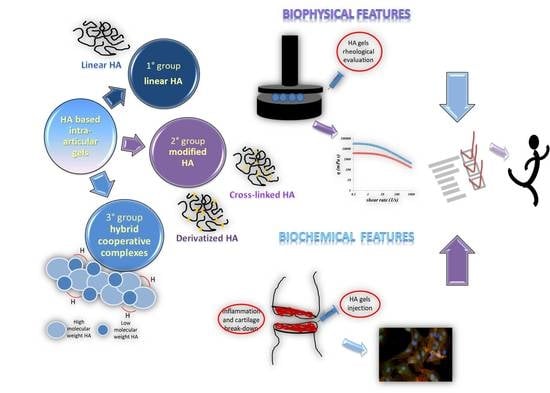
Hyaluronan and Derivatives: An In Vitro Multilevel Assessment of Their Potential in Viscosupplementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Water-Soluble HA Quantification and Hydrodynamic Analyses
2.2.2. Rheological Characterization
2.2.3. Sample Rheology during Enzymatic Degradation
2.2.4. In Vitro Model of Osteoarthritis for Comparative Evaluation of Diverse HA-Based Injective Hydrogels
Human Primary Cell Cultures Setting Up
Viability Assay
Gene Expression Analyses of OA Biomarkers through qRT-PCR
Western Blot Analyses Performed on Pathological Chondrocytes
Immunofluorescence Analyses
3. Results
3.1. SEC-TDA Analyses
3.2. Rheological Characterization
3.3. Sample Sensitivity to Enzymatic Degradation: A Rheology-Based Comparison
3.4. In Vitro Model of Osteoarthritis for Comparative Evaluation of Diverse HA-Based Injective Hydrogels
3.4.1. Cell Viability Assay in Presence of HA-Based Gels
3.4.2. Gene Expression Analyses of OA Biomarkers by qRT-PCR
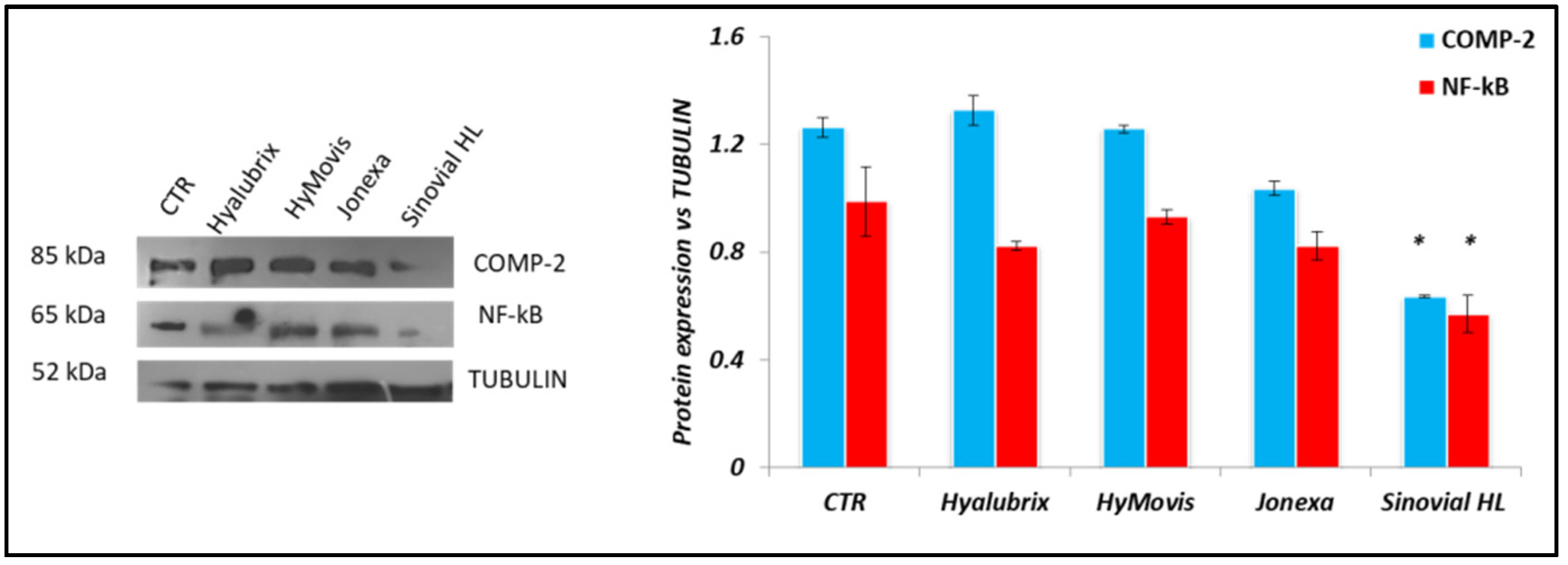
3.4.3. Western Blot Analyses Performed on Pathological Chondrocytes
3.4.4. Immunofluorescence Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuggle, N.R.; Cooper, C.; Oreffo, R.; Price, A.J.; Kaux, J.F.; Maheu, E.; Cutolo, M.; Honvo, G.; Conaghan, P.G.; Berenbaum, F.; et al. Alternative and complementary therapies in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, B.; Vajda, E.; Nagy, E.E. Regulatory Effects and Interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK Signaling at the Bone-Cartilage Interface in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, N.; Hosseini, S.; Alini, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Eslaminejad, M.B. Targeted cell delivery for articular cartilage regeneration and osteoarthritis treatment. Drug. Discov. Today 2019, 24, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, H.; Bryant, J.T.; Kontopoulou, M. Rheological properties of synovial fluids. Biorheology 2007, 44, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuanantanondh, P.; Grecov, D.; Kwok, E.; Guy, P. Rheology of osteoarthritic synovial fluid mixed with viscosupplements: A pilot study. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2011, 1, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebenda, D.; Vrbka, M.; Nečas, D.; Toropitsyn, E.; Yarimitsu, S.; Čípek, P.; Pravda, M.; Hartl, M. Rheological and frictional analysis of viscosupplements towards improved lubrication of human joints. Tribol. Int. 2021, 160, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellavato, A.; de Novellis, F.; Reale, S.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Hybrid complexes of high and low molecular weight: Evaluation using an in vitro model of osteoarthritis. J. Boil. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30 (Suppl. 1), 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, C.; Jordan, O.; Allémann, E. Osteoarthritis In Vitro Models: Applications and Implications in Development of Intra-Articular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiraldi, C.; Stellavato, A.; De Novellis, F.; La Gatta, A.; de Rosa, M. Hyaluronan viscosupplementation: State of the art and insight into the novel cooperative hybrid complexes based on high and low molecular weight HA of potential interest in osteoarthritis treatment. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2016, 13, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapasin, R.; Segatti, F.; Mercuri, D.; de Conti, G.; Spagnul, C.; Fusi, S. Rheological studies dedicated to the development of a novel injectable polymeric blend for viscosupplementation treatment. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2015, 29, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, D.; Franceschi, F. Viscosupplementation with high molecular weight native hyaluronan. Focus on a 1500–2000 KDa fraction (Hyalubrix®). Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 3326–3338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finelli, I.; Chiessi, E.; Galesso, D.; Renier, D.; Paradossi, G. A new viscosupplement based on partially hydrophobic hyaluronic acid: A comparative study. Biorheology 2011, 48, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzacchiello, A.; Mayol, L.; Schiavinato, A.; Ambrosio, L. Effect of hyaluronic acid amide derivative on equine synovial fluid viscoelasticity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 92, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuanantanondh, P.; Grecov, D.; Kwok, E. Rheological Study of Viscosupplements and Synovial Fluid in Patients with Os-teoarthritis. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2010, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellavato, A.; Vassallo, V.; La Gatta, A.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; de Rosa, M.; Balato, G.; D’Addona, A.; Tirino, V.; Ruosi, C.; Schiraldi, C. Novel Hybrid Gels Made of High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Induce Proliferation and Reduce Inflammation in an Osteoarthritis In Vitro Model Based on Human Synoviocytes and Chondrocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4328219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, A.; Bizzi, E.; de Lucia, O.; Sedie, A.D.; Bentivegna, M.; Mahmoud, A.; Foti, C. Differences among Branded Hyaluronic Acids in Italy, Part 1: Data from In Vitro and Animal Studies and Instructions for Use. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 9, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, M.; Manjoo, A.; Shaw, P.; Niazi, F.; Rosen, J. A Comparison between Rheological Properties of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Preparations and Reported Human Synovial Fluid. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; D’Este, M.; Vadalà, G.; Cattani, C.; Papalia, R.; Alini, M.; Denaro, V. Platelet Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Blend for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Rheological and Biological Evaluation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.; Galesso, D.; Secchieri, C.; Guarise, C. Hyaluronic acid alkyl derivative: A novel inhibitor of metalloproteases and hyaluronidases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.E.; Bolia, I.K.; Trasolini, N.A. Biological strategies for osteoarthritis: From early diagnosis to treatment. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.M.; Russell, A.K.; Schiavinato, A.; Little, C.B. A hexadecylamide derivative of hyaluronan (HYMOVIS®) has superior beneficial effects on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and synoviocytes than unmodified hyaluronan. J. Inflamm. 2013, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavinato, A.; Finesso, M.; Cortivo, R.; Abatangelo, G. Comparison of the effects of intra-articular injections of Hyaluronan and its chemically cross-linked derivative (Hylan G-F20) in normal rabbit knee joints. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2002, 20, 12175098. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, A.L.S.; E Albuquerque, R.S.P.; Da Silva, E.B.; Fayad, S.G.; Acerbi, L.D.; De Almeida, F.N.; Ooka, N.H.M.; Franco, J.S.; Gameiro, V.S. Viscosupplementation in patients with severe osteoarthritis of the knee: Six month follow-up of a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotevoglu, N.; Iyıbozkurt, P.C.; Hız, O.; Toktaş, H.; Kuran, B.; Hiz, O. A prospective randomised controlled clinical trial comparing the efficacy of different molecular weight hyaluronan solutions in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2005, 26, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Dutta, A.; Day, N.; Sharma, H.; Shaw, C.; Johnson, G. Efficacy of Hylan G-F 20 and Sodium Hyaluronate in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee—A prospective randomized clinical trial. Knee 2008, 15, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, A.; Massafra, U.; Bizzi, E.; Vacca, F.; Martin-Martin, S.; Granata, M.; Alimonti, A.; Tormenta, S. Comparative, double-blind, controlled study of intra-articular hyaluronic acid (Hyalubrix®) injections versus local anesthetic in osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrotin, Y.; Bannuru, R.; Malaise, M.; Ea, H.-K.; Confavreux, C.; Bentin, J.; Urbin-Choffray, D.; Conrozier, T.; Brasseur, J.-P.; Thomas, P.; et al. Hyaluronan derivative HYMOVIS® increases cartilage volume and Type II collagen turnover in osteoarthritic knee: Data from MOKHA study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benazzo, F.; Perticarini, L.; Padolino, A.; Castelli, A.; Gifuni, P.; Lovato, M.; Manzini, C.; Giordan, N. A multi-centre, open label, long-term follow-up study to evaluate the benefits of a new viscoelastic hydrogel (Hymovis®) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 20, 959–968. [Google Scholar]
- Papalia, R.; Zampogna, B.; Russo, F.; Vasta, S.; Tirindelli, M.C.; Nobile, C.; Di Martino, A.C.; Vadalà, G.; Denaro, V. Com-paring hybrid hyaluronic acid with PRP in end career athletes with degenerative cartilage lesions of the knee. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30 (Suppl. 1), 28002896. [Google Scholar]
- Gigante, A.; Callegari, L. The role of intra-articular hyaluronan (Sinovial®) in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 31, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.D.; Rosen, J.E.; Bloch, D.A.; Hatoum, H.T.; Korner, P. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Saline-Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety of EUFLEXXA® for Treatment of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee, With an Open-Label Safety Extension (The FLEXX Trial). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gatti, R. The safety and efficacy of intra-articular dual molecular weighted hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: The I.D.E.H.A. study. Orthop. Rev. 2013, 5, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hyalubrix® [leaflet]; Fidia Farmaceutici S.p.A.: Abano Terme, Padova, Italy. Available online: https://www.fogliettoillustrativo.net/bugiardino/hyalubrix-sir-30mg-2ml-902522414 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Migliore, A.; Bizzi, E.; Massafra, U.; Vacca, F.; Giovannangeli, F.; Tormenta, S. Intra-articular administrations of Jonexa® in patients with symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hip. Data from a monocentric cohort study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, S480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, R.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Smith, H.; Crandall, D.; Flannery, C.R.; Conrozier, T. Systematic clinical evidence review of NASHA (Durolane hyaluronic acid) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, O.; Jerosch, J.; Yoon, S.; Sayre, T.; Ngai, W.; Filippou, G. One-year efficacy and safety of single or one to three weekly injections of hylan G-F 20 for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.; Galesso, D.; Menon, G.; Renier, D.; Guarise, C. Hyaluronan derivatives: Alkyl chain length boosts viscoelastic behavior to depolymerization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonexa Hyalastan SGL-80TM [leaflet]; Genzyme Corporation: Pleasant View Terrace, Ridgefield, CT, USA. Available online: https://www.fogliettoillustrativo.net/bugiardino/jonexa-sir-soft-gel-4ml-920892712 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Bernetti, A.; Agostini, F.; Alviti, F.; Giordan, N.; Martella, F.; Santilli, V.; Paoloni, M.; Mangone, M. New Viscoelastic Hydrogel Hymovis MO.RE. Single Intra-articular Injection for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis in Sportsmen: Safety and Efficacy Study Results. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HyMovis® [leaflet]; Fidia Farmaceutici S.p.A.: Abano Terme, Padova, Italy. Available online: https://www.fogliettoillustrativo.net/bugiardino/hymovis-sir-24mg-3ml-2pz-970971228 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Sinovial HL [leaflet]; IBSA Farmaceutici Italia Srl.: Lodi, Italy. Available online: https://www.fogliettoillustrativo.net/bugiardino/sinovial-hl-sir-32-2ml-935184539 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- De Rosa, M.; D’Agostino, A.; La Gatta, A.; Schiraldi, C. Hybrid Cooperative Complexes of Hyaluronic Acid. WO Patent WO/2012/032,151, 23 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, R.; Vassallo, V.; Stellavato, A.; Valletta, M.; Cimini, D.; Pedone, P.V.; Schiraldi, C.; Chambery, A. Differential Secretome Profiling of Human Osteoarthritic Synoviocytes Treated with Biotechnological Unsulfated and Marine Sulfated Chondroitins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, V.; Stellavato, A.; Cimini, D.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; Alfano, A.; Cammarota, M.; Balato, G.; D’Addona, A.; Ruosi, C.; Schiraldi, C. Unsulfated biotechnological chondroitin by itself as well as in combination with high molecular weight hyaluronan improves the inflammation profile in osteoarthritis in vitro model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gatta, A.; de Rosa, M.; Marzaioli, I.; Busico, T.; Schiraldi, C. A complete hyaluronan hydrodynamic characterization using a triple detector-SEC system during in vitro enzymatic degradation. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 404, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gatta, A.; Salzillo, R.; Catalano, C.; D’Agostino, A.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Hyaluronan-based hy-drogels as dermal fillers: The biophysical properties that translate into a “volumetric” effect. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellavato, A.; Abate, L.; Vassallo, V.; Donniacuo, M.; Rinaldi, B.; Schiraldi, C. An in vitro study to assess the effect of hyaluronan-based gels on muscle-derived cells: Highlighting a new perspective in regenerative medicine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenti, S.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Giannotti, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Giordano, N.G.; Fioravanti, A. Can hybrid hyaluronic acid represent a valid approach to treat rizoarthrosis? A retrospective comparative study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Gatta, A.; Salzillo, R.; Catalano, C.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; D’Agostino, A.; Bedini, E.; Cammarota, M.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Hyaluronan-based hydrogels via ether-crosslinking: Is HA molecular weight an effective means to tune gel performance? Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, P.; Conrozier, T.; Vignon, E.; Rozand, Y.; Rinaudo, M. Rheologic Behavior of Osteoarthritic Synovial Fluid after Addition of Hyaluronic Acid: A Pilot Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merola, F.; Scrima, M.; Melito, C.; Iorio, A.; Pisano, C.; Giori, A.M.; Ferravante, A. A novel animal model for residence time evaluation of injectable hyaluronic acid-based fillers using high-frequency ultrasound-based approach. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.-Y. Relationship between structure and cytocompatibility of divinyl sulfone cross-linked hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gatta, A.; Ricci, G.; Stellavato, A.; Cammarota, M.; Filosa, R.; Papa, A.; D’Agostino, A.; Portaccio, M.; Delfino, I.; De Rosa, M.; et al. Hyaluronan hydrogels with a low degree of modification as scaffolds for cartilage engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.B.; Mix, K.S.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Role In Arthritis. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehana, E.-S.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-Blehi, S.S. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konttinen, Y.T.; Li, T.-F.; Mandelin, J.; Ainola, M.; Lassus, J.; Virtanen, I.; Santavirta, S.; Tammi, M.; Tammi, R. Hyaluronan synthases, hyaluronan, and its CD44 receptor in tissue around loosened total hip prostheses. J. Pathol. 2001, 194, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnevie, E.D.; Galesso, D.; Secchieri, C.; Bonassar, L.J. Frictional characterization of injectable hyaluronic acids is more predictive of clinical outcomes than traditional rheological or viscoelastic characterization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Formulation | HA Amount (Declared on the Label) | Chemical Features | Dose/Syringe Needle Used | Suggested Posology | Classification According to This Research/Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyalubrix® | 15 mg/mL | Linear, unmodified HA | 18 or 20 G | 3 or more injections at weekly intervals | 1st group |
| HyMovis® HYADD 4 | 8 mg/mL | Modified (derivatized)-HA | 18 or 20 G | 2 injections at weekly intervals | 2nd group |
| Jonexa Hyalastan SGL-80™ | 10.5 ± 1 mg/mL | Modified (crosslinked)-HA + unmodified HA | 18 or 20 G | 1 injection (4 mL) or 2 injections (4 mL + 4 mL) 15 days apart | 2nd group |
| Sinovial HL® 64 | 16 + 16 mg/mL | Hybrid cooperative complexes NaHyCo | 22 G × 1 ½″ | 2 injections 15 days apart (or differently based on clinical evidence) | 3rd group |
| Gene Name (Symbol) | PCR Primer Sequence 5′→3′ | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG | 118 |
| Type II collagen (COLII) | CAACACTGCCAACGTCCAGAT CTGCTTCGTCCAGATAGGCAA | 102 |
| Hyaluronan synthase 1 (HAS1) | GGGGATCTTCCCCAAGACC CTCGGAGATTCGGTGGACTA | 115 |
| Matrix metallopeptidase 13 (MMP-13) | TCCCTGAAGGGAAGGAGC CTCGTCCAGGATGGCGTAG | 105 |
| Cartilage oligomeric protein matrix 2 (COMP-2) | GAGAACTTTGCCGTTGAAGC GCTTCCTGTAGGTGGCAATC | 107 |
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6) | GTGGAGATTGTTGCCATCAACG CAGTGGATGCAGGGATGATGTTCTG | 112 |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) | CGAGTGACAAGCCTGTAGC GGTGTGGGTGAGGAGCACAT | 102 |
| Formulation | Hydrodynamic Parameters for the Soluble Fractions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mw (kDa) | Mn (kDa) | Mw/Mn | [η] (dL/g) | Rh (nm) | Concentration mg/mL | ||
| 1st group | Hyalubrix® | 1180 ± 10 | 840 ± 10 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 19 ± 1 | 70 ± 1 | 14 ± 1 |
| 2nd group | HyMovis® | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Jonexa Hyalastan SGL-80™ | 1300 ± 300 | 800 ± 200 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 5 | 71 ± 1 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | |
| 3rd group | Synovial HL 64 | 1220 ± 20 | 960 ± 50 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 18 ± 1 | 70 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 |
| 140 ± 50 | 140 ± 10 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 4 ± 1 | 22 ± 1 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Gatta, A.; Stellavato, A.; Vassallo, V.; Di Meo, C.; Toro, G.; Iolascon, G.; Schiraldi, C. Hyaluronan and Derivatives: An In Vitro Multilevel Assessment of Their Potential in Viscosupplementation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193208
La Gatta A, Stellavato A, Vassallo V, Di Meo C, Toro G, Iolascon G, Schiraldi C. Hyaluronan and Derivatives: An In Vitro Multilevel Assessment of Their Potential in Viscosupplementation. Polymers. 2021; 13(19):3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193208
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Gatta, Annalisa, Antonietta Stellavato, Valentina Vassallo, Celeste Di Meo, Giuseppe Toro, Giovanni Iolascon, and Chiara Schiraldi. 2021. "Hyaluronan and Derivatives: An In Vitro Multilevel Assessment of Their Potential in Viscosupplementation" Polymers 13, no. 19: 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193208
APA StyleLa Gatta, A., Stellavato, A., Vassallo, V., Di Meo, C., Toro, G., Iolascon, G., & Schiraldi, C. (2021). Hyaluronan and Derivatives: An In Vitro Multilevel Assessment of Their Potential in Viscosupplementation. Polymers, 13(19), 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193208