Improving Interlayer Adhesion of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA)/Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Laminates Prepared by Plasma Treatment and Hot Pressing Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Oxygen Plasma Treatment
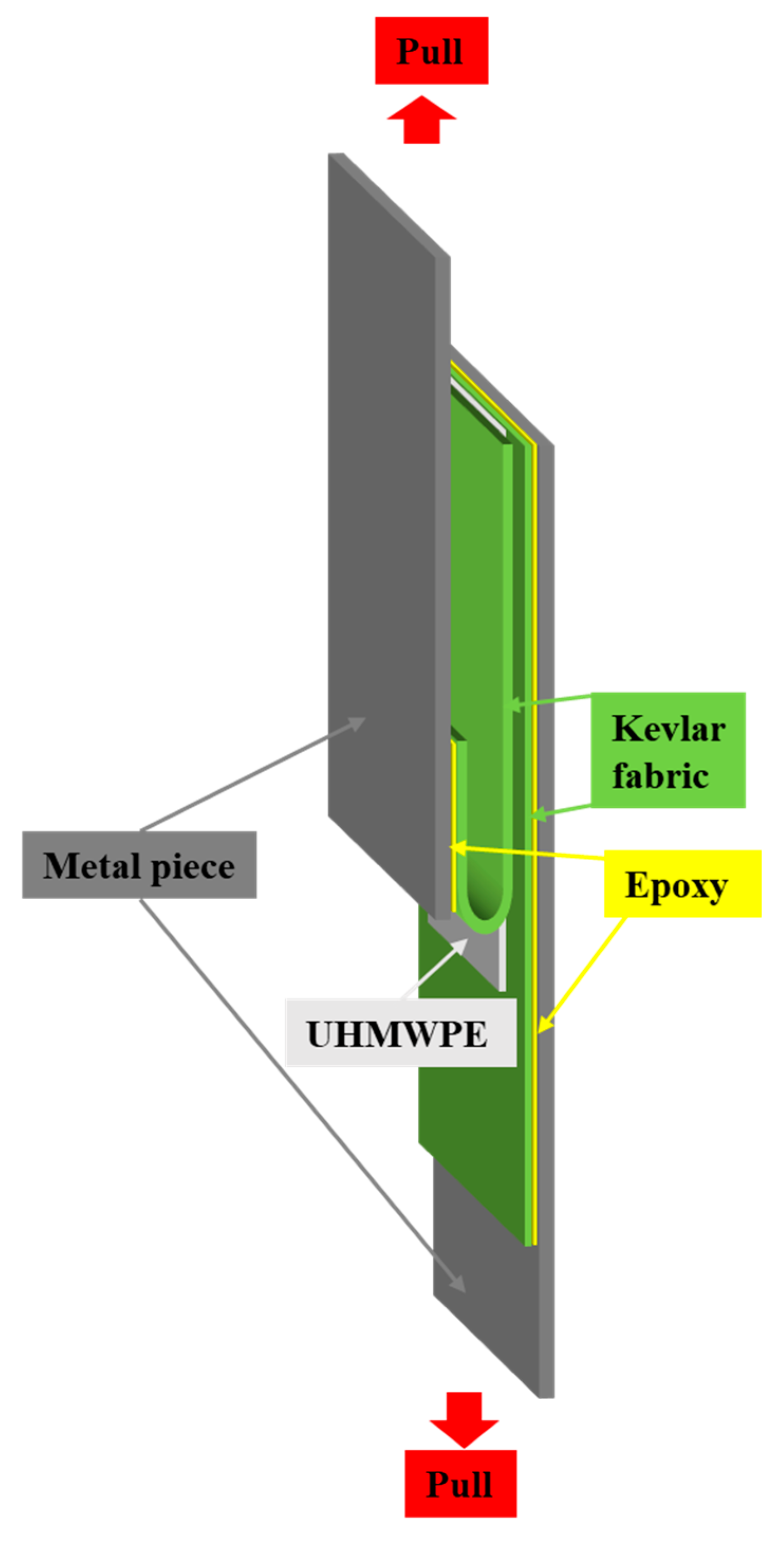
2.3. Preparation of PPTA/UHMWPE/PPTA Laminate
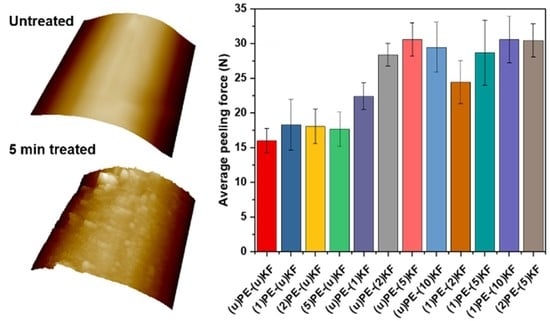
2.4. 180-Degree Peel Test
2.5. Characterization of PPTA Fabrics and UHMWPE
3. Results and Discussion
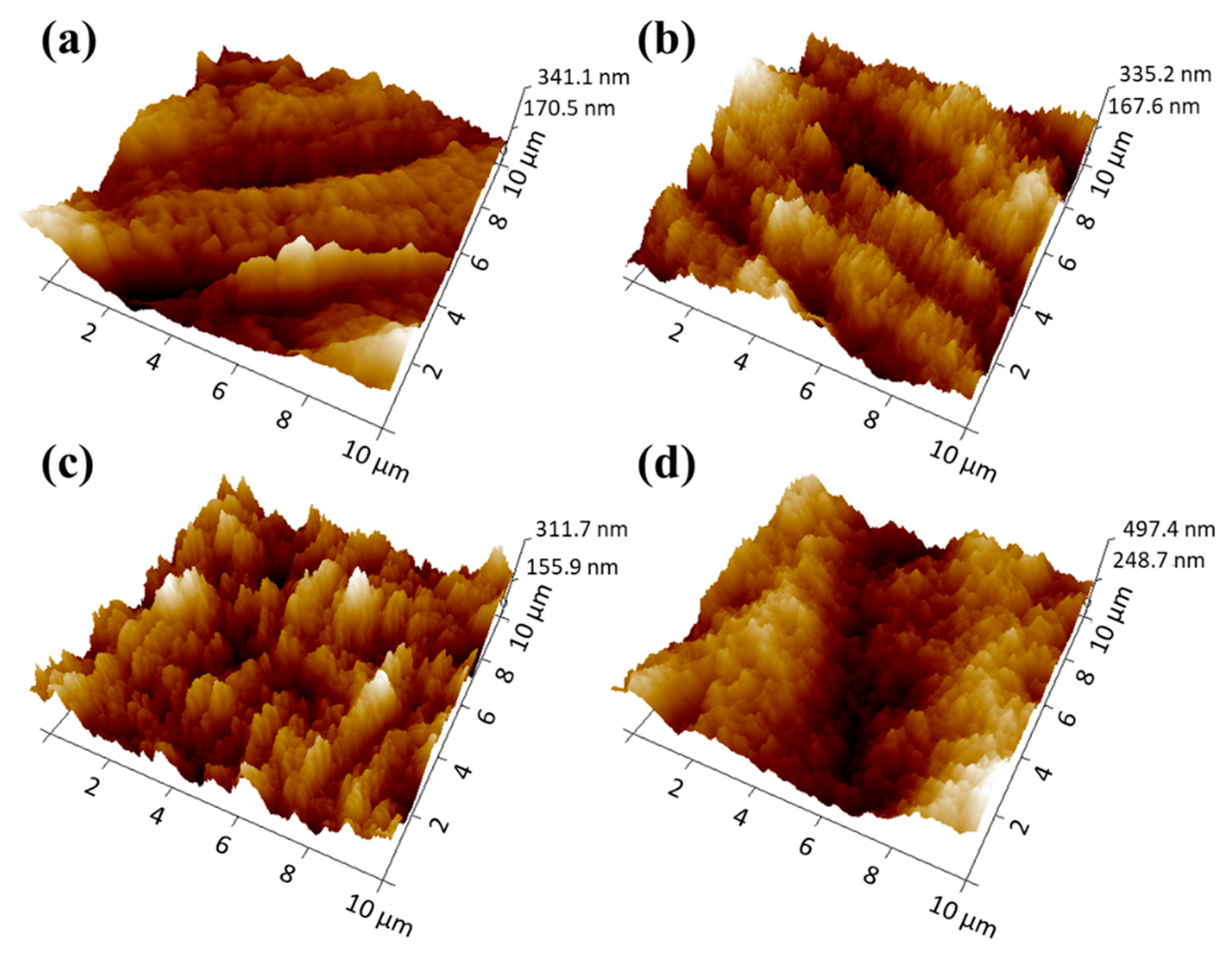
3.1. Morphologies of PPTA Fabric and UHMWPE Film
3.2. Surface Chemical Analysis of PPTA and UHMWPE Samples
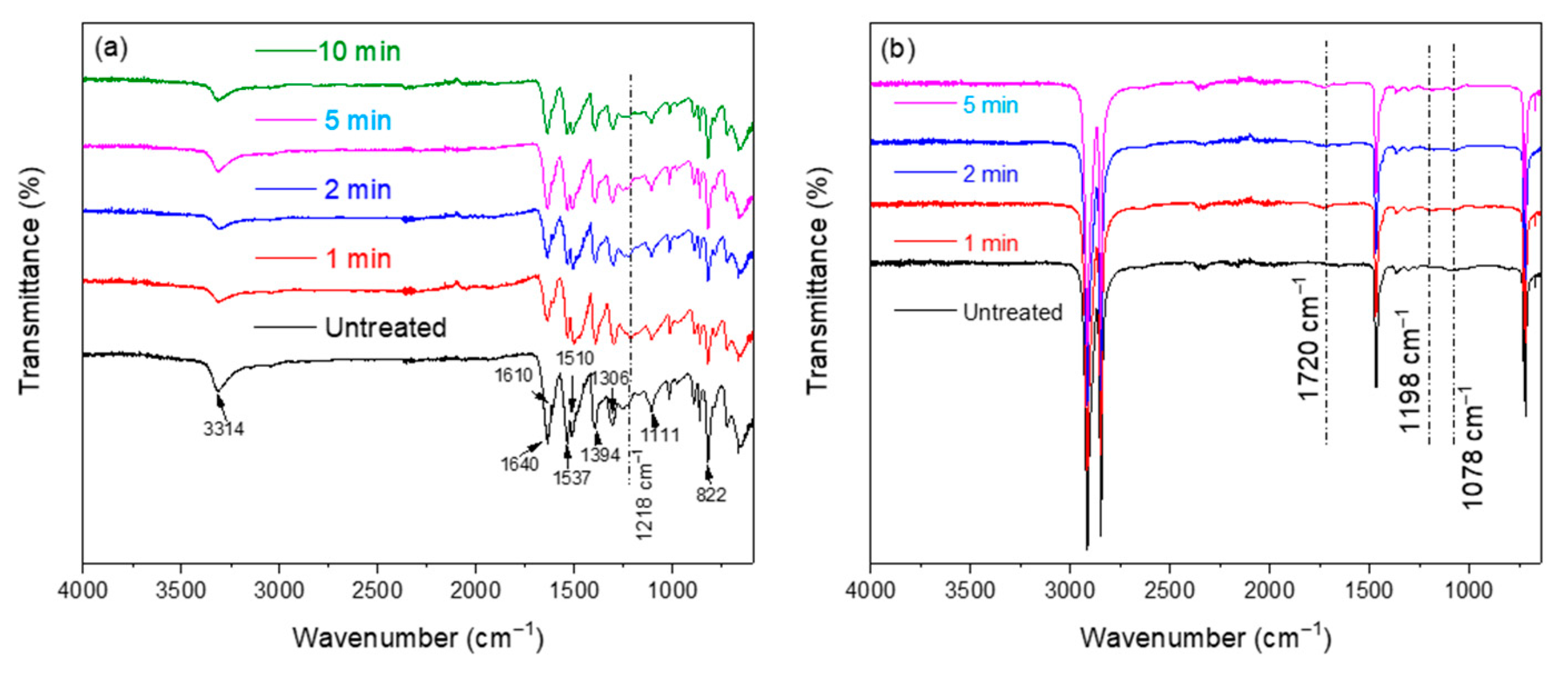
3.2.1. FTIR
3.2.2. XPS
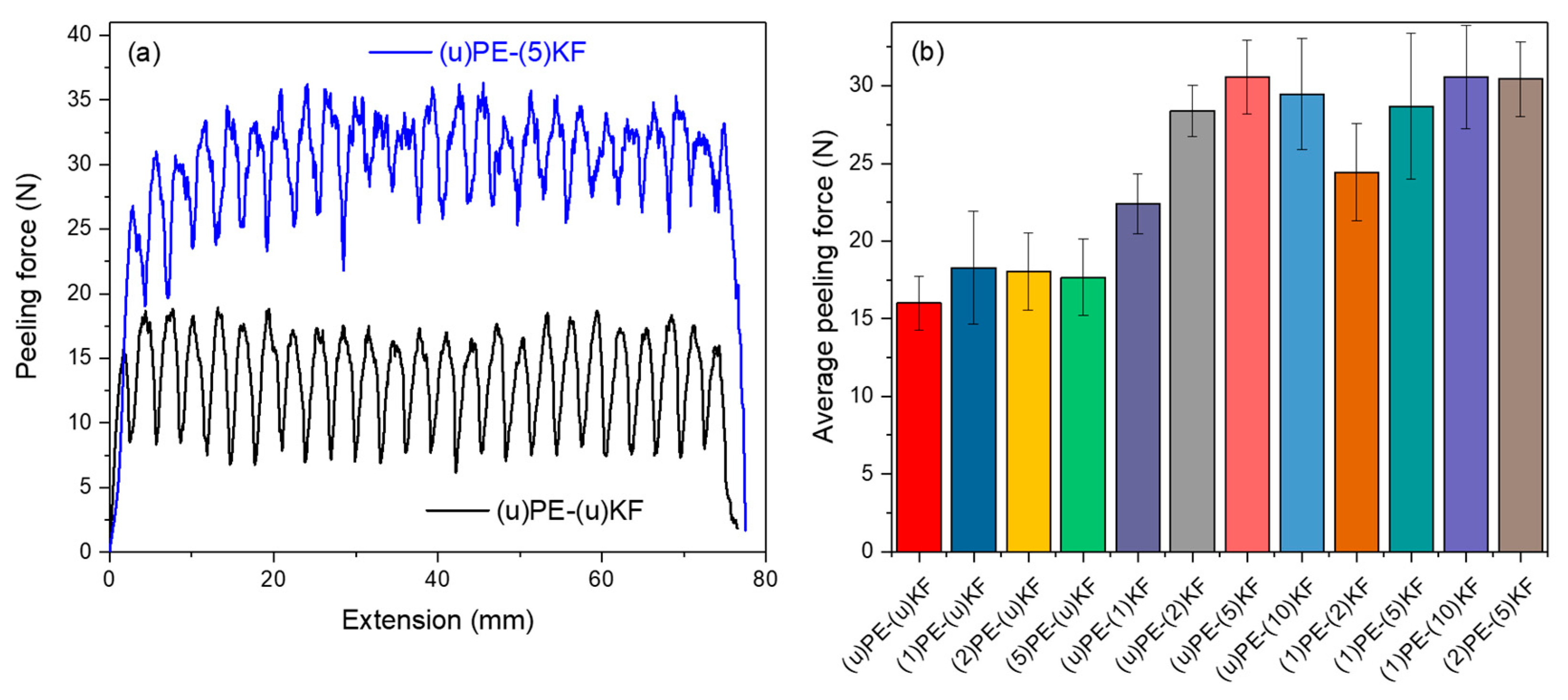
3.3. Adhesion Properties
3.4. Failure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacks, D.J. Simple model for the temperature-dependent compressive strength of polymer fibers. Mater. Lett. 2000, 44, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Tasaka, S.; Kawai, H. Surface modification of Kevlar® fiber by a combination of plasma treatment and coupling agent treatment for silicone rubber composite. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.H.; Rao, K.P. Mechanical properties of Kevlar-49 fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2012, 20, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Mobasher, B.; Erni, J.; Bansal, S.; Rajan, S.D. Strain rate and gage length effects on tensile behavior of Kevlar 49 single yarn. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.R.; Sheu, G.S.; Shyu, S.S. Kevlar fiber–epoxy adhesion and its effect on composite mechanical and fracture properties by plasma and chemical treatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 62, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Guo, F. Effects of air plasma treatment on tribological properties of hybrid PTFE/Kevlar fabric composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3980–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chalivendra, V.B.; Kim, Y.K. Fracture and impact characterization of novel auxetic Kevlar®/Epoxy laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 168, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, M.; Karahan, M.; Nawab, Y.; Ashraf, M.; Hussain, T. Effect of silica nanoparticles on mechanical properties of Kevlar/epoxy hybrid composites. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, F.; Yin, Z.; Jiang, D.; Huo, Y. A study on the tribological behavior of hybrid PTFE/Kevlar fabric composites filled with nano-SiC and/or submicron-WS2 fillers. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, S.; Bougherara, H. A comprehensive review on surface modification of UHMWPE fiber and interfacial properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.R.; Zhang, L. Mechanical properties of surface-modified ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber reinforced natural rubber composites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, X.; Shi, M.; Zhou, G. Surface modification of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetti, T.A.; Walter, M.; Staniszewski, J.; Cline, J. Interlaminar shear characterization of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 98, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attwood, J.P.; Fleck, N.A.; Wadley, H.N.G.; Deshpande, V.S. The compressive response of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibres and composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 71, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.G.; Satapathy, S.S.; Vargas-Gonzalez, L.R.; Walsh, S.M. Ballistic impact response of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, M.; Jabbar, A.; Karahan, N. Ballistic impact behavior of the aramid and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, K.; Jabbar, A.; Karahan, M.; Karahan, N.; Nawab, Y. Study of dynamic compressive behaviour of aramid and ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composites using Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofsté, J.M.; Bergmans, K.J.R.; De Boer, J.; Wevers, R.; Pennings, A.J. Short aramid-fiber reinforced ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Polym. Bull. 1996, 36, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofste, J.M.; Schut, J.A.; Pennings, A.J. The effect of chromic acid treatment on the mechanical and tribological properties of aramid fibre reinforced ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ye, F.B. Effect of surface modification of Kevlar fibre on friction and wear properties of UHMWPE composites. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2010, 39, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, T.; Verma, N.; Zafar, S.; Jain, V. Fabrication of Kevlar®-reinforced ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composite through microwave-assisted compression molding for body armor applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2021, 40, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaei, A.; Ahmadi, M.S. Effect of structural parameters on the cut resistance of para-aramid and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene weft knitted fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 111, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.I.; Umair, M.; Nawab, Y.; Hamdani, S.T.A. Development of 3D auxetic structures using para-aramid and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene yarns. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Shukla, D.K.; Prasad, N.E. Fracture behaviour of p-Aramid and ultra high molecular weight polyethylene based hybrid composite. Procedia Struct. Integrity 2019, 14, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.F.; Lavoratti, A.; Pereira, I.M.; Dias, R.R.; Amico, S.C.; Zattera, A.J. Development of multilaminar composites for vehicular ballistic protection using ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene laminates and aramid fabrics. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 51, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B Bigdilou, M.; Eslami-Farsani, R.; Ebrahimnezhad-Khaljiri, H.; Mohammadi, M.A. Experimental assessment of adding carbon nanotubes on the impact properties of Kevlar-ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers hybrid composites. J. Ind. Text. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ye, L.; Mai, Y.W. Application of plasma technologies in fibre-reinforced polymer composites: A review of recent developments. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 28, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, C.X.; Su, X.L.; Wu, G.P.; Wang, X.K. Effect of nano-SiO2 modified emulsion sizing on the interfacial adhesion of carbon fibers reinforced composites. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3601–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çökeliler, D.; Erkut, S.; Zemek, J.; Biederman, H.; Mutlu, M. Modification of glass fibers to improve reinforcement: A plasma polymerization technique. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liu, W.M.; Su, F.H.; Zhang, H.J. Effect of plasma treatment of Kevlar fabric on the tribological behavior of Kevlar fabric/phenolic composites. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.M. Oxygen plasma treatment of high performance fibers for composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Seong, D.G.; Kang, T.J.; Youn, J.R. Effects of surface modification on rheological and mechanical properties of CNT/epoxy composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.M.; Hung, C.H.; You, J.H.; Liu, S.J. Surface modification of reinforcement fibers for composites by acid treatments. J. Polym. Res. 2004, 11, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X. Effect of surface modification on carbon fiber and its reinforced phenolic matrix composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, A.; Jiang, K.; Dukes, D.; Andrews, R.; Schadler, L.S. Surface modification of multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Toward the tailoring of the interface in polymer composites. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3198–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Xie, M.; Yang, B. Surface modification of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene by the poly (ethylene glycol)-grafted method and its effect on the adsorption of proteins and the adhesion of blood platelets. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xiong, D. Fabrication and properties of UHMWPE grafted with acrylamide polymer brushes. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsbay, M.; Güven, O. Surface modification of cellulose via conventional and controlled radiation-induced grafting. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pei, Y.; Xie, D.; Deng, X.; Leng, Y.X.; Jin, Y.; Huang, N. Surface modification of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) by argon plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3941–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Bao, L.; Wang, B.; Fan, M.; Feo, L. Plasma surface modification and bonding enhancement for bamboo composites. Compos. B. Eng. 2018, 138, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, X. Plasma modification of Kevlar fabrics for ballistic applications. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Gu, A.; Liang, G.; Yuan, L. The effect of oxygen-plasma treatment on Kevlar fibers and the properties of Kevlar fibers/bismaleimide composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3158–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, E.M.; Martinu, L.; Wertheimer, M.R. Plasma surface modification of polymers for improved adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1993, 7, 1091–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.R. Improvement of interfacial adhesion and nondestructive damage evaluation for plasma-treated PBO and Kevlar fibers/epoxy composites using micromechanical techniques and surface wettability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombaldoni, F.; Mahmood, K.; Varesano, A.; Songia, M.B.; Aluigi, A.; Vineis, C.; Mazzuchetti, G. Adhesion enhancement of electrospun nanofiber mats to polypropylene nonwoven fabric by low-temperature oxygen plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 216, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Kang, T.J.; Yoon, T.H. Enhanced interfacial adhesion of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers by oxygen plasma treatment. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1998, 12, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tu, Q.; Shen, X.; Pan, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, C. Surface modification of Poly (p-phenylene terephthalamide) fibers by polydopamine-polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide multilayer films to enhance interfacial adhesion with rubber matrix. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, T.G.; da Cunha, R.D.; de Medeiros, N.J.F.; da Cunha, R.A.D.; de Carvalho, C.T.H.; Feitor, M.C. Structural Analysis of Kevlar Fabric Treated with Oxygen Plasma. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2020, 28, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.E.; Dave, J.R.; Makar, P.K.; Bhoraskar, S.V.; Premkumar, S.; Tomar, G.B.; Mathe, V.L. Surface modification of UHMWPE using ECR plasma for osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, M.; El-Shafei, A.; Hauser, P.J. Surface nanostructuring of kevlar fibers by atmospheric pressure plasma-induced graft polymerization for multifunctional protective clothing. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Tasaka, S.; Kawai, H. Surface modification of aromatic polyamide film by oxygen plasma. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1995, 33, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Treatment Time (min) | Chemical Composition (%) | Atom Ratio | Functional Groups (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | N1s | O1s | O/C | N/C | –C–C– | –C–N– | –C=O | –COO– | |
| Untreated | 80.05 | 6.85 | 13.10 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 49.64 | 31.35 | 12.57 | 0 |
| 1 | 63.71 | 8.47 | 27.83 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 40.10 | 19.84 | 13.49 | 26.57 |
| 2 | 63.12 | 7.84 | 29.04 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 30.66 | 28.24 | 3.50 | 38.06 |
| 5 | 59.66 | 6.85 | 33.49 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 28.44 | 28.14 | 18.40 | 25.03 |
| 10 | 69.48 | 5.77 | 24.75 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 45.06 | 30.15 | 10.98 | 13.81 |
| Treatment Time (min) | Chemical Composition (%) | Atom Ratio | Functional Groups (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | O1s | N1s | O/C | C–C | C–O | C=O | O–C=O | |
| Untreated | 92.73 | 7.27 | 0 | 0.08 | 78.51 | 21.49 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 77.97 | 22.03 | 0 | 0.28 | 69.78 | 14.32 | 9.42 | 6.47 |
| 2 | 76.02 | 23.08 | 0.90 | 0.30 | 58.32 | 26.64 | 6.50 | 8.54 |
| 5 | 78.24 | 21.76 | 0 | 0.28 | 70.78 | 18.11 | 5.64 | 5.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Dikin, D.A.; Percec, S.; Ren, F. Improving Interlayer Adhesion of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA)/Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Laminates Prepared by Plasma Treatment and Hot Pressing Technique. Polymers 2021, 13, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162600
Zhu L, Dikin DA, Percec S, Ren F. Improving Interlayer Adhesion of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA)/Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Laminates Prepared by Plasma Treatment and Hot Pressing Technique. Polymers. 2021; 13(16):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162600
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Long, Dmitriy A. Dikin, Simona Percec, and Fei Ren. 2021. "Improving Interlayer Adhesion of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA)/Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Laminates Prepared by Plasma Treatment and Hot Pressing Technique" Polymers 13, no. 16: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162600
APA StyleZhu, L., Dikin, D. A., Percec, S., & Ren, F. (2021). Improving Interlayer Adhesion of Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA)/Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Laminates Prepared by Plasma Treatment and Hot Pressing Technique. Polymers, 13(16), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13162600