Removal of Toxic Copper Ion from Aqueous Media by Adsorption on Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Adsorbent
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
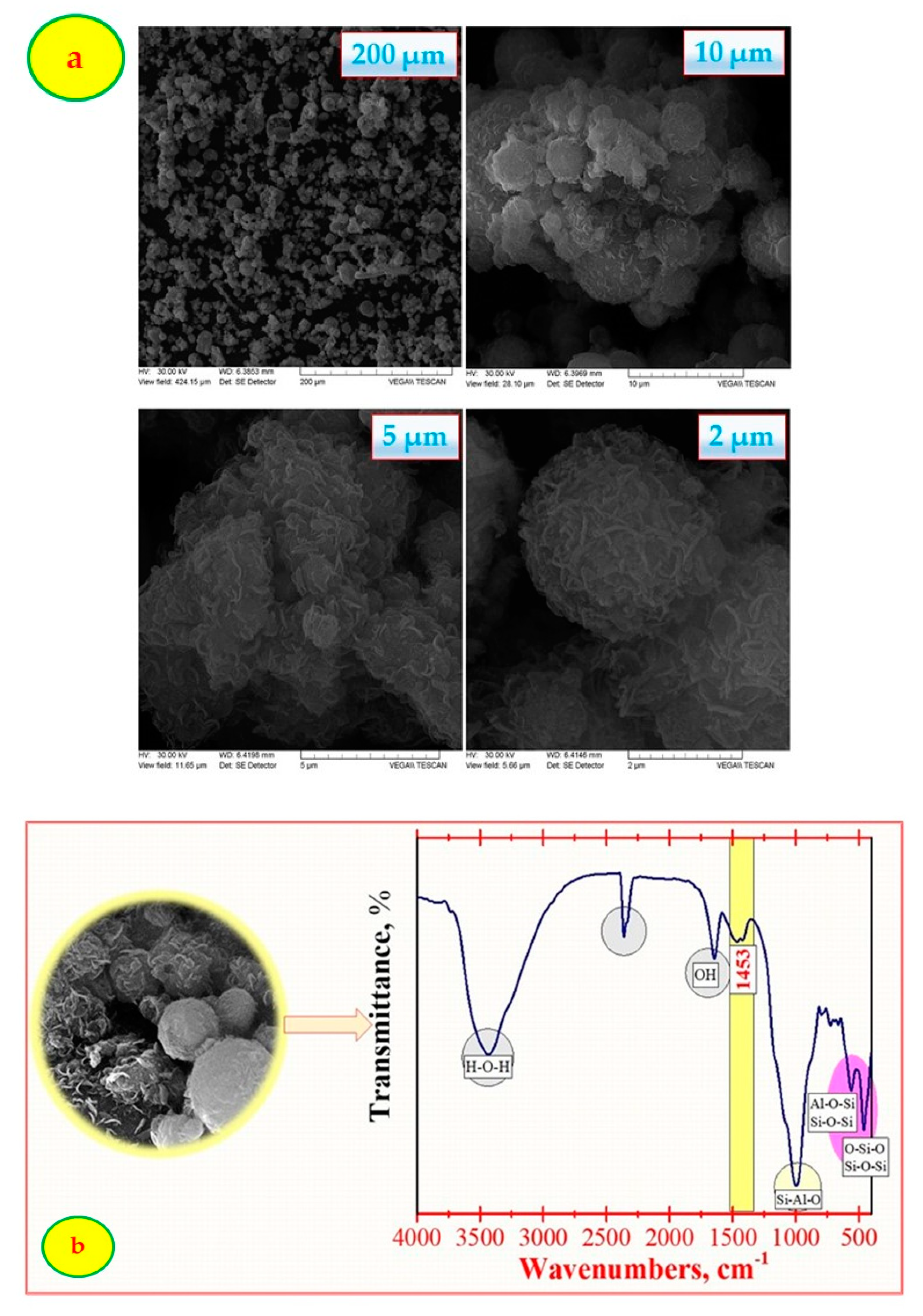
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbent
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2.2. Kinetics of the Adsorption Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhagat, S.K.; Pyrgaki, K.; Salih, S.Q.; Tiyasha, T.; Beyaztas, U.; Shahid, S.; Yaseen, Z.M. Prediction of copper ions adsorption by attapulgite adsorbent using tuned-artificial intelligence model. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saydeh, S.A.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zaidi, S.J. Copper removal from industrial wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidu, R.; Matei, E.; Predescu, A.M.; Alhalaili, B.; Pantilimon, C.; Tarcea, C.; Predescu, C. Removal of heavy metals from wastewaters: A challenge from current treatment methods to nanotechnology applications. Toxics 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekgoba, T.; Ntuli, F.; Falayi, T. Application of coal fly ash for treatment of wastewater containing a binary mixture of copper and nickel. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.X.; Liang, J.L.; Li, N.; Xiao, H.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhao, R.S. Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm investigations of Cu2+ and Zn2+ adsorption on Li-Al hydrotalcite-like compound. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Ciobanu, G.; Bucur, R.D.; Bucur, D.; Favier, L.; Harja, M. Performance assessment of five adsorbents based on fly ash for removal of cadmium ions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukayat, O.O.; Usman, M.F.; Elizabeth, O.M.; Abosede, O.O.; Faith, I.U. Kinetic Adsorption of Heavy Metal (Copper) On Rubber (Hevea Brasiliensis) Leaf Powder. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrashoub, M.; Bakhtiari, S. The efficiency of activated carbon/magnetite nanoparticles composites in copper removal: Industrial waste recovery, green synthesis, characterization, and adsorption-desorption studies. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 311, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, H.; Güngör, C. Adsorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from grape bagasse. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Nguyen, T.B.; Singhania, R.R.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Adsorption of copper (II) in aqueous solution using biochars derived from Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha Rani, K.; Srinivas, B.; Gourunaidu, K.; Ramesh, K.V. Removal of copper by adsorption on treated laterite. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Zeng, W.Y. Adsorption of Cu(II) by Poly-γ-glutamate/Apatite Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczuk-Karpisz, K.; Bogatyrov, V.M.; Galaburda, M.; Sokołowska, Z. Study on Adsorption and Aggregation in the Mixed System of Polyacrylamide, Cu(II) Ions and Innovative Carbon–Silica Composite. Polymers 2020, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.D.; Ciobanu, G. Fly Ash Coated with Magnetic Materials: Improved Adsorbent for Cu (II) Removal from Wastewater. Materials 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, F.F.; Kow, K.W.; Chua, H.S.; Yeap, S.P.; Kiew, P.L.; Chan, C.H.; Yusoff, R. Magnetically aligned nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for copper ions removal. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2124, 020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzhelele, E.P.; Ayinde, W.B.; Mudzielwana, R.; Gitari, W.M. Synthesis of Fe Doped Polyp-Phenylenediamine Composite: Co-Adsorption Application on Toxic Metal Ions (F− and As3+) and Microbial Disinfection in Aqueous Solution. Toxics 2021, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renugopal, L.; Kow, K.W.; Kiew, P.L.; Yeap, S.P.; Chua, H.S.; Chan, C.H.; Yusoff, R. Selective adsorption of copper and cadmium ions using nano-particles aligned in silica gel matrix. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2124, 020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Uzun, H.I.; Ustundag, C.B.; Debik, E. Adsorption of copper ion from aqueous solutions by well-crystalized nanosized hydroxyapatite. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.A.; Azha, S.F.; Sellaoui, L.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Ismail, S. Adsorption of copper (II) cation on polysulfone/zeolite blend sheet membrane: Synthesis, characterization, experiments and adsorption modelling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 124980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buema, G.; Harja, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Forminte, L.; Ciobanu, G.; Bucur, D.; Bucur, R.D. Adsorption Performance of Modified Fly Ash for Copper Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water 2021, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Eom, J.H.; Lee, S.L.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.W.; Yun, J.J.; Cho, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Seo, D.C. Exploration of the potential capacity of fly ash and bottom ash derived from wood pellet-based thermal power plant for heavy metal removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harja, M.; Ciobanu, G. Eco-friendly Nano-adsorbents for Pollutant Removal from Wastewaters. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Kharissova, O., Martínez, L., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycheva, S.; Zgureva, D.; Lazarova, H.; Popova, M. Comparative studies of carbon capture onto coal fly ash zeolites Na-X and Na–Ca-X. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, I.V.; Tosheva, L.; Doyle, A.M. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions via adsorption on FAU-type zeolites prepared from coal fly ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. Methods for characterization of composition of fly ashes from coal-fired power stations: A critical overview. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, M.; Gan, T.; Bao, B. Quantifying gel properties of industrial waste-based geopolymers and their application in Pb2+ and Cu2+ removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 128203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predeanu, G.; Slăvescu, V.; Bălănescu, M.; Mihalache, R.D.; Marin, M.; Marin, A.C.; Drăgoescu, M.F. Coal bottom ash processing for capitalization according to circular economy concept. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.T.; Vo, L.N.H.; Tran, N.T.T.; Phan, T.D.; Nguyen, D.B. Enhancing the removal efficiency of methylene blue in water by fly ash via a modified adsorbent with alkaline thermal hydrolysis treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 20292–20302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, H.; Wirsching, U. Zeolites formation from fly ash. Fortschr. Miner. 1985, 63, 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sočo, E.; Kalembkiewicz, J. Removal of Copper(II) and Zinc(II) Ions From Aqueous Solution by Chemical Treatment of Coal Fly Ash. Croat. Chem. Acta 2015, 88, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hałas, P.; Kołodyńska, D.; Płaza, A.; Gęca, M.; Hubicki, Z. Modified fly ash and zeolites as an effective adsorbent for metal ions from aqueous solution. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darmayanti, L.; Notodarmodjo, S.; Damanhuri, E.; Mukti, R.R. Removal of Copper (II) Ions in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Alkali Activated Fly Ash. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 147, 04007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paramitha, T.; Wulandari, W.; Rizkiana, J.; Sasongko, D. Performance Evaluation of Coal Fly Ash Based Zeolite A for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption of Wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2019, 543, 012095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarvizhi, T.S.; Santhi, T. Lignite fired fly ash modified by chemical treatment for adsorption of zinc from aqueous solution. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2473–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Sutiman, D.M.; Munteanu, C.; Bucur, D. Low-cost adsorbents obtained from ash for copper removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seracu, D.I. Handbook of Analytical Chemistry; Technic Publisher: Bucharest, Romania, 1989. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Zare, A.; Lashanizadegan, A.; Darvishi, P.; Zerafat, M.M. Synthesis and characterization of NaP zeolite nanocrystals using [C12mim][Cl] ionic liquid. Chem. Pap. 2020, 7, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, M.M.; Higgins, J.B. Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Noli, F.; Buema, G.; Misaelides, P.; Harja, M. New materials synthesized from ash under moderate conditions for removal of toxic and radioactive metals. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 303, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, Á.; Gonzalez-Delgado, Á.D. Adsorption of Azo-Anionic Dyes in a Solution Using Modified Coconut (Cocos nucifera) Mesocarp: Kinetic and Equilibrium Study. Water 2021, 13, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Injy, M.M.; Eman, M.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M. Highly Efficient Removal for Methylene Blue and Cu2+ onto UiO-66 Metal–Organic Framework/Carboxylated Graphene Oxide-Incorporated Sodium Alginate Beads. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23528–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Roman, T.; Porcescu, M.; Ciobanu, G.; Burghila, D.V.; Harja, M. Eco-Friendly Materials Obtained by Fly Ash Sulphuric Activation for Cadmium Ions Removal. Materials 2020, 13, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguba, M.A.M.; Ong, D.C.; Ensano, B.M.B.; Kan, C.C.; Grisdanurak, N.; Yee, J.J.; de Luna, M.D.G. Nonlinear Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of Cu(II) and Pb(II) Uptake from Water by MnFe2O4/Chitosan Nanoadsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moftakhar, M.K.; Yaftian, M.R.; Ghorbanloo, M. Adsorption efficiency, thermodynamics and kinetics of Schiff base-modified nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culita, D.C.; Simonescu, C.M.; Patescu, R.E.; Preda, S.; Stanica, N.; Munteanu, C.; Oprea, O. Polyamine Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles as Novel Adsorbents for Cu(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2017, 27, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadri, M.; Sassi, M.; Bengueddach, A. Preparation of Economical and Environmentaly Friendly Modified Clay and Its Application for Copper Removal. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2019, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ketife, A.M.D.; Almomani, F.; Znad, H. Sustainable removal of copper from wastewater using chemically treated bio-sorbent: Characterization, mechanism and process kinetics. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Effect of Working Parameters | Adsorbent Dose | Initial Concentration | Contact Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of adsorbent dose | 1 g/100 mL, 2 g/100 mL, 3 g/100 mL, 4 g/100 mL | 300 mg/L | 24 h |
| Effect of initial concentration | 1 g/100 mL | 100–700 mg/L | 24 h |
| Effect of contact time | 1 g/100 mL | 300 mg/L | 1–240 min |
| O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Ti | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.98 | 3.42 | 1.02 | 13.29 | 16.97 | 0.68 | 2.31 | 1.03 | 8.02 |
| O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Ti | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43.32 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 19.19 | 30.81 | 1.75 | 1.15 | 1.54 | 3.05 |
| Type of Isotherm | Equation | Linearization of Equation | Constants | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax = 53.5 mg/g = 0.094 L/g | 0.9969 | ||
| Freundlich | = 10.23 (mg/g)/(L/mg) 1/n = 0.3438 | 0.7413 |
| qe, exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1, (1/min) | R2 | qcal, (mg/g) | k2 (g/mg min) | R2 | |
| 28.6 | 0.0419 | 0.9732 | 30 | 0.0028 | 0.9986 |
| Adsorbent. | qmax, mg/g | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Nanosilica particles modified by Schiff base Ligands 3-methoxy salicylaldimine propyl triethoxysilane (MNS1) | 3.73 | [44] |
| Nanosilica particles modified by 5-bromo salicylaldimine propyl triethoxysilane | 4.12 | [44] |
| Nanosilica particles modified by 3-hydroxy salicylaldimine propyl triethoxysilane (MNS3) | 5.82 | [44] |
| Fe3O4@TETA | 39.2 | [45] |
| Fe3O4@DETA | 44.2 | [45] |
| Fe3O4@DAMP | 52.3 | [45] |
| Natural bentonite treated with H2SO4 (ARH) | 17.24 | [46] |
| Calcium homoionic clay (ARC) | 18.18 | [46] |
| Sodium homoionic clay (ARS) | 24.39 | [46] |
| Acid-treated bio-sorbent (ATB) | 8 | [47] |
| Untreated bio-sorbent (UTB) | 19 | [47] |
| Base treated bio-sorbent (BTB) | 25 | [47] |
| Detergent treated bio-sorbent (DTB) | 28 | [47] |
| Treated fly ash | 53.5 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buema, G.; Trifas, L.-M.; Harja, M. Removal of Toxic Copper Ion from Aqueous Media by Adsorption on Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203468
Buema G, Trifas L-M, Harja M. Removal of Toxic Copper Ion from Aqueous Media by Adsorption on Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Polymers. 2021; 13(20):3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203468
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuema, Gabriela, Luisa-Maria Trifas, and Maria Harja. 2021. "Removal of Toxic Copper Ion from Aqueous Media by Adsorption on Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies" Polymers 13, no. 20: 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203468
APA StyleBuema, G., Trifas, L.-M., & Harja, M. (2021). Removal of Toxic Copper Ion from Aqueous Media by Adsorption on Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Polymers, 13(20), 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203468








