Controllable Release of Povidone-Iodine from Networked Pectin@Carboxymethyl Pullulan Hydrogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Session
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Methods
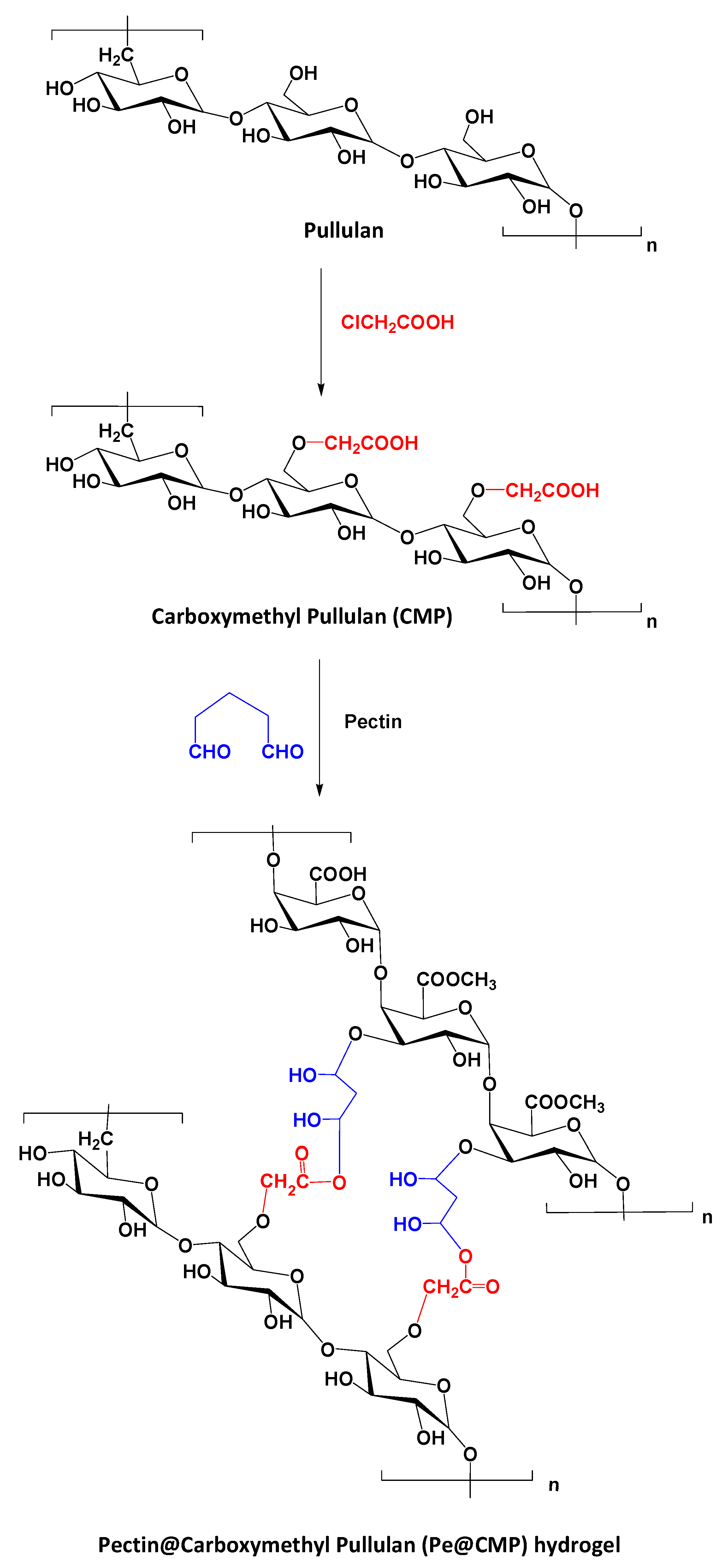
Preparation of Carboxymethyl Pullulan
Preparation of Pe@CMP Hydrogel
2.2. Bioactivity of PI
2.3. Characterization and Analysis
2.3.1. Carboxylic Content and Degree of Substitution
2.3.2. Infrared Spectra (FTIR)
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.4. Rheological Properties
2.3.5. Solution Uptake and Swelling
2.4. Release of Povidone-Iodine
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Pe@CMP Hydrogel
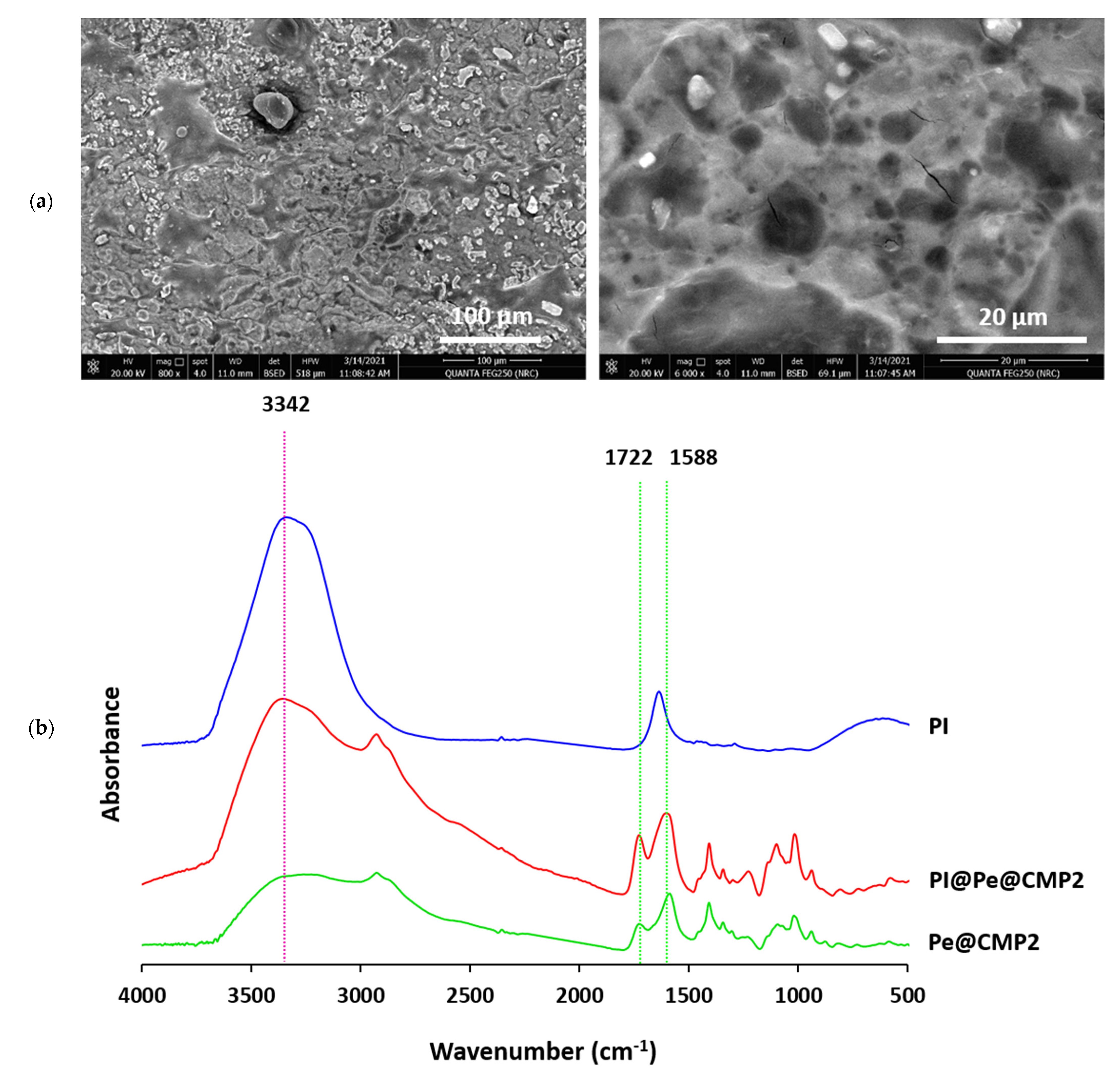
3.1.1. FTIR Spectra
3.1.2. Micrographs
3.1.3. Rheological Properties
3.1.4. Solution Uptake and Swelling Properties
3.1.5. Release Properties of Povidone-Iodine (PI)
3.1.6. Kinetic and Releasing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.L.; Mooney, D. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: Scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4337–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.; van Nostrum, C. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 54, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloxin, A.M.; Kasko, A.M.; Salinas, C.N.; Anseth, K.S. Photodegradable Hydrogels for Dynamic Tuning of Physical and Chemical Properties. Science 2009, 324, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buwalda, S.J.; Boere, K.W.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Feijen, J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels in a historical perspective: From simple networks to smart materials. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Ge, M.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Recent Progress of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Interfaces for Wound Healing and Tissue Engineering. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiao, H.; Seidi, F.; Jin, Y. Natural Polymer-Based Antimicrobial Hydrogels without Synthetic Antibiotics as Wound Dressings. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2983–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Demitri, C. Polymeric hydrogels for burn wound care: Advanced skin wound dressings and regenerative templates. Burn. Trauma 2014, 2, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghobril, C.; Grinstaff, M. The chemistry and engineering of polymeric hydrogel adhesives for wound closure: A tutorial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, J.; Brandl, F.P.; Goepferich, A.M. Hydrogel wound dressings for bioactive treatment of acute and chronic wounds. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Demirci, A.; Catchmark, J.M. Pullulan: Biosynthesis, production, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S. Pullulan and its applications. Process. Biochem. 1974, 9, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Leathers, T.D. Biotechnological production and applications of pullulan. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekha, M.; Sharma, C.P. Pullulan as a promising biomaterial for biomedical applications: A perspective. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2007, 20, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto-Rogers, Y.; Iio, N.; Takemura, A.; Iwata, T. Synthesis and characterization of pullulan alkyl esters. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 66, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Vishwasrao, C.; Singhal, R.S.; Ananthanarayan, L. n-Octenyl succinylation of pullulan: Effect on its physico-mechanical and thermal properties and application as an edible coating on fruits. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar-Aziz, M.; Yarmand, M.S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Mousavi, M.; Gharaghani, M.; Kennedy, J.F.; Hosseini, S.S. Chemical modification of pullulan exopolysaccharide by octenyl succinic anhydride: Optimization, physicochemical, structural and functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3485–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercea, M.; Biliuta, G.; Avadanei, M.; Baron, R.I.; Butnaru, M.; Coseri, S. Self-healing hydrogels of oxidized pullulan and poly(vinyl alcohol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 206, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yi, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of pullulan derivative/chitosan composite film for potential antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, L.T.; Paula, M.L.d.; de Moraes, R.M.; Alves, G.M.; Lacerda, T.M.; Santos, J.C.d.; Santos, A.M.d.; Medeiros, S.d.F. Chemical Modification of Pullulan Exopolysaccharide by Grafting Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)(PHBHV) via Click Chemistry. Polymers 2020, 12, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.T.; Moraes, R.M.; Alves, G.M.; Lacerda, T.M.; Santos, J.C.; Santos, A.M.; Medeiros, S.F. Synthesis of amphiphilic pullulan-graft-poly(ε-caprolactone) via click chemistry. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 145, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and disinfectants: Activity, action, and resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bigliardi, P.L.; Alsagoff, S.A.L.; El-Kafrawi, H.Y.; Pyon, J.-K.; Wa, C.T.C.; Villa, M.A. Povidone iodine in wound healing: A review of current concepts and practices. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 44, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, V.; Bruno, A.; di Trapani, B.; Tomasello, G. Who Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection: A New Step to Improve PATIENTS’SAFETY before, During and After Surgery; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, J.-M.; Castel, O.; Casado, A.F.; Leroy, B.; Micali, G.; Tennstedt, D.; Lambert, J. Antiseptics in the era of bacterial resistance: A focus on povidone iodine. Clin. Pract. 2013, 10, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Zayed, B.; Bischoff, P.; Kubilay, N.Z.; de Jonge, S.; de Vries, F.; Gomes, S.M.; Gans, S.; Wallert, E.D.; Wu, X.; et al. New WHO recommendations on intraoperative and postoperative measures for surgical site infection prevention: An evidence-based global perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e288–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, N.; Casillis, R.; Reder, R.; Roth, R.; Ripa, S.; Paulson, D. Clinical Applications of Povidone-Iodine as a Topical. In Handbook of Topical Antimicrobials, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; 22p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaper, D.J.; Schultz, G.; Carville, K.; Fletcher, J.; Swanson, T.; Drake, R. Extending the TIME concept: What have we learned in the past 10 years? Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. On-Demand Dissolvable Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Cellulose Nanocrystal for Deep Partial Thickness Burn Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41076–41088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Pan, W.; Tong, X.; Zeng, Q.; Su, T.; Qi, X.; Shen, J. Polydopamine-incorporated dextran hydrogel drug carrier with tailorable structure for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 253, 117213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Qi, X.; Mao, R.; Pan, W.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Shen, J.; Deng, H.; Hu, R. Construction of functional curdlan hydrogels with bio-inspired polydopamine for synergistic periodontal antibacterial therapeutics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhao, W.; Wu, L.; Dong, W.; Qi, X. Facile fabrication of functional hydrogels consisting of pullulan and polydopamine fibers for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, I.; Rizzello, L.; Bayer, I.S.; Pompa, P.P.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Controlled antiseptic release by alginate polymer films and beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Chaudhary, N. Study of povidone iodine loaded hydrogels as wound dressing material. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2010, 23, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, E.L.; Valentini, P.; Mussino, F.; Pompa, P.P.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Antibacterial bioelastomers with sustained povidone-iodine release. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, N.; Khan, S.M.; Khalid, S.; Zia, S.; Islam, A.; Sabir, A.; Sultan, M.; Hussain, F.; Khan, R.U.; Butt, M.T.Z. Designing of biocompatible and biodegradable chitosan based crosslinked hydrogel for in vitro release of encapsulated povidone-iodine: A clinical translation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4370–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydak, K.; Junka, A.; Dydak, A.; Brożyna, M.; Paleczny, J.; Fijalkowski, K.; Kubielas, G.; Aniołek, O.; Bartoszewicz, M. In Vitro Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose Dressings Chemisorbed with Antiseptics against Biofilm Formed by Pathogens Isolated from Chronic Wounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; El-Bisi, M.K. Merely Ag nanoparticles using different cellulose fibers as removable reductant. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4219–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; El-Zawahry, M.M.; Ahmed, H.B. One-pot fabrication of AgNPs, AuNPs and Ag-Au nano-alloy using cellulosic solid support for catalytic reduction application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.A. Thixotropic—A Review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1997, 70, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; Ahmed, H.B.; Bechtold, T. In-situ deposition of Cu2O micro-needles for biologically active textiles and their release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepelletier, D.; Maillard, J.Y.; Pozzetto, B.; Simon, A. Povidone Iodine: Properties, Mechanisms of Action, and Role in Infection Control and Staphylococcus aureus Decolonization. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B.; El Hawary, N.; Emam, H.E. Self-assembled AuNPs for ingrain pigmentation of silk fabrics with antibacterial potency. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Tao, F.; Cui, Y. Cellulose-based film modified by succinic anhydride for the controlled release of domperidone. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1233–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, H.E.; Saad, N.M.; Abdallah, A.E.; Ahmed, H.B. Acacia gum versus pectin in fabrication of catalytically active palladium nanoparticles for dye discoloration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Optimization of Pectin Enzymatic Extraction from Malus domestica ‘Fălticeni’ Apple Pomace with Celluclast 1.5 L. Molecules 2019, 24, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramasubramaniam, S.; Govindarajan, C.; Nasreen, K.; Sudha, P. Removal of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution using chitosan/starch polymer blend. Compos. Interfaces 2013, 21, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, J.; Wagner, N.J. Thixotropy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, J.; Wagner, N.J. Current trends in suspension rheology. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2009, 157, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, D.; Gładysz, O.; Szulc, M.; Zborowski, J.; Junka, A.; Janeczek, M.; Lipińska, A.; Skalec, A.; Karolewicz, B. Development and Evaluation of a Polyvinylalcohol-Cellulose Derivative-Based Film with Povidone-Iodine Predicted for Wound Treatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Du, R. Immobilization of povidone-iodine on surfaces of silica gel particles and bactericidal property. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hixson, A.W.; Crowell, J.H. Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation (I) theoretical consideration. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; Abdelhamid, A.E.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Refining of liquid fuel from N-Containing compounds via using designed Polysulfone@Metal organic framework composite film. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.M.; Emam, H.E. Design of ZIF (Co & Zn)@ wool composite for efficient removal of pharmaceutical intermediate from wastewater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample | Pullulan:CAA Ratio (wt:wt) | Carboxyl Content (mmol/kg) | Degree of Substitution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pullulan | 1.0:0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | - |
| CMP1 | 1.0:1.0 | 24.2 ± 1.8 | 0.42 |
| CMP2 | 1.0:1.5 | 38.5 ± 2.2 | 0.66 |
| CMP3 | 1.0:2.0 | 51.2 ± 2.7 | 0.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emam, H.E.; Mohamed, A.L. Controllable Release of Povidone-Iodine from Networked Pectin@Carboxymethyl Pullulan Hydrogel. Polymers 2021, 13, 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183118
Emam HE, Mohamed AL. Controllable Release of Povidone-Iodine from Networked Pectin@Carboxymethyl Pullulan Hydrogel. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183118
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmam, Hossam E., and Amina L. Mohamed. 2021. "Controllable Release of Povidone-Iodine from Networked Pectin@Carboxymethyl Pullulan Hydrogel" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183118
APA StyleEmam, H. E., & Mohamed, A. L. (2021). Controllable Release of Povidone-Iodine from Networked Pectin@Carboxymethyl Pullulan Hydrogel. Polymers, 13(18), 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183118







