Combined Effects of Cellulose Nanofiber Nucleation and Maleated Polylactic Acid Compatibilization on the Crystallization Kinetic and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Preparation of Nanocomposites
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Crystallization Kinetics Analysis
2.3.2. Mechanical Analysis
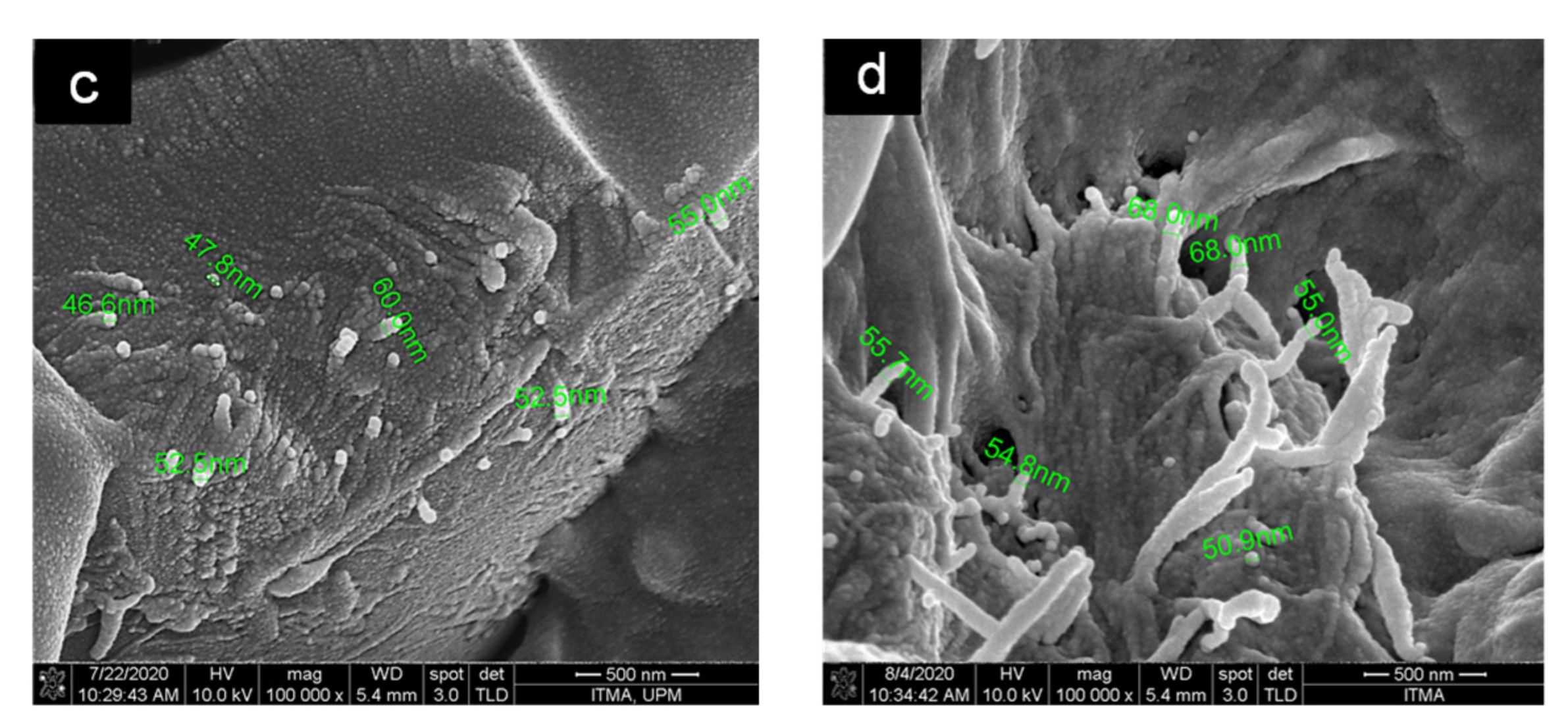
2.3.3. Morphological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Grafting Analysis and Characterization of PLA-g-MA
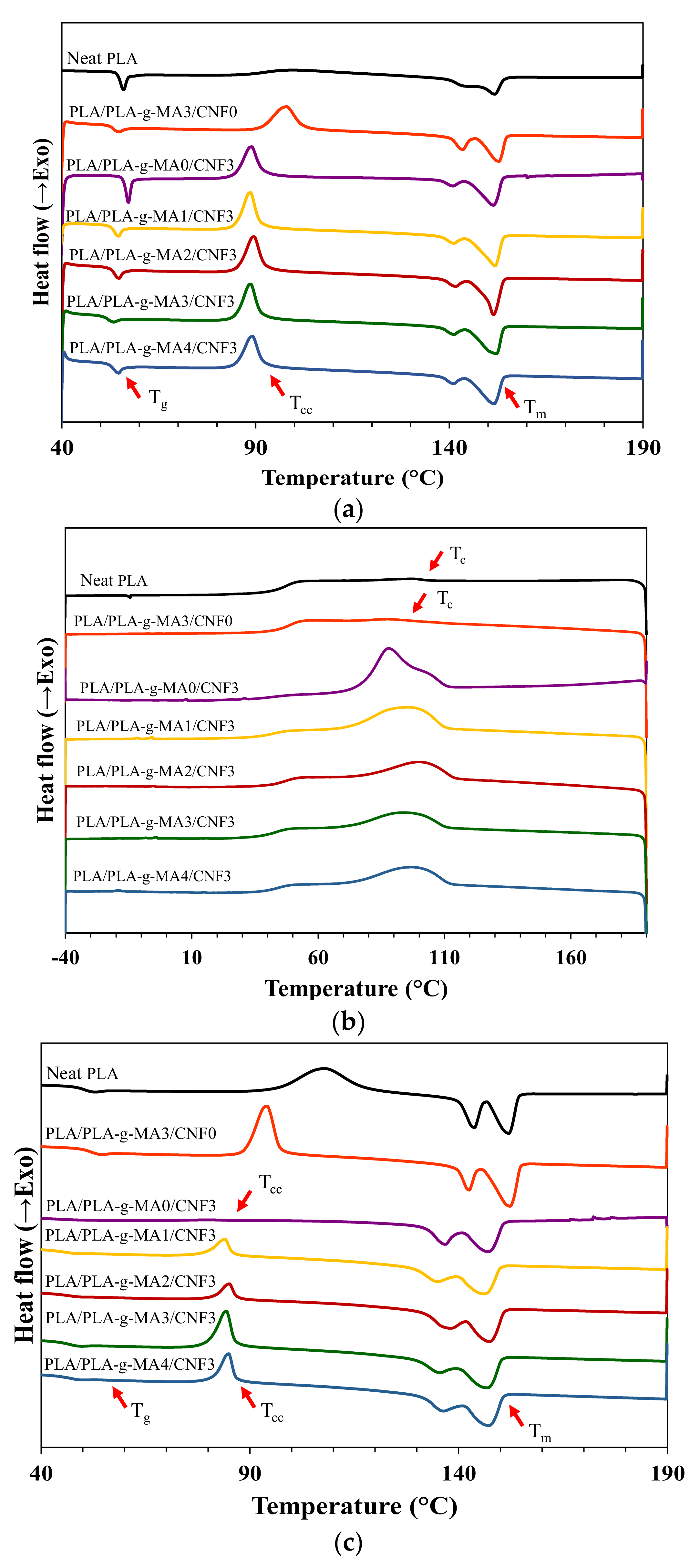
3.2. Non-Isothermal Crystallization Kinetics
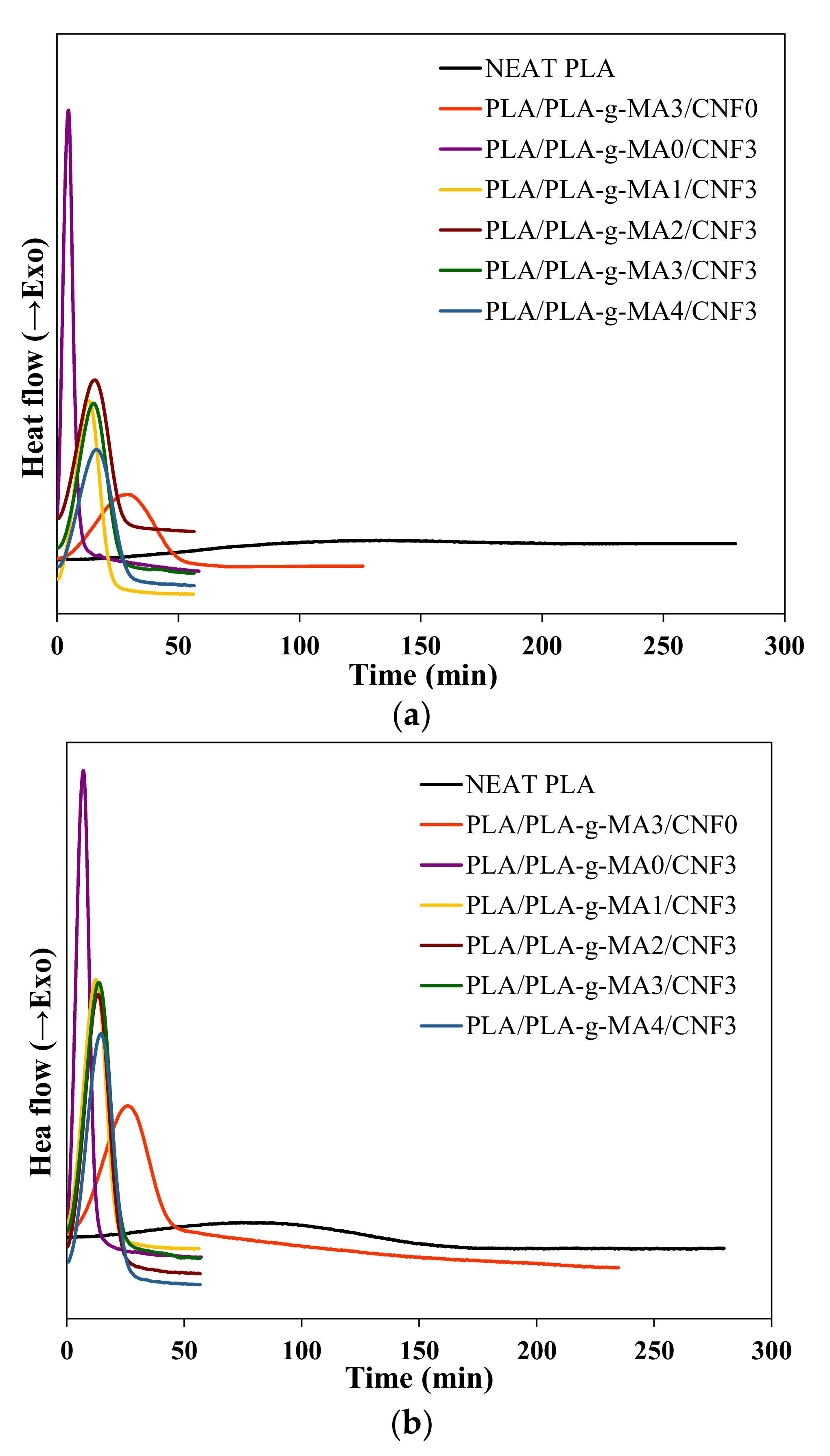
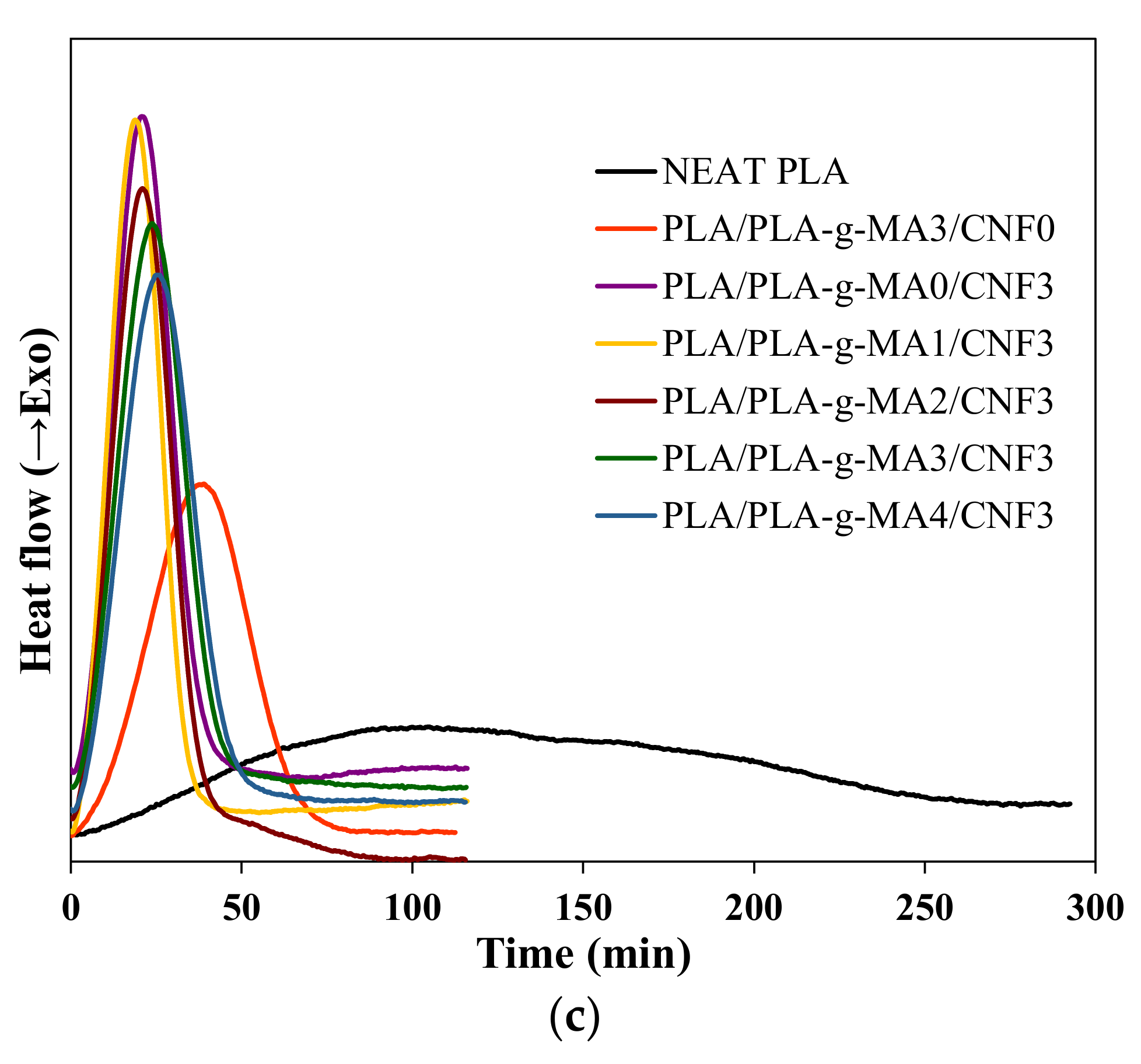
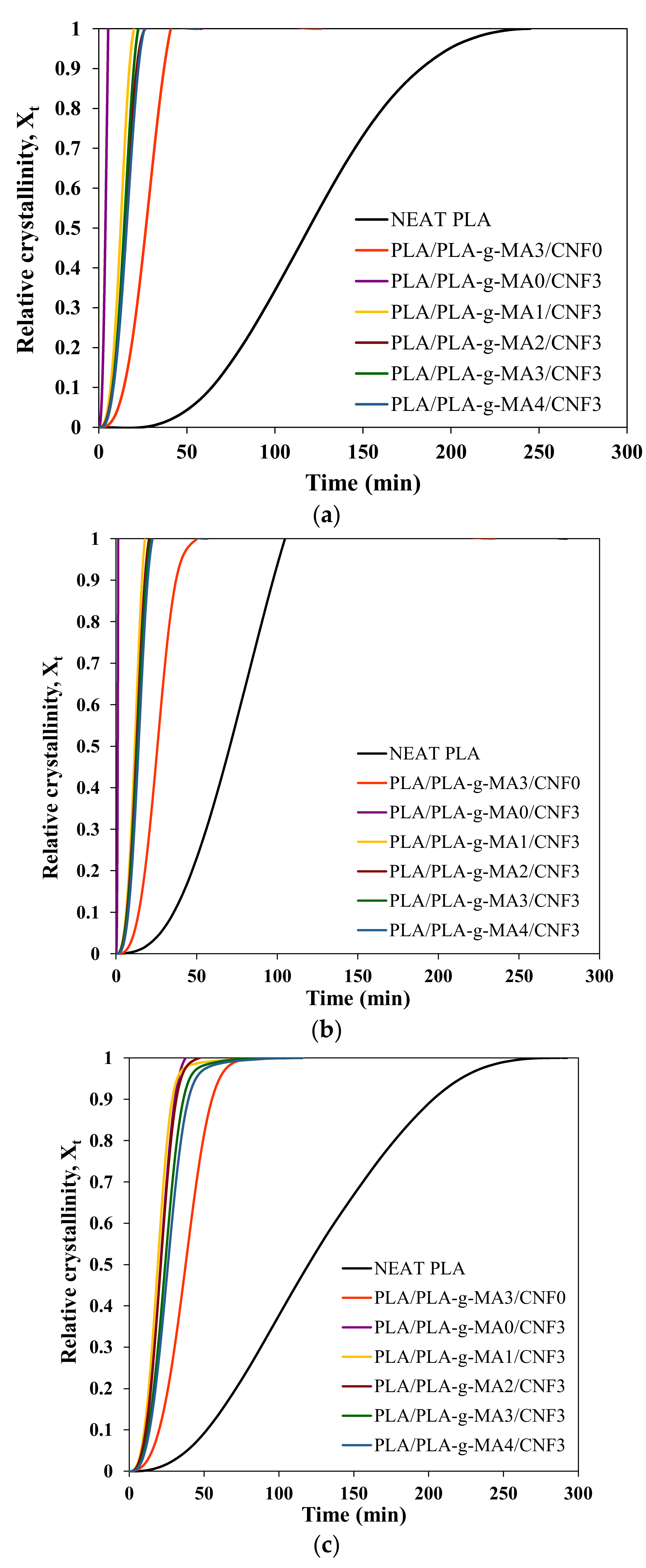
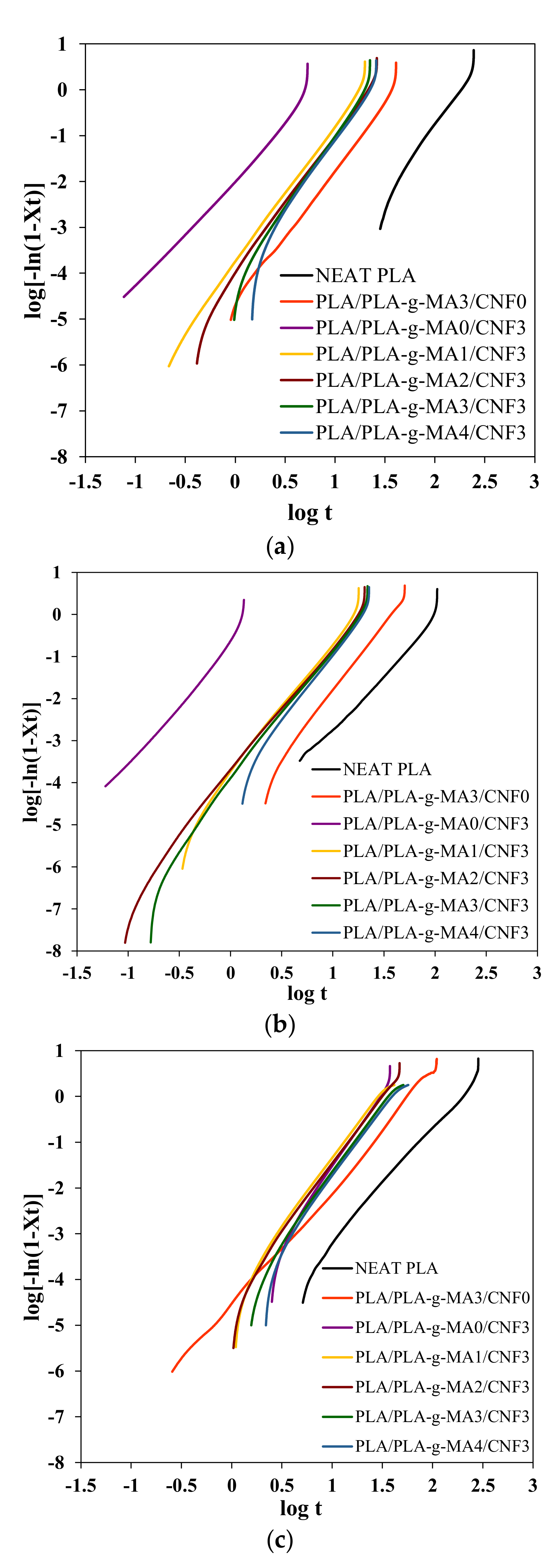
3.3. Isothermal Crystallization Kinetics
3.4. Mechanical Properties
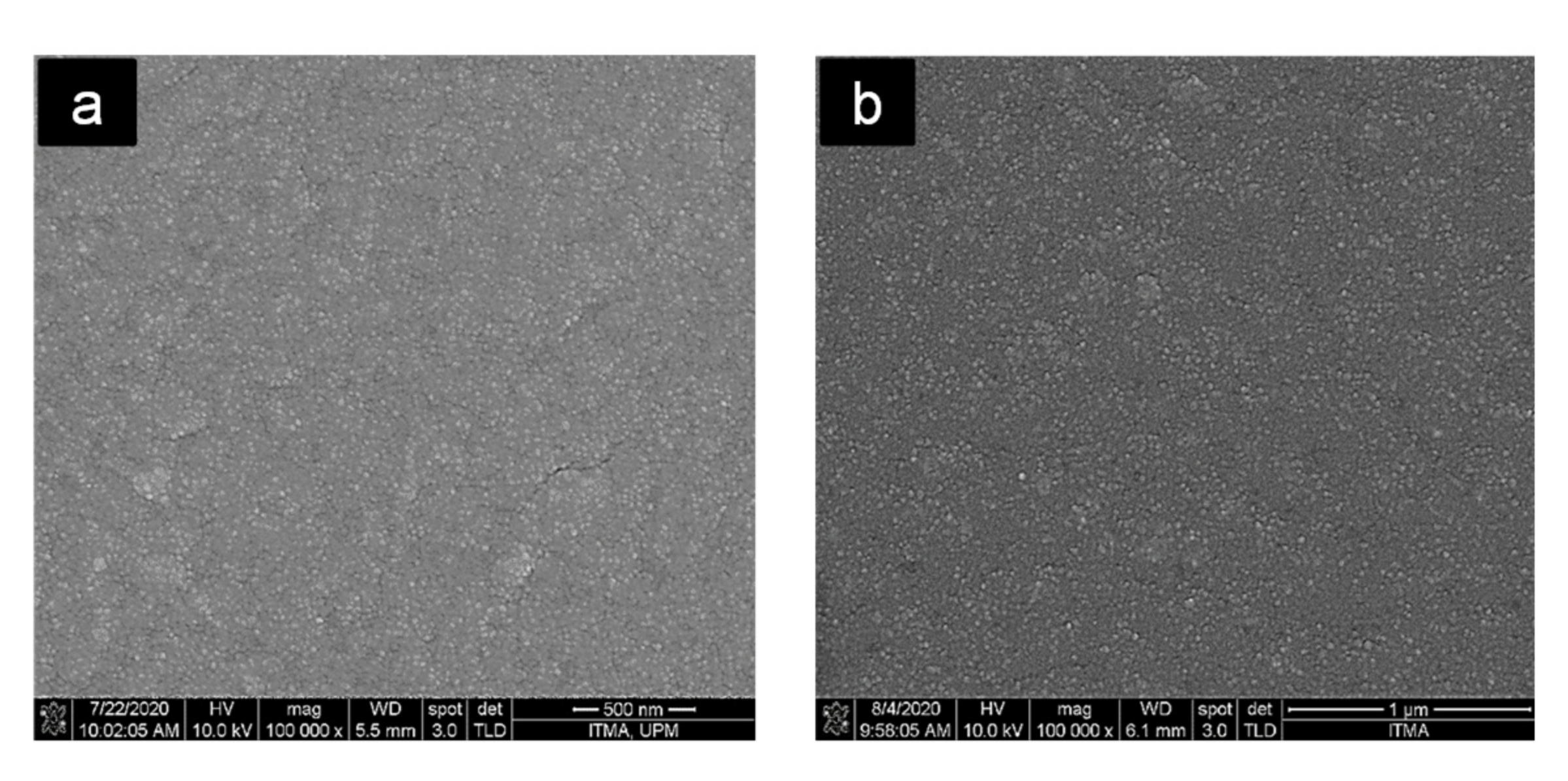
3.5. Morphological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bari, S.S.; Chatterjee, A.; Mishra, S. Biodegradable polymer nanocomposites: An overview. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B. Biopolymer-based lightweight materials for packaging applications. ACS Symp. Ser. 2014, 1175, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.A.; Purwar, A.H. Bioderadable Polymers in Food Packaging. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2013, 2, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bratovcic, A.; Odobasic, A.; Catic, S.; Sestan, I. Application of polymer nanocomposite materials in food packaging. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.L. Reactive Blending of Biodegradable Polymers: PLA and Starch. J. Polym. Environ. 2000, 8, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanegara, L.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. The effect of crystallization of PLA on the thermal and mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Fortunati, E. Biobased and biodegradable plastics. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 2955–2976. ISBN 978-3-319-68255-6. [Google Scholar]
- Norio, A.; Fujimura, A.; Sakai, T.; Hama, Y.; Yano, H. Production of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC)-reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) nanocomposites from sheets obtained by a papermaking-like process. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Berlioz, S.; Chailan, J.-F.; Panaitescu, D.M. Morphology and thermal properties of PLA—Cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.M.; Canevarolo, S.V.; Chinelatto, M.A. Isothermal crystallization kinetics of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends compatibilized with low-molecular weight block copolymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, E161–E169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, X.; Gu, Q.; Pan, Z. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly (lactic acid)/graphene nanocomposites. J. Polym. Eng. 2013, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Su, L.F.; Miao, J.B.; Chen, P.; Qian, J.S.; Xia, R.; Liu, J.W. Melting and Crystallization Behaviors of Poly(Lactic Acid) Modified with Graphene Acting as a Nucleating Agent. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2019, 58, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, T.F.; Silva, A.L.N.D.; Silva, A.H.M.D.F.T.D.; Sousa, A.M.F.D.; Silva, G.M.D.; Rocha, M.G. Thermal, Rheological and Morphological Properties of Poly (Lactic Acid) (PLA) and Talc Composites. Polímeros 2014, 24, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowlks, A.C.; Narayan, R. The Effect of Maleated Polylactic Acid (PLA) as an Interfacial Modifier in PLA-Talc Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaa, Z.; Boutaous, M.; Rousset, F.; Fulchiron, R.; Zinet, M.; Xin, S.; Bourgin, P. Crystallization kinetics of poly-(lactic acid) with and without talc: Optical microscopy and calorimetric analysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1593, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Gong, R.H.; Hogg, P.J. Poly(lactic acid) fibre reinforced biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B 2014, 62, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Renewable resource-based composites of recycled natural fibers and maleated polylactide bioplastic: Characterization and biodegradability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y. Study on short ramie fiber/poly (lactic acid) composites compatibilized by maleic anhydride. Compos. Part A 2014, 64, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, L.; Nie, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, D. Study on Poly (lactic acid)/Natural Fibers Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E526–E533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonoobi, M.; Harun, J.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Lucia, L.A.; Sain, M. Cellulosic Nanocomposites: A Review. BioResources 2008, 3, 929–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manocha, L.M.; Valand, J.; Patel, N.; Warrier, A.; Manocha, S. Nanocomposites for structural applications. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2006, 44, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, J.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Recent advances in the application of natural fiber based composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthapulakkal, S.; Sain, M. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanofibril films from wood fibre and their thermoplastic polycarbonate composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Liu, H. Cellulose nanofiber reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) composite film with high visible light transmittance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sain, M. The effect of chemically coated nanofiber reinforcement on biopolymer based nanocomposites. BioResources 2007, 2, 371–388. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Rodriguez, K.; Renneckar, S.; Vikesland, P.J. Environmental science and engineering applications of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites. Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, T.; Bordeanu, N.; Strub, E. Properties of nanofibrillated cellulose from different raw materials and its reinforcement potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiziltas, A.; Nazari, B.; Gardner, D.J.; Bousfield, D.W. Polyamide 6—Cellulose Composites: Effect of Cellulose Composition on Melt Rheology and Crystallization Behavior. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, R.; Kondo, T. Size effects of cellulose nanofibers for enhancing the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanegara, L.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Thermo-mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced partially crystallized PLA composites. Cellulose 2010, 17, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tashiro, K.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Bin, Y. Crystallization behavior of poly (lactic acid)/microfibrillated cellulose composite. Polymer 2013, 54, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, H.; Yasim, T.A.T.; Amadi, N.I.; Nadia, F. Characterization of Cellulose Nanofiber From Various Tropical Plant Resources. In Lignocellulose for Future Bioeconomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 71–90. ISBN 9780128163542. [Google Scholar]
- Hussin, M.H.; Trache, D.; Chuin, C.T.H.; Fazita, M.R.N.; Haafiz, M.K.M.; Hossain, M.S. Extraction of Cellulose Nano fi bers and Their Eco-friendly Polymer Composites. In Sustainable Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites; Inamuddin, T.S., Mishra, R.K., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 653–691. ISBN 9783030053994. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, S.; Behrooz, R.; Ghasemi, I. Investigating the properties of maleated poly(lactic acid) and its effect on poly (lactic acid)/cellulose nanofiber composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, M.A.; Geever, L.M.; Killion, J.A.; Lyons, J.G.; Higginbotham, C.L. Improvement in Mechanical Properties of Grafted Polylactic Acid Composite Fibers via Hot Melt Extrusion. Polym. Compos. 2008, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, B.A.; Soule, J.; Sobkowicz, M.J. Synthesis and characterization of compatibilizers for blends of polypropylene carbonate and polybutylene succinate via free-radical grafting of maleic anhydride. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 47553, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, X. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Poly (lactic acid)/Starch Blends with Dioctyl Maleate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetwarotai, W.; Potiyaraj, P.; Aht-ong, D. Properties of Compatibilized Polylactide Blend Films with Gelatinized Corn and Tapioca Starches. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Seib, P. Strengthening Blends of Poly (lactic acid) and Starch with Methylenediphenyl Diisocyanate. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Seib, P. Effects of Starch Moisture on Properties of Wheat Starch/Poly (Lactic Acid) Blend Containing Methylenediphenyl. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Ruksakulpiwat, C.; Ruksakulpiwat, Y. Effect of cellulose nanofibers from cassava pulp on physical properties of poly(lactic acid) biocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 33, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigolin, T.R.; Takahashi, M.C.; Kondo, D.L.; Bettini, S.H.P. Compatibilizer Acidity in Coir-Reinforced PLA Composites: Matrix Degradation and Composite Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Behrooz, R.; Ghasemi, I.; Yassar, R.S.; Long, F. Development of nanocellulose-reinforced PLA nanocomposite by using maleated PLA (PLA-g-MA). J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 31, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazleen, S.S.; Yasim-Anuar, T.A.T.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Ariffin, H. Functionality of Cellulose Nanofiber as Bio-Based Nucleating Agent and Nano-Reinforcement Material to Enhance Crystallization and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite. Polymers 2021, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnin-yauri, A.U.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Zainuddin, N.; Abdan, K.; Then, Y.Y.; Chieng, B.W. Effect of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Poly (lactic acid) on the Properties of Its Hybrid Fiber Biocomposites. Polymers 2017, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Jiang, L.; Ye, T.; Dong, W.; Chen, M. Melt Free-Radical Grafting of Maleic Anhydride onto Biodegradable Poly(lactic acid) by Using Styrene as a Comonomer. Polymer 2014, 6, 1528–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syazana, N.; Sani, A.; Arsad, A.; Rahmat, A.R. Synthesis of a compatibilizer and the effects of monomer concentrations. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 554, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenprasat, D.; Suttireungwong, S.; Tongpin, C. Functionalization of Poly (Lactic Acid) with Maleic Anhydride for Biomedical Application. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2010, 20, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, E.E.M.; Luyt, A.S. Morphology, Thermal, and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Sisal Whisker Nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2008, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.E.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; Cisneros-López, E.O.; Manríquez-González, R.; Ramírez-Arreola, D.E.; Rodrigue, D.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R. Effect of Maleated PLA on the Properties of Rotomolded PLA-Agave Fiber Biocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, I.P.; Schneider, F.S.S.; Caro, M.S.B.; da Conceição, T.F.; Caramori, G.F.; Pires, A.T.N. Polylactic acid, maleic anhydride and dicumyl peroxide: NMR study of the free-radical melt reaction product. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsilkova, R.; Angelova, P.; Batakliev, T.; Angelov, V.; Di Maio, R.; Silvestre, C. Study on Aging and Recover of Poly (Lactic) Acid Composite Films with Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes Produced by Solution Blending and Extrusion. Coatings 2019, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisa, N.; Mohammad, B.; Arsad, A.; Syazana, N.; Sani, A. Effect of Compatibilisers on Thermal and Morphological Properties of Polylactic Acid/Natural Rubber Blends. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 56, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lan, Q.; Zhai, T.; Nie, S.; Luo, J.; Yan, W. Melt crystallization behavior and crystalline morphology of Polylactide/Poly(ε-caprolactone) blends compatibilized by lactide-caprolactone copolymer. Polymers 2018, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.; Carvalho, B.D.M.; Pinheiro, L.A.; Bretãs, R.E.S.; Canevarolo, S.V.; Marini, J. Effect of Compatibilization and Reprocessing on the Isothermal Crystallization Kinetics of Polypropylene/Wood Flour Composites. Polimeros 2013, 23, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetwarotai, W.; Aht-Ong, D. Isothermal crystallization behaviors and kinetics of nucleated polylactide/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend films with talc: Influence of compatibilizer contents. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Hosseinzadeh, J.; Ashori, A.; Dadashi, S.; Takzare, Z. Preparation and characterization of modified cellulose nanofibers reinforced polylactic acid nanocomposite. Polym. Test. 2014, 35, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Hosseinzadeh, J.; Dadashi, S.; Mousavi, M. A study of morphological, thermal, mechanical and barrier properties of PLA based biocomposites prepared with micro and nano sized cellulosic fibers. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2015, 49, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Compatibilizing effects of maleated poly(lactic acid) (PLA) on properties of PLA/soy protein composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 7786–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
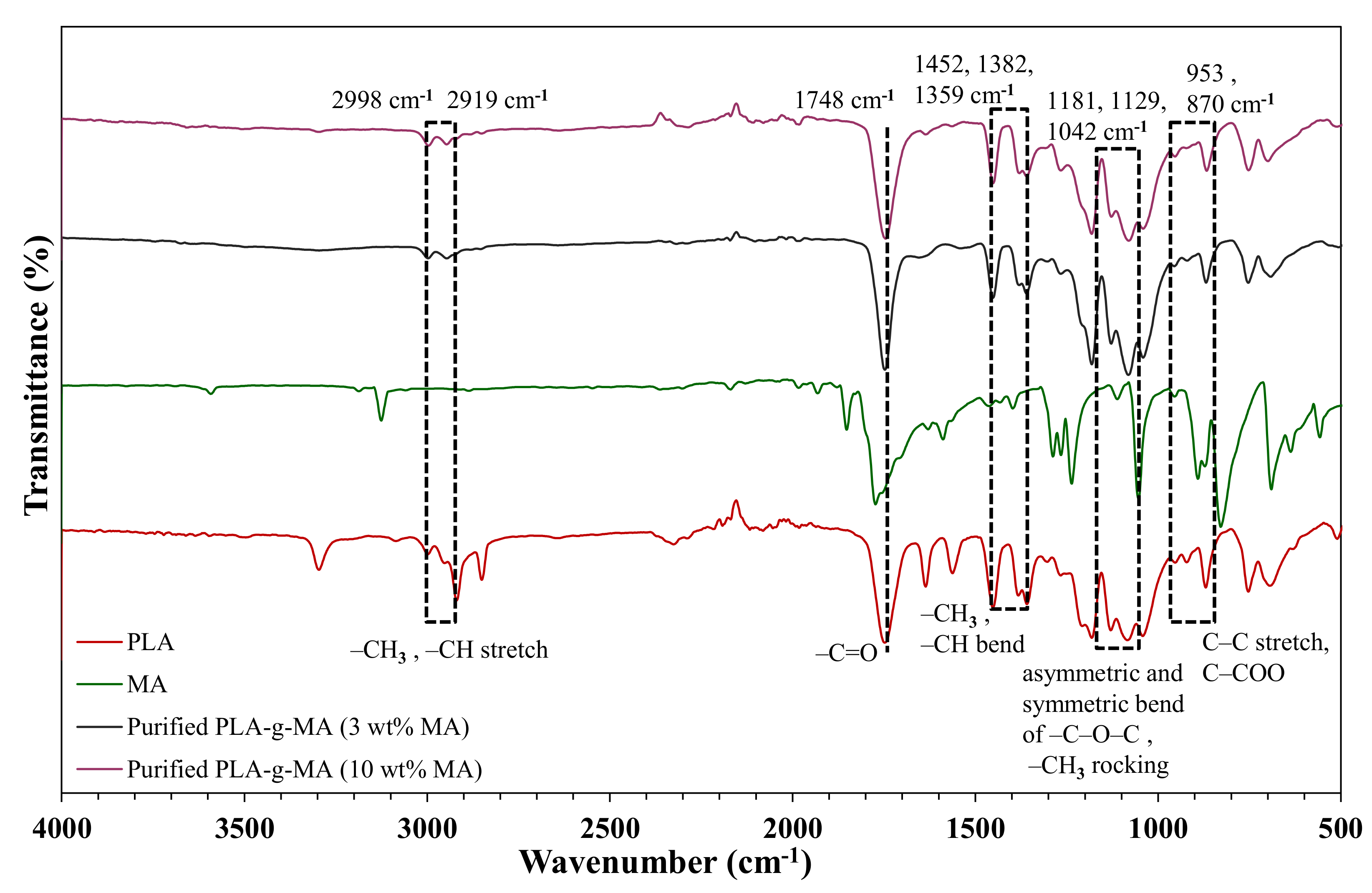
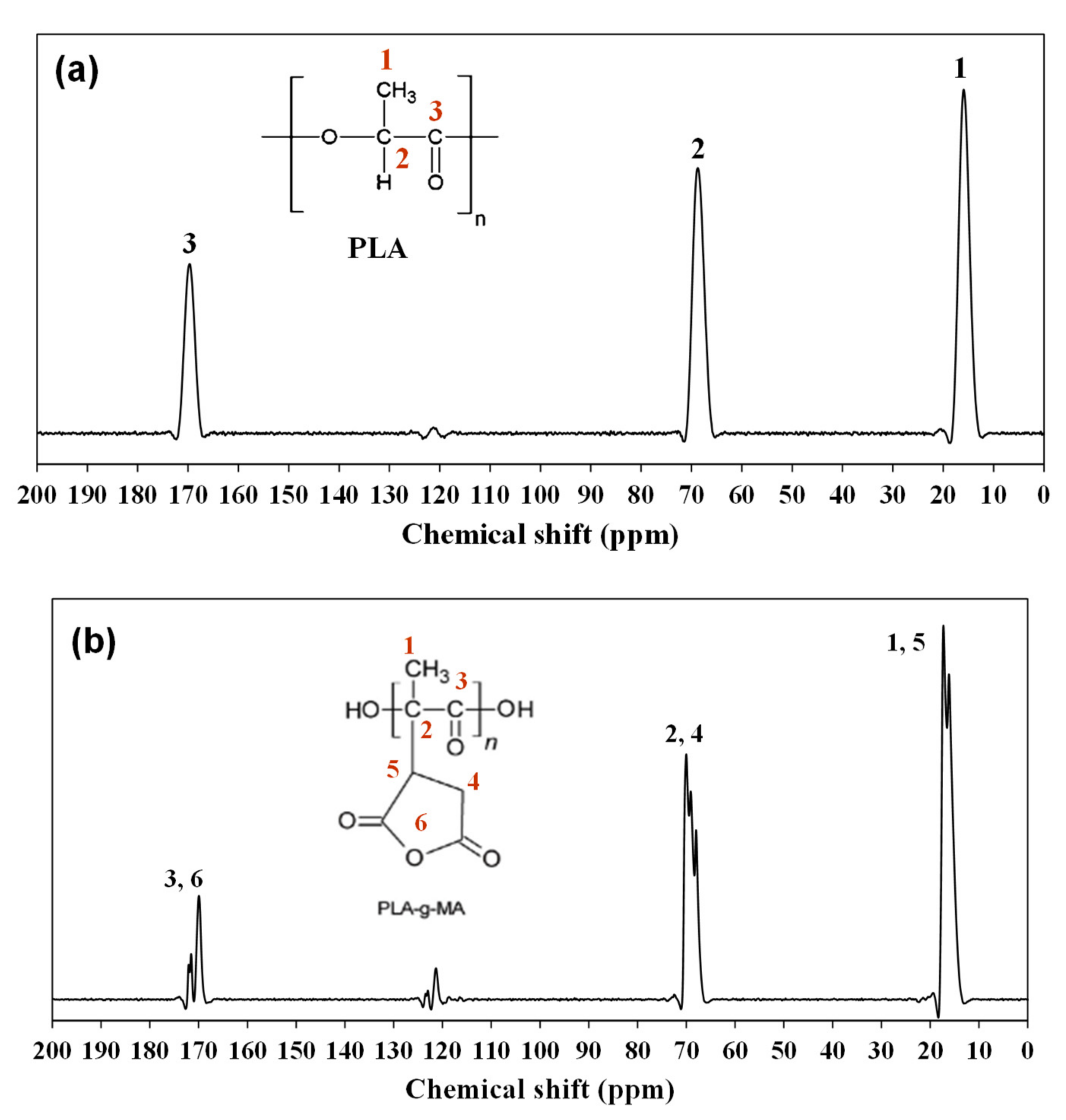


| PLA-g-MA (MA wt.%) | Composition (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Maleic Anhydride (MA) | Dibenzoyl Peroxide (DBPO) | |
| 3 | 36.25 | 3 | 0.75 |
| 10 | 29.25 | 10 | 0.75 |
| Sample | Composition (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Maleated PLA (PLA-g-MA) | Cellulose Nanofiber (CNF) | |
| Neat PLA | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF0 | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA0/CNF3 | 97 | 0 | 3 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA1/CNF3 | 97 | 1 | 3 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA2/CNF3 | 95 | 2 | 3 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF3 | 97 | 3 | 3 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA4/CNF3 | 96 | 4 | 3 |
| PLA-g-MA (MA wt.%) | MA Grafting (%) | Grafting Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.15 ± 0.0 | 3.13 ± 0.4 |
| 10 | 2.10 ± 0.3 | 13.20 ± 2.2 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | ∆Hc (J/g) | ∆Hcc (J/g) | ∆Hm (J/g) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA | 50.4 | 106.1 | 91.3 | 143.5 | 152.1 | 1.3 | 33.4 | 35.6 | 2.3 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF0 | 51.9 | 96.5 | 84.5 | 142.6 | 152.3 | 2.0 | 27.1 | 33.9 | 6.7 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA0/CNF3 | 43.9 | 114.6 | 71.0 | 136.7 | 147.1 | 33.6 | 0.9 | 42.3 | 44.2 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA1/CNF3 | 45.9 | 112.7 | 75.5 | 135.3 | 146.1 | 24.5 | 8.8 | 35.4 | 28.4 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA2/CNF3 | 46.1 | 115.1 | 78.5 | 137.1 | 147.4 | 29.0 | 7.4 | 35.3 | 29.8 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF3 | 46.3 | 113.8 | 75.8 | 135.3 | 146.6 | 16.8 | 14.1 | 41.6 | 29.4 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA4/CNF3 | 47.3 | 113.3 | 77.9 | 136.1 | 147.0 | 21.1 | 12.4 | 41.0 | 30.5 |
| Sample | Tc = 90 °C | Tc = 100 °C | Tc = 110 °C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | k (min−n) | t1/2 (min) | 1/t1/2 (min−1) | n | k (min−n) | t1/2 (min) | 1/t1/2 (min−1) | n | k (min−n) | t1/2 (min) | 1/t1/2 (min−1) | |
| Neat PLA | 3.22 | 5.72 × 10−8 | 158.01 | 0.006 | 2.74 | 2.83 × 10−6 | 92.72 | 0.011 | 2.46 | 2.46 × 10−6 | 165.59 | 0.006 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF0 | 2.98 | 1.82 × 10−5 | 34.27 | 0.029 | 3.21 | 9.18 × 10−6 | 33.22 | 0.030 | 2.67 | 1.90× 10−5 | 51.33 | 0.019 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA0/CNF3 | 2.59 | 1.09 × 10−2 | 4.99 | 0.200 | 3.11 | 2.45 × 10−1 | 1.40 | 0.716 | 3.34 | 1.20 × 10−5 | 26.63 | 0.038 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA1/CNF3 | 3.04 | 1.60 × 10−4 | 15.73 | 0.064 | 3.12 | 1.62 × 10−4 | 14.64 | 0.068 | 2.95 | 4.63 × 10−5 | 26.06 | 0.038 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA2/CNF3 | 3.10 | 9.71 × 10−5 | 17.45 | 0.057 | 2.98 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 16.15 | 0.062 | 2.99 | 3.30 × 10−5 | 28.01 | 0.036 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF3 | 3.27 | 5.53 × 10−5 | 17.90 | 0.056 | 3.10 | 1.14 × 10−4 | 16.60 | 0.060 | 2.99 | 2.06 × 10−5 | 32.63 | 0.031 |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA4/CNF3 | 3.21 | 4.79 × 10−5 | 19.69 | 0.051 | 3.27 | 5.91 × 10−5 | 17.51 | 0.057 | 2.94 | 1.89 × 10−5 | 35.75 | 0.028 |
| Composition | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA | 70.8 ± 0.1 b | 2.9 ± 0.0 f | 2.54 ± 0.1 a |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF0 | 70.0 ± 0.3 c | 11.0 ± 0.9 d | 2.46 ± 0.4 b |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA0/CNF3 | 74.1 ± 0.1 a | 3.3 ± 0.1 e | 2.34 ± 0.1 c |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA1/CNF3 | 66.1 ± 0.5 d | 11.5 ± 0.2 c | 2.17 ± 0.3 d |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA2/CNF3 | 65.9 ± 0.8 d,e | 11.6 ± 0.1 c | 2.14 ± 0.1 d |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA3/CNF3 | 65.7 ± 0.1 e | 11.7 ± 0.4 b,c | 2.11 ± 0.1 e |
| PLA/PLA-g-MA4/CNF3 | 65.5 ± 0.2 e | 11.8 ± 0.1 b,c | 2.05 ± 0.3 f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shazleen, S.S.; Foong Ng, L.Y.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Ariffin, H. Combined Effects of Cellulose Nanofiber Nucleation and Maleated Polylactic Acid Compatibilization on the Crystallization Kinetic and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite. Polymers 2021, 13, 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193226
Shazleen SS, Foong Ng LY, Ibrahim NA, Hassan MA, Ariffin H. Combined Effects of Cellulose Nanofiber Nucleation and Maleated Polylactic Acid Compatibilization on the Crystallization Kinetic and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite. Polymers. 2021; 13(19):3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193226
Chicago/Turabian StyleShazleen, Siti Shazra, Lawrence Yee Foong Ng, Nor Azowa Ibrahim, Mohd Ali Hassan, and Hidayah Ariffin. 2021. "Combined Effects of Cellulose Nanofiber Nucleation and Maleated Polylactic Acid Compatibilization on the Crystallization Kinetic and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite" Polymers 13, no. 19: 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193226
APA StyleShazleen, S. S., Foong Ng, L. Y., Ibrahim, N. A., Hassan, M. A., & Ariffin, H. (2021). Combined Effects of Cellulose Nanofiber Nucleation and Maleated Polylactic Acid Compatibilization on the Crystallization Kinetic and Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite. Polymers, 13(19), 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193226







