Transformation of Oil Palm Waste-Derived Cellulose into Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Investigating the Crucial Role of Plasticizers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction Cellulose from Oil Palm Waste
2.3. Carboxymethylation of Cellulose
2.4. Fabrication of CMC-Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Oil Palm Waste
3.2. Chemical Interactions within the Polymer Film
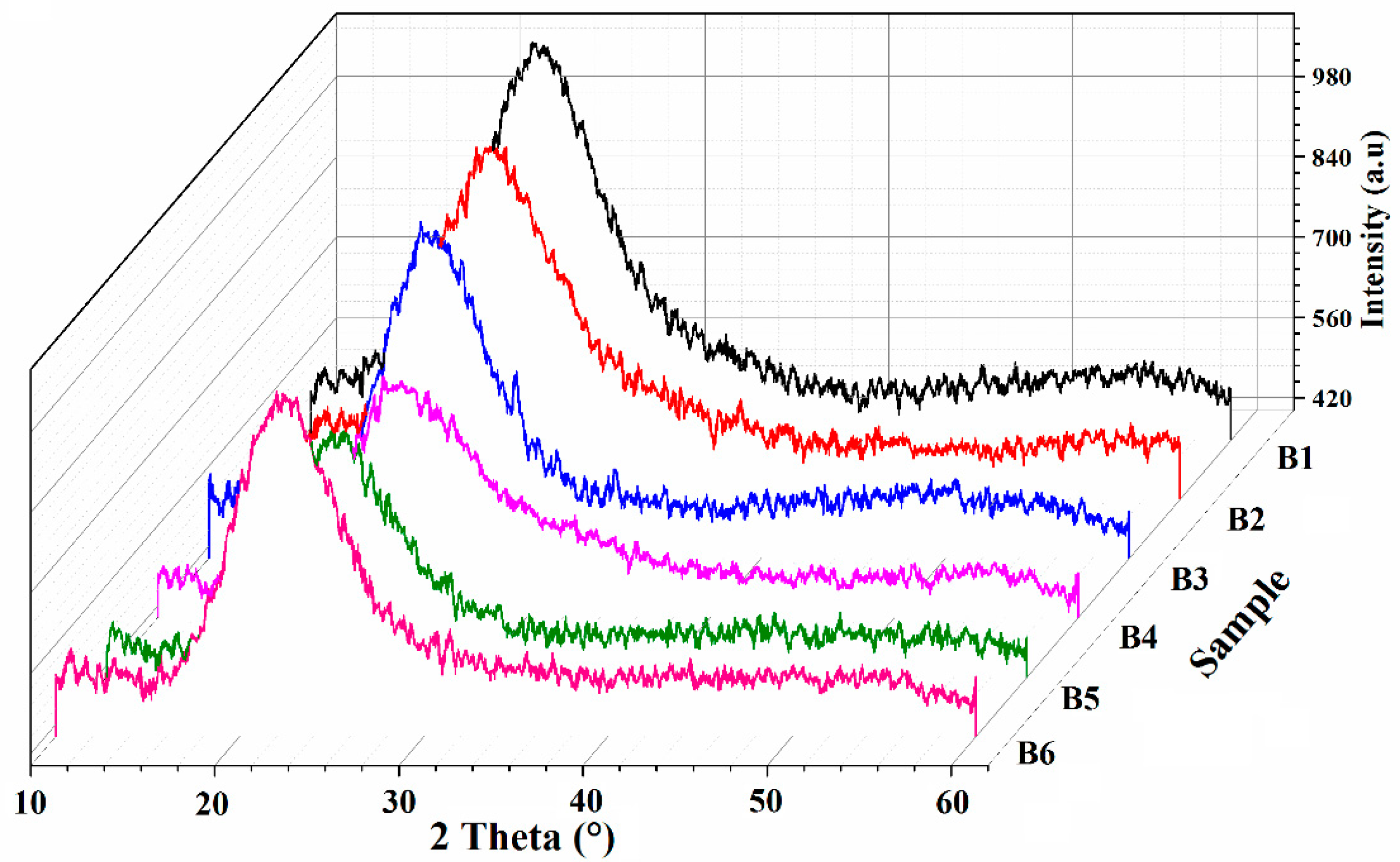
3.3. Crystallinity Analysis
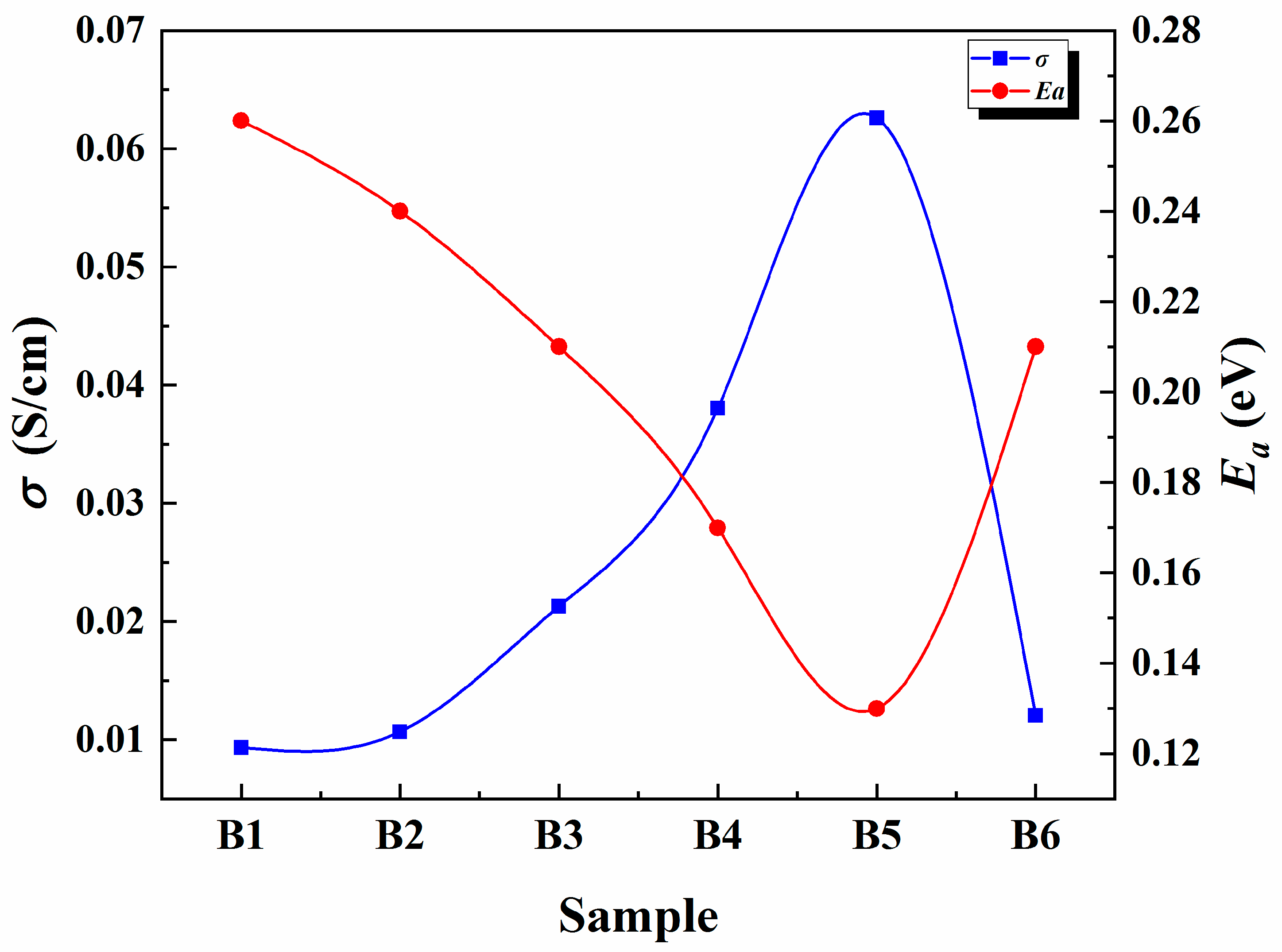
3.4. Conductivity Analysis
3.5. Temperature-Dependent Conductivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Chang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. A composite membrane based on a biocompatible cellulose as a host of gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 270, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guan, S.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Xu, C. A novel hybrid quasi-solid polymer electrolyte based on porous PVB and modified PEG for electrochromic application. Org. Electron. 2018, 56, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwon, P.; Andrade, J.R.; Lapkowski, M.; Pawlicka, A. Hydroxypropyl cellulose-based gel electrolyte for electrochromic devices. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 159, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Kang, L.; Ran, F. Biopolymer-based carboxylated chitosan hydrogel film crosslinked by HCl as gel polymer electrolyte for all-solid-sate supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2019, 426, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jiang, X.; Xiang, X.; Chen, K.; Chen, G.; Jiang, X.; Hou, L. High-performance and flexible solid-state supercapacitors based on high toughness and thermoplastic poly(vinyl alcohol)/NaCl/glycerol supramolecular gel polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 324, 134874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M.; Jaseetharan, T.; Senadeera, G.; Mellander, B.-E.; Albinsson, I.; Furlani, M.; Kumari, J. Solid-state solar cells co-sensitized with PbS/CdS quantum dots and N719 dye and based on solid polymer electrolyte with binary cations and nanofillers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 405, 112915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, M.; Bhat, D.K. LiClO4doped cellulose acetate as biodegradable polymer electrolyte for supercapacitors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Varshney, P.K. Effect of plasticizer on the conductivity of carboxymethyl cellulose-based solid polymer electrolyte. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 6169–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, J.; He, K.; Wang, N. The Effects of Different Plasticizers on the Properties of Thermoplastic Starch as Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, P.R.; Zhang, H.; Wunder, S.L. Blends of Pegylated Polyoctahedralsilsesquioxanes (POSS-PEG) and Methyl Cellulose as Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 170, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitjinda, G.; Nimchua, T.; Sukyai, P. Effect of xylanase-assisted pretreatment on the properties of cellulose and regenerated cellulose films from sugarcane bagasse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Ou, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Utilization of pineapple peel for production of nanocellulose and film application. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Jiang, S.; Farooq, A.; Naeem, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Liu, L. Structure and properties of high quality natural cellulose nano fibrils from a novel material Ficus natalensis barkcloth. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 51, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatun, A.; Jannah, M.; Ahmad, A.; Taba, P. Synthetic Bioplastic Film from Rice Husk Cellulose. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1463, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, D.C.; Pérez, C.D.; Fissore, E.N.; De’Nobili, M.D.; Rojas, A.M. Pectin-based composite film: Effect of corn husk fiber concentration on their properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.Y.; Azzahari, A.D.; Abouloula, C.N.; Sonsudin, F.; Shahabudin, N.; Yahya, R. Cellulose-based polymer electrolyte derived from waste coconut husk: Residual lignin as a natural plasticizer. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.S.A.; Rudhziah, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohamed, N.S. Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber. Polymers 2014, 6, 2371–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouloula, C.N.; Rizwan, M.; Selvanathan, V.; Abdullah, C.I.; Hassan, A.; Yahya, R.; Oueriagli, A. A novel application for oil palm empty fruit bunch: Extraction and modification of cellulose for solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 2018, 24, 3827–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Adhikari, R.; Guo, Q.; Adhikari, B. Preparation and characterization of glycerol plasticized (high-amylose) starch–chitosan films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudhziah, S.; Rani, M.; Ahmad, A.; Mohamed, N.; Kaddami, H. Potential of blend of kappa-carrageenan and cellulose derivatives for green polymer electrolyte application. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 72, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colò, F.; Bella, F.; Nair, J.R.; Destro, M.; Gerbaldi, C. Cellulose-based novel hybrid polymer electrolytes for green and efficient Na-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 174, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, Y.M.; Majid, N.A.; Kasmani, R.M.; Illias, H.A.; Kadir, M.F.Z. The Effect of Plasticization on Conductivity and Other Properties of Starch/Chitosan Blend Biopolymer Electrolyte Incorporated with Ammonium Iodide. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 603, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerlof, G. Dielectric constants of some organic solvent-water mixtures at various temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 4125–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Varshney, P.K. Effect of plasticizer concentration on structural and electrical properties of hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)-based polymer electrolyte. Ionics 2017, 23, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.; Ferreira, H.; Pawlicka, A. Influence of plasticizer contents on the properties of HEC-based solid polymeric electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 3827–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, A. A renewable gel polymer electrolyte based on the different sized carboxylated cellulose with satisfactory comprehensive performance for rechargeable lithium ion battery. Polymer 2020, 208, 122943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, C.-H.; Lee, M.L.-Y.; Ahmad, I.; Phang, S.-W. Development of grafted rubber/polyaniline/carboxymethyl cellulose film as green conductive polymer film. Polym. Bull. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syairah, A.; Khanmirzaei, M.H.; Saidi, N.M.; Farhana, N.K.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. Effect of different imidazolium-based ionic liquids on gel polymer electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Ionics 2019, 25, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. A High-Performance Graphene Oxide-Doped Ion Gel as Gel Polymer Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Supercapacitor Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, S.; Mathavan, T.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Benial, A.M.F.; Aristatil, G.; Mani, N.; Premalatha, M.; Pandi, D.V. Investigation of bio polymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate-ammonium nitrate for potential use in electrochemical devices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.B.; Nirmale, T.C.; Khupse, N.D.; Kale, B.B.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Pavitran, S.; Gosavi, S.W. Cellulose-Derived Flame-Retardant Solid Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Abdullah, R.M.; Kadir, M.F.Z. A Promising Polymer Blend Electrolytes Based on Chitosan: Methyl Cellulose for EDLC Application with High Specific Capacitance and Energy Density. Molecules 2019, 24, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selvanathan, V.; Ruslan, M.H.; Aminuzzaman, M.; Muhammad, G.; Amin, N.; Sopian, K.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. Resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF) as a novel plasticizer for starch-based solid biopolymer electrolyte. Polymers 2020, 12, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouloula, C.N.; Rizwan, M.; Selvanathan, V.; Hassan, A.; Yahya, R.; Oueriagli, A. Oil palm waste based phthaloyl cellulose: A product of photosynthesis as an electrolyte of photovoltaics. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukur, M.F.; Ithnin, R.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of potato starch-magnesium acetate biopolymer electrolytes: The effect of glycerol and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Ionics 2016, 22, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Designations | CMC (g) | LiI (g) | Glycerol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | w/w (%) | |||
| B1 | 0.2 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 5 |
| B2 | 0.03 | 10 | ||
| B3 | 0.05 | 15 | ||
| B4 | 0.07 | 20 | ||
| B5 | 0.08 | 25 | ||
| B6 | 0.10 | 30 | ||
| Sample | % Glycerol (w/w) | Degree of Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CMC powder | - | 36.9 |
| B1 | 5 | 25.0 |
| B2 | 10 | 22.9 |
| B3 | 15 | 20.1 |
| B4 | 20 | 18.3 |
| B5 | 25 | 17.6 |
| B6 | 30 | 23.8 |
| Polymeric Content | Salt | Additives | Ionic Conductivity (S cm−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | Lithium tetrafluoroborate | Glycerol | 0.0037 | [24] |
| Carboxylated cellulose | Lithium hexafluorophosphate | Ethylene carbonate + dimethyl carbonate + ethyl methyl carbonate | 0.0018 | [26] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | - | Polyaniline | 0.018 | [27] |
| Poly(ethylene oxide) | Sodium iodide | 1-methyl-3-propylimidazolium iodide | 0.0094 | [28] |
| Poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoro propylene | - | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate + graphene oxide | 0.025 | [29] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | Lithium iodide | Glycerol | 0.063 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abouloula, C.N.; Rizwan, M.; Selvanathan, V.; Yahya, R.; Althubeiti, K.; Alkhammash, H.I.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Oueriagli, A. Transformation of Oil Palm Waste-Derived Cellulose into Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Investigating the Crucial Role of Plasticizers. Polymers 2021, 13, 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213685
Abouloula CN, Rizwan M, Selvanathan V, Yahya R, Althubeiti K, Alkhammash HI, Akhtaruzzaman M, Oueriagli A. Transformation of Oil Palm Waste-Derived Cellulose into Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Investigating the Crucial Role of Plasticizers. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213685
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbouloula, Cheyma Naceur, Muhammad. Rizwan, Vidhya Selvanathan, Rosiyah Yahya, Khaled Althubeiti, Hend I. Alkhammash, Md. Akhtaruzzaman, and A. Oueriagli. 2021. "Transformation of Oil Palm Waste-Derived Cellulose into Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Investigating the Crucial Role of Plasticizers" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213685
APA StyleAbouloula, C. N., Rizwan, M., Selvanathan, V., Yahya, R., Althubeiti, K., Alkhammash, H. I., Akhtaruzzaman, M., & Oueriagli, A. (2021). Transformation of Oil Palm Waste-Derived Cellulose into Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Investigating the Crucial Role of Plasticizers. Polymers, 13(21), 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213685







