Surfactant-Induced Reconfiguration of Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Enables Improved Surface Properties and Gluability of Bamboo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
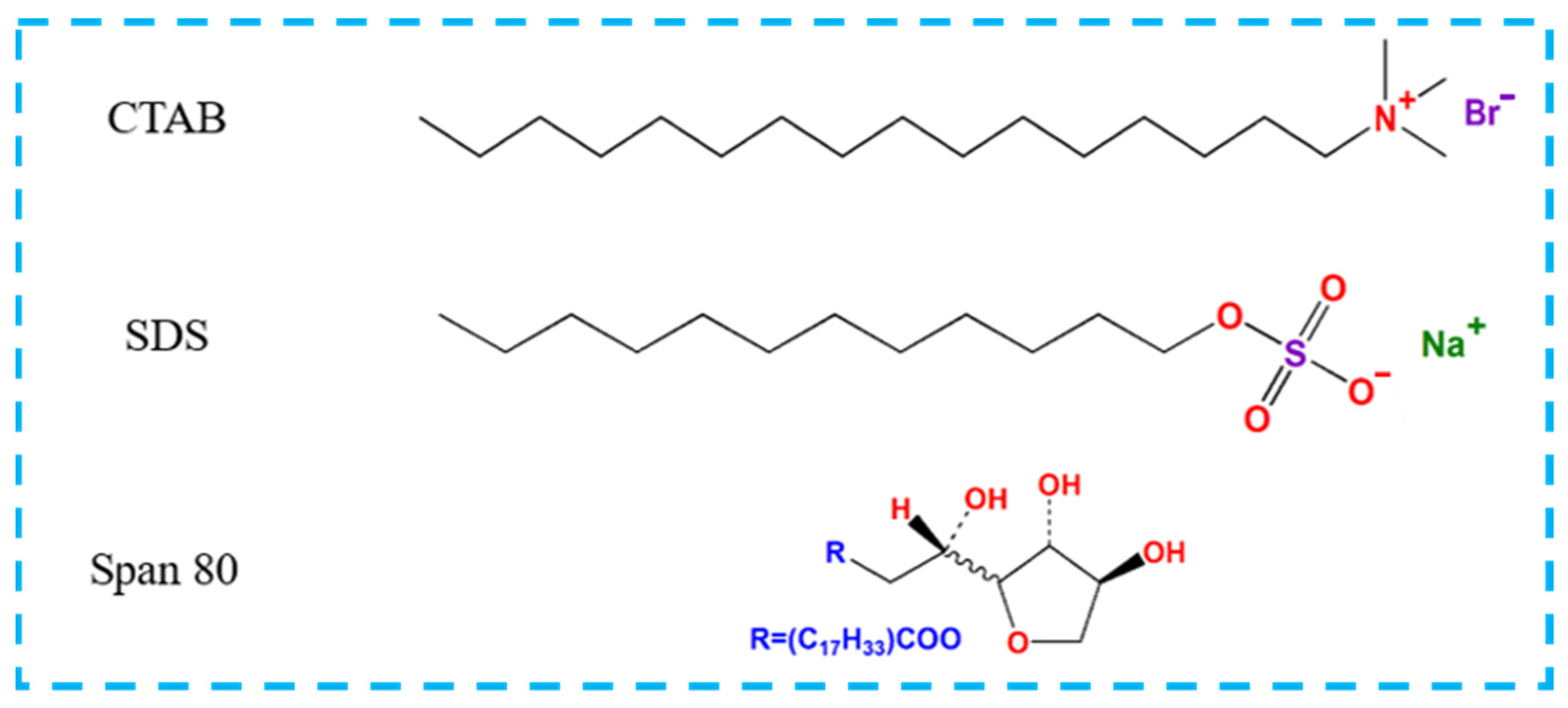
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Urea-Formaldehyde (UF) Resin and Reconfigured UF Resins
2.3. Preparation of the Basal Substrates
2.4. Viscosity and Surface Tension Test
2.5. Spreading Performance Test
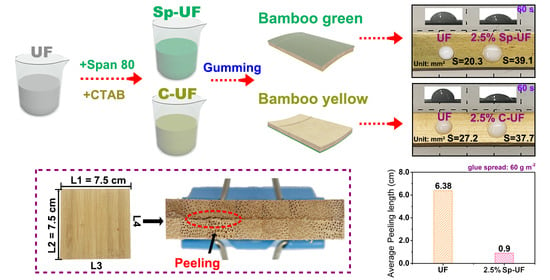
2.6. Laminated Bamboo Veneers and Its Dipping Peel Test
2.7. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of the Surfactants on the Viscosity and Surface Tension of the UF Resins
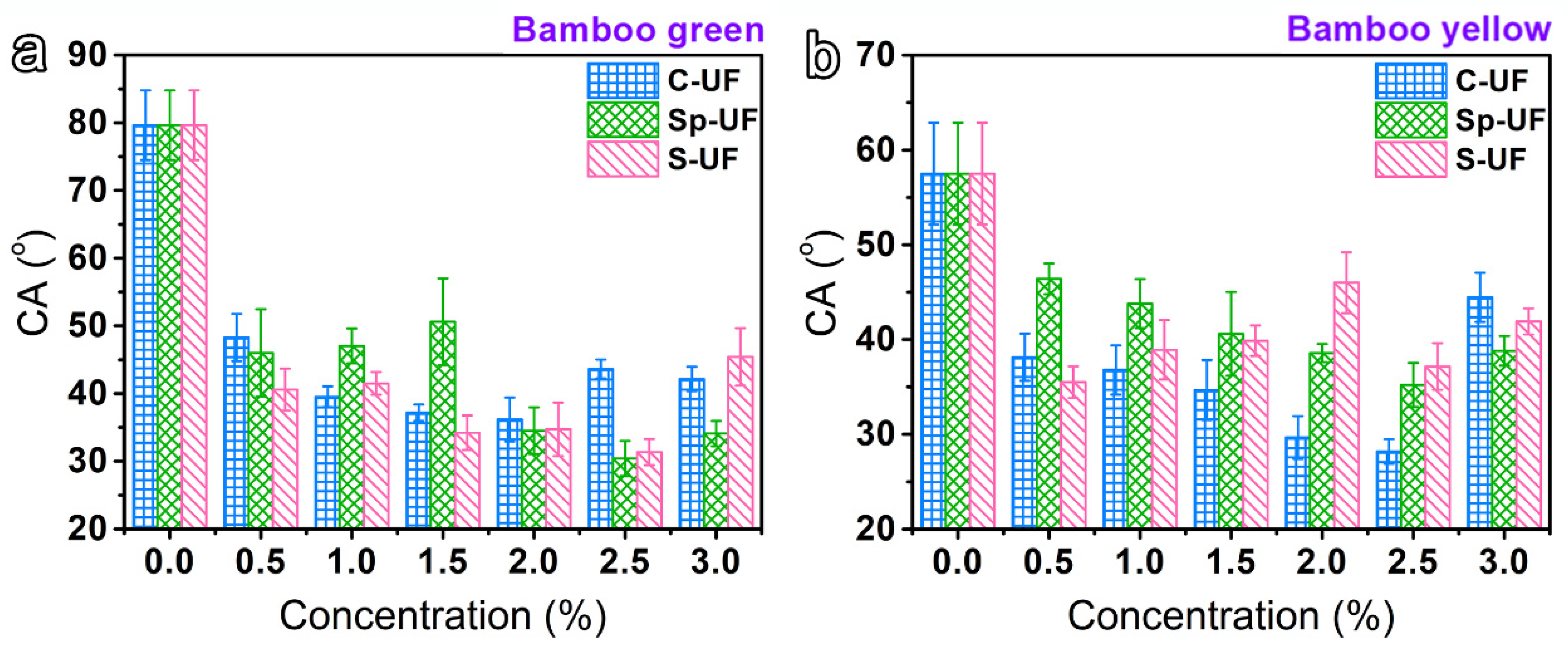
3.2. The Wettability of UF and Reconfigured UF Resins on the Bamboo Green or Bamboo Yellow Surface
3.3. Spreading Performance of the UF and Reconfigured UF Resins
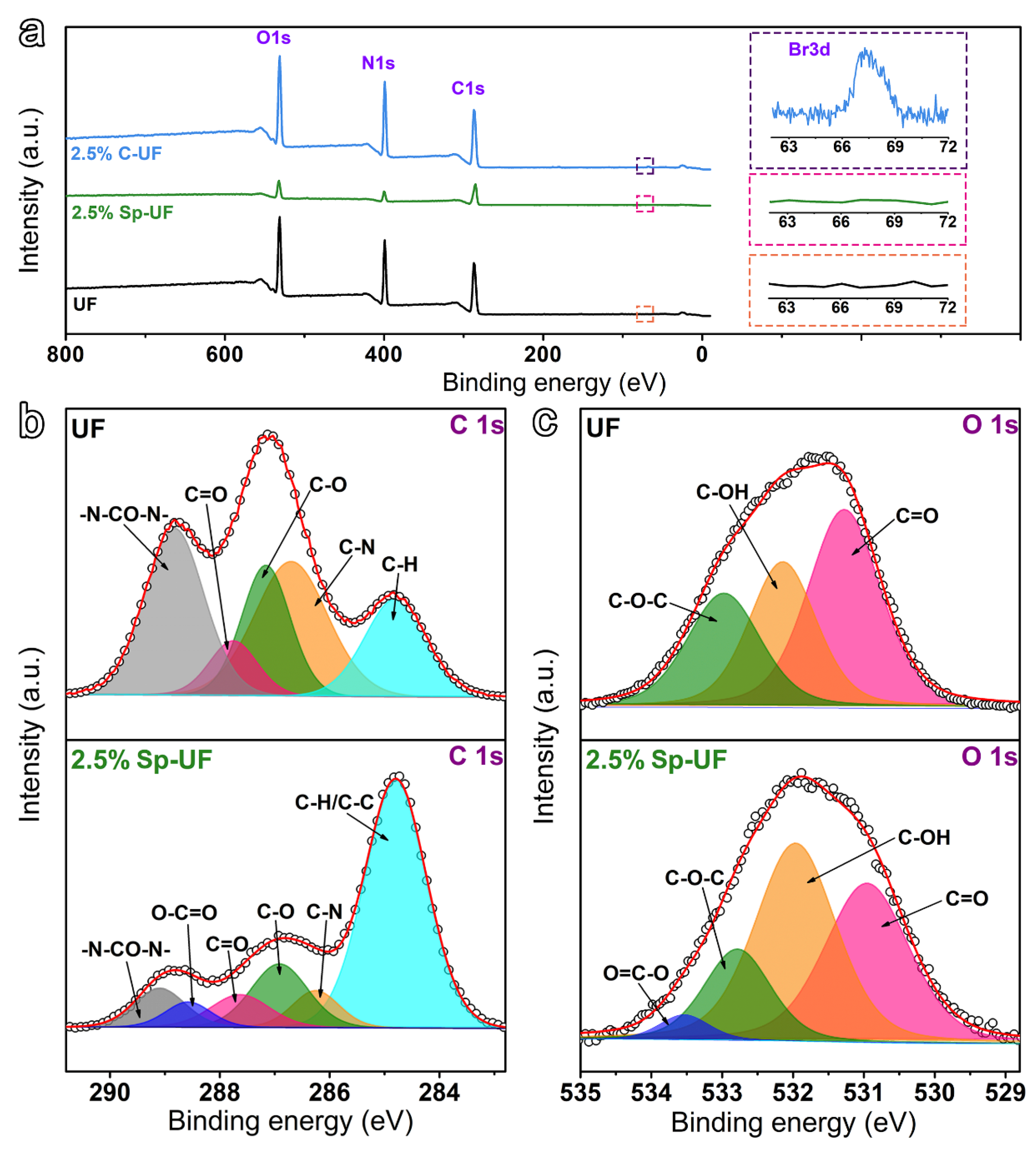
3.4. Morphology and Compositions of UF and Reconfigured UF Resins
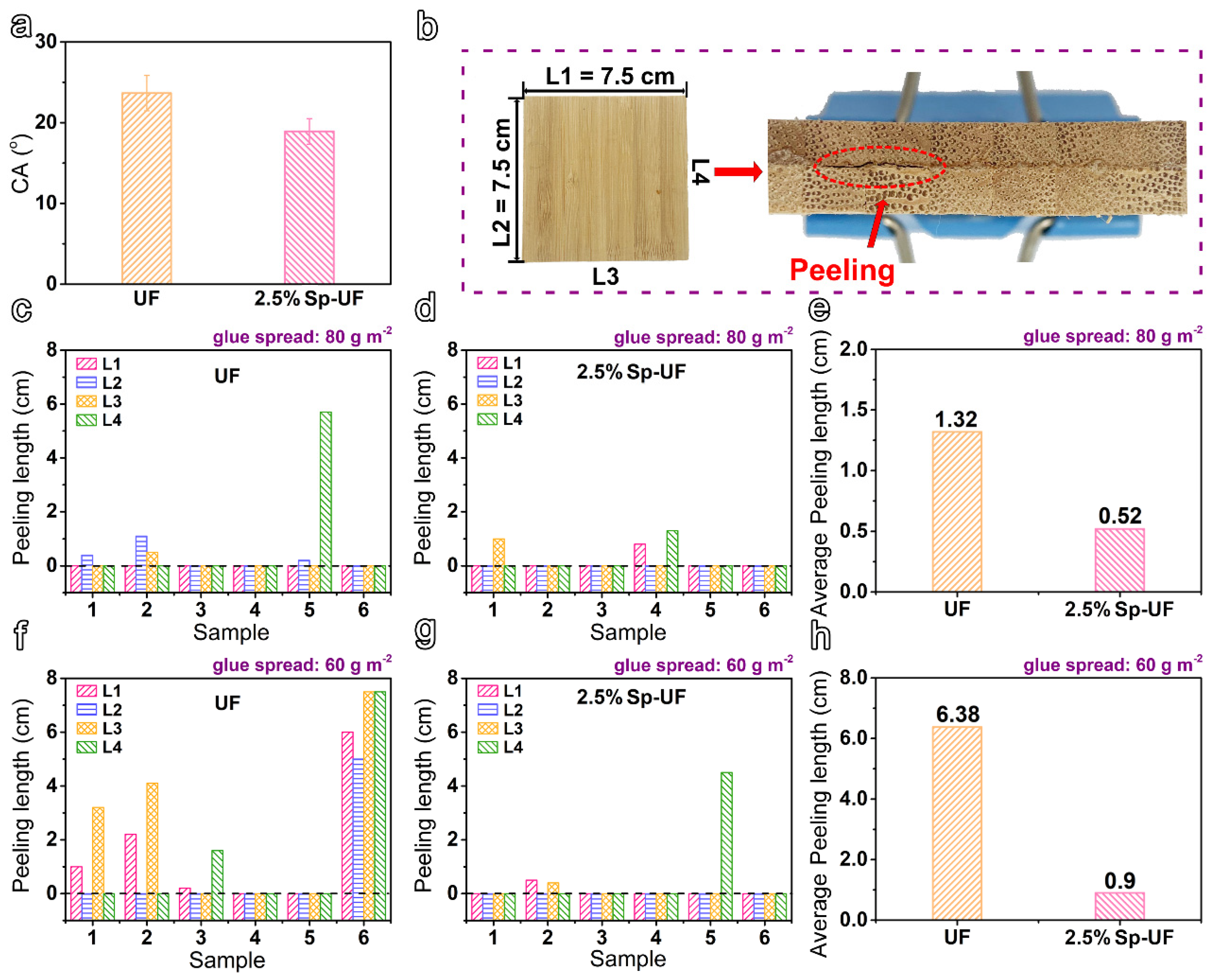
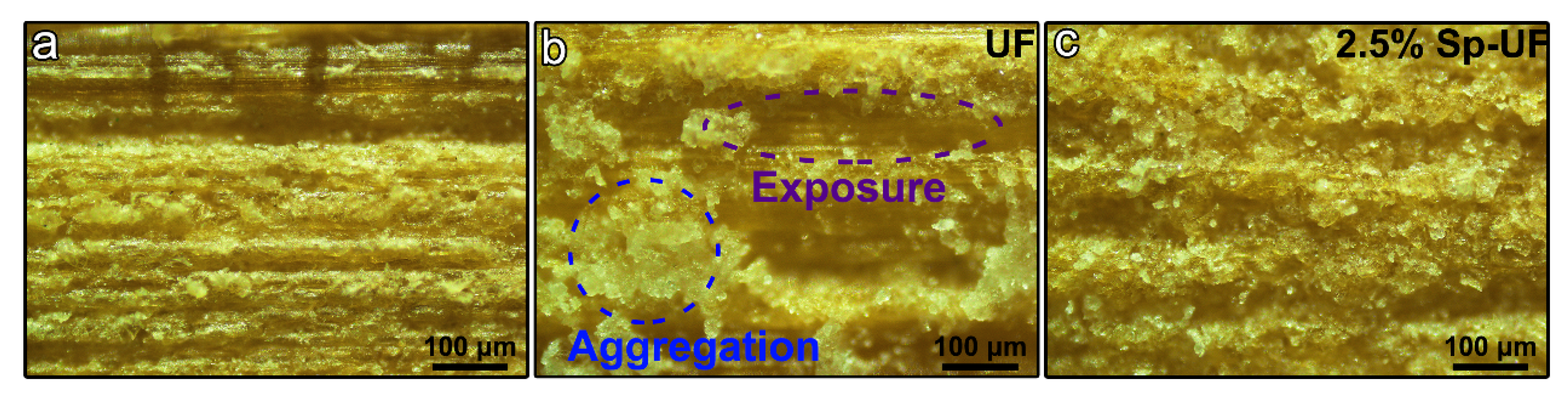
3.5. The Applications of Modified UF Resins on Laminated Bamboo Veneers
3.6. The Wettability Study of UF and Reconfigured UF Resins on the Other Substrates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, L.; Xiao, S.; Gan, W.; Zhan, X.; Li, J. Durable superamphiphobic wood surfaces from Cu2O film modified with fluorinated alkyl silane. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98203–98208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, J.; Li, T.; Gong, A.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; Luo, W.; Henderson, D.; Hu, L. Highly Anisotropic, Highly Transparent Wood Composites. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5181–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaowana, P. Bamboo: An Alternative Raw Material for Wood and Wood-Based Composites. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-Q.; Li, Y.-Q.; Huang, P.; Yang, B.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.-Y. High-Performance Bamboo Steel Derived from Natural Bamboo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yu, W. Development of bamboo scrimber: A literature review. J. Wood. Sci. 2019, 65, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Clouston, P.L.; Arwade, S.R. Development of Laminated Bamboo Lumber: Review of Processing, Performance, and Economical Considerations. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2011, 23, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, R.Z.; Shan, B. Production, environmental impact and mechanical properties of glubam. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Study on the Properties of Transparent Bamboo Prepared by Epoxy Resin Impregnation. Polymers 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Zhou, G.; Du, H.; Lu, D.; Mo, L.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Current and potential carbon stocks in Moso bamboo forests in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-D.; Yu, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Yu, W.-J.; Gao, J.-M. Surface chemical composition analysis of heat-treated bamboo. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wu, B.; Hu, Y.A.; Yu, W. Fabrication, material properties, and application of bamboo scrimber. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, D.J.; López, L.F. 18-Bamboo material characterisation. In Nonconventional and Vernacular Construction Materials, 2nd ed.; Harries, K.A., Sharma, B., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 491–520. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, M.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, D. Shear Strength and Microscopic Characterization of a Bamboo Bonding Interface with Phenol Formaldehyde Resins Modified with Larch Thanaka and Urea. BioResources 2016, 11, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W. Effect of removing extent of bamboo green on physical and mechanical properties of laminated bamboo-bundle veneer lumber (BLVL). Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, K.J. Effect of Glow-Discharge Plasma Treatment on Contact Angle and Micromorphology of Bamboo Green Surface. Forests 2020, 11, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Manalo, A.; Ferdous, W.; Abousnina, R.; Salih, C.; Heyer, T.; Schubel, P. Investigation on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of epoxy polymer matrix with crumb rubber and short fibres for composite railway sleepers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotbehsara, M.M.; Manalo, A.; Aravinthan, T.; Ferdous, W.; Benmokrane, B.; Nguyen, K.T.Q. Synergistic effects of hygrothermal conditions and solar ultraviolet radiation on the properties of structural particulate-filled epoxy polymer coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Bao, L.; Wang, B.; Fan, M.; Feo, L. Plasma surface modification and bonding enhancement for bamboo composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 138, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Guan, X.; Lin, J.; Li, J. Development of laminated bamboo lumber with high bond strength for structural uses by O2 plasma. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, J. Factors Affecting the Temperature Increasing Rate in Arc-shaped Bamboo Pieces during High-frequency Heating. BioResources 2020, 15, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Pizzi, A.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z. The study of linear vibrational welding of moso bamboo. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, H.; Ju, Z.; Hong, L.; Brosse, N.; Lu, X. Robust and durable bonding performance of bamboo induced by high voltage electrostatic field treatment. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 137, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, K.E.; Vnučec, D.; Kutnar, A.; Kamke, F.A.; Mikuljan, M.; Smith, G.D. Bonding of THM modified Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens Mazel) using modified soybean protein isolate (SPI) based adhesives. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Noshchenko, G.; Réh, R.; Kristak, L.; Sedliačik, J.; Antov, P.; Mirski, R.; Savov, V. Properties of Eco-Friendly Particleboards Bonded with Lignosulfonate-Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesives and pMDI as a Crosslinker. Materials 2021, 14, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łebkowska, M.; Załęska-Radziwiłł, M.; Tabernacka, A. Adhesives based on formaldehyde–environmental problems. BioTechnologia 2017, 98, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Trichkov, N.; Krišťák, Ľ.; Réh, R.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Pizzi, A.; Kunecová, D.; Pachikova, M. Properties of High-Density Fiberboard Bonded with Urea–Formaldehyde Resin and Ammonium Lignosulfonate as a Bio-Based Additive. Polymers 2021, 13, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pizzi, A.J.A.f.W.; Materials, L. Urea-Formaldehyde Resins; Wiley-Scrivener Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 61–100. [Google Scholar]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Behrooz, R.; Bahramifar, N.; Pinkl, S.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Application of surface chemical functionalized cellulose nanocrystals to improve the performance of UF adhesives used in wood based composites-MDF type. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 206, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Xia, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Urea Formaldehyde Resin Resultant Plywood with Rapid Formaldehyde Release Modified by Tunnel-Structured Sepiolite. Polymers 2019, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chu, F.; Xu, F.; Zhang, D. Unexpected role of amphiphilic lignosulfonate to improve the storage stability of urea formaldehyde resin and its application as adhesives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Wan, H. “Greener” adhesives composed of urea-formaldehyde resin and cottonseed meal for wood-based composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunky, M. Adhesives in the Wood Industry. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, P.; Ghosh, A.; Scarso, A.; Saha, B. Surfactant for better tomorrow: Applied aspect of surfactant aggregates from laboratory to industry. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 6021–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, H.R.; Thomas, R.R.; Garnier, S.; Pizzi, A. Fluorinated polyether additives to improve the performance of urea–formaldehyde adhesives for wood panels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ziaud, D.; Fei, P.; Jin, W.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Z. Enhancing the performance of starch-based wood adhesive by silane coupling agent(KH570). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.; Singh, R.; Sharma, K. Volumetric, compressibility, surface tension and viscometric studies of CTAB in aqueous solutions of polymers (PEG and PVP) at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 103, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chauhan, S.; Sharma, K. Surface Tension, Viscosity, and Refractive Index of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) in Aqueous Solution Containing Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP), and Their Blends. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Huang, H.-J.; Leng, L.-J.; Li, H.; Peng, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.-M. Study on the solubilization capacity of bio-oil in diesel by microemulsion technology with Span80 as surfactant. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 118, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, B. Bio-Inspired Polymeric Structures with Special Wettability and Their Applications: An Overview. Polymers 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Panigrahi, P.; Saw, R.K.; Mandal, A. Interfacial Interaction of Cationic Surfactants and Its Effect on Wettability Alteration of Oil-Wet Carbonate Rock. Energ. Fuel. 2016, 30, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-T.; Fan, S.-Y. Effects of ultraviolet irradiation treatment on the surface properties and adhesion of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Hong, L.; Yuan, M.; Cui, J.; Cheng, L.; Lu, X. Strong, Durable, and Aging-Resistant Bamboo Composites Fabricated by Silver In Situ Impregnation. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16647–16658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Bio-inspired cellulose nanofiber-reinforced soy protein resin adhesives with dopamine-induced codeposition of “water-resistant” interphases. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanhua, Z.; Jiyou, G.; Haiyan, T.; XiangKai, J.; Junyou, S.; Yingfeng, Z.; Xiangli, W. Fabrication, performances, and reaction mechanism of urea–formaldehyde resin adhesive with isocyanate. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2191–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, Y.C.G.; Ng, G.M.; Huan, C.H.A. Identification of functional groups and determination of carboxyl formation temperature in graphene oxide using the XPS O 1s spectrum. Thin Solid Films 2015, 590, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Bijwe, J. Exploration of thermoplastic polyimide as high temperature adhesive and understanding the interfacial chemistry using XPS, ToF-SIMS and Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Gatóo, A.; Bock, M.; Ramage, M. Engineered bamboo for structural applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cheng, D.-L.; Wålinder, M.E.P.; Zhou, D.-G. Wettability of oil heat-treated bamboo and bonding strength of laminated bamboo board. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 69, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaowana, P.; Jindawong, K.; Sungkaew, S. Adhesion and Bonding Performance of Laminated Bamboo Lumber made from Dendrocalamus sericeus. In Product Design and Technology, Proceedings of the 10th World Bamboo Congress, Damyang, Korea, 17–22 September 2015; World Bamboo Organization: Antwerp, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Anokye, R.; Bakar, E.S.; Ratnasingam, J.; Yong, A.C.C.; Bakar, N.N. The effects of nodes and resin on the mechanical properties of laminated bamboo timber produced from Gigantochloa scortechinii. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, C.; Pang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Surfactant-Induced Reconfiguration of Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Enables Improved Surface Properties and Gluability of Bamboo. Polymers 2021, 13, 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203542
Liang L, Zheng Y, Wu Y, Yang J, Wang J, Tao Y, Li L, Ma C, Pang Y, Chen H, et al. Surfactant-Induced Reconfiguration of Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Enables Improved Surface Properties and Gluability of Bamboo. Polymers. 2021; 13(20):3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Lulu, Yu Zheng, Yitian Wu, Jin Yang, Jiajie Wang, Yingjie Tao, Lanze Li, Chaoliang Ma, Yajun Pang, Hao Chen, and et al. 2021. "Surfactant-Induced Reconfiguration of Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Enables Improved Surface Properties and Gluability of Bamboo" Polymers 13, no. 20: 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203542
APA StyleLiang, L., Zheng, Y., Wu, Y., Yang, J., Wang, J., Tao, Y., Li, L., Ma, C., Pang, Y., Chen, H., Yu, H., & Shen, Z. (2021). Surfactant-Induced Reconfiguration of Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Enables Improved Surface Properties and Gluability of Bamboo. Polymers, 13(20), 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203542