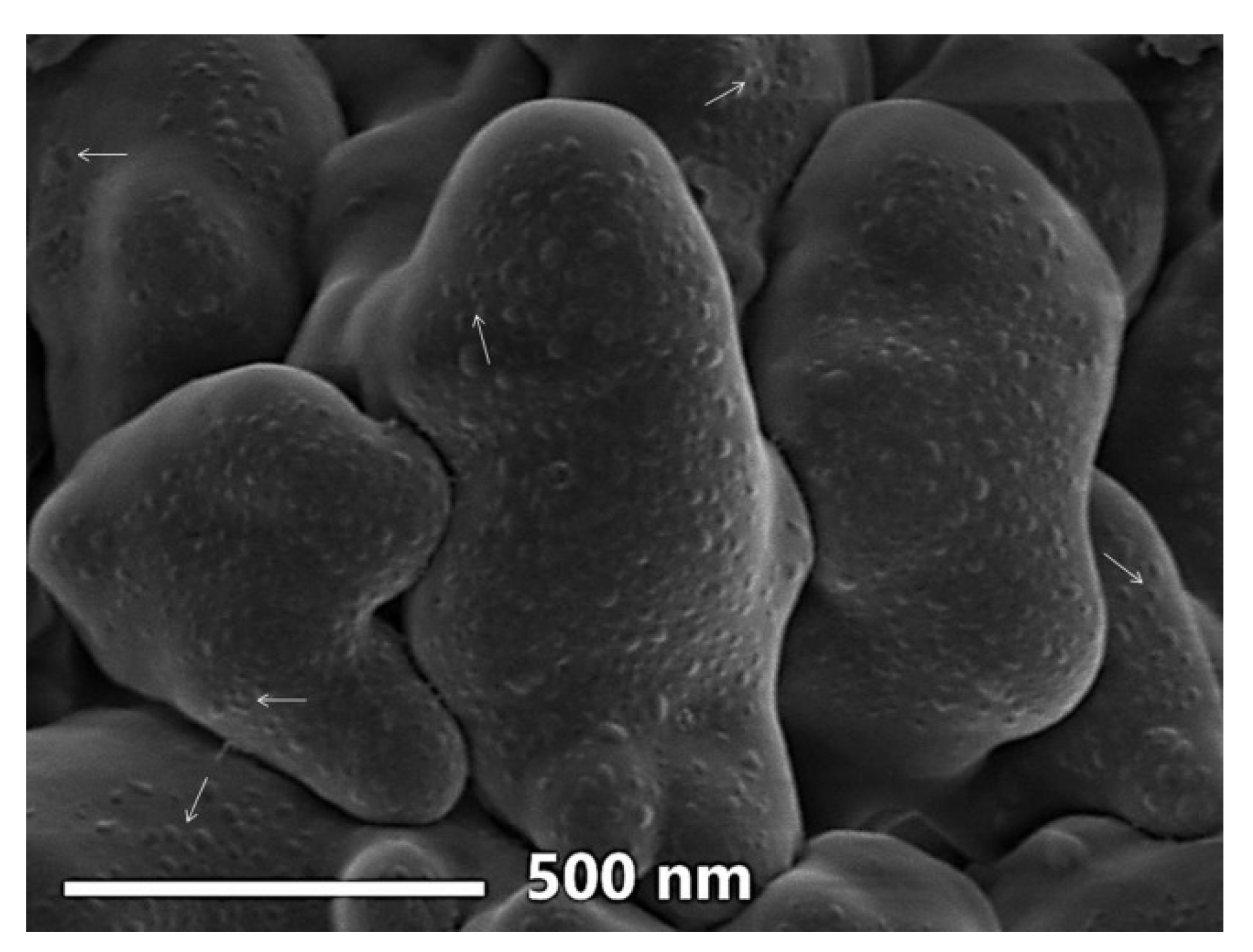
3.2.2. SEM Imaging
3.2.3. Nanomaterials’ Size and Charge
3.3. Batch Adsorption of Cr(VI)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crini, G. Historical review on chitin and chitosan biopolymers. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Pal, A.; Nakashima, K.; Yadav, B.K. Applications of chitosan in environmental remediation: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 266, 128934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Padil, V.V.; Škodová, M.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Agarwal, S. Hierarchically porous bio-based sustainable conjugate sponge for highly selective oil/organic solvent absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Padil, V.V.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Eco-Friendly and Economic, Adsorptive Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes by Bio-Based Karaya Gum—Chitosan Sponge. Polymers 2021, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Zare, E.N.; Makvandi, P.; Zheng, X.Q.; Iftekhar, S.; Wu, A.; Padil, V.V.; Mokhtari, B.; Varma, R.S.; Tay, F.R.; et al. Cytotoxic aquatic pollutants and their removal by nanocomposite-based sorbents. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.A.; Bourbon, A.I.; Vicente, A.A.; Cerqueira, M.A. Alginate/chitosan nanoparticles for encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin B2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.; Opwis, K.; Knittel, D.; Schollmeyer, E.; Nickisch- Hartfiel, A. Inhibition of Microbial Pathogens by Fungal Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Al-Saman, M.A.; Moussa, S.H. Production of fungal chitosan from date wastes and its application as a biopreservative for minced meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, S.H.; Tayel, A.A.; Alsohim, A.S.; Abdallah, R.R. Botryticidal Activity of Nanosized Silver-Chitosan Composite and its Application for the Control of Gray Mold in Strawberry. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, M1589–M1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, A.A.; El-Tras, W.F.; Elguindy, N.M. The Potentiality of Cross-linked Fungal Chitosan to Control Water Contamination through Bioactive Filtration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayel, A.A.; Gharieb, M.M.; Zaki, H.R.; Elguindy, N.M. Bio-Clarification of Water from Heavy Metals and Microbial Effluence using Fungal Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharari, S.; Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.H. Soil Emendation with Nano Fungal Chitosan for Heavy Metals Biosorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Colombi, L.C.; Wei, G. Recent advances in nanoporous membranes for water purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Rabey, H.A.; Almutairi, F.M.; Alalawy, A.I.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Sakran, M.I.; Zidan, N.S.; Tayel, A.A. Augmented control of drug-resistant Candida spp. via fluconazole loading into fungal chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, F.M.; El Rabey, H.A.; Tayel, A.A.; Alalawy, A.I.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Sakran, M.I.; Zidan, N.S. Augmented anticancer activity of curcumin loaded fungal chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalawy, A.I.; El Rabey, H.A.; Almutairi, F.M.; Tayel, A.A.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Zidan, N.S.; Sakran, M.I. Effectual Anticancer Potentiality of loaded bee venom onto fungal chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 2020, 2785304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Diab, A.M.; Elzahy, A.F.; Mazrou, K.E.; Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.H. Green Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles by Cinnamon Extract and Their Antimicrobial Activity and Application as Edible Coatings with Nano-Chitosan. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 6670709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. Chitosan derivatives obtained by chemical modifications for biomedical and environmental applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Synthesis and characterization of novel water soluble derivative of chitosan as an additive for polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 440, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Bissoon, R.; Bajnath, E.; Mohammed, K.; Lee, T.; Bissram, M.; John, N.; Jalsa, N.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Ward, K. Multistage extraction and purification of waste Sargassum natans to produce sodium alginate: An optimization approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Gao, B. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.J.; Huang, X.L.; Yang, F.; Zhao, W.F.; Zhou, X.Z.; Zhao, C.S. Engineering sodium alginate-based crosslinked beads with high removal ability of toxic metal ions and cationic dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 187, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K. Chitosan-alginate nanoparticles (CANPs) as potential nanosorbent for removal of Hg (II) ions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokila, S.; Gomathi, T.; Sudha, P.N.; Anil, S. Removal of the heavy metal ion chromium (VI) using Chitosan and Alginate nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.; Wu, H.F.; Gopal, J.; Sivanesan, I.; Chun, S. Exploiting microbial polysaccharides for biosorption of trace elements in aqueous environments—scope for expansion via nanomaterial intervention. Polymers 2017, 9, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M. Synthesis and application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in water treatment, environmental remediation, catalysis, and their biological effects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Z.; Hao, L.; Dong, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; Yu, H. The innovative application of organosolv lignin for nanomaterial modification to boost its heavy metal detoxification performance in the aquatic environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, A.R.; Mirrahimi, M.A.S. Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Khairudin, N.N.; Bt Mohamad, S.E.; Lee, K.X. Green Synthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Namvar, F.; Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mohamad, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using brown marine macroalga, Sargassum Muticum aqueous extract. Materials 2013, 6, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, D.M.; Ismail, M.M.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A. Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial potency of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using algae harvested from the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saggaf, M.S.; Tayel, A.A.; Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Moussa, S.H. Synergistic antimicrobial action of phyco-synthesized silver nanoparticles and nano-fungal chitosan composites against drug resistant bacterial pathogens. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSaied, B.E.; Diab, A.M.; Tayel, A.A.; Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Moussa, S.H. Potent antibacterial action of phycosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Spirulina platensis extract. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggaf, M.S.; Diab, A.M.; ElSaied, B.E.; Tayel, A.A.; Moussa, S.H. Application of ZnO Nanoparticles Phycosynthesized with Ulva fasciata Extract for Preserving Peeled Shrimp Quality. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.J. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products. A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubayed, N.M.; Al Houri, H.J.; Al Khulaifi, M.M.; Al Farraj, D.A. Antimicrobial, antioxidant properties and chemical composition of seaweeds collected from Saudi Arabia (Red Sea and Arabian Gulf). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, M.; Namvar, F.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mohamad, R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Sargassum muticum) aqueous extract. Molecules 2013, 18, 5954–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A.; Gharib, S.M. Green synthesis of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using two selected brown seaweeds: Characterization and application for lead bioremediation. Acta. Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, S.M.; Taherpoor, A.; Ebrahiminezhad, A. Algae and microalgae mediated synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their applications. J. Adv. Med. Sci. Appl. Technol. 2020, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Goycoolea, F.M.; Lollo, G.; Remuñán-López, C.; Quaglia, F.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan-alginate blended nanoparticles as carriers for the transmucosal delivery of macromolecules. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, J.; Lhotský, O.; Cajthaml, T. Nanoscale zero-valent iron application for in situ reduction of hexavalent chromium and its effects on indigenous microorganism populations. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2014, 485, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertah, M.; Belfkira, A.; Dahmane, E.M.; Taourirte, M.; Brouillette, F. Extraction and characterization of sodium alginate from Moroccan Laminaria digitata brown seaweed. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3707–S3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskewycz, A.; Shukla, R.; Ball, A.S. Phytofabrication of Iron Nanoparticles for Hexavalent Chromium Remediation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 10781–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, C. FTIR, SEM, EDS and GCMS Metabolite Profiling of Macroalgae–Sargassum wightii. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 6791–6797. [Google Scholar]
- Jesumani, V.; Du, H.; Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Huang, N. Comparative study on skin protection activity of polyphenol-rich extract and polysaccharide-rich extract from Sargassum vachellianum. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, M.; Nayak, P.L. Ecofriendly green synthesis of iron nanoparticles from various plants and spices extract. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Cortés, A.G.; Almendariz-Tapia, F.J.; Gómez-Álvarez, A.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Luque-Alcaraz, A.G.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Quevedo-López, M.Á.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M. Toxicological assessment of cross-linked beads of chitosan-alginate and Aspergillus australensis biomass, with efficiency as biosorbent for copper removal. Polymers 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongjanyakul, T.; Rongthong, T. Enhanced entrapment efficiency and modulated drug release of alginate beads loaded with drug–clay intercalated complexes as microreservoirs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafshgari, M.H.; Khorram, M.; Mansouri, M.; Samimi, A.; Osfouri, S. Preparation of alginate and chitosan nanoparticles using a new reverse micellar system. Iran. Polym. J. 2012, 21, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.L.; Gan, L.; Lan, X.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.F.; Li, F.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Development of sustainable carrier in thermosensitive hydrogel based on chitosan/alginate nanoparticles for in situ delivery system. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. Preparation, characterization and application of polysaccharide-based metallic nanoparticles: A review. Polymers 2017, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, L.; Chen, A.; Shang, C.; Lei, M.; He, K.; Luo, S.; Shao, J.; Zeng, Q. Chitosan-stabilized FeS magnetic composites for chromium removal: Characterization, performance, mechanism, and stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, J.; Ray, S.K. Chitosan based nano composite adsorbent—Synthesis, characterization and application for adsorption of binary mixtures of Pb(II) and Cd (II) from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Mu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Ai, Z. Magnetic Fe3O4–FeB nano composites with promoted Cr(VI) removal performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.P.; Inamdar, M.S. Aqueous behaviour of chitosan. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 2010, 9395367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Peyravi, M. Chitosan-sodium alginate multilayer membrane developed by Fe0@ WO3 nanoparticles: Photocatalytic removal of hexavalent chromium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, M.R.G.; Gomathi, T.; Saranya, M.; Sudha, P.N. Adsorption and kinetic studies on the removal of chromium and copper onto Chitosan-g-maliec anhydride-gethylene dimethacrylate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singanan, M. Removal of toxic heavy metals from synthetic wastewater. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Asia 2011, 37, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Singh, S.A.; Patel, C.M.; Anitha, K.L. Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 251, 117000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Katubi, K.M.; Amari, A.; Ben Rebah, F.; Tahoon, M.A. Synthesis of Polymer-Based Magnetic Nanocomposite for Multi-Pollutants Removal from Water. Polymers 2021, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Nanoparticles | Particles Range (nm) | Mean Diameter (nm) | Median Diameter (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-NPs | 12.5–83.1 | 21.4 | 22.1 | −25.6 |
| Cht/Alg NPs | 162.6–514.6 | 311.2 | 332.6 | −23.2 |
| Cht/Alg/Fe NPs | 173.9–568.5 | 342.6 | 382.5 | −34.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutairi, F.M.; El Rabey, H.A.; Alalawy, A.I.; Salama, A.A.M.; Tayel, A.A.; Mohammed, G.M.; Aljohani, M.M.; Keshk, A.A.; Abbas, N.H.; Zayed, M.M. Application of Chitosan/Alginate Nanocomposite Incorporated with Phycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticles for Efficient Remediation of Chromium. Polymers 2021, 13, 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152481
Almutairi FM, El Rabey HA, Alalawy AI, Salama AAM, Tayel AA, Mohammed GM, Aljohani MM, Keshk AA, Abbas NH, Zayed MM. Application of Chitosan/Alginate Nanocomposite Incorporated with Phycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticles for Efficient Remediation of Chromium. Polymers. 2021; 13(15):2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152481
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutairi, Fahad M., Haddad A. El Rabey, Adel I. Alalawy, Alzahraa A. M. Salama, Ahmed A. Tayel, Ghena M. Mohammed, Meshari M. Aljohani, Ali A. Keshk, Nasser H. Abbas, and Mohamed M. Zayed. 2021. "Application of Chitosan/Alginate Nanocomposite Incorporated with Phycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticles for Efficient Remediation of Chromium" Polymers 13, no. 15: 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152481
APA StyleAlmutairi, F. M., El Rabey, H. A., Alalawy, A. I., Salama, A. A. M., Tayel, A. A., Mohammed, G. M., Aljohani, M. M., Keshk, A. A., Abbas, N. H., & Zayed, M. M. (2021). Application of Chitosan/Alginate Nanocomposite Incorporated with Phycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticles for Efficient Remediation of Chromium. Polymers, 13(15), 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152481