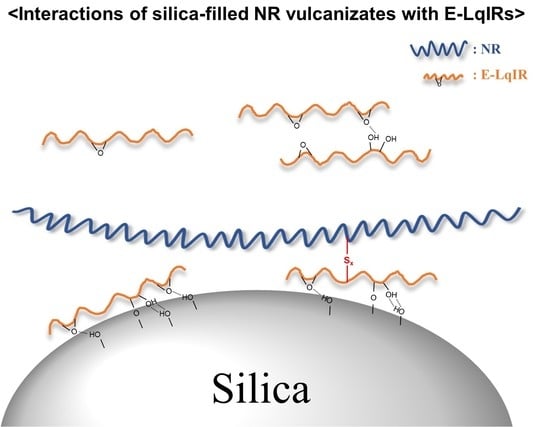
Effect of the Epoxide Contents of Liquid Isoprene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of Silica-Filled Natural Rubber Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Polymerization
2.1.2. Epoxidation
2.1.3. Compounding
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Gel Permeation Chromatography
2.2.2. H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMR)
2.2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.2.4. Payne Effect
2.2.5. Mooney Viscosity
2.2.6. Bound Rubber Content
2.2.7. Curing Characteristics
2.2.8. Crosslink Density and Vulcanizate Structure Analysis
2.2.9. Mechanical Properties
2.2.10. Abrasion Resistance
2.2.11. Viscoelastic Properties
2.3. Synthesis of Epoxidized Liquid Isoprene Rubbers
2.4. Preparation of Rubber Compounds and Vulcanizates
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Epoxidized LqIR
3.2. Curing Characteristics and Mooney Viscosity
3.3. Crosslink Density and Vulcanizate Structure Analysis
3.4. Mechanical Properties and DIN Abrasion Loss
3.5. Dynamic Viscoelastic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodgers, B. Tire Engineering: An Introduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, V.D.; Rossignol, T.M.; Crespo, J.S.; Carli, L.N. Tire Tread Compounds with Reduced Rolling Resistance and Improved Wet Grip. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkawi, S.S.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Natural Rubber-Silica Combinations for Low Rolling Resistance Truck Tyre Treads. Rubber World 2012, 2012, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.-J.; Zhang, P.; Mahmud, K. Carbon—Silica Dual Phase Filler, a New Generation Reinforcing Agent for Rubber: Part IX. Application to Truck Tire Tread Compound. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2001, 74, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkawi, S.S.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Morphology of Silica-Reinforced Natural Rubber: The Effect of Silane Coupling Agent. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2015, 88, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dierkes, W.; Sengloyluan, K.; Kaewsakul, W.; Noordermeer, J.; Sahakaro, K.; Blume, A. New Approaches to Increase the Compatibility of Natural Rubber and Silica for Reduction of Rolling Resistance of Truck and Bus Tires. In Proceedings of the ITEC in Focus: Green Tire, Cuyahoga Falls, OH, USA, 25–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazono, T.; Matsumoto, A. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Aging Behavior of Styrene-Butadiene Rubbers Vulcanized Using Liquid Diene Polymers as the Plasticizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Zetterlund, P.B.; Yamada, B. Effects of Storage and Service on Tire Performance: Oil Component Content and Swelling Behavior. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2003, 76, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ahn, B.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, W. Effects of Molecular Weight of Functionalized Liquid Butadiene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of SSBR/Silica Compounds. Polymers 2021, 13, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruendken, M. Liquid Rubber for Safer and Faster Tires. In Proceedings of the Tire Technology EXPO 2018, Hannover, Germany, 20–22 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, K. Bio Liquid Polymer for Winter Tires. In Proceedings of the Tire Technology EXPO 2018, Hannover, Germany, 20–22 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, G.; Kim, D.; Song, S.; Hwang, K.; Ahn, B.; Kim, W. Effect of Epoxide Content on the Vulcanizate Structure of Silica-Filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) Compounds. Polymers 2021, 13, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.; Quirk, R.P. Anionic Polymerization: Principles and Practical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, B.; Yao, W.; Cong, H.; Shao, H.; Du, A. Epoxidation of High Trans-1, 4-Polyisoprene and Its Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2986–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salort, F.; Henning, S.K. Silane-Terminated Liquid Poly (Butadienes) in Tread Formulations: A Mechanistic Study. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2021, 94, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkornsurapranee, E.; Vennemann, N.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Nakason, C. Novel Thermoplastic Natural Rubber Based on Thermoplastic Polyurethane Blends: Influence of Modified Natural Rubbers on Properties of the Blends. Iran. Polym. J. 2012, 21, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengloyluan, K.; Sahakaro, K.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Silica-Reinforced Tire Tread Compounds Compatibilized by Using Epoxidized Natural Rubber. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 51, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shao, H.; Yao, W.; Huang, B. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectral Analysis of Polyisoprene of a Different Microstructure. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, O.; Takahashi, T.; Kurihara, H.; Ueno, H. Monomer Unit Sequence Distribution in Partly-Epoxidized Trans-1, 4-Polyisoprene. Polym. J. 1981, 13, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burfield, D.R.; Lim, K.-L.; Law, K.-S.; Ng, S. Analysis of Epoxidized Natural Rubber. A Comparative Study of DSC, NMR, Elemental Analysis and Direct Titration Methods. Polymer 1984, 25, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrattanakul, V.; Wattanathai, B.; Tiangjunya, A.; Muhamud, P. In Situ Epoxidized Natural Rubber: Improved Oil Resistance of Natural Rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.R.; Whittaker, R.E. Low Strain Dynamic Properties of Filled Rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1971, 44, 440–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Mishra, Y.K. Nanocarbon Reinforced Rubber Nanocomposites: Detailed Insights about Mechanical, Dynamical Mechanical Properties, Payne, and Mullin Effects. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Polymer–Filler Interaction of Fumed Silica Filled Polydimethylsiloxane Investigated by Bound Rubber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, C.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, W. Effect of the Functional Group of Silanes on the Modification of Silica Surface and the Physical Properties of Solution Styrene-Butadiene Rubber/Silica Composites. Compos. Interfaces 2019, 26, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Ahn, B.; Kim, W.; Moon, H.; Paik, H.-J.; Kim, W. The Effect of Accelerator Contents on the Vulcanizate Structures of SSBR/Silica Vulcanizates. Compos. Interfaces 2017, 24, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Ahn, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, W.; Moon, H.; Kim, W. Effect of Organosilane Agents on the Vulcanizate Structure and Physical Properties of Silica-Filled Solution Styrene Butadiene Rubber Compounds. Compos. Interfaces 2018, 25, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Park, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, W. Influence of End-Functionalized Solution Styrene–Butadiene Rubber on Silica-Filled Vulcanizates with Various Silica–Silane Systems. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2019, 92, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, I.J.; Han, S.; Kim, W. Effects of Silane Agents and Curing Temperatures on Vulcanizate Structures. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2020, 93, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Ahn, B.; Kim, D.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W. Vulcanizate Structures and Mechanical Properties of Rubber Compounds with Silica and Carbon Black Binary Filler Systems. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2021, 94, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Kim, D.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W. Vulcanizate Structures of SBR Compounds with Silica and Carbon Black Binary Filler Systems at Different Curing Temperatures. Polymers 2020, 12, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Kim, D.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, W. Vulcanizate Structures of NR Compounds with Silica and Carbon Black Binary Filler Systems at Different Curing Temperatures. Elastom. Compos. 2021, 56, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Mun, D.; Morita, K.; Kim, W. Effect of Silane and Sulfur Variation on the Vulcanizate Structure of Silica-Filled Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Compounds. Elastom. Compos. 2021, 56, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.-J. Effect of Polymer-Filler and Filler-Filler Interactions on Dynamic Properties of Filled Vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 71, 520–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kim, W.-S.; Mun, D.-Y.; Ahn, B.; Kim, W. Effect of Coupling Agents on the Vulcanizate Structure of Carbon Black Filled Natural Rubber. Compos. Interfaces 2020, 27, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, S.; Tire, S.-F. Tread Compounds: An Investigation into the Viscoelastic Properties of the Rubber Compounds and Their Relation to Tire Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Suchiva, K.; Sirisinha, C.; Sae-Oui, P.; Thapthong, P. Development of Tyre Tread Compounds for Good Wet-Grip: Effects of Rubber Type. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 17–21 December 2018; p. 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.C.; Ninan, K.N.; Groeninckx, G.; Thomas, S. Styrene–Butadiene Rubber/Natural Rubber Blends: Morphology, Transport Behavior, and Dynamic Mechanical and Mechanical Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 1280–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.K. Natural Rubber Blends with Epoxidized Natural Rubber. J. Macromol. Sci. B 1997, 36, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Silica (Ultrasil 7000GR) | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 |
| TESPT (1) | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| TDAE oil | 10 | - | - | - |
| E-LqIR (2) | - | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| ZnO | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Stearic acid | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 6PPD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TMQ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sulfur | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| CBS | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| DPG | 1.06 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 1.06 |
| PVI | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Time (min:s) | Action | |
|---|---|---|
| First stage | 0:00–1:30 | NR mastication (initial temp.: 100 °C) |
| 1:30–2:40 | Add silica 1/2, TESPT 1/2, and oil or E-LqIRs 1/2 | |
| 2:40–3:40 | Add remaining silica, TESPT, and oil or E-LqIRs | |
| 3:40–5:30 | Add ZnO, St/A, 6PPD, and TMQ | |
| 5:30 | Ram up | |
| 5:30–7:30 | Extra mixing and dump (dump temp.: 150–155 °C) | |
| Second stage | 0:00–0:30 | Master batch from first stage (initial temp.: 50 °C) |
| 0:30–2:30 | Add curatives and dump (dump temp.: 80–90 °C) |
| LqIR | E-LqIRs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-06 | E-22 | E-34 | ||
| Mn (g/mol) | 3639 | 3761 | 4200 | 4401 |
| Polydispersity | 1.10 | 1.09 | 1.10 | 1.12 |
| 3,4-Addition (mol%) | 14.7 | 14.0 | 14.8 | 14.6 |
| 1,4-Addition (mol%) | 85.3 | 80.0 | 63.1 | 51.0 |
| Epoxide contents (mol%) | 0 | 6.0 | 22.1 | 34.4 |
| Tg (°C) | −77.60 | −72.46 | −60.28 | −47.44 |
| Functionality (epoxide/chain) | 0 | 3.3 | 13.0 | 20.6 |
| Compounds | TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG′ (0.28–40.04%, MPa) | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| Compounds | TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mooney viscosity (ML1+4@100 °C) | 56.7 | 53.7 | 49.8 | 48.9 |
| Bound rubber contents (%) | 32.5 | 31.3 | 29.1 | 28.1 |
| Tmin (N-m) | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Tmax (N-m) | 1.52 | 1.41 | 1.35 | 1.31 |
| ΔT (N-m) | 1.34 | 1.25 | 1.22 | 1.19 |
| Compound | TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss after extraction (wt%) | 8.48 | 7.24 | 6.52 | 5.89 |
| Weight loss after extraction of 10 phr TDAE oil or E-LqIRs (%) | 100 | 74.5 | 59.7 | 46.7 |
| Total crosslink density (chemical crosslink density + filler–rubber interaction) | 9.66 | 9.08 | 9.01 | 8.99 |
| Chemical crosslink density | 7.26 | 6.25 | 6.43 | 6.54 |
| Filler–rubber interaction | 2.40 | 2.83 | 2.58 | 2.45 |
| Compound | TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M100% (kgf/cm2) | 21.0 | 19.2 | 19.4 | 20.3 |
| M300% (kgf/cm2) | 77.2 | 72.0 | 69.3 | 68.3 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 690 | 710 | 680 | 700 |
| Tensile strength (kgf/cm2) | 279 | 275 | 261 | 264 |
| DIN abrasion loss (mg) | 152.3 | 149 | 162.5 | 168.5 |
| Compound | TDAE Oil | E-06 | E-22 | E-34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak of tan δ | 1.20 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.87 |
| E″ at 0 °C (MPa) | 1.74 | 1.44 | 2.11 | 4.29 |
| tan δ at 60 °C | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.065 | 0.079 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, G.; Kim, D.; Song, S.; Hwang, K.; Kim, W. Effect of the Epoxide Contents of Liquid Isoprene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of Silica-Filled Natural Rubber Compounds. Polymers 2021, 13, 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183026
Ryu G, Kim D, Song S, Hwang K, Kim W. Effect of the Epoxide Contents of Liquid Isoprene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of Silica-Filled Natural Rubber Compounds. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183026
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Gyeongchan, Donghyuk Kim, Sanghoon Song, Kiwon Hwang, and Wonho Kim. 2021. "Effect of the Epoxide Contents of Liquid Isoprene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of Silica-Filled Natural Rubber Compounds" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183026
APA StyleRyu, G., Kim, D., Song, S., Hwang, K., & Kim, W. (2021). Effect of the Epoxide Contents of Liquid Isoprene Rubber as a Processing Aid on the Properties of Silica-Filled Natural Rubber Compounds. Polymers, 13(18), 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183026