Synthesis and Heavy-Metal Sorption Studies of N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Copolymerization
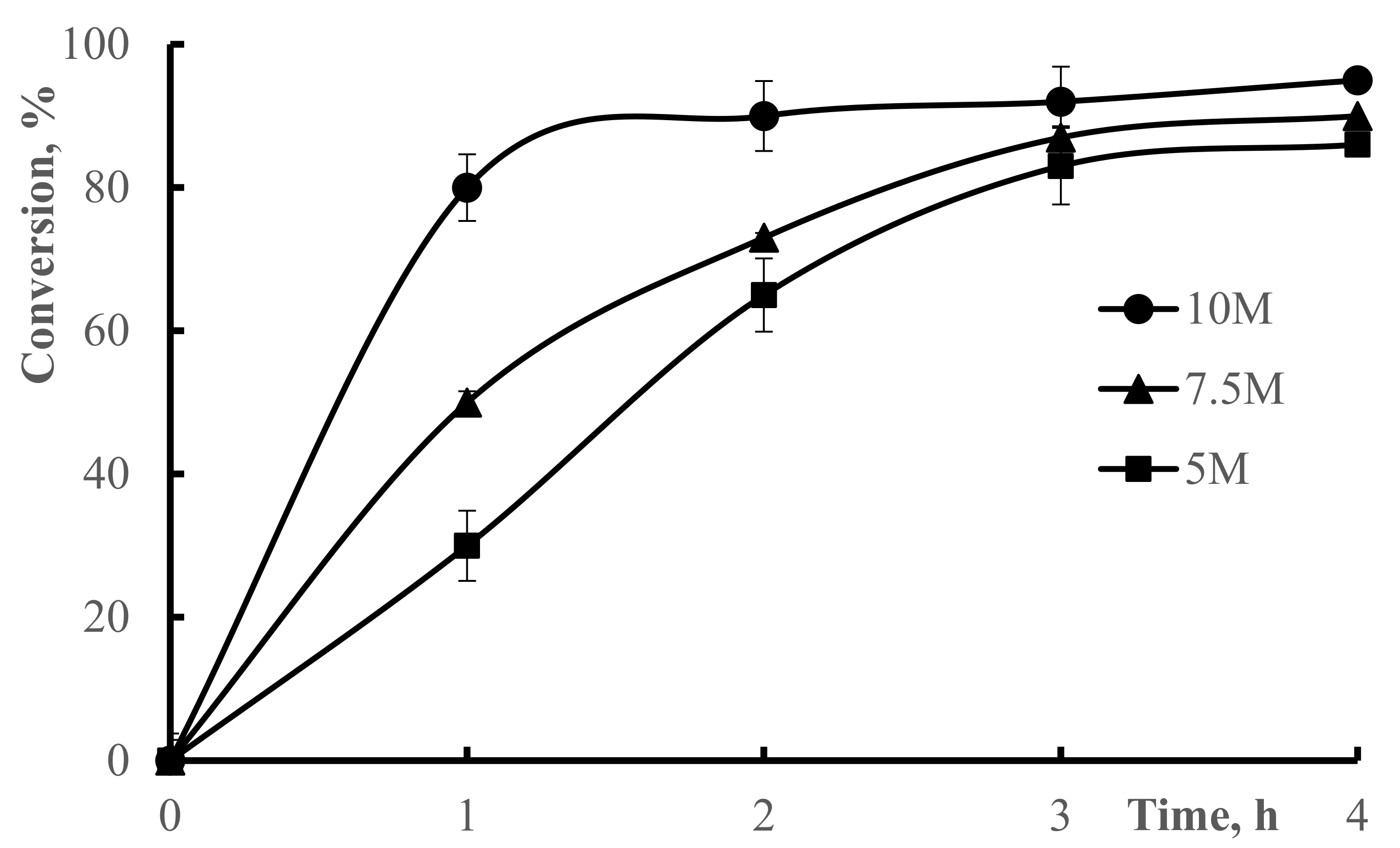
2.3. Conversion of Polymerization
2.4. Swelling Measurements
2.5. Metal-Ion Absorbency Studies
2.6. Data Presentation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Metal-Ion Sorption Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raju, K.M.; Raju, M.P. Synthesis of novel superabsorbing copolymers for agricultural and horticultural applications. Polym. Int. 2001, 50, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Rico, A.; Cucchiarini, M. Supramolecular Cyclodextrin-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Gene Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamidi, M.; Azadi, A.; Rafiei, P. Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chu, J.S.; Fix, J.A. Colon-specific drug delivery: New approaches and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha, K.L.; Harding, D.R.K. Synthesis and evaluation of sucrose-containing polymeric hydrogels for oral drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-R.; Chun, C.; Ahn, S.-W.; Ki, M.-H.; Cho, C.-S.; Song, S.-C. Sustained delivery of human growth hormone using a polyelectrolyte complex-loaded thermosensitive polyphosphazene hydrogel. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, N.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, M. Hydrogels for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Crit. Rev. Drug Carr. Syst. 2005, 22, 107–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Martin, B.D.; Neubauer, T.K.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S.; Rethwisch, D.G. Enzymatic and chemoenzymatic approaches to synthesis of sugar-based polymer and hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, K.N.; Jeffrey, S.M. Patterned Dual pH-Responsive Core−Shell Hydrogels with Controllable Swelling Kinetics and Volumes. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6535–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panprung, S.; Uracha, R.; Supaphol, P. Preparation and characterization of asiaticoside-loaded alginate films and their potential for use as effectual wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, M.; Santos, L.; Azeredo, J.; Yebra-Pimentel, E.; Real Oliveira, M.E.C.D. The effect of lens wear on refractive index of conventional hydrogel and silicone-hydrogel contact lenses: A comparative study. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2008, 31, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Martínez, A.R.; Lujan-Montelongo, J.A.; Silva-Cuevas, C.; Mota-Morales, J.D.; Cortez-Valadez, M.; Ruíz-Baltazar, Á.D.J.; Cruz, M.; Herrera-Ordonez, J. Swelling and methylene blue adsorption of poly(N, N -dimethylacrylamide- co -2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 122, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakan, U.; Mun, G.A.; Shaikhutdinov, Y.M.; Yeligbayeva, G.Z.; Bieerkehazhi, S.; Negim, E.S.; Samatovna, B.S.; Nauryzova, S.Z. Hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and 2-hydroxyethylacrylate: Synthesis, characterization and investigation its antibacterial activity. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Wiemer, E.A.; Macossay, J.; Bucio, E. Radiation grafting of N,N-dimethylacrylamide and 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate onto polypropylene films by one step method. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2013, 84, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiping, M.; Dongzhi, Y.; Qianzhu, L.; Kemin, W.; Binling, C.; Kennedy, J.F.; Jun, N. Injectable hydrogels based on chitosan derivative/polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate/N,N-dimethylacrylamide as bone tissue engineering matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melek, P.A.; Oguz, O. Highly stretchable self-healing poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 59, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdiyev, K.Z.; Toktarbay, Z.; Zhenissova, A.Z.; Zhursumbaeva, M.B.; Kainazarova, R.N.; Nuraje, N. The new effective flocculants—Copolymers of N,N-dimethyl-N,N-diallyl-ammonium chloride and N,N-dimethylacrylamide. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 480, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborina, O.E.; Gasanov, R.G.; Peregudov, A.S.; Lozinsky, V.I. Cryostructuring of polymeric systems. The causes of the covalently-crosslinked cryogels formation upon the homopolymerization of N,N-dimethylacrylamide in moderately-frozen aqueous media. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Garcia, A.; Bucio, E.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Surface functionalization of polypropylene devices with hemocompatible DMAAm and NIPAAm grafts for norfloxacin sustained release. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kawashima, M.; Katono, H.; Sanui, K.; Ogata, N.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Temperature-Responsive Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Constructed with Poly(acrylic acid) and Poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide). Macromolecules 1994, 27, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, S.; Okay, O. Acrylamide/2-acrylamido-2- methyl propane sulfonic acid sodium salt -based hydrogels: Synthesis and characterization. Polymer 2000, 41, 3693–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuermann, S.; Buback, M.; Hesse, P.; Junkers, T.; Lacík, I. Free-radical polymerization kinetics of 2acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tong, Z.; Hu, O. Swelling equilibria of hydrogels with sulfonate groups in water and in aqueous salt solutions. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 3813–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Liu, X. Swelling equilibria and volume phase transition in hydrogels with strongly dissociating electrolytes. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Shi, K.; Zhang, L.; Ju, X.; Wang, W.; Xie, R.; Chu, L. Reduced graphene oxide-containing smart hydrogels with excellent electro-response and mechanical properties for soft actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15758–15767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Vaughan, D. Hydrogel dressings in the management of a variety of wound types: A review. J. Orthop. Nurs. 2005, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalampang, K.; Panjakha, R.; Molloy, R.; Tighe, B.J. Structural effects in photo-polymerized sodium AMPS hydrogels crosslinked with poly(ethylene glycol) dia-crylate for use as burn dressings. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiari, V.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Bokias, G.; Lianos, P. Use of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) hydrogel to extract cationic dyes and metals from water. Colloids Surf. A 2008, 312, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of Salecan/poly(AMPS-co-HMAA) semi-IPN hydrogels for cell adhesion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Jacques, A.L.; Lujan-Montelongo, J.A.; Silva-Cuevas, C.; Cortez-Valadez, M.; Estevez, M.; Hernandez-Martínez, A.R. Lead (II) removal by poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate). Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayatzhan, A.; Tashenov, A.; Nurgeldi, A.; Zhanar, O.; Zhexenbek, T.; Kaldibek, A.; Nuraje, N. P (DADMAAC-co-DMAA): Synthesis, thermal stability, and kinetics. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 32, 2669–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Zhicheng, Z.; Haiting, J.; He, W.; Ge, X. Formation of Monodisperse Polyacrylamide Particles by Radiation-Induced Dispersion Polymerization: Particle Size and Size Distribution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 253, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdiyev, K.Z.; Toktarbay, Z.; Zhenissova, A.Z.; Zhursumbaeva, M.B.; Kainazarova, R.N. Copolymerization of N,N-dimethyll-N,N-diallylammonium Chloride with N,N-dimethylacrylamide. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2015, 57, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaona, W.; Qinyan, Y.; Baoyu, G.; Xiaohui, S.; Xun, S.; Shengxiao, Z. Kinetics of dispersion polymerization of dimethyl diallylammonium chloride and acrylamide. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 18, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasaswini, T.; Dinesh Kumar, M.; Mithilesh, Y.; Kunj, B. Synthesis, characterization and applications of graft copolymer (chitosan-g-N,N-dimethylacrylamide). Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauletov, Y.; Nuraje, N.; Abdiyev, K.; Toktarbay, Z.; Zhursumbaeva, M. Copolymers of Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride and Vinyl Ether of Monoethanolamine: Synthesis, Flocculating, and Antimicrobial Properties. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2019, 22, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, C.; Ilkay, A. Synthesis and network structure of ionic poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) hydrogels: Comparison of swelling degree with theory. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Guo, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Takahata, M.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J.P. Sliding friction of zwitterionic hydrogel and its electrostatic origin. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Mazidi, R. Modified carrageenan. Synthesis and swelling behavior of crosslinked-g-AMPS superabsorbent hydrogel with antisalt and pH-responsiveness properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthong, P.; Nuisin, R.; Kiatkamjornwong, S. Graft copolymerization, characterization, and degradation of cassava starch-g-acrylamide/itaconic acid superabsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Narzary, A. Release dynamics of brufen from a drug loaded polymer hydrogel containing polyvinyl alcohol, 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid and acrylamide. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2012, 61, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Feng, L.; Wei, W.; Xie, A.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. Synthesis and characterization of a novel semi-IPN hydrogel based on Salecan and poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Tang, K.; Wang, G. Removing Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by a Promising Absorbent of Tannin-Immobilized Cellulose Microspheres. Polymers 2019, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longinos, S.N.; Mahmut, P.M. Kinetic Analysis of Methane—Propane Hydrate Formation by the Use of Different Impellers. ASC Omega 2021, 6, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M. The Effect of Experimental Conditions on Methane (95%)–Propane (5%) Hydrate Formation. Energies 2020, 13, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M. Kinetic Analysis of Dual Impellers on Methane Hydrate Formation. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2020, 19, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Longinos, S.N.; Parlaktuna, M. The Effect of Experimental Conditions on Methane Hydrate Formation by the Use of Single and Dual Impellers. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2021, 132, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Proc. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Ofomaja, A. Pseudo-second-order model for lead ion sorption from aqueous solutions onto palm kernel fiber. J. Hazard Mater. 2006, 129, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Concentration | 1 h Standard Errors | 2 h Standard Errors | 3 h Standard Errors | 4 h Standard Errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.45% | 0.65 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.39 |
| 0.85% | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.37 |
| Concentration | 1st Experiment | 2nd Experiment | Standard Deviation | Root | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.45% | 5 | 6.3 | 0.91 | 1.41 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhmetzhan, A.; Abeu, N.; Longinos, S.N.; Tashenov, A.; Myrzakhmetova, N.; Amangeldi, N.; Kuanyshova, Z.; Ospanova, Z.; Toktarbay, Z. Synthesis and Heavy-Metal Sorption Studies of N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2021, 13, 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183084
Akhmetzhan A, Abeu N, Longinos SN, Tashenov A, Myrzakhmetova N, Amangeldi N, Kuanyshova Z, Ospanova Z, Toktarbay Z. Synthesis and Heavy-Metal Sorption Studies of N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183084
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhmetzhan, Ayatzhan, Nurgeldi Abeu, Sotirios Nik. Longinos, Ayezkhan Tashenov, Nurbala Myrzakhmetova, Nurgul Amangeldi, Zhanar Kuanyshova, Zhanar Ospanova, and Zhexenbek Toktarbay. 2021. "Synthesis and Heavy-Metal Sorption Studies of N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183084
APA StyleAkhmetzhan, A., Abeu, N., Longinos, S. N., Tashenov, A., Myrzakhmetova, N., Amangeldi, N., Kuanyshova, Z., Ospanova, Z., & Toktarbay, Z. (2021). Synthesis and Heavy-Metal Sorption Studies of N,N-Dimethylacrylamide-Based Hydrogels. Polymers, 13(18), 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183084






