Abstract
The natural polymer chitosan is the second most abundant biopolymer on earth after chitin and has been extensively explored for preparation of versatile drug delivery systems. The presence of two distinct reactive functional groups (an amino group at C2, and a primary and secondary hydroxyl group at C3 and C6) of chitosan are involved in the transformation of expedient derivatives such as acylated, alkylated, carboxylated, quaternized and esterified chitosan. Amongst these, quaternized chitosan is preferred in pharmaceutical industries owing to its prominent features including superior water solubility, augmented antimicrobial actions, modified wound healing, pH-sensitive targeting, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. It has been explored in a large realm of pharmaceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and the biomedical arena. Immense classy drug delivery systems containing quaternized chitosan have been intended for tissue engineering, wound healing, gene, and vaccine delivery. This review article outlines synthetic techniques, basic characteristics, inherent properties, biomedical applications, and ubiquitous challenges associated to quaternized chitosan.
1. Introduction
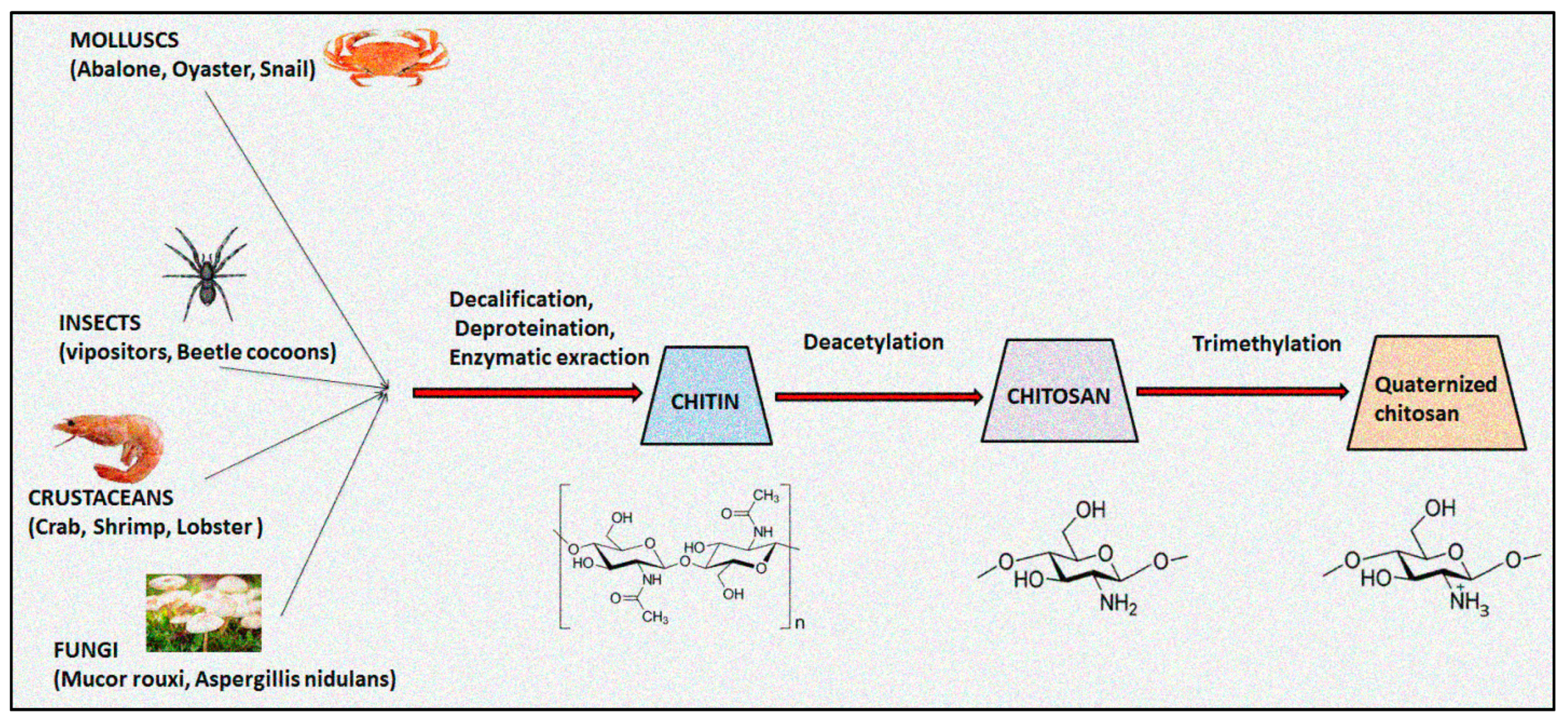
Chitosan, an aminoglucopyran polysaccharide, is widely utilized in pharmaceuticals, cosmeceuticals, biomedicals, agricultures, foods and packaging sectors owing to its inherent properties including biodegradability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity [1,2]. The natural biopolymer chitosan is predominantly obtained from the exoskeletons of marine crustaceans, mollusks, insects, and fungi through an alkali deacetylation process. Figure 1 illustrated the schematic developmental process of quaternized chitosan from native chitin [3]. In contrast to natural occurring chitin, chitosan is very soluble in acidic solvents and fluroalcohols. Chitosan is a weak base, possessing pKa ranging from 6.2 to 7.0, and tends to be biodegradable in both in vitro and in vivo into non-toxic metabolites. It can be easily digested by lysozyme into non-active oligosaccharide and is thus a desirable component for designing absorbable sutures, osteoconductive implants and tissue scaffolds [4]. The biological functions of chitosan biopolymer are based on its molecular weight, degree of acetylation, charge density and extent of quaternization [5]. The physicochemical and biological properties of chitosan are primarily affected by the degree of deacetylation that directly impact on its molecular weight, pKa, crystallinity, hydrophilicity, degradation, and biological actions [6,7]. A degree of deacetylation value close to 0% or 100% prolongs biodegradation and cell adhesion, whereas transitional values of the degree of deacetylation display speedy degradation rates of chitosan. The physicochemical properties including the degree of acetylation and the molecular weight of chitosan and its derivatives are accountable for its biological responses [8]. USFDA-approved chitosan is highly utilized in tissue engineering, skin regeneration and wound healing drug delivery systems [9]. The presence of inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds demonstrates crystalline behaviour, which accounts for its poor aqueous solubility. The limited solubility in a wide range of physiological solutions restricts the use of chitosan in designing drug delivery systems [10].
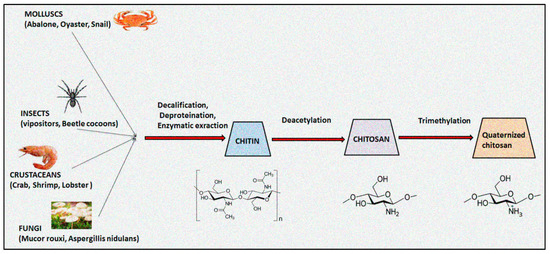
Figure 1.
Schematic developmental process of quaternized chitosan from native chitin.
Conformational changes in the chitosan skeleton are reliant on local environmental conditions including the pH, pKa, N-substitution group, process temperature and types of acids. The functional groups (hydroxyl and amino) contribute an essential role for imparting solubility to the chitosan molecule. At low pH, the attached amino group undergoes protonation, solubilizes and provides positive charge to the medium, offering strong electrostatic interaction with negative charge cell components. Moreover, the pKa of amino group highly depends on the degree of acetylation (DA); hence, the solubility of chitosan is also reliant on DA [11].
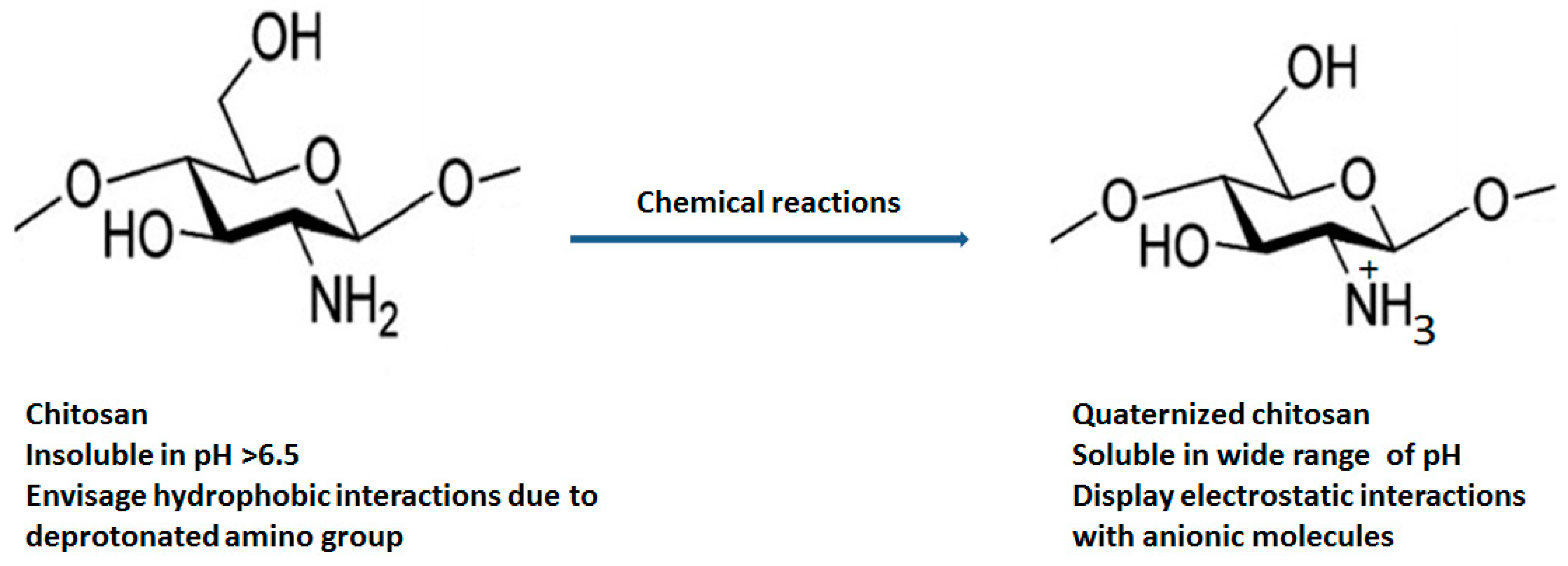
Various chemical modification such as acetylation (insertion of anhydride and acyl chloride) [12], alkylation (alkyl group) [13], carboxylation (glyoxylic acid, chloroalkanoic acid) [14], quaternization (quaternary ammonium salts) [15], esterification (sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid and chlorosulfonic acid) [16] and etherification (chloroacetic acid, ethylene oxide, dimethyl sulphate) [17] at the C2, C3 and C6 position of chitosan are carried out to improve its physicochemical (enhanced aqueous solubility, improved absorption, high bioavailability, etc.) and biological properties (improved antimicrobial action and antioxidant, high penetration across cell membrane, mucoadhesiveness, etc.) Figure 2 displays the structural differentiation between chitosan and quaternized chitosan [18].
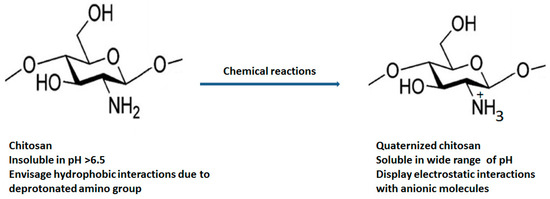
Figure 2.
Structural differentiation between chitosan and quaternized chitosan.
2. Quaternized Chitosan Derivatives and Physicochemical Properties
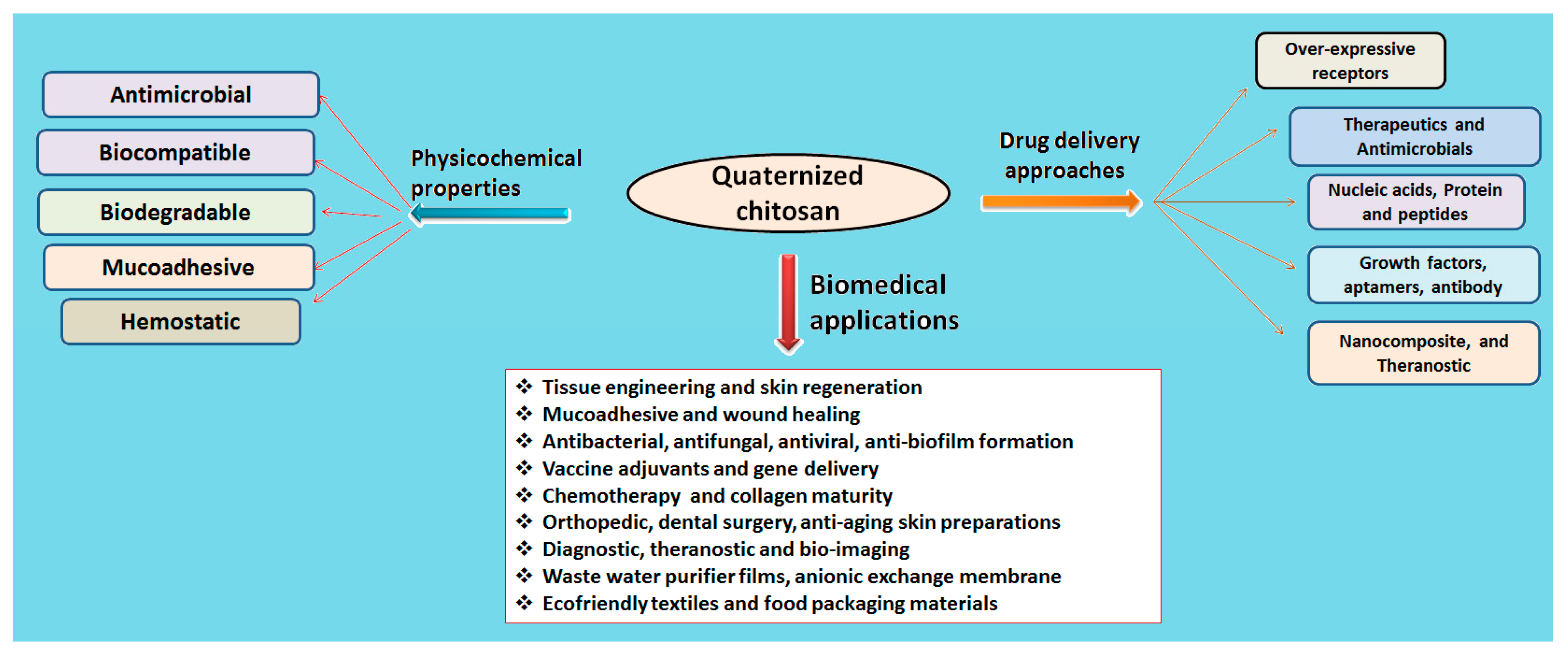
The quaternization of chitosan involves the insertion of a hydrophilic group via any of three methods: direct quaternary ammonium substitution, epoxy derivative open loop and N-alkylation. A high degree of substitution provides better aqueous solubility and enhanced antimicrobial action, and lessens cytotoxicity with innate mucoadhesiveness and efficient penetration. The degree of quaternization and molecular weight are a few essential parameters that elicit physicochemical and biological actions (Table 1). Figure 3 compiles drug delivery approaches and biomedical applications of quaternized chitosan [19].

Table 1.
Effect of parameters influencing the biological responses [20,21].
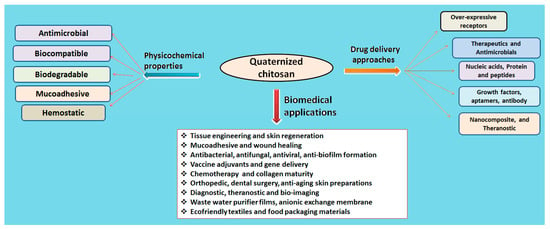
Figure 3.
Quaternized chitosan and its physicochemical and drug delivery approaches.
Quaternization not only enhances solubility but also escalates chargeability and antibacterial efficacy [22].
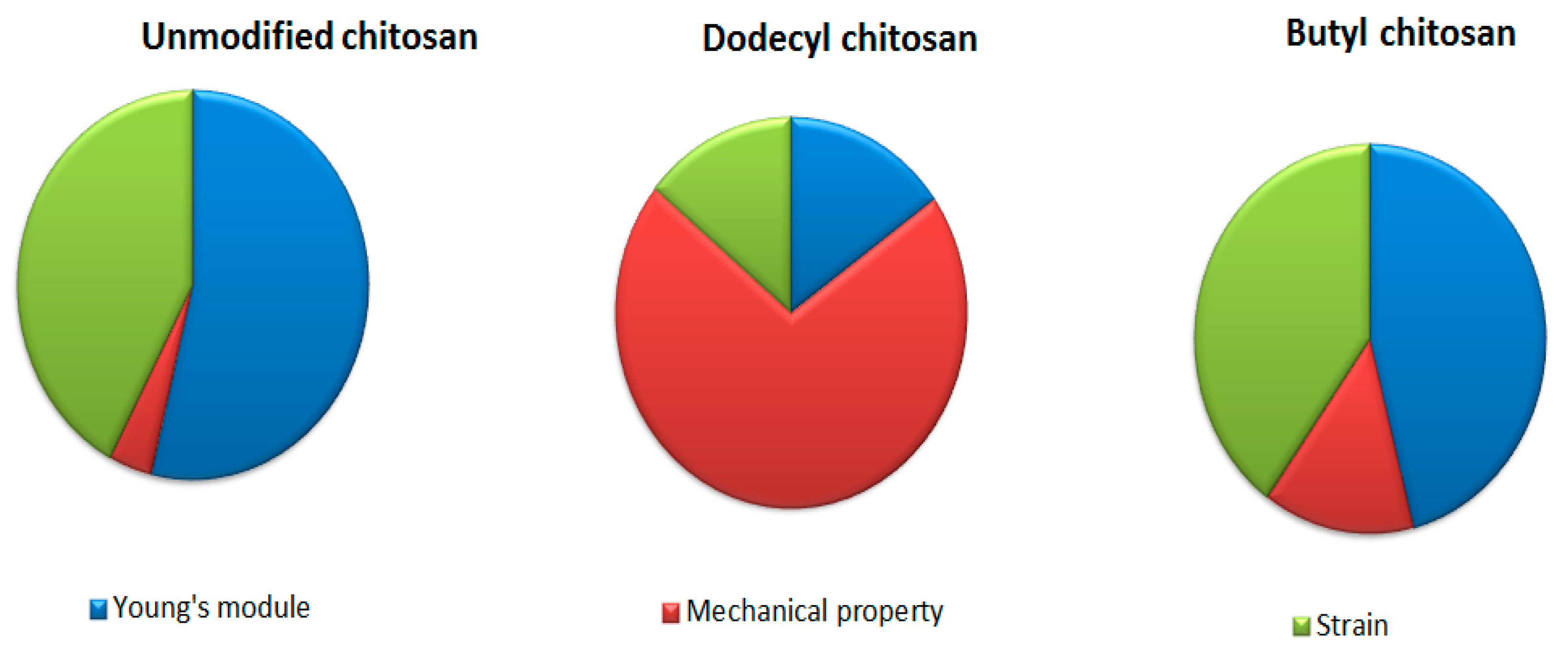
The mechanical property plays a vital role in imparting biomedical application. It is observed that mechanical property of chitosan enhances on increasing its concentration owing to high crystallinity. Jana et al. (2012) investigated the comparative tensile strength of scaffolds fabricated from chitosan solution (4–12%). As the concentration of chitosan increased in scaffold, augmented mechanical strength (from 1.74 MPa to 17.99 Mpa) was displayed through XRD patterns. The degree of protonation and extent of crystallinity mediated the high strength of chitosan [23,24,25]. Britto et al. (2007) synthesized quaternary salts of chitosan through dimethylsulphate reaction. The mechanical strength, Young’s modulus and maximum strain were compared to the unmodified, N-alkylated and quaternized chitosan films, which are well depicted in Figure 4. Unmodified chitosan film exhibited higher mechanical strength compared to quaternized (N-dodecyl chitosan) and alkylated (butyl chitosan) in order of 44.0 Mpa > 38.3 Mpa > 13.4 Mpa, respectively [26,27,28].
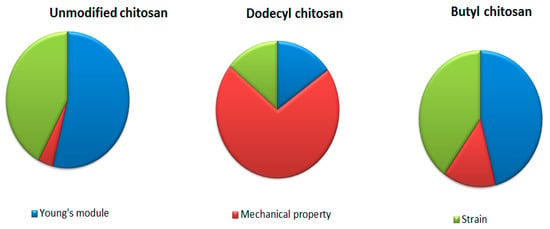
Figure 4.
Comparative mechanical properties of chitosan and its derivatives.
2.1. N,N,N-Trimethyl Chitosan Chloride
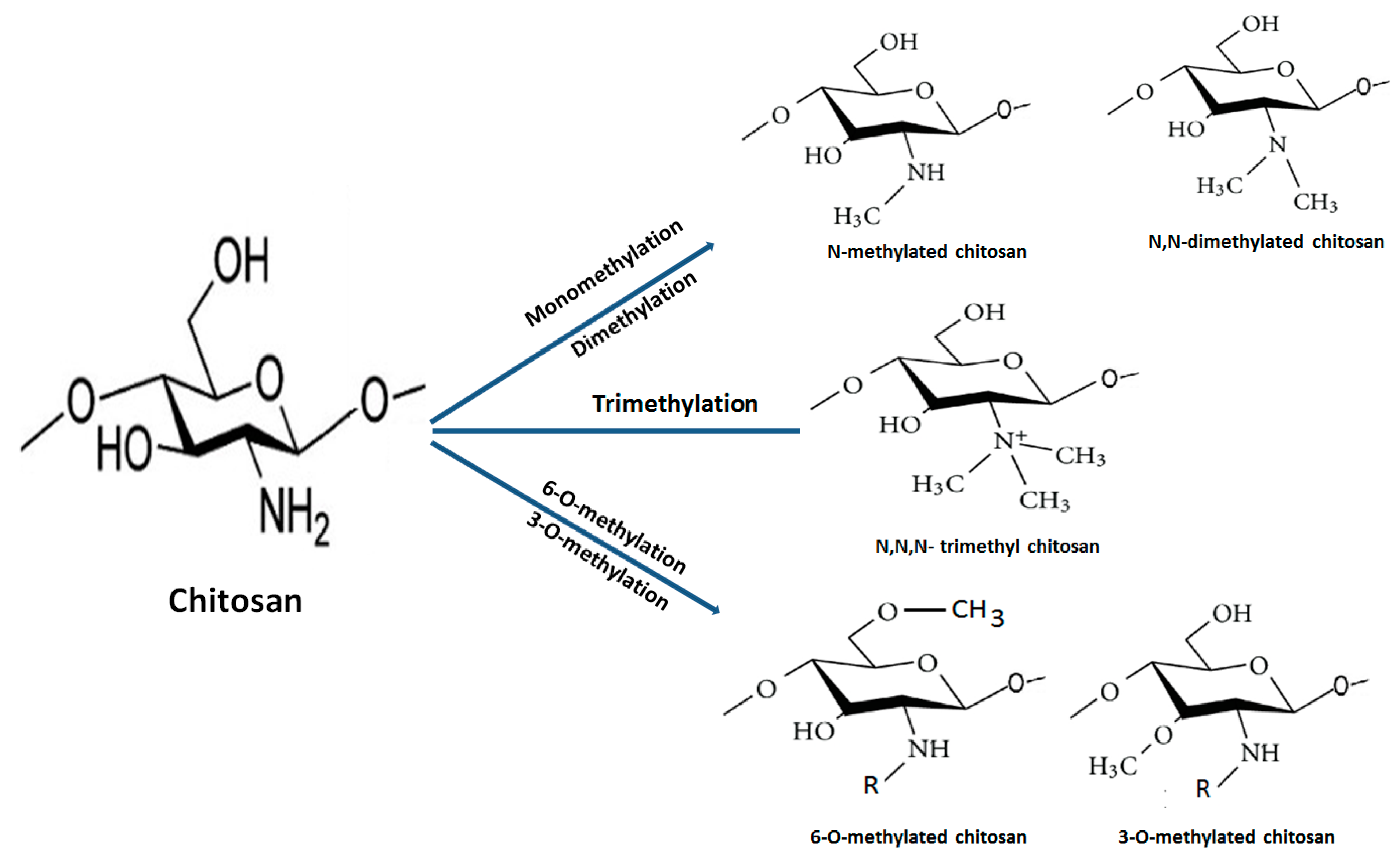
The quaternization (trimethylation and triethylation) of decorated amino groups in molecular structure of chitosan is carried out by treating it with methyl iodide at a high temperature in alkali medium. Subsequently, the degree of quaternization of different grades of deacetylated chitosans is optimized through the modification of a number of reaction steps and time. N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan chloride (TMC), the most abundantly explored QCh derivative, has been utilized in the formulation of pharmaceutical products. It is obtained through the methylation of the amino group at the C2 site of chitosan backbone (Figure 4). QCH substituted through N-(3-chloro-2-hydroxy-propyl) trimethylammonium chloride has increased pharmacokinetic and antimicrobial properties. The extent of N-substitution (ES) affected antimicrobial action of QCH. The literature envisaged that when ES is 20% high, the efficacy of QCH derivative against pathogenic E. coli (16 to 64 μg/mL) and S. aureus (8 to 64 μg/mL) is enhanced. Furthermore, N-methylated, N-arylated, N,N-dimethylaminophenyl and pyridyl-substituted QCH are very soluble in water irrespective of the pH and exhibited superior antibacterial efficacy [29].
The multifunctional quaternized chitosan derivatives, their synthesis and biomedical applications are displayed in Figure 5 [30]. Other byproducts such as 6-O-methylated, 3-O-methylated and N, N-dimethylated chitosan are infrequently used due to their unfavourable properties. The very first TMC was synthesized by Terayama and coworkers and was called macramin [31,32]. A higher degree of quaternization achieved after O-methylation of chitosan at position 3-OH and 6-OH results in less soluble trimethyl chitosan iodide. The methylation process is considerably decreased through recycling of the basic reaction until the desired product is achieved. Furthermore, preparation of trimethyl chitosan (N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan) is accomplished through an ion exchange process that possesses high solubility and basicity. Reports have cited that the intermediate degree of quaternization (~40%) evidences the highest solubility regardless of the molecular weight and degree of acetylation of chitosan due to the replacement of the attached primary amino functional group with quaternary amino groups at the C2 position [33]. The molecular weight of TMC increases during the course of reductive methylation because the methyl group is added to the previously attached ammonium group of the repeated monomers. Moreover, a significant decrease in molecular weight is noticed after treating with strong alkali at an elevated temperature, which causes degradation of the polymeric chain. Furthermore, an increase in the degree of quaternization of TMC polymers causes a decrease in the intrinsic viscosity [34]. The mucoadhesive property decreases with an increase in the degree of quaternization, owing to the alteration of conformation of polymers during the quaternization process, which affects the interaction between fixed positive charges on each polymeric chain at C2 position. It also decreases the polymer–polymer flexibility. Furthermore, attached functional groups (methyl, ethyl, propyl, benzyl, etc.) on amino groups may hide positive charges and this causes a steric effect. Both decrease the polymeric chain flexibility and produce steric effects that influence the extent of charge transfer between cationic TMC and anionic sialic acid present in the mucus, thus resulting in inferior mucoadhesiveness [35].
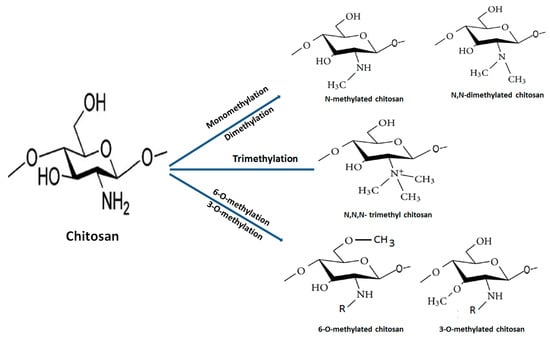
Figure 5.
Different pathways for synthesis of methylated chitosan from native chitosan.
2.2. N-[(2-Hydroxyl-3-Trimethyl Ammonium) Propyl] Chitosan
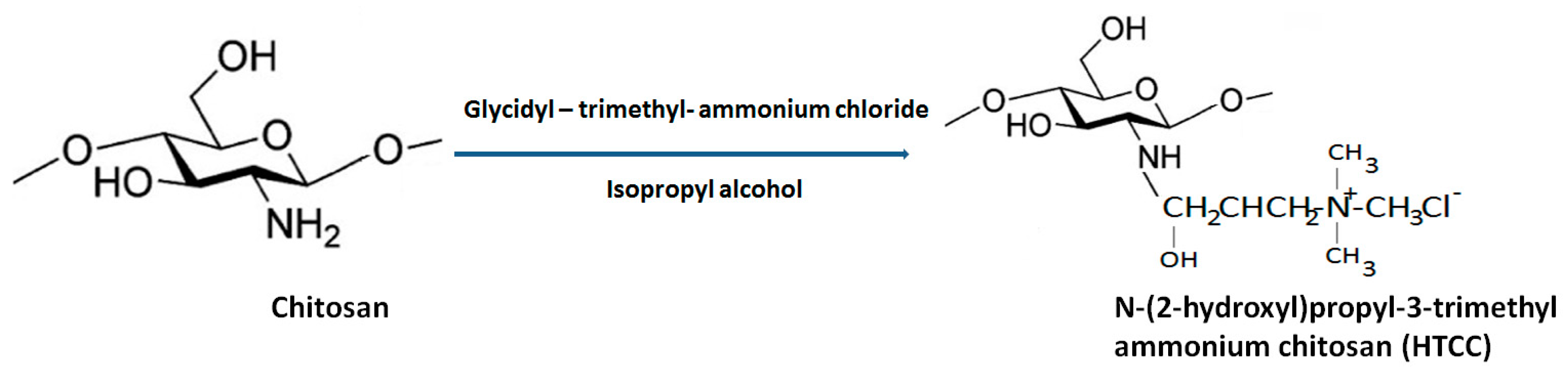
N-[(2-hydroxyl-3-trimethyl ammonium) propyl] chitosan or HTCC is the second most-popular QCh prepared via alkylation process involving insertion of quaternary ammonium group at the outside the chitosan structure. Lang et al. 1980 synthesized the first HTCC through chitosan modification [36]. The reagent ‘glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride’ (GTMAC) is often used for direct replacement of hydrogen from attached amino and hydroxyl functional groups from chitosan at the C6 position to obtain O, N-substituted quaternized chitosan (HTCC), which enhances the aqueous solubility and superior antibacterial efficacy (Figure 6) [37]. The generated HTCC polymers have different degrees of quaternization that refer to the extent of positive charge [38].
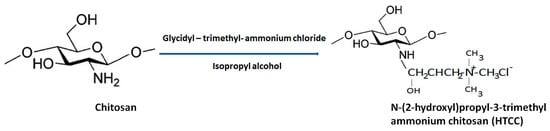
Figure 6.
General synthesis of HTCC from biopolymer chitosan.
HTCC presents non-toxicity, improved aqueous solubility, and modified antimicrobial action along with biocompatibility and bioavailability features. Xiao et al. (2012) demonstrated that HTCC is more amorphous than crystalline chitosan. Quaternization weakens inter-/intra molecular hydrogen bonds and results in unorganized HTCC polymer that not only facilitates solubilization but also favours better absorption due to the diffusion of free water molecules from the HTCC chains [39].
Similarly, increased antimicrobial action is also defined due to abundant positive charge on HTCC that is attracted by negative surface charge present on the bacterial cell surface. HTCC encompasses permanent positive charges on its surface. The physicochemical properties of HTCC are highly reliant on the degree of quaternization. Wang et al. (2018) studied the effect of quaternization on the physicochemical and biological properties of HTCC. The outcomes revealed that the apparent viscosity, solubility, and elasticity are amplified by an increase in the degree of quaternization on storage. A lesser degree of quaternization produces hydrophobic HTCC polymer that is employed as an efficient vaccine adjuvant to adsorb antigens via hydrogen bonding formed through unoccupied amino groups [40]. Furthermore, Shagdarova et al. (2019) explained that a high degree of quaternization resulted in improved antibacterial action against E. coli and S. epidermis [41]. The versatile HTCC is widely combined with other chemicals such as poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) carboxylic acid, poly (l-caprolactone) and polyacrylonitrile to improve the solubility, tensile strength, and antimicrobial action for commercial purposes.
2.3. Pyridine Salt Grafted Quaternized Chitosan
Different new QCh-based pyridine salts have been derived that explore synergistic antiviral, antifungal and antibacterial action owing to the attached cationic pyridine salts. In this context, PACS (pyridine chloroacetyl chitosan), BHPACS (4-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylideneamino)-pyridine) and CHPACS (4-(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylideneamino)-pyridine) synthetic quaternized chitosan derivatives have been derived from reacting chloroacetyl chitosan and pyridine. These synthetic QCh-based substances exhibit strong antifungal potency towards Monilinia fructicola, F. oxysporum, Cladosporium cucumerinum and Colletotrichum legenarium [42]. The antifungal effect occurred through polycationic-charged pyridine consisting of QCh and negatively charged fungal cell surface. The sturdy electrostatic interaction causes the disorganization and denaturation of proteins present in cell membranes, and ultimately cell death. The literature also reports the synthesis of N-methyl-pyridinium and N-methyl-1, 2, 3-triazolium grafted QCh derivatives that were quite effective for phytopathogenic fungi including F. wilt, Collectotrichum lagenarium and F. oxysporum.
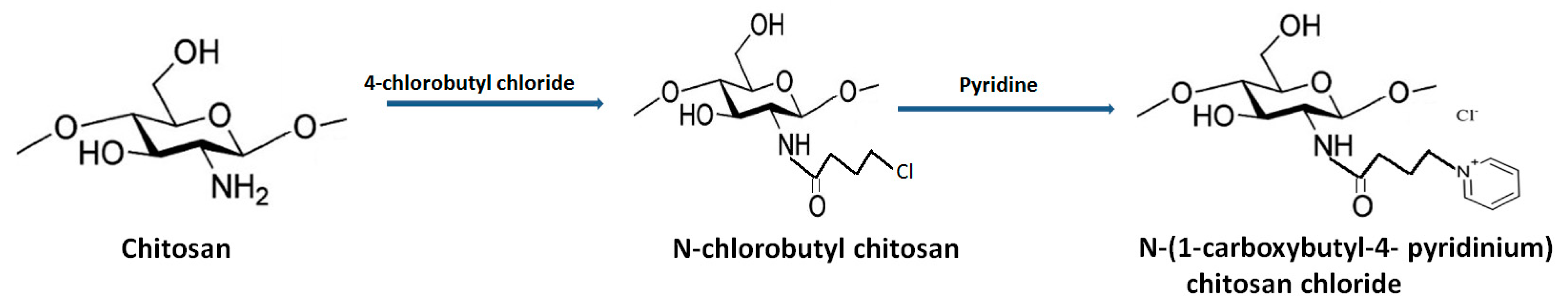
The presence of a pyridine ring and 1, 2, 3-trizolium in the QCh backbone depicted enhanced solubility in alkaline medium and mediated superior antifungal action compared to unmodified chitosan [43]. Jia et al. (2016) synthesized N-(1- carboxbutyl-4-pyridinium) chloride chitosan through introducing nucleophilic substitution on pyridine molecules (Figure 7 [44]. The antifungal activity against B. cinerea and F. fulva revealed disturbance in cell permeability owing to the adsorbed cationic charges on the fungal cell surface. Consequently, deformation of fungal hypha and cell death was reported [45].
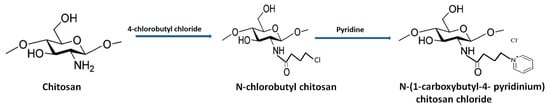
Figure 7.
Synthetic route for the development of pyridine-grafted quaternized chitosan.
2.4. Phosphonium Salt Grafted Quaternized Chitosan
Multifunctional quaternary phosphonium salts are organophosphate biocides, basically obtained from the nucleophilic substitution reaction between halide salts and phosphine. These compounds have better antimicrobial action than QCh polymers and are employed in gene therapy, vaccine adjuvant and in water purification units. One of the reported water-soluble quaternary phosphonium salt (WSPCS) has been synthesized from QCh with a minimal degree of quaternization (~4%). The developed WSPCS also exhibited better solubility in organic solvents. Figure 8 illustrates the basic pathway for the synthesis of WSPCS. Increasing the substitution resulted in low cytotoxicity (for mouse fibroblast) and greater antimicrobial action [46]. The cross-linked quaternary-phosphonium chitosan is widely used in wastewater treatment as the phosphonium ion has greater efficiency for the adsorption of chromium ions. Zeng et al. developed quaternary chitosan phosphonium particles loaded with pEGFP (plasmid type enhanced green fluorescent protein) for the formulation of novel gene vectors. The synthesized particles exhibited biosafety and high potential for gene transfection [47].

Figure 8.
Synthesis of WSPCS from chitosan molecule.
2.5. Other Quaternized Chitosan Derivatives
N-betainates and mono/diquaternary piperazine derivatives of chitosan revealed a varied degree of quaternization without any side reactions. The development of these derivatives provided well-defined structural determinants that are accountable for extreme solubility (4–6% w/v) at pH = 7 and better absorption/permeation enhancer [48]. Table 2 enlists novel quaternized chitosan derivatives and their biomedical usage.

Table 2.
Newly introduced quaternized chitosan derivatives and their biomedical application.
Rahimi et al. (2019) introduced QC-IMDZ, a novel quaternized chitosan, after grafting quaternary imidazole into the hydroxyl groups of chitosan backbone. Wound dressing material embedded with silver nanocomposite on the QC-IMDZ surface was fabricated that showed superior antimicrobial actions for both bacteria and fungi due to the presence of cationic imidazole. However, excess silver nanocomposite embedded film showed lower solubility and required a prolonged clotting time compared to a low amount silver-nanocomposites-embedded QC-IMDZ films [49].
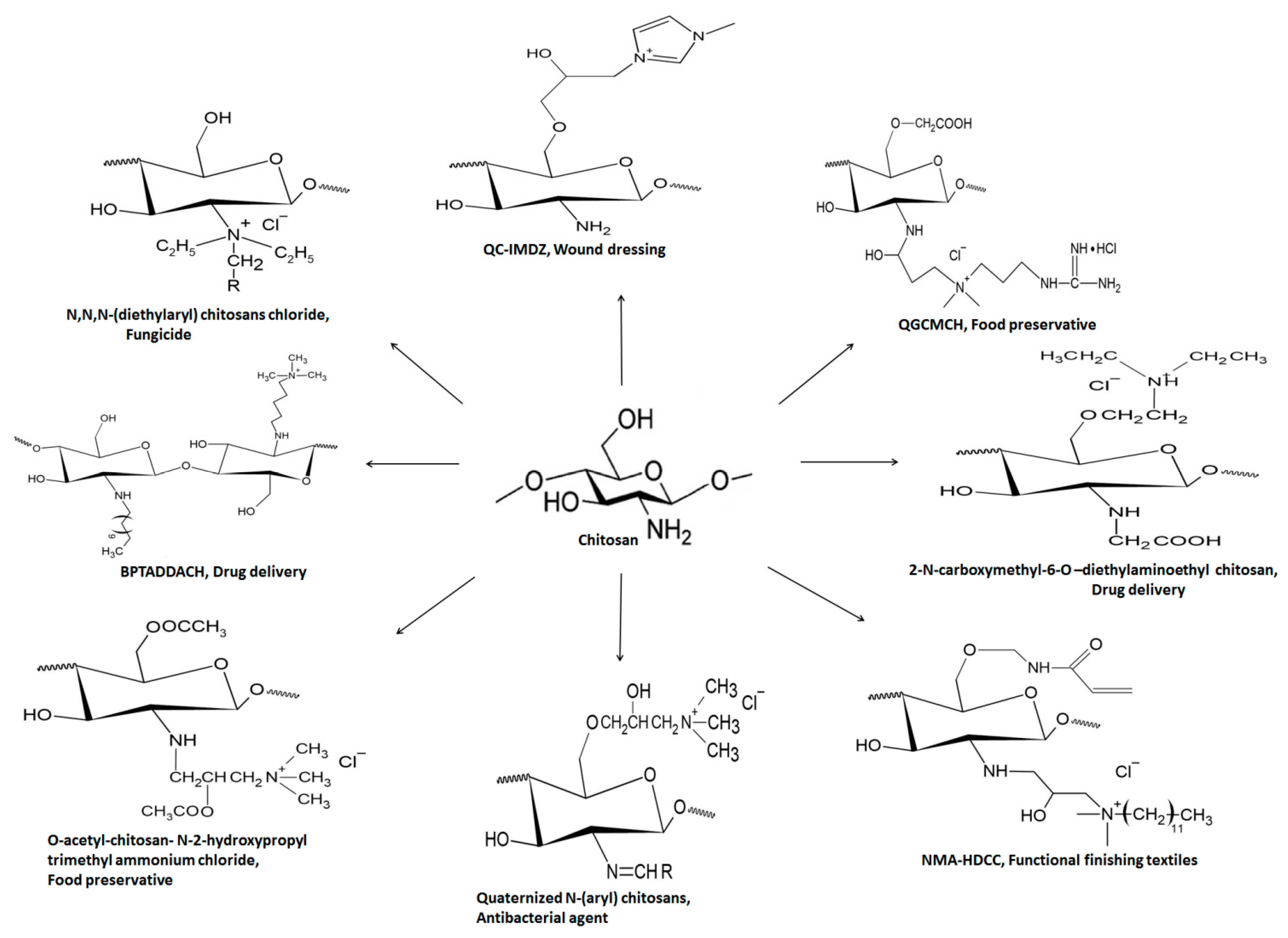
Another quaternized chitosan derivative ‘N-O-[N,N-diethylammoniomethyl (diethyldimethylene ammonium) methyl chitosan has the efficiency to modify the penetration of drug candidates irrespective of their affinity towards mucosal epithelium. Improved drug penetration through porcine buccal epithelium was observed via the paracellular route [50]. Furthermore, ex vivo and in vivo studies suggested satisfactory permeation of dexamethasone in rabbit cornea through the transcellular transport route compared to widely used TMC [51]. Figure 9 summarizes structural and biomedical applications of diverse QCh derivatives synthesized from natural chitosan. Figure 9 compiles a few quaternized chitosan derivatives and their biomedical applications [52,53].
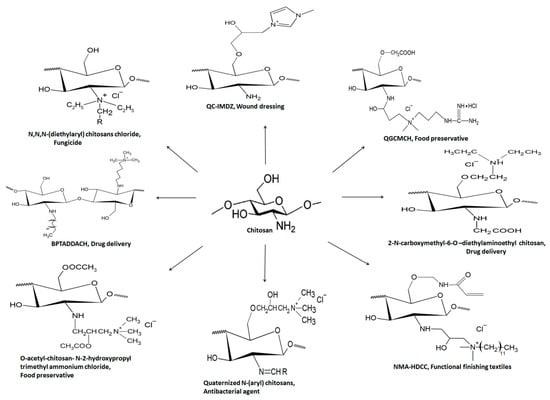
Figure 9.
Structural illustration of different QCh derivatives and their biomedical applications.
Wang et al. (2016) developed five aqueous soluble quaternized chitosan derivatives (O-quaternary ammonium salt-chitosan) that contained N-methyl-N-R-N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium bromide. Grafted R substituents were benzyl chloride, dodecyl, tetradecyl, hexadecyl and octadecyl. All the O-quaternized derivatives exhibited greater solubility, better antibacterial action for Gram-positive bacteria and lower cytotoxicity against AT2 cell lines. Furthermore, dodecyl- and tetradecyl-grafted O-quaternary ammonium salt chitosan exhibited better biological properties compared to other derivatives and suggested a facile way to design QCh-based hydrogels, membranes, coated beads, scaffolds, dressing materials and bandages and nanoparticles owing to extreme solubility, permanent cationic charges, and characteristic antibacterial actions [67].
Few fatty acids were conjugated on quaternized chitosan nanoparticles for the efficient insulin delivery in liver. Strong electrostatic interaction between positively charged quaternized chitosan and negatively charged insulin was observed. Furthermore, the addition of fatty acids increased the surface hydrophobicity, which mediated hepatocyte absorption, enhanced insulin accumulation in liver cells and illustrated a better antidiabetic effect. Insulin-embedded quaternized chitosan nanoparticles consisting of lauric acid and oleic acid exhibited impressive bioavailability of 233% and 311%, respectively, after subcutaneous administration [68].
3. Biomedical Applications of Quaternized Chitosan Derivatives
3.1. Antimicrobial
The chemical configuration of polycationic QCh is a desirable requisite for the antimicrobial action. Electrostatic interaction between cationic QCh and anionic microorganisms plays an important part for antibacterial activity. A higher degree of substitution of ammonium groups adorned on the backbone of QCh imparts a positive charge that neutralizes cell surfaces of bacteria and disturbs cytoplasmic integrity [37,69]. Moreover, hydrophobic alkyl substitutions on QCh stimulate significant bacterial death as they preferably interact with the inner surface of the bacterial cell wall. The antibacterial effect is prominent in neutral and high pH rather than acidic. The literature envisages that high-molecular-weight and solid QCh derivatives are unable to pass through the cell membrane. They are only adsorbed at the microbial cell surface, channelize electrostatic interactions, hamper nutrient transport, and cause alteration in cell permeability. Conversely, low-molecular-weight water-soluble QCh particles penetrate the bacterial cell wall, intercalate with DNA, and inhibit the transcription process [70]. QCh derivatives always remain positively charged and are soluble at all physiological pH.
The antibacterial activity of the very first N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan was reliant on the degree of quaternization from the [−N(CH3)3] structure present in the molecule. A higher degree of quaternization improved its aqueous solubility. Additionally, the presence of hydrophobic methyl groups increased the interaction with the lipoidal cell membrane of the microorganism and depicted superior antimicrobial action [71]. Another derivative, N,N-di-ethyl-N-methyl quaternized chitosan (DMCHT) was synthesized via reductive alkylation of aldehydes, through the formation of Schiff base. The developed QCh exhibited antimicrobial efficacy owing to the formation of polyelectrolyte complexes between QCh derivative and peptidoglycan of bacterial cell, which, in turn, inhibited the growth of bacteria [72]. The antimicrobial efficacy of TMC and DMCHT was compared at 50% degree of quaternization. The results showed superior antibacterial activity of TMC against S. aureus owing to the presence of smaller alkyl groups that enabled easy interaction with the cell wall of the bacteria. Voluminous DMCHT was comprised of heavy N-ethyl functional groups on its structure [73].
Furthermore, comparative antimicrobial efficiency was assessed among DMCHT (N, N-di-ethyl-N-methyl quaternized chitosan), BZDCHT (N-benzyl-N-N-di methyl chitosan) and BDCHT (N-butyl-N,N-dimethylchitosan) against S. aureus and E. coli at pH 7.4. The outcomes displayed prominent antimicrobial activity of these QCh as compared to chitosan. DMCHT and BDCHT showed higher hydrophilicity required for better antimicrobial efficacy in comparison to BZCHT. Insertion of hydrophobic groups (phenyl and benzyl) decreased the antimicrobial action by virtue of shielding interaction between N-quaternized site and the cell wall of the bacteria [74]. Reports cite that the protonated amine groups including +NH3 and +ND/+NM (non-quaternized amine group) are highly effective antibacterials compared to +NT (N-trimethylated) ones. However, the chains of TMC derivatives are more flexible and readily interact with the bacterial cells than chitosan at pH ≥ 5.5 suggesting promising antibacterial potential where neutral pH required [75].
Fu et al. (2011) synthesized O, N-quaternized chitosan through attaching benzyl radical on N-quaternized chitosan followed by treatment with ethyl iodide in the presence of alkali at 36 °C. Developed cationic O,N-quaternized chitosan possessed enormous quaternary ammonium chloride moieties that interacted with negative residues of S. aureus cell surface. Therefore, affected cell integrity (protein, lipopolysaccharide and techoic acid), altered plasma membrane permeability, leakage of nutrients and mediated cell death [76]. Similar antibacterial action was observed for Gram-negative E. coli that contains a thick layer of extracellular lipopolysaccharide and checks the entry of foreign molecules. O-quaternized chitosan exhibited slightly less antibacterial action compared to O,N-quaternized chitosan derivatives by virtue of the reduced electron donation through N-benzyl modification [77,78].
Several natural and synthetic polymers are utilized either alone or in combination for the development of antibacterial systems [79]. In this context, the fabrication of non-woven nanofibers from QCh derivatives; i.e., N-(2-hydroxy)-propyl-3-trimethylammonium salt of chloride has been employed to elaborate wound healing properties of biomaterials including hydrophilicity, water retention capacity, mucoadhesiveness, antimicrobial efficacy, etc. [80]. However, the presence of ionogenic groups in quaternized chitosan generates high repulsive force that limits uniform fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning. Thus, non-ionic polymers (poly-L-Lactide-co-d and poly vinyl alcohol) are incorporated to make the polymeric solution electrospinnable [81].
3.2. Antiproliferative
Biocompatible quaternized chitosan displays adequate antimicrobial and antiproliferative activity both in vitro and in vivo. For instance, QCh-coated sutures exhibited comparatively high anti-infection and cytocompatibility compared with triclosan-coated sutures, owing to the presence of ample positive charge on decorated quaternary ammonium functional groups that interact with the negatively charged phosphoryl groups of microorganisms [82]. Triclosan, a widely used antibacterial agent, has a significant advantage over other antibiotics by virtue of its low drug resistance and potent inhibition of biofilm formation. However, triclosan-coated sutures are effective in controlling surgical site infections, but the occurrence of tissue toxicity and induction of tumor proliferation and endocrine disorders limit its practice in surgical operation. The above investigation favored the usage of broad spectrum antibacterial QCh as an alternative to triclosan in orthopedic surgery [83].
Yang et al. (2016) elucidated limitations associated with vicryl plus (triclosan coated polyglactin) sutures such as surgical site infections and toxicity. Vicryl plus sutures were modified through surface coating of QC. Bacterial cell adhesion efficiency of modified HV sutures against Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus revealed significant antibacterial efficiency for both pathogens for 48 h. Furthermore, the HV sutures were found to be cytocompatible with human-skin-derived fibroblast cells. The procedural flexibility and economic value of QCh-modified HV sutures laid down a suitable strategy to manage suture-related infections in orthopedic surgeries [84,85].
Furthermore, Li et al. (2018) focused on the clinical application of QCh in malignant melanoma (B-RafV600E), one of the most invasive skin carcinomas. Human melanoma cells were interacted individually with vermurafenib (B-RafV600E inhibitor), QCh and a combination of both, to investigate cell permeability, proliferation, apoptosis, and viability. The outcomes revealed that the presence of QCh promoted an antiproliferative effect against melanoma cells. Moreover, QCh could enhance cell permeability at the preliminary stage, thus facilitating intracellular drug uptake. Interestingly, polycationic QCh made electrostatic interactions with negatively charged cancerous cells that disturbed their cytoplasmic integrity. The investigation concluded that QCh upset the surface charges on melanoma cell, which may be an important parameter to change cell permeability [86]. Wongwanakul et al. (2017) examined cell proliferation and cell differentiation properties of QCh on the intestinal barrier through CaCo-2 cell lines in vitro model. Poor cytotoxicity and superior biocompatibility on the intestinal barrier were observed from a lesser degree of substitution and low dose of QCh. The study suggested potential usage of QCH in designing oral drug delivery system [87].
3.3. Antibiofilm
Biofilms, the complex colonies of living microorganisms developed at the infection site, are extremely resistant to antibiotics and antimicrobials. These biofilms consist of a well-recognized self-produced extracellular matrix made up of protein, polysaccharide, and DNA [88]. Bacterial adherence and the biofilm formation at the implantation site involve two typical processes. Initially, the accumulation of microbial community starts, which releases polysaccharide intracellular adhesion, an extracellular substance. Furthermore, PIA is mediated through intracellular adhesion that comprised of different core genes such as ica A, B, C, ica D and one regulatory gene icaR. The icaA gene is an index of biofilm preparation. A high concentration of QCh is capable of preventing icaA transcription, thus limiting biofilm formation or microbial viability [89].
Biofilms produced at the post-surgical infection sites are mostly associated with the use of medical devices including catheters, implants, endotracheal tubes, valves, etc. Both Gram-positive (S. aureus, S. epidermis) and Gram-negative (P. aeruginosa) bacterial communities grow on healthcare devices [90]. These pathogenic bacteria can survive even in the presence of high doses of antibiotics (1000 times high) than required to eliminate their planktonic population. Once well-organized biofilm is formed around the surgical implants surface, it becomes difficult to completely rule out through antibiotic therapy [91].
Most of the existing antibiotics and antimicrobials are unable to eradicate biofilms, owing to their similar activity spectrum and common modes of action. QCh can be employed for the elimination of biofilm by virtue of its anti-infective property against bacteria, viruses, and fungi [77,92]. Both high- and low-molecular-weight QCh functionalized with hydrophobic residues (thiol protected 6-mercaptonicotinamide and methylated cyclodextrins) are reported as unconventional antimicrobial agents as they display improved wound healing, mucoadhesiveness and antibiofilm potential [93].
Piras et al. (2019) proved the biomedical application of QCh to be possible, i.e., antibacterial, anti-adhesive and antibiofilm. They demonstrated collective data of high- and low-molecular-weight QCh and their efficacy against common pathogens including P. aeruginosa and S. epidermis. Low-molecular-weight QCh derivatives were efficacious biofilm eliminators at very low concentrations, whereas high-molecular-weight QCh after covalent immobilization on titanium plates could be applied as spray or liquid plasters for the inhibition of bacterial adhesion. Thus, QCh-modified titanium implants mediated the dynamic strategy to terminate biofilm associated with medical devices [94].
3.4. Antifungal Activity
As with antibacterial activity, the occurrence of ample positive charge on QCh supposed to interact with the anionic residues of macromolecules present on the fungal surface resulted in the leakage of intracellular electrolytes and nutrients. Reports cite that QCh affects morphogenesis of the fungal cell wall and controls the functions of enzymes accountable for growth [95]. Guo et al. (2007) synthesized different QCh derivatives for the study of antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum lagenarium. Four QCh derivatives, i.e., N-(2-hydroxyl-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl CS, N-(5-bromic-2-hydroxyl-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl CS, N-(2-hydroxyl-5-nitro-phenyl)N,N-dimethtyl CS and N-(5-chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl CS, were developed, which exhibited better antifungal effects compared to the unmodified chitosan [96]. The result emphasized that high molecularity of QCh is accountable for stronger antifungal efficacy [97].
Insertion of an arylfurfural group to the N-quaternized chitosan indicated amplified antifungal effects compared to unmodified chitosan. Moreover, N-quaternized arylfuran chitosan (QACHT) substituted with chlorine and nitrogen oxide further modified the antimicrobial and the antifungal effects that interacted with anionic macromolecules of fungal cell wall and mediating seepage of intracellular electrolytes [98]. Deacetylated chitosan functionalized with propyl and pentyl trimethylammonium bromide exhibited increased antifungal activity, i.e., three- and six-fold higher for A. flavus. In vitro antifungal assay evaluated the minimum inhibitory concentration for 72 h by varying the QCh derivatives concentration (0.5–16 g/L). The outcomes revealed that QCh derivatives inhibited mycelium growth even at one quarter of the concentration of deacetylated chitosan [99].
The antifungal activity of QCh can also be improved by the addition of more quaternary ammonium groups such as N-trimethyl. Increased molecular weight, positive charge, degree of quaternization and hydrophobic functional moieties intensify antifungal action. Il’ina et al. (2017) synthesized synthetic metal (Cu II) complexes of QCh (N-propyl chitosan derivative) and evaluated the antifungal efficacy against yeast (C. albicans and R. rubra) and mycelial fungi (F. oxysporum and C. herbarum). N-propyl-derived QCh was developed through treatment with glycidyl trimethyl ammonium chloride under controlled conditions. Amalgamation of N-propyl QCh (53%) and copper ions (13%) proved efficient against common fungal plant pathogen F. oxysporum [100]. Viegas de Souza et al. (2017) synthesized low-molecular-weight QCh derivative (dodecyl aldehyde-treated propyl trimethyl-ammonium bromide chitosan) to investigate the antifungal effect on A. parasiticus and A. flavus. The outcomes revealed that amphiphilic QCh derivatives exhibited amplified inhibition indices that were reliant on hydrophobicity and polymer concentrations. These QCh derivatives opened novel avenues for the development of chitosan-based biofungicides [101].
3.5. Mucoadhesiveness
N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan is widely utilized as a penetration enhancer for the delivery of peptides and macromolecular compounds across the mucosa in alkaline and neutral pH medium. Here, the degree of quaternization has a direct impact on the property of mucoadhesiveness and penetration across the membrane. Snyman et al. (2003) studied the effect of extent of quaternization (22–48%) and molecular mass (100,000 g/mole) on the biological activity of synthesized TMC polymers. The outcomes suggested decreased mucoadhesiveness on increased quaternization of TMC polymers [35,102].
The ocular or ophthalmic drug delivery system encounters several route barriers related to nasolacrimal drainage, stimulated lacrimation, blinking, blood ocular barrier and corneal impermeability. The use of mucoadhesive polymers such as chitosan derivatives facilitates effective ocular drug delivery owing to their elite interaction with the mucosal membrane. The presence of positive charge mediates the electrostatic interaction with the anionic mucin of the mucosal layer [103]. The ocular drug absorption of therapeutics depends on their aqueous solubility and mucoadhesiveness. Quaternized chitosan shows better candidature for enhanced permeation across ophthalmic tissues owing to their improved solubility and mucoadhesive property. However, beta-cyclodextrin conjugated chitosan has been employed for the ocular delivery of dexamethasone but restricted mucoadhesive limited their use.
Piras et al. (2018) demonstrated the development of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin grafted quaternary ammonium chitosan that was processed through treatment with hexamethylene diisocyanate. The QCh derivative efficiently carried dexamethasone, exhibited drastic changes in solubility and bioavailability. Moreover, a stable, mucoadhesive and controlled release formulation could be achieved. Preliminary assessments revealed that the developed conjugate has promising potential for the effective management of ocular disorders [93]. Yostawonkul et al. (2017) developed mucoadhesive oleoyl- quaternized chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). Alpha-mangostin, a hydrophobic drug was embedded in the developed NLC, which exhibited more than 90% entrapment efficiency and minimum polydispersity. Excellent mucoadhesive, higher physical stability and greater cytotoxicity were observed against cancerous Caco-2 cells over Hela cells [104].
Konovalova et al. (2018) analyzed the comparative mucoadhesive property of chitosan (20 kDa) and its hydrophobic and quaternized hydrophobic chitosan derivatives (HC and QHC). The unmodified chitosan exhibited large aggregates in the keratinocytes and colon cells of murine small intestine, whereas HC and QHC showed mucoadhesiveness as a fine dotted line when observed through confocal microscopy [105]. Hydrophobic derivatives of chitosan mediated local drug release and improved biodegradation.
3.6. Drug Carriers
3.6.1. Nanofibers
Nanofibers have always been a lucrative tool for the preparation of scaffolds, either as topically applied dressing material or in the membrane unit for filtration. Water purification systems enclosing membrane filtration units are widely accepted strategies for the retention of pathogens including bacteria and viruses according to their size. Table 3 compiles few novel biomedical usages of QCh-based nanofibers. Reports cite that holding small-sized viruses (<25 nm) necessitates enormous membrane surface area along with low water flux and high transmembrane pressure. Moreover, the filtration membrane unit has to be replaced with another new membrane frequently. To overcome this downside, Bai et al. (2013) fabricated an electro spun nanofibrous membrane comprised of quaternized chitosan polymer (HTCC) and graphene allotrope. HTCC has the proficiency to adsorb pathogenic non-enveloped porcine parvovirus on its surface. Distinctive attributes of graphene hydrophobicity and ionogenic HTCC enhanced the functional efficiency of developed nanofibers (95% virus retention). The developed nanofibers embedded with a blend of HTCC/graphene depicted effective microfiltration membrane water purification systems featured with low pressure technology for the significant removal of pathogens [106].

Table 3.
Quaternized chitosan-embedded nanofibers in diverse biomedical arena.
Santos et al. (2018) extended the study and fabricated antibacterial nanofibers from a blend of N-(2-hydroxy)-propyl-3-trimethylammonium chitosan chloride (QCh) and polycaprolactone (PCL) polymeric solutions. The produced nanofibers displayed improved hydrophilicity and tissue compatibility with superior mechanical strength when evaluated for enzymatic degradation, cell adhesion, and cytotoxicity against neonatal human dermal fibroblasts cells. The viscosity and degree of deacetylation of QCh strongly affected the alignment of nanofibers that was required for relative orientation with cancerous cells for better cytotoxic activity. The fabricated QCh/PCL nanofibers possessed essential benchmarks required for designing wound dressing materials in the domain of tissue engineering [107].
Amplified antimicrobial efficiency of quaternized chitosan was exploited by Cheah et al. (2019) as they performed surface grafting of PAN nanofibers (P-CN) with quarternary amine (glycidyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) functionalized chitosan under acidic, neutral, and alkaline conditions. Developed water-stable quaternized chitosan nanofibrous membranes (P-HTCC) were subjected for evaluation of antibacterial activity against E. coli. The outcomes from the microbiological assessment revealed that the quaternized chitosan-derived membrane developed in acidic medium exhibited stronger antibacterial action (99.95% for E. coli) compared to the neutral and alkaline medium. The fabricated P-HTCC membranes had the potential to be assembled into a microfiltration unit for the disinfection of Gram-negative pathogen E. coli [108].
Mi et al. (2014) addressed the issue of unsafe drinking water containing countless microbial loads and toxic impurities accountable for millions of deaths every year. An economical antiviral filtration material was fabricated utilizing ionogenic quaternized chitosan (HTCC) and non-ionogenic polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). The electrospun material embraced the high surface area required for effective water adsorption. Furthermore, HTCC/PVA nanofibers were treated with glutaraldehyde (cross linking agent) to control the water solubility and enhance the water stability (only 30% swelling in 6 h). The system could retain both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. The HTCC-/PVA-embedded microfiltration membrane was affordable and proved to be an efficient low-pressure filtration unit by virtue of significant retention of pathogens [109].
3.6.2. Hydrogel
Hydrogels have a cross-linked network of variable hydrophilic functional groups containing polymers that can absorb plentiful water. Surface-adorned hydrophilic groups such as amine (–NH2), hydroxyl (−OH), sulphate (−SO3H), and amide (−CONH−) empower hydrogel to absorb watery fluid that expands their volume due to swelling. Hydrogel-based dressing materials provide several advantages, including ample absorption of tissue exudate, maintenance of optimum moisture content at the site and encouraging cell proliferation (Table 4). Antibacterial hydrogels are highly required in the health care sector to accelerate the wound healing cure rate. In this context, Xiao et al. (2020) prepared hydrogel consisting of QCh, chemical cross-linker ‘polyacrylamide’, and silver nanoparticles. The developed hydrogel exhibited desirable tensile strength (approximately 100 kPa) with a shear stress of 104 Pa. Excellent swelling capacity, a synergistic antibacterial effect, and low toxicity of Ag-mediated hydrogel reinforced the designing of appropriate wound dressing materials [115].

Table 4.
Biomedical utility of QCh-derived hydrogels.
You et al. (2016) synthesized quaternized chitosan via reaction of chitosan with 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride in an alkaline solution. Thereafter, the polyelectrolyte complex hydrogel was prepared through in situ polymerization of poly acrylic acid monomers in quaternized chitosan solution. Resultant elastic, mechanically strong and surface tunable hydrogel was developed that displayed superb solvent-induced shape memory performance [116].
Mamidi et al. (2021) demonstrated a pH- and thermal-responsive chitosan-based nanocomposite (CNP) hydrogel that has potential applications in nanomedicine and nanotechnology. They developed an integrated chitosan nanocomposite containing poly (N(4-aminophenyl) methacrylamide)- carbon and diclofenac. The system possessed several conductive physicochemical properties such as spherical shape and uniform particle size. Additionally, the CNPs were pH- and heat-sensitive and exhibited controlled release for 15 days. Moreover, the designed CNP showed significant cell viability for human fibroblast cells [117].
3.6.3. Beads
Thermoduric bacteria that can survive even after pasteurization of milk pose momentous threat to dairy and beverages industries. To overcome this challenge, biodegradable HTCC-anchored magnetic cellulose beads were developed via the dropping technique which could resist temperature up to 300 °C. Extended antibacterial efficacy against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris suggested the potential application of developed beads for food safety management [125]. Furthermore, quaternized chitosan beads were developed to adsorb phosphate and nitrate ions present in aqueous solution. Quaternized chitosan beads were formulated through reacting cross-linked chitosan with trimethyl ammonium chloride. The quaternized chitosan beads were quite effective in the pH range of 3–9 and exhibited an adsorption capacity for phosphate (97.5%) and nitrate ions (99%) that followed Freundlich isotherm model. The presence of common ions such as chloride, sulphate and bicarbonate did not alter the sorption capacity of quaternized chitosan beads [126].
The literature envisages that polycationic ammoniated polymers are fascinating options for the adsorption of negatively charged ions and sulphated polysaccharides through electrostatic interaction. In this regard, QCh has been explored for capturing anions, even at high pH. Eskandarloo et al. (2018) proposed the formulation of quaternized chitosan/polystyrene microbeads (CS/PS) for the selective adsorption of heparin, an anticoagulant from porcine intestinal mucosa sample. The comparative adsorption efficiency of CS/PS microbeads and marketed Amberlite FPA98 Cl resin was evaluated utilizing a heparin-bovine serum albumin model in pH range 4.1–9.2. The outcomes depicted superior adsorption efficiency of CS/PS micro beads (2.84 mg/g) and could be regenerated after treating with sodium chloride solution. Furthermore, the recovered microbeads can be reused for adsorption of heparin without any loss of adsorption capacity. Moreover, CS/PS microbeads could adsorb heparin from real biological sample containing heparin [127].
Quinlan et al. (2016) utilized quaternized chitosan hydrogel beads for efficient adsorption of 2-naphthoxyacetic acid from oil sand processed water (OSPW) system. 2-naphthoxyacetic acid is highly toxic and occurs in significant concentrations (40–70 mg/L) in OSPW that requires prolonged time for degradation. Hence, it necessitates removal of 2-naphthoxyacetic acid through either filtration, advanced oxidation, or adsorption methods. QCh has been identified as an attractive adsorbent by virtue of adsorption of anionic ions. The research emphasized retention of aromatic organic carboxylate site present in 2-naphthoxyacetic acid through polycationic QCh via the ion exchange adsorption process. The mode of adsorption signified Langmuir isotherm following pseudo first-order kinetics. The developed QCh hydrogel beads were moderately swellable and demonstrated effective adsorption of 2-naphthoxyacetic acid (91%) at the initial concentration of 200 mg/mL [128].
3.6.4. Nanoparticles
Splendid accomplishments have been anticipated through chitosan-based nanoparticles for the management of different diseases over past decade. These biodegradable and biocompatible nanoparticles are not only exhibit improved solubility, site specific/localized action but also minimize undesirable toxicity. Highly demanded chitosan is frequently explored as a carrier in drug delivery systems, fabrication of wound dressing materials, management of skin regeneration and tissue engineering. Quaternized chitosan-based nanoparticles (QCh NPs) have attracted wide interest owing to their exclusive physicochemical and biological features. Chemical modification such as grafting, functionalization, Schiff base formation and quaternization are few strategies that expand physicochemical and biological features of chitosan. Quaternization of chitosan significantly improves the aqueous solubility in neutral pH hence enhances the diffusion of drug moiety across biological membrane in neutral/alkaline physiological conditions. The positive charge facilitates pronounced mucoadhesiveness, antimicrobial activity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability as well as widening its biomedical applications. Numerous trimethyl, triethyl, dimethyl ethyl, and N-(2-hydroxy-3 trimethyl ammonium) propyl derivatives of quaternized chitosans have been discussed in Table 5 as potential carriers for the transportation of proteins, genes, vaccines, and chemotherapeutics at the target site [39,129].

Table 5.
QCh-based nanoparticles and their biomedical applications.
3.6.5. Quaternized Chitosan Nanocomposites
Strong interaction between bifunctional quaternized chitosan and carbon nanocomposite displayed superior mechanical properties (tensile strength), improved ionic absorption, enhanced antimicrobial action owing to their enormous surface-to-volume ratio (surface area), smaller size, and higher dispersion in given media. Abdel-Aziz et al. (2020) have developed a novel antituberculosis delivery system composed of N,N,N-trimethyl chloride (TMC)/Ag nanocomposite synthesized through a one pot green route. Synthesized nanocomposite (11–17 nm) system has exhibited promising antimycobacterial action (MIC 1.95 μg/mL). The observed antitumor activity displayed less toxicity (IC50 357.2 μg/mL) for normal (WI 38) lung cells and preeminent growth inhibition for A549 cancerous cells (IC50 12.3 μg/mL) [130]. Luo et al. (2015) initially synthesized nanocomposites from chitosan/montmorillonite resin and quaternized modifier 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan/montmorillonite resin. The developed quaternized chitosan-containing nanocomposites were small, spherical, smooth, dense, and exhibiting good dispersibility in water. The adsorption study performed on methyl orange revealed that quaternized chitosan/montmorillonite was strongly adsorbed compared to without montmorillonite, and thus can be a prospective material for column packing and wastewater treatment [131]. In this series, mechanical and ionic conductive properties of QCH functionalized carbon nanotube membrane matrix were evaluated. Improved dispersion of carbon nanotube promoted the load transfer and assisted hydroxide ion exchange through the membrane matrix. Reduced ionic conductivity and modified tensile strength indicated the potential application in preparation of anionic exchange membrane fuel cells [132]. Similarly, Gong et al. (2019) developed a layered double hydroxide ion conductor composed of QCH/PVA and carbon nanotubes. The system exhibited 1.57-fold enhanced tensile strength, 47 mS/cm2 ionic conductivity at 80 °C, and displayed a good reinforcing property [133].
QCh nanoparticles are highly acclaimed for designing oral drug delivery systems by virtue of significant drug diffusion and improved penetration across the epithelial barrier. Several ‘bottom up’ methods for nanoparticles development are widely emphasized, including emulsion droplet coalescence, ionic gelation, the reverse micelle method, self-assembly, chemical alteration, coacervation, and precipitation. Methods such as milling, ultrasonication, and high-pressure homogenization listed as ‘top down’ are also employed for nanoparticles synthesis [140]. Omar et al. (2021) developed novel oral drug nanocarriers composed of quaternized aminated chitosan and curcumin to enable the slow release of curcumin at the site of colon.
The ionic gelation method was opted for to formulate nanoparticles (Q-AmCs NPs) employing different concentration of crosslinker ‘sodium triphosphate’. Formulated Q-AmCs NPs were comparatively nanoscaled (~162 nm) with higher entrapment efficiency (~94.4%) and maximum potential of +48.3 mV than aminated chitosan (~231 nm, 75%, +32.8 mV). The in vitro drug release study in various physiological media (simulate gastric fluid, pH = 1.2; and simulated colon fluid, pH = 7.4) exhibited controlled cumulative drug release in alkaline pH (74%). The NPs depicted acceptable biocompatibility and biodegradability that suggested potential use for cancer management [141]. Improved solubility of quaternized chitosan in variable pH ranges encourages versatile biomedical usage [142]. Advanced applications of quaternized chitosan NPs are reported in vaccine development as well. The occurrence of cationic charge on quaternary ammonium groups is independent of any pH of surrounding media. Moreover, the positive charge facilitates advanced bioadhesion and drug delivery across mucosal membrane via strong electrostatic interaction with negatively charged endothelial regions [143].
3.6.6. Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine adjuvants are essential components that modify vaccine potency through encouraging cell-mediated or humoral immune responses via vaccine antigens. An ideal adjuvant should have the efficacy to solubilize antigens, facilitate transportation across mucosal barrier and potential for encouraging systemic and mucosal immunity. Chitosan and chitosan derivatives are fascinating candidates for vaccine adjuvants by virtue of their remarkable physicochemical (solubility, stability, biodegradability) and biological values (cytocompatibility, non-toxicity, antimicrobial). Reports cited that quaternized chitosan have greater potential to induce antigen-presenting cells (APCs), encourage cytokine stimulation and produce preferred humoral, cellular, and mucosal immune responses [144].
A lot of chemical structure modifications have been performed with the primary amine group of chitosan to enable it to have high aqueous solubility without altering exclusive biological properties. QCh decorated with N, O-carboxymethyl and N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl functional moieties are frequently preferred for the synthesis of vaccine adjuvants. During vaccine preparation, the pH of QCh ranges from 4.3 to 5.5, which facilitates protonation of chitosan and makes natural electrostatic interaction with negatively charged encapsulated antigen [145]. QCh and its derivatives are utilized as potential mucosal vaccine adjuvants owing to their biological features including the formation of natural electrostatic interaction between cationic chitosan and anionic sialic acid in mucus that assists improved mucosal absorption of antigen. TMC possesses all these virtues along with higher aqueous solubility, greater mucoadhesiveness and more stability in diverse ionic conditions than chitosan; hence, it is utilized broadly in vaccine development. Moreover, TMC finds vital role in vaccine development because of its similar functional performance as that of synthetic adjuvants including alum, cyclic guanosine monophosphate and Freund’s adjuvant, etc. [146]. Moreover, QCh has a better capacity to open tight mucosa junctions than chitosan, which facilitate permeability of antigens within the mucosal cells [147]. Biocompatible, non-reactogenic, economical and biodegradable QCh are also reported for their immunomodulation ability [148].
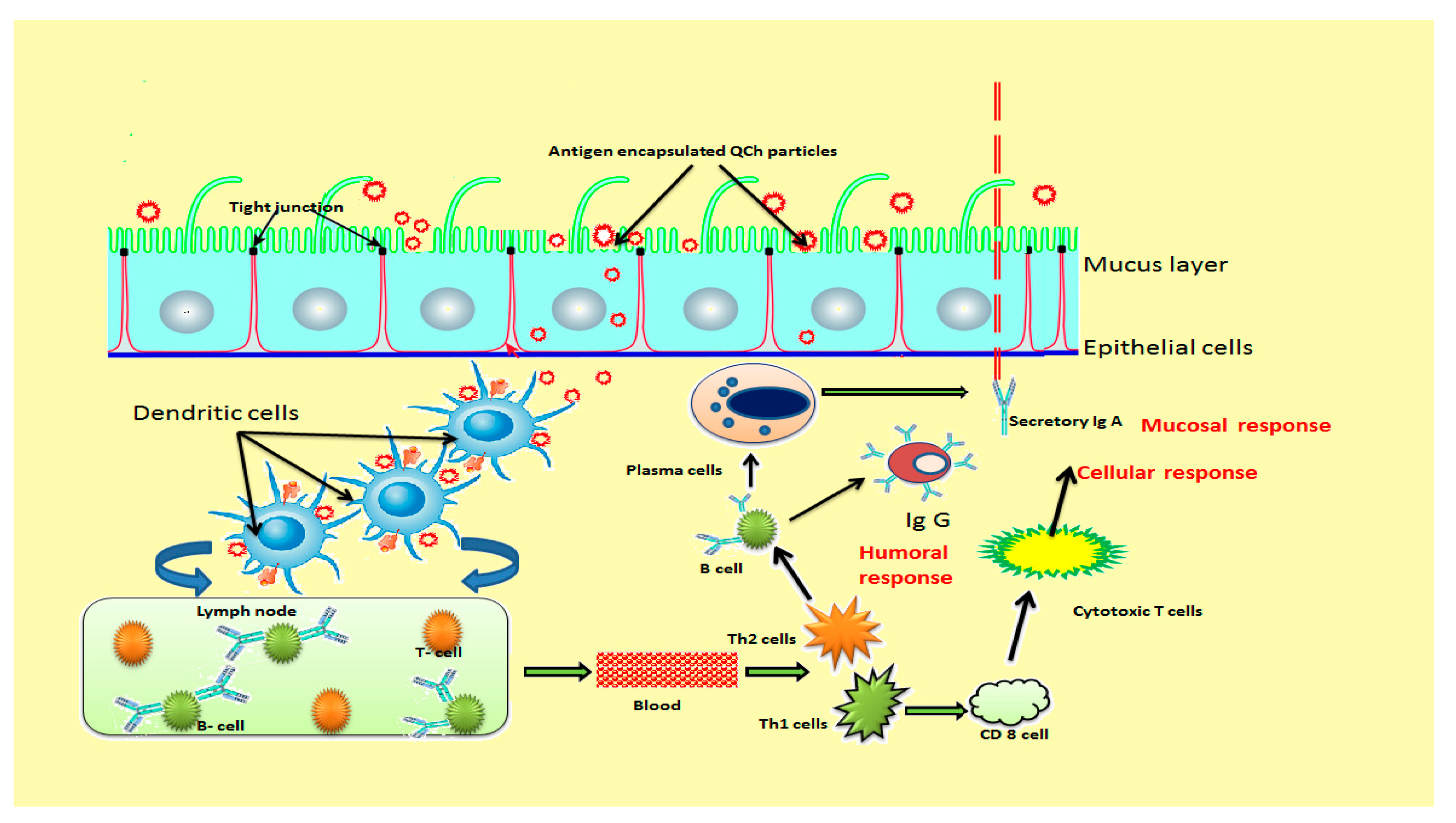
Recently, many novel vaccine adjuvants have been engineered for the modification of adaptive immune responses to deliver antigen in the body that enhance the potency and maintain immunity for a long duration. Alum has been the sole vaccine adjuvant approved for human use but limits significant stimulation of cell-mediated immune responses. In this context, Tao et al. (2017) evaluated immune-modifying features of N-(2-hydroxy) propyl-3-trimethylammonium chitosan chloride (HTCC) as a vaccine adjuvant for HEV (hepatitis E virus). HTCC showed strong immune-modifying effects when co-administered with HEV recombinant polypeptide inoculum via intramuscular way. The outcomes revealed enhanced serum HE-recognized IgG antibodies, amplified CD4+, CD8- T lymphocytes, proliferation of splenocytes, and growths of IFN-γ-secreting T helper cells in peripheral blood after vaccination [149]. Hence, HTCC adjuvant has the potential to induce significant antibody responses via stimulating Th-1 and Th-2 cells, cytotoxic T cells and macrophages that initiate typical mechanisms of the host defense process [150]. Th-1 cells are associated with protection against intracellular pathogens and encourage delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, whereas Th-2 cells encounter extracellular pathogens and mediate humoral responses. Figure 10 illustrates the development of immunity after the administration of mucoadhesive QCH-based vaccine adjuvant [151].
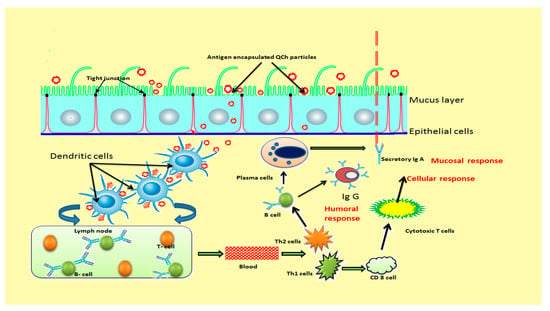
Figure 10.
Schematic illustration of immunity development after administration of mucoadhesive QCh-based vaccine adjuvant.
Wu et al. (2012) extended the study and demonstrated safe usage of HTCC supported hydrogel for efficient nasal immunization. A novel thermosensitive hydrogel was developed utilizing α, β-glycerophosphate and different quaternized degree having HTCC (QD 41%, 60%, 79%, 99%). The developed adjuvant was linked with Zaire Ebola virus glycoprotein antigen and evaluated for intranasal vaccine delivery efficacy. HTCC with moderate quaternization (60% and 79%) induced high immune-modulating effects and extensively released IgG-G1-G2a antibodies in serum and IgA in lungs, probably due to prolonged resistance due to the thermosensitive nature of hydrogel. Furthermore, HTCC mediated the higher release of IFN-γ and interleukins (IL-2, IL-10, IL-4), and Th1 and Th2 cells displayed enhanced cellular immune responses [151,152].
Wang et al. (2016) developed quaternized chitosan-based microgel adjuvant for H5N1 spilt vaccine. Microgels were prepared through the premix membrane emulsification method without the addition of a chemical crosslinker. The formed polycationic QCh microgels were smaller (807 nm), pH-sensitive, biocompatible, and capable of enhancing both cellular/humoral immunity. Microgels containing QCh with a moderate degree of quaternization (41% and 60%) exhibited favorable immune responses at lower doses when investigated against bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells [153]. Traditional immunization techniques including subcutaneous and intramuscular administration can provoke systemic immunoresponses. These approaches are unable to evoke resilient local immunity, specifically in the mucosal region, the first line of defense against pathogens [154].
The nasopharynx lymphoid tissues cannot support strong mucosal immunity or immune responses. While antigen or foreign particles enter on the nasal mucosal surface, antigen presenting cells on epithelial cells identify and present them to macrophages or lymphocytes that cause their differentiation, activation, and proliferation. Non-adherent antigens are not entertained by the tightly bound epithelial cells, so they produce poor immunogenicity [155]. To overcome the above downside, Zhang et al. (2018) developed curdlan sulphate complexed O-HTCC nanoparticles adjuvant to improve immunogenicity of antigen ovalbumin (Ova) through intranasal vaccination. Soluble curdlan sulphate is an extracellular polysaccharide that particularly identifies the dectin1 receptor on immune cell surfaces. Reports cited that curdlan sulphate elicited satisfactory cellular or humoral responses. However, being anionic in nature, it is hardly adsorbed over nose epithelial cells that limit its application in mucosal immunotherapy. Hence, polycationic, immunogenic O-HTCC was chosen to make complex with negatively charged curdlan sulphate (CS) followed by entrapment of antigen ovalbumin (Ova). An efficient Ova-loaded vaccine adjuvant (Ova/CS/O-HTCC) was developed under mild conditions. When administered through nasal mucosa dripping in BALB/c mice (Bagg albino laboratory bred strain), adjuvant Ova/CS/O-HTCC activated APCs and enhanced both cellular and humoral activity of Ova. The adjuvant also ameliorated Th-2 cells responses and reduced allergic reactions [156].
Nevagi et al. (2018) developed an efficient self-adjuvating TMC-peptide vaccine based on ionic interaction between cationic TMC and anionic alpha-poly- (l-glutamic acid) peptide antigen. The designed system induced higher systemic and mucosal antibodies compared to the reference cholera toxin B, a mucosal adjuvant conjugated with TMC. A self-adjuvant evident reduction in bacterial burden in nasal secretions of immunized mice was thus found to be effective for group A Streptococcus pathogen [157].
4. Miscellaneous
4.1. Orthopedic Surgery
Biomaterial-related infections are serious glitches in orthopedic surgery. The application of antibiotics either locally or given systemically has proven valuable in clinical research. Bone cements are applied to deliver antibiotics locally in high doses without triggering systemic toxicity. However, at a high level, these antibiotics may reduce the osteoblasts cell viability, proliferation, and alkaline phosphatase action that hinders physiological functions of bone marrow mesenchymal cells, resulting in compromised bone healing process. To overcome the above issue, quaternized chitosan derivative ‘hydroxy-propyl-trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan (HACC)’ loaded on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement was investigated to resolve the formed biofilm on the surface of bone cement. HACC-functionalized PMMA bone cement exhibited better antibacterial action compared to control against versatile clinically isolated microbes including S. epidermidis 389, methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis and methicillin-resistant S. aureus [158]. The developed system proved to have the potential to combat implant infections related to osteomyelitis. Moreover, the findings demonstrated better stem cell proliferation; osteogenesis and cell differentiation on the surface of HACC-loaded bone cement compared to antibiotic gentamycin-loaded bone cement [159]. Therefore, quaternized chitosan-based derivatives HACC finds biomedical roles in osteogenic activity, arthroplasty, and gene expression osteogenesis [160].
Furthermore, HACC with 6%, 18% and 44% degrees of quaternization coated on the titanium surface have been utilized for the evaluation of biofilm preventing efficiency. Titanium-based bioactive agents are widely used orthopedic implants due to their biocompatibility, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and light weight. However, these implants provide a favorable environment for bacterial colonization followed by biofilm formation. Thus, prolonged application was compromised with defective osteoproliferation, poor osteogenesis and serious microbial infections. HACC-coated titanium implants would overcome the above issues with an enhanced anti-infective effect at the same time. HACCs (18% and 44% degree of quaternization) were biocompatible with osteogenic cells and significantly eradicated the developed biofilm around orthopaedic implants at very low MIC values [161].
Yang et al. (2016) extended biomedical applications of HACC-modified titania nanotubes to improve the in vivo anti-infection potential. Orthopaedic intramedullary nails are widely used for the treatment of open and closed ‘tibial and femoral’ fractures. However, there may be postoperative infections due to implanted intramedullary nails [162]. A high dose of antibiotics is recommended that causes systemic toxicity and osteomyelitis, and delays bone cells proliferation. Hence, implants with an advanced anti-infective property are required to fix the high rate of infections. This innovative research detailed formation of various titania nanotube (NT) loaded with HACC (NT-H) and chitosan (NT-C) and evaluated their comparative cytocompatibility, antimicrobial efficiency and osteoblastic activity against human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The developed NT-H depicted impressive osteogenic action compared to other NT and NT-C nanotubes when assessed on a rat model having femoral medullary cavity implantation and methicillin-resistant S. aureus infection. Superior antibacterial effect, cytocompatibility, and profound osteogenesis focused the clinical application of NT-H to manage orthopedic surgical implant-related infections.
Kadama et al. (2021) studied the antibacterial effect of HACC-coated 3D-printed titanium cage during the treatment of improper intervertebral disc space in a rat model. Ti-HACC and non-coated Ti with bioluminescent S. aureus were inserted in the caudal discs of model rat. From the in vivo imaging system (IVIVS), the post-operative infection-related changes such as bone destruction and the movement of the implanted cage were assessed on the first, third, and fifth day through micro-computer tomography. The outcomes defined the vital role of Ti-HACC for effective wound healing, improved tartrate-resistant acid phosphate-positive osteoclasts, better antibacterial action against S. aureus and preservation of structural damage in caudal disc in rat [163].
4.2. Dental Care and Cosmetics
Chitosan derivative N-[(2-hydroxy-3-trimethylammonium) propyl chitosan chloride, HTCC has better solubility in neutral and alkaline solutions. HTCC has been utilized for the preparation of dental care products owing to its enhanced antimicrobial action [164]. Quaternized chitosan and its substituents have promising action in reducing dental plaque associated with various pathogens. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Streptococcus mutans and Prevotella intermedia cause plaques and periodontal diseases. Endodontic cements based on QCh derivatives reduce inflammation and facilitate bone regeneration [165]. Literature reports promising antibacterial action of HTCC against Enterococcus faecalis that is associated with endodontic infection. E. faecalis, a Gram-positive bacteria, has been isolated from persistent endodontic infection that may cause severe root canal disorder. This pathogen may exist in non-culturable conditions and maintain viability through the year without requiring nutrients, thus damaging dentinal tubules and develop biofilms. Once biofilm is formed, E. faecalis becomes more virulent, can protect itself either from adverse condition or high doses of antibiotics [166].
Patel et al. (2020) explored the antibacterial efficiency of chitosan and HTCC against E. faecalis pathogen in the state of planktonic and biofilm. A colony-forming-unit study was performed to define the status of three strains of E. faecalis (ATCC 29212, P25RC, P52Sa) after treating with serially diluted (20–2500 μg/mL) chitosan and HTCC. Both chitosan (70 μg/mL) and HTCC (140 μg/mL) exhibited significantly higher antibacterial efficacy in double-distilled water as compared to phosphate-buffered saline. The presence of charged ions (Na+, K+, Cl− and H2PO4−) in phosphate-buffered saline might disrupt the involved electrostatic interaction that results in less antibacterial action [167]. Moreover, the biocompatibility of natural biopolymer chitosan and its derivative HTCC for the purpose of sealing/obturation of the root canal is far better, compared to other traditionally employed toxicity elicited substances such as zinc oxide, glass ionomers, resins, calcium hydroxide, etc. [168].
Thus, the biocompatibility and characteristic antibacterial efficacy of both chitosan and HTCC focus biomedical application in root canal therapy [169]. Lee et al. (2018) examined the antifungal activity of quaternized chitosan ‘2-[(acryloyloxy) ethyl] trimethylammonium’ as tissue conditioner in the pathological condition ‘denture stomatitis’. Candida albicans is a main etiological cause for denture stomatitis that affects mucosa underneath diseased teeth. QCh-based tissue conditioner of size 1 mm thickness and 10 cm diameter was prepared and co cultured with C. albicans. Significantly diminished fungal colonies were observed with less than 5% QCh concentration compared to the resin denture base. Moreover, this amount did not affect the viability of gingival epithelium cells [170]. Table 6 collects novel research reports on QCh-based systems that have been explored for dental and cosmetic applications.

Table 6.
Research highlights few dental/cosmetic uses of QCh derivatives.
Quaternized chitosan derivatives are highly utilized for the preparation of cosmetics including skin creams, shampoo, sprays, and dental remedies. Being natural with exclusive biological features, these biopolymers find an attractive domain in cosmeceuticals. Water-soluble quaternized chitosan (73% degree of quaternization) has been grafted with cyclodextrin (QCD-g-CS) to improve its antibacterial effect against several microorganisms, namely C. albicans, S. mutans, and S. oralis [171].
Sakulwech et al. (2018) extended the study by uploading the negatively charged hydrophilic guest (hyaluronic acid) on the QCD-g-CS to improve penetration enhancement. Hyaluronic acid is generally applied in skin remedies owing to improved skin elasticity, an antiwrinkle effect and the retention of moisture content. Furthermore, it is popularly used for treating osteoarthritis and manifesting wound healing. The high molecular weight of hyaluronic acid limits its benefit in cosmetics. Amalgamation of quaternized chitosan and cyclodextrin facilitated enhanced solubility, absorption, and bioavailability to the dermal cells. The developed nanoparticles enhanced the penetration of hyaluronic acid in deeper tissues and provided a moisturizing effect. The developed nanoparticles were safe when investigated against skin fibroblast cells [174].
Khalaji et al. (2020) developed biocompatible and antibacterial scaffolds with a blend of synthetic PVA and natural water-soluble HTCC. Fabricated scaffolds exhibited sufficient mechanical strength that was appropriate for skin regeneration during dermal damage. Moreover, the embedded collagen provided additional biological properties, such as extracellular matrix simulation, better cell attachment and proliferation. Hence, fabricated scaffolds can be medically utilized as skin care products [175]. Chen et al. (2017) developed nanocomposite containing quaternized carboxylated chitosan and organic montmorillonite through solution-induced intercalation. A cosmetic cream against skin aging was prepared that exhibited better moisture adsorption, efficient UV protection and moisture retention behaviour without dermal irritation owing to the presence of quaternized carboxylated chitosan [22].
5. Future Prospective
Quaternized chitosan (QCH) derivatives have been extensively utilized for biomedical applications (tissue engineering, drug/gene delivery, antimicrobial, antiviral and immunoadjuvant) owing to their bio and cytocompatibility attributes. With the advancement of nanotechnology, QCH together with nanocomposites (carbon nanotubes and nanofillers) provide superior alternatives to the new arena of drug delivery and regenerative medicines. The reports and findings detailed that QCH derivatives are increasingly focused for the formulation of vaccine adjuvants, chemotherapeutic agents, ecofriendly textiles, and purified membrane matrix. Improved physicochemical properties including improved solubility, mucoadhesiveness, absorption and bioavailability pave QCH derivatives for the synthesis of less invasive and more effective formulations for the management of diverse disorders.
6. Conclusions
Multifunctional QCh derivatives have attracted high attention in the last two decades by their inherent virtues that have broadened biomedical applications. Reports cite extensive research on QCh-based drug carriers, vaccine adjuvant, anticancerous nanoparticles, antibacterial hydrogel, tissue scaffolds, and purification membranes that explore their exclusive physiochemical and biological actions. Furthermore, QCh derivative polymers exhibit high stability, biodegradability and biocompatibility that are essential benchmark for successful therapeutic remedies. However, the synthesis of QCh derivatives including pyridinium and phosphonium salts should be properly channelized at an industrial level to expose their superior biomedical applications on a large scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.P., S.K.M., T.B. and A.N.; investigation, A.S. and S.S.; resources, R.G.; data curation, S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.P., S.S., A.S. and T.B.; writing—review and editing, A.N., S.B. and T.B.; visualization, S.S.; supervision, A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript, and have equal contribution to this paper.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the collection, analyses, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mourya, V.K.; Inamdar, N.N. Chitosan-modifications and applications: Opportunities galore. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 1013–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. The virtuous potential of chitosan oligosaccharide for promising biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuvian, M.A.R.; Islam, M.N. Chitin and Chitosan: Structure, Properties and Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahya, N. Water Soluble Chitosan Derivatives and their Biological Activities: A Review. Polym. Sci. 2019, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofuji, K.; Qian, C.; Nishimura, M.; Sugiyama, I.; Murata, Y.; Kawashima, S. Relationship between physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of chitosan. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, T.; Koh, H.S.; Kazazian, K.; Shoichet, M.S. Controlling cell adhesion and degradation of chitosan films by N-acetylation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Betsy, M.; Chesnutt, W.; Haggard, O.; Bumgardner Joel, D. Deacetylation of Chitosan: Material Characterization and in vitro Evaluation via Albumin Adsorption and Pre-Osteoblastic Cell Cultures. Materials 2011, 4, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.; Som, C.; Schmutz, M.; Borges, O.; Borchard, G. How the Lack of Chitosan Characterization Precludes Implementation of the Safe-by-Design Concept. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2020, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Knidri, H.; Belaabed, R.; Addaou, A.; Laajeb, A.; Lahsini, A. Extraction, chemical modification and characterization of chitin and chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt A, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Kumar, A.S.H.; Abanti, S.; Kumar, R.P. Physicochemical properties and characterization of chitosan synthesized from fish scales, crab and shrimp shells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104 Pt B, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Fan, B.; Yan, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Preparation and characterization of N-benzoyl-O-acetyl-chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, M.; Kennedy, J.F.; Nie, J. Preparation and characterization of water-soluble N-alkylated chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E.; Daraei, H.; Ghanbari, R.; Dehestani Athar, S.; Zandsalimi, Y.; Ziaee, A.; Maleki, A.; Yetilmezsoy, K. Synthesis of carboxylated chitosan modified with ferromagnetic nanoparticles for adsorptive removal of fluoride, nitrate, and phosphate anions from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsdóttir, B.E.; Baldursson, Ó.; Másson, M. Challenges in evaluation of chitosan and trimethylated chitosan (TMC) as mucosal permeation enhancers: From synthesis to in vitro application. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Subhapradha, N.; Thinesh, T.; Selvin, J.; Selvan, K.M.; Shanmugam, V.; Shanmugam, A. Characterization of bioactive chitosan and sulfated chitosan from Doryteuthis singhalensis (Ortmann, 1891). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; You, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Homogeneous synthesis and characterization of chitosan ethers prepared in aqueous alkali/urea solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Shen, D.; Xu, W. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M.; Gebicki, J.M.; Iohara, D.; Tomida, H.; Uekama, K.; Maruyama, T.; Hirayama, F.; Otagiri, M. Antioxidant activities of chitosans and its derivatives in in vitro and in vivo studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 1, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Weinhold, M.X.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Biomedical Activity of Chitin/Chitosan Based Materials—Influence of Physicochemical Properties Apart from Molecular Weight and Degree of N-Acetylation. Polymers 2011, 3, 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengíbar, M.; Harris, R.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Calderon, L.; Sanchez, A.; Heras, A. Role of Physicochemical Properties of Chitin and Chitosan on their Functionality. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2014, 8, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Guo, B.; Luo, J. Quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/organic montmorillonite nanocomposite as a novel cosmetic ingredient against skin aging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Florczyk, S.; Leung, M.; Zhang, M. High-strength pristine porous chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6291–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabb Zavala, J.M.; Leija Gutiérrez, H.M.; Segura-Cárdenas, E.; Mamidi, N.; Morales-Avalos, R. Manufacture and mechanical properties of knee implants using SWCNTs/UHMWPE composites. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 120, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, N.; Velasco Delgadillo, R.M.; Barrera, E.V. Covalently Functionalized Carbon Nano-Onions Integrated Gelatin Methacryloyl Nanocomposite Hydrogel Containing γ-Cyclodextrin as Drug Carrier for High-Performance pH-Triggered Drug Release. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, D.; Assis, O. Synthesis and mechanical properties of quaternary salts of chitosan-based films for food application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, N.; Velasco Delgadillo, R.M.; Gonzáles Ortiz, A.; Barrera, E.V. Carbon Nano-Onions Reinforced Multilayered Thin Film System for Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Velasco Delgadillo, R.M.; Castrejon, J.V. Unconventional and facile production of a stimuli-responsive multifunctional system for simultaneous drug delivery and environmental remediation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2081–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajomsang, W.; Tantayanon, S.; Tangpasuthadol, V.; Daly, W.H. Quaternization of N-aryl chitosan derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, G.; Delair, T. Chitosan-based Colloidal Polyelectrolyte Complexes for Drug Delivery: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, H.; Terayama, E. High molecular antibacterial substances derived from chitin. About the manufacture of Macramin. J. Antibiot. 1948, 2, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Polnok, A.; Borchard, G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Sarisuta, N.; Junginger, H.E. Influence of methylation process on the degree of quaternization of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintapattanakit, S.; Mao, T.; Kissel, V.B.J. Trimethyl chitosan and its applications in drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, D.J.H.; Hamman, J.S.; Kotze, J.E.; Rollings, A.F.K. The relationship between the absolute molecular weight and the degree of quaternisation of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. Carbohydr. Polym 2002, 50, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, D.; Hamman, J.H.; Kotze, A.F. Evaluation of the Mucoadhesive Properties of N-Trimethyl Chitosan Chloride. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Chitin and Chitosan; Muzzarelli, R., Jeuniaux, C., Gooday, G.W., Eds.; Plenum Press: Senigallia, Italy, 1986; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Xin, M.; Li, M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of N,O-quaternary ammonium chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.S.; Whang, H.S.; Ko, S.W. Synthesis of a Quaternary Ammonium Derivative of Chito-oligosaccharide as Antimicrobial Agent for Cellulosic Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zha, Q.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and characterization of N-(2-hydroxy)propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride for potential application in gene delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Qiao, C.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, C. Effects of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt on the physicochemical properties of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-based films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagdarova, B.; Lunkov, A.; Il’ina, A.; Varlamov, V. Investigation of the properties of N-[(2-hydroxy-3-trimethylammonium) propyl] chloride chitosan derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, P. Synthesis, characterization, and antifungal activity of novel quaternary chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Li, Q.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.; Luan, F.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z. Novel cationic chitosan derivative bearing 1,2,3-triazolium and pyridinium: Synthesis, characterization, and antifungal property. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, Q.; Tan, W.; Dong, F.; Luan, F.; Guo, Z.; Saso, L.; Dux, L.; Wegrzyn, G.; Csont, T. Synthesis,characterization, and the antioxidant activity of double quaternized chitosan derivatives. Molecules 2017, 22, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Duan, Y.; Fang, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Pyridine-grafted chitosan derivative as an antifungal agent. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Guo, S.; Peng, Z.; Tang, T. Novel water soluble phosphonium chitosan derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Lin, F.X.; Xie, J.; Wang, M.Z.; Rong, J.L.; Zhao, Y.; You, Y.Z.; Asif, A.; Ge, X.W. Chitosan modified by g-ray-induced grafting of poly(tributyl-(4-vinylbenzyl)phosphonium) as a biosafe and high-efficiency gene carrier. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, J.; Hjálmarsdóttir, M.; Másson, M.; Rúnarsson, Ö.; Asplund, T.; Soininen, P.; Nevalainen, T.; Järvinen, T. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan N-betainates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Ahmadi, R.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V. A novel bioactive quaternized chitosan and its silver-containing nanocomposites as a potent antimicrobial wound dressing: Structural and biological properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambito, Y.; Uccello-Barretta, G.; Zaino, C.; Balzano, F.; Di Colo, G. Novel transmucosal absorption enhancers obtained by aminoalkylation of chitosan. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambito, Y.; Zaino, C.; Burchielli, S.; Carelli, V.; Serafini, M.F.; Di Colo, G. Novel quaternary ammonium chitosan derivatives for the promotion of intraocular drug absorption. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.D.; Moura, C.F., Jr.; Kerwald, J.; Beppu, M.M. An Overview of Current Knowledge on the Properties, Synthesis and Applications of Quaternary Chitosan Derivatives. Polymers 2020, 12, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.D.; Patel, H.M.; Surana, S.J.; Vanjari, Y.H.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Pardeshi, C.V. N,N,N-Trimethyl chitosan: An advanced polymer with myriad of opportunities in nanomedicine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 875–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimulescu, I.A.; Nechifor, A.C.; Bǎrdacǎ, C.; Oprea, O.; Paşcu, D.; Totu, E.E.; Albu, P.C.; Nechifor, G.; Bungău, S.G. Accessible Silver-Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Nanomaterial for Supported Liquid Membranes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holappa, J.; Nevalainen, T.; Safin, R.; Soininen, P.; Asplund, T.; Luttikhedde, T.; Másson, M.; Järvinen, T. Novel water-soluble quaternary piperazine derivatives of chitosan: Synthesis and characterization. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Quaternized Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Controlled Pesticide Release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, W.; Xiong, J.; Qu, N.; Li, H.; Yao, G. Synthesis and properties of N,N-dimethyl-O-quaternary ammonium chitosan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 152, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Fan, B.; Yan, J.; Xu, Y. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity of O-acetyl-chitosan-N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, R.D.O.; Schmitt, C.C.; Neumann, M.G. Syntheses and characterization of amphiphilic quaternary ammonium chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Ding, D.; Ren, J.; Zhu, X.; Yao, Y. Synthesis, characterization, and drug-release behavior of amphiphilic quaternary ammonium chitosan derivatives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.; Rabea, E.I. Synthesis and antifungal property of N-(aryl) and quaternary N-(aryl) chitosan derivatives against Botrytis cinerea. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lin, Q. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of quaternized of N-aromatic chitosan derivatives. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 138, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Tang, Z.; He, M.Y.; Hua, Y.P.; Xu, Q. Synthesis and preservative application of quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan containing guanidine groups. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, R. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan derivatives with dual-antibacterial functional groups. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkahtane, A.A.; Ghanem, E.; Bungau, S.G.; Alarifi, S.; Ali, D.; Albasher, G.; Alkahtani, S.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Carnosic acid alleviates chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in mice cerebral and ocular tissues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11663–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.S.; dos Santos, D.M.; Almeida, A.; Marchiori, L.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Sarmento, B. N-(2-Hydroxy)-propyl-3-trimethylammonium, O-Mysristoyl Chitosan Enhances the Solubility and Intestinal Permeability of Anticancer Curcumin. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Liu, W.S.; Sun, J.F.; Hou, G.G.; Chen, Q.; Cong, W.; Zhao, F. Non-toxic O-quaternized chitosan materials with better water solubility and antimicrobial function. Int. J. Biolo. Macromol. 2016, 84, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, X.; Xu, G.; Yao, P. Fatty acid and quaternary ammonium modified chitosan nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 170, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahariah, P.; Gaware, V.S.; Lieder, R.; Jónsdóttir, S.; Hjálmarsdóttir, M.Á.; Sigurjonsson, O.E.; Másson, M. The Effect of Substituent, Degree of Acetylation and Positioning of the Cationic Charge on the Antibacterial Activity of Quaternary Chitosan Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4635–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmila, V.; Vavríková, E. Chitosan derivatives with antimicrobial, antitumour and antioxidant activities-a review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar]
- Sajomsang, W.; Gonil, P.; Saesoo, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of methylated N-(4-N,N-dimethylaminocinnamyl) chitosan chloride. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avadi, M.R.; Sadeghi, A.M.M.; Tahzibi, A.; Bayati, K.; Pouladzadeh, M.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M. Diethylmethyl chitosan as an antimicrobial agent: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial effects. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Avadi, M.R.; Saadat, P.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M.; Junginger, H.E. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activities of chitosan, N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC) and N-diethylmethyl chitosan (DEMC) nanoparticles loaded with insulin using both the ionotropic gelation and polyelectrolyte complexation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallapa, N.; Wiarachai, O.; Thongchul, N.; Pan, J.; Tangpasuthadol, V.; Kiatkamjornwong, S.; Hoven, V.P. Enhancing antibacterial activity of chitosan surface by heterogeneous quaternization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xin, M.; Li, M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, S. Synthesis, characteristic and antibacterial activity of N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan and its carboxymethyl derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Huang, D.; Yan, Y. Chitosan derivatives with dual-antibacterial functional groups for antimicrobial finishing of cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.F.; Facchi, S.P.; Follmann, H.D.; Pereira, A.G.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan derivatives containing N-quaternized moieties in its backbone: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20800–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, H.; Qiu, M.; Geng, X.; Yang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, C. Antibacterial activity evaluation of quaternary chitin against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 52, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, H.J.; Matulewicz, M.C. Cationization of polysaccharides: A path to greener derivatives with many industrial applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 52, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, K.A.; Birch, N.P.; Schiffman, J.D. Designing electrospun nanofiber mats to promote wound healing—A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4531–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.G.; Manolova, N.E.; Toshkova, R.A.; Rashkov, I.B.; Gardeva, E.G.; Yossifova, L.S.; Alexandrov, M.T. Electrospun nanofibrous mats containing quaternized chitosan and polylactide with in vitro antitumor activity against HeLa cells. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, M.; Naiman, D.Q.; Lakind, J.S. Systematic review of the literature on triclosan and health outcomes in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Kashimura, N.; Noji, T.; Suzuki, O.; Ambo, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Kishida, A. Triclosan-coated sutures reduce the incidence of wound infections and the costs after colorectal surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Surgery 2013, 153, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.B.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, S.H.; Yu, Z.F.; Tang, T.T. Bacterial inhibition potential of quaternised chitosan-coated VICRYL absorbable suture: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Orthop. Translat. 2016, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ao, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Z.; Tang, T. Cytocompatibility with osteogenic cells and enhanced in vivo anti-infection potential of quaternized chitosan-loaded titania nanotubes. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y. Quaternized chitosan promotes the antiproliferative effect of vemurafenib in melanoma cells by increasing cell permeability. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 8293–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongwanakul, R.; Jianmongkol, S.; Gonil, P.; Sajomsang, W.; Maniratanachote, R.; Aueviriyavit, S. Biocompatibility study of quaternized chitosan on the proliferation and differentiation of Caco-2 cells as an in vitro model of the intestinal barrier. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2017, 32, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Gillings, M.; Paulsen, I.T. Antibiotic discovery: Combatting bacterial resistance in cells and in biofilm communities. Molecules 2015, 20, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, R.; Lin, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, T. Quaternized Chitosan as an Antimicrobial Agent: Antimicrobial Activity, Mechanism of Action and Biomedical Applications in Orthopedics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1854–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L. Implant infections: Adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R. Biofilm and antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaha, D.C.; Bungau, S.; Uivarosan, D.; Tit, D.M.; Maghiar, T.A.; Maghiar, O.; Pantis, C.; Fratila, O.; Rus, M.; Vesa, C.M. Antibiotic Consumption and Microbiological Epidemiology in Surgery Departments: Results from a Single Study Center. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, A.M.; Zambito, Y.; Burgalassi, S.; Monti, D.; Tampucci, S.; Terreni, E.; Fabiano, A.; Balzano, F.; Uccello-Barretta, G.; Chetoni, P. A water-soluble, mucoadhesive quaternary ammonium chitosan-methyl-_-cyclodextrin conjugate forming inclusion complexes with dexamethasone. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, A.M.; Esin, S.; Benedetti, A.; Maisetta, G.; Fabiano, A.; Zambito, Y.; Batoni, G. Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antiadhesive Properties of Different Quaternized Chitosan Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Q.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, J.M.; Zhang, W.F.; Tang, X.X. Molecular weight-dependent antifungal activity and action mode of chitosan against Fulvia fulva (Cooke) Ciffrri. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Xing, R.G.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Z.M.; Ji, X.; Wang, L.; Li, P.C. The influence of the cationic of quaternized chitosan on antifungal activity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Xing, R.E.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Z.M.; Ji, X.; Wang, L.; Li, P.C. The influence of molecular weight of quaternized chitosan on antifungal activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethan, P.D.; Vishalakshi, B.; Sathish, L.; Ananda, K.; Poojary, B. Preparation of substituted quaternized arylfuran chitosan derivatives and their antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Pedro, R.; Takaki, M.; Gorayeb, T.C.; Del Bianchi, V.L.; Thomeo, J.C.; Tiera, M.J.; de Oliveira Tiera, V.A. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal activity of quaternary derivatives of chitosan on Aspergillus flavus. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’Ina, A.V.; Shagdarova, B.T.; Lun’Kov, A.P.; Kulikov, S.N.; Varlamov, V.P. In vitro antifungal activity of metal complexes of a quaternized chitosan derivative with copper ions. Microbiology 2017, 86, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.H.F.V.; Takaki, M.; Pedro, R.D.O.; Gabriel, J.D.S.; Tiera, M.J.; Tiera, V.A.D.O.; De Souza, R.V. Hydrophobic effect of amphiphilic derivatives of chitosan on the antifungal activity against Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Molecules 2013, 18, 4437–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechifor, A.C.; Pîrțac, A.; Albu, P.C.; Grosu, A.R.; Dumitru, F.; Dimulescu, I.A.; Oprea, O.; Pașcu, D.; Nechifor, G.; Bungău, S.G. Recuperative Amino Acids Separation through Cellulose Derivative Membranes with Microporous Polypropylene Fiber Matrix. Membranes 2021, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yostawonkul, J.; Surassmo, S.; Iempridee, T.; Pimtong, W.; Suktham, K.; Sajomsang, W.; Gonil, P.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. Surface modification of nanostructure lipid carrier (NLC) by oleoyl-quaternized-chitosan as a mucoadhesive nanocarrier. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.B.; Pardeshi, S.; Patil, R.P.; Patil, P.B.; Mujumdar, A. Mucoadhesive Micro-/Nano Carriers in Ophthalmic Drug Delivery: An Overview. BioNano Sci. 2020, 10, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, M.; Shagdarova, B.; Zubareva, A.; Generalov, A.; Grechikhina, M.; Svirshchevskaya, E. Development of mucoadhesive chitosan-based drug delivery system. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 2018, 203, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Mi, X.; Xiang, X.; Heiden, P.A.; Heldt, C.L. Non-enveloped virus reduction with quaternized chitosan nanofibers containing graphene. Carbohydr Res. 2013, 18, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santosa, D.M.; Leiteb, I.S.; de Lacerda Bukzema, A.; de Oliveira Santosa, R.P.; Frollinia, E.; Inadab, N.M.; Campana-Filho, S.P. Nanostructured electrospun nonwovens of poly(ε-caprolactone)/quaternized chitosan for potential biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Ng, I.S.; Lin, G.Y.; Chiu, C.Y.; Chang, Y.K. Antibacterial activity of quaternized chitosan modified nanofiber membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Vijayaragavan, K.S.; Heldt, C. Virus adsorption of water-stable quaternized chitosan nanofibers. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 387C, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Heldt, C.L. Adsorption of a non-enveloped mammalian virus to functionalized nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Yossifova, L.; Gardeva, E.; Manolova, N.; Toshkova, R.; Rashkov, I.; Alexandrov, M. Antiproliferative activity of nanofibers containing quaternized chitosan and/or doxorubicin against MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell line by apoptosis. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Mao, J.; Gu, S.; Xu, W. Potential of quaternization-functionalized chitosan fiber for wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 52, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Mei, L.; Fan, R.; He, M.; Wang, C.; Tong, A.; Chen, H.; Guo, G. Stereocomplexed electrospun nanofibers containing poly (lactic acid) modified quaternized chitosan for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tsen, W.C.; Jang, S.C.; Hu, F.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Wen, S.; et al. Composite membranes from quaternized chitosan reinforced with surface-functionalized PVDF electrospun nanofibers for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, J.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. High-efficient and synergetic antibacterial nanocomposite hydrogel with quaternized chitosan/Ag nanoparticles prepared by one-pot UV photochemical synthesis. Biopolymers 2020, 111, e23354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Xie, S.; Cao, J.; Ge, H.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Quaternized Chitosan/Poly(acrylic acid) Polyelectrolyte Complex Hydrogels with Tough, Self-Recovery, and Tunable Mechanical Properties. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Delgadillo, R.M.V. Design, fabrication and drug release potential of dual stimuli-responsive composite hydrogel nanoparticle interfaces. Colloid Surf. B 2021, 204, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Hu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wei, C.; Cao, F.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y.; Endo, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Quaternized chitosan-Matrigel-polyacrylamide hydrogels as wound dressing for wound repair and regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, A.; Huang, P.; Wang, W.; Deng, L. Dual-crosslinked nanocomposite hydrogels based on quaternized chitosan and clindamycin-loaded hyperbranched nanoparticles for potential antibacterial applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Bian, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Pan, H.; Zhao, X. Catechol modified quaternized chitosan enhanced wet adhesive and antibacterial properties of injectable thermo-sensitive hydrogel for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 249, 116826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, P.; Omidi, M.-Y.; Mozafari, M.; Zamanian, A. Synthesis and characterization of timolol maleate-loaded quaternized chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel: A transparent topical ocular delivery system for the treatment of glaucoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, X.P.; Ma, X.; Guo, B. Injectable hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan, gelatin and dopamine as localized drug delivery system to treat Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.-J.; Jia, P.-Y.; Shan, J.-J.; Wu, J.; Ma, G.-H.; Su, Z.-G. The potential adjuvanticity of quaternized chitosan hydrogel based microparticles for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus inactivated vaccine. Int. Immunopharm. 2016, 39, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riham, R.; Mohamed Mahmoud, H.; Abu Elella, M.; Sabaa, W. Synthesis, characterization and applications of N-quaternized chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Wu, H.; Xie, T.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization and antibacterial effect of quaternized chitosan anchored cellulose beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, A.; Meenakshi, S. An efficient and regenerable quaternary amine modified chitosan beads for the removal of nitrate and phosphate anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarloo, H.; Godec, M.; Arshadi, M.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I.; Abbaspourrad, A. Multi-porous quaternized chitosan/polystyrene microbeads for scalable, efficient heparin recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, P.; Nathan, G.; Kam, T. Removal of 2-naphthoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution using quaternized chitosan beads. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Hu, G.; Cui, X.; Sun, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Evaluation of Chitosan Derivatives Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Delivery Carrier. Molecules 2021, 26, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Elella, M.H.A.; Mohamed, R.R. Green synthesis of quaternized chitosan/silver nanocomposites for targeting mycobacterium tuberculosis and lung carcinoma cells (A-549). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Han, G.; Xie, M.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X. Quaternized chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite resin and its adsorption behavior. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-C.; Chuang, F.-S.; Tsen, W.-C.; Kuo, T.-W. Quaternized chitosan/functionalized carbon nanotubes composite anion exchange membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunli, G.; Shujun, Z.; Wen-Chin, T.; Fuqiang, H.; Fei, Z.; Bingqing, Z.; Hai, L. Hierarchical layered double hydroxide coated carbon nanotube modified quaternized chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. J Power Sources 2019, 441, 227176. [Google Scholar]
- Dhiman, P.; Bhatia, M. Ketoconazole loaded quaternized chitosan nanoparticles-PVA film: Preparation and evaluation. Polym. Bull. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.X.; Zhao, Q.S.; Deng, J.; Lü, R. A novel injectable chlorhexidine thermosensitive hydrogel for periodontal application: Preparation, antibacterial activity and toxicity evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Yen, H.J.; Shyu, H.F.; Cheng, K.M.; Chen, X.A.; Chen, C.C.; Young, J.J.; Kau, J.H. A fucoidan-quaternary chitosan nanoparticle adjuvant for anthrax vaccine as an alternative to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z. Quaternized chitosan nanoparticles loaded with the combined attenuated live vaccine against Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis elicit immune response in chicken after intranasal administration. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Lu, S.; Huang, F.; Li, G. Preparation of quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan nanoparticles and their textile properties on Antheraea pernyi silk modification. Textile Res. J. 2014, 84, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sheng, L.; Lian, X.J. Preparation and In Vitro Release Study of Quaternized Chitosan Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1053, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abueva, S.D.; Kim, C.; Lee, B.; Nath, B.T. Chitosan-hyaluronic acid polyelectrolyte complex scaffold crosslinked with genipin for immobilization and controlled release of BMP-2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, A.M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Tamer, T.M.; Khalifa, R.E.; Hassan, M.A.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Formulation of Quaternized Aminated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Efficient Encapsulation and Slow Release of Curcumin. Molecules 2021, 26, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Hao, S.; Sun, B.; Zhao, D.; Yan, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Quaternized Chitosan Nanoparticles in Vaccine Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 4932–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chu, C.H. Dual stimuli responsive glycidyl methacrylate chitosan-quaternary ammonium hybrid hydrogel and its bovine serum albumin release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, R.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Yu, H.; Li, P. Immunostimulatory effect of chitosan and quaternary chitosan: A review of potential vaccine adjuvants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheul, R.J.; Amidi, M.; van der Wal, S.; van Riet, E.; Jiskoot, W.; Hennink, W.E. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro biological properties of O-methyl free N,N,N-trimethylated chitosan. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, V.; Gogoi, H.; Bhatnagar, R. Novel application of trimethyl chitosan as an adjuvant in vaccine delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7959–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammona, O.; Kiparissides, C. Recent advances in nanocarrier-based mucosal delivery of biomolecules. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Shi, C.; Guo, C.; Dai, C.; Chen, Q.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Preparation and efficacy of Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zheng, H.Q.; Fu, T.; He, Z.J.; Hong, Y. N-(2-hydroxy) propyl-3-trimethylammonium chitosan chloride: An immune-enhancing adjuvant for hepatitis E virus recombinant polypeptide vaccine in mice. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heyman, B. Regulation of antibody responses via antibodies, complement, and Fc receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 709–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalik, A.; Alradwan, I.; Majrashi, M.A.; Alsaffar, B.A.; Algarni, A.T.; Alsuabeyl, M.S.; Alrabiah, H.; Tirelli, N.; Alhasan, A.H. Cellular responses of hyaluronic acid-coated chitosan nanoparticles. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, S.; Hou, L.; Wei, W.; Zhou, M.; Su, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, G. Novel thermal-sensitive hydrogel enhances both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses by intranasal vaccine delivery. Eur. J. 2012, 81, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Fan, Q.Z.; Liu, Y.; Yue, H.; Ma, X.W.; Wu, J.; Ma, G.H.; Su, Z.G. Improving adjuvanticity of quaternized chitosan-based microgels for H5N1 split vaccine by tailoring the particle properties to achieve antigen dose sparing effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brokstad, K.A.; Eriksson, J.C.; Cox, R.J.; Tynning, T.; Olofsson, J.; Jonsson, R.; Davidsson, A. Parenteral vaccination against influenza does not induce a local antigen-specific immune response in the nasal mucosa. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neutra, M.R.; Kozlowski, P.A. Mucosal vaccines: The promise and the challenge. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Lu, L.; Song, X.; Li, P.; Wang, F. Curdlan sulfate-O-linked quaternized chitosan nanoparticles: Potential adjuvants to improve the immunogenicity of exogenous antigens via intranasal vaccination. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevagi, R.J.; Khalil, Z.G.; Hussein, W.M.; Powell, J.; Batzloff, M.R.; Capon, R.J.; Good, M.F.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Polyglutamic acid-trimethyl chitosan-based intranasal peptide nano-vaccine induces potent immune responses against group A streptococcus. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.L.; Peng, Z.X.; Li, Q.T.; Xu, X.F.; Guo, S.R.; Tang, T.T. The use of quaternised chitosan-loaded PMMA to inhibit biofilm for-mation and downregulate the virulence-associated gene expression of antibiotic-resistant staphylococcus. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Guo, S.R.; Yang, S.B.; XU, X.F.; Tang, T.T. Physical characterization and osteogenic activity of the quaternized chitosan-loaded PMMA bone cement. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Ao, H.Y.; Ma, R.; Lin, W.T.; Tang, T.T. In vivo effect of quaternized chitosan-loaded polymethylmethacrylate bone cement on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis infection of the tibial metaphysis in a rabbit model. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2014, 58, 6016–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Guo, S.R.; Wang, X.Q.; Tang, T.T. Adjustment of the antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan by varying the degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Du, Y.; Fan, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan and application as pulp-cap. Polymer 2006, 47, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadama, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, T.; Kushioka, J.; Okada, R.; Tsukazaki, H.; Tateiwa, D.; Nakagawa, S.; Ukon, Y.; Bal, Z.; et al. Antibacterial efficacy of quaternized chitosan coating on 3D printed titanium cage in rat intervertebral disc space. Spine J. 2021, 21, 1529–9430. [Google Scholar]
- Verlee, A.; Mincke, S.; Stevens, C.V. Recent developments in antibacterial and antifungal chitosan and its derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavaria, F.K.; Costa, E.M.; Pintado, M.M.; Pina-Vaz, I.; Carvalho, M.F.; Pintado, M.M. A quitosana como biomaterial odontológico: Estado da arte. Rev. Bras. Eng. Bioméd. 2013, 29, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Du, J.; Peng, Z. Correlation between Enterococcus faecalis and persistent intraradicular infection compared with primary intraradicular infection: A systematic review. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, E.; Pradeep, P.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Oroactive dental biomaterials and their use in endodontic therapy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, G.; Perrone, D.; Dioguardi, M.; Buonavoglia, A.; Ardito, F.; Lo Muzio, L. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic activity of three epoxy resin-based endodontic sealers. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Mei, L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Wang, S. Antibacterial effect of chitosan and its derivative on Enterococcus faecalis associated with endodontic infection. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3805–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Wang, R.S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chuang, C.C.; Chan, H.R.; Chiu, H.C.; Wang, Y.B.; Chen, K.Y.; Fu, E. Antifungal effect of tissue conditioners containing poly(acryloyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride)-grafted chitosan on Candida albicans growth in vitro. J. Dent. Sci. 2018, 13, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonil, P.; Sajomsang, W.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Pimpha, N.; Sramala, I.; Nuchuchua, O.; Saesoo, S.; Chaleawlertumpon, S.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S. Novel quaternized chitosan containing β-cyclodextrin moiety: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.X.; de Zhong, Y.; Lü, R.; Zhang, W.Q.; Deng, J.; Chen, X.G. In vitro evaluation of the biomedical properties of chitosan and quaternized chitosan for dental applications. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.X.; Deng, J.; Yu, X.B.; Xu, Q.C.; Xu, X.Y. An in vitro evaluation of the antibacterial activity of chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel against periodontal pathogens. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 2009, 18, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakulwech, S.; Lourith, N.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Kanlayavattanakul, M. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles from quaternized cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan associated with hyaluronic acid for cosmetics. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaji, S.; Golshan Ebrahimi, N.; Hosseinkhani, H. Enhancement of biocompatibility of PVA/HTCC blend polymer with collagen for skin care application. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).