Physical Properties of Shellac Material Used for Hot Melt Extrusion with Potential Application in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Grinding
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5. Melt Flow Index (MFI)
2.6. Rheometer
2.7. Dissolution Test
3. Results and Discussion
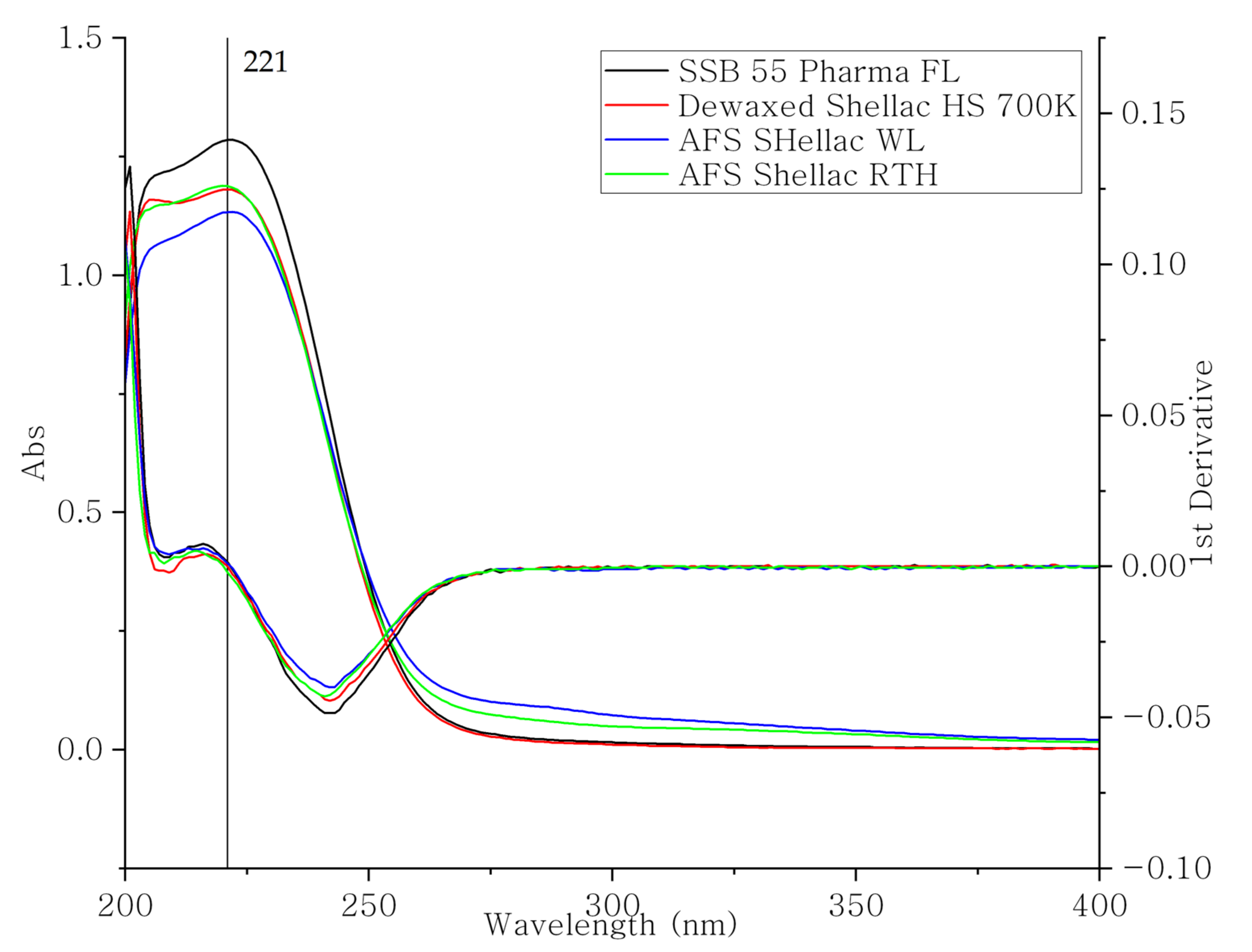
3.1. IR Spectrum
3.2. Melt Flow Index Analysis
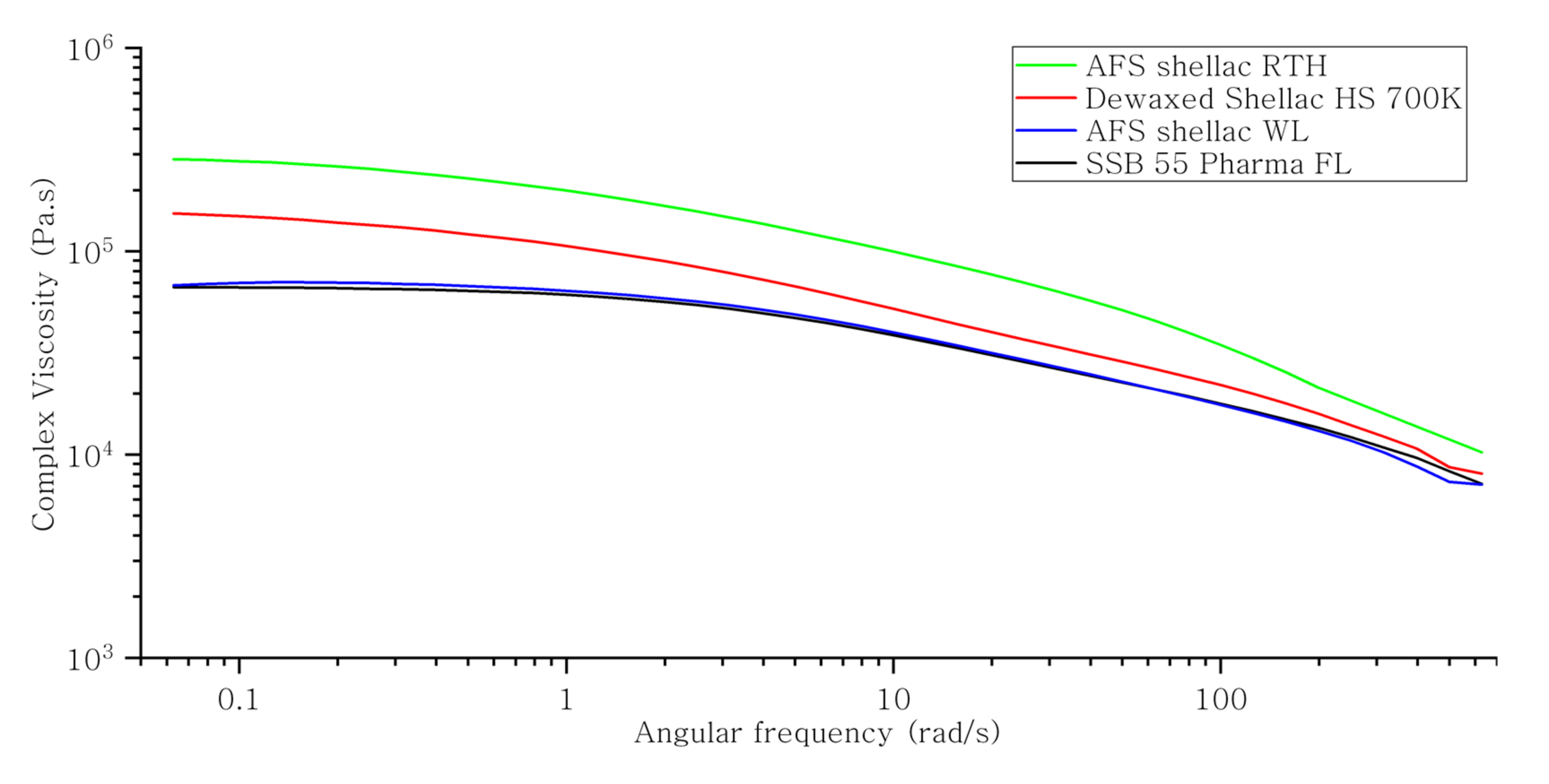
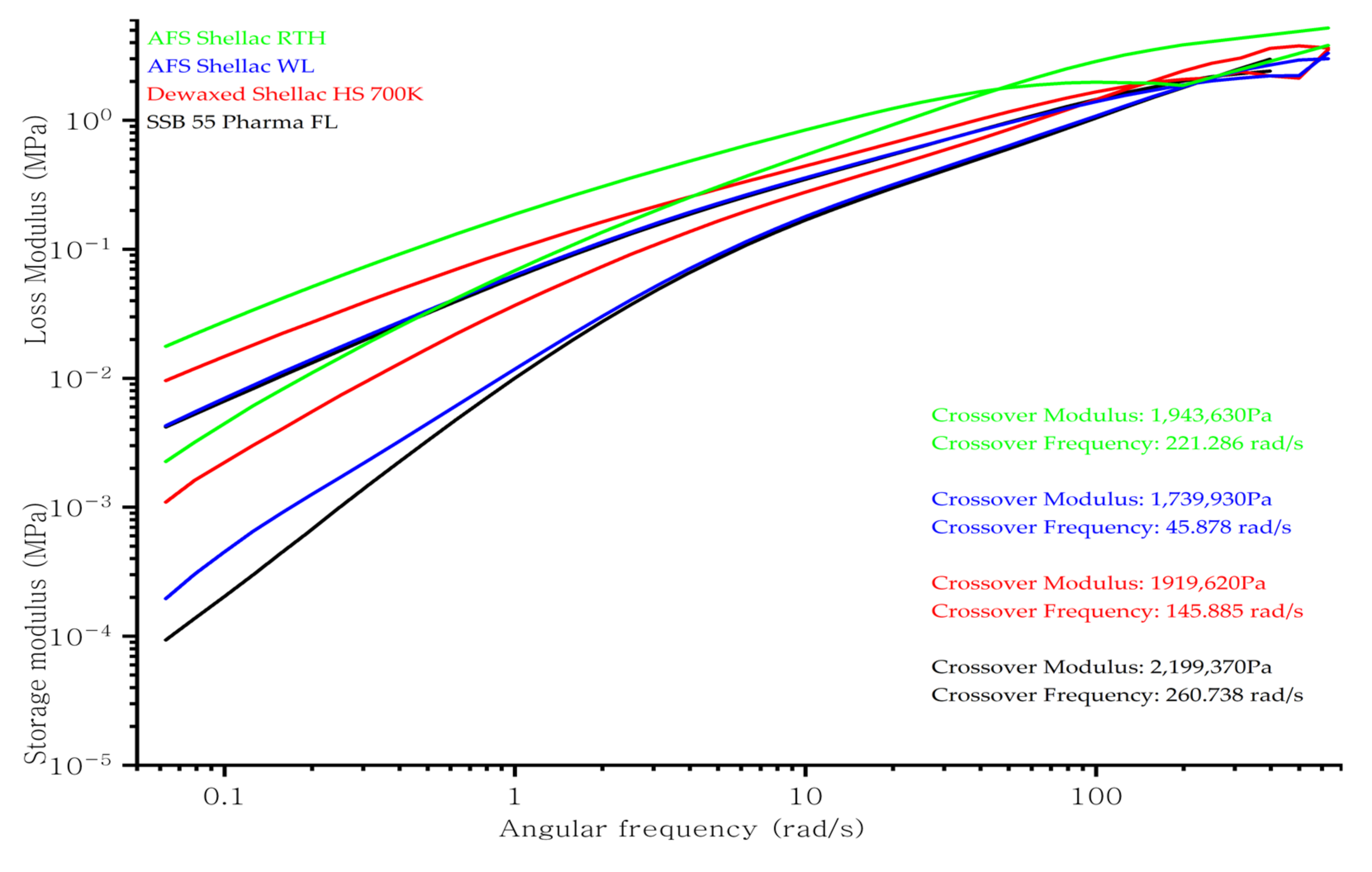
3.3. Rheology
3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
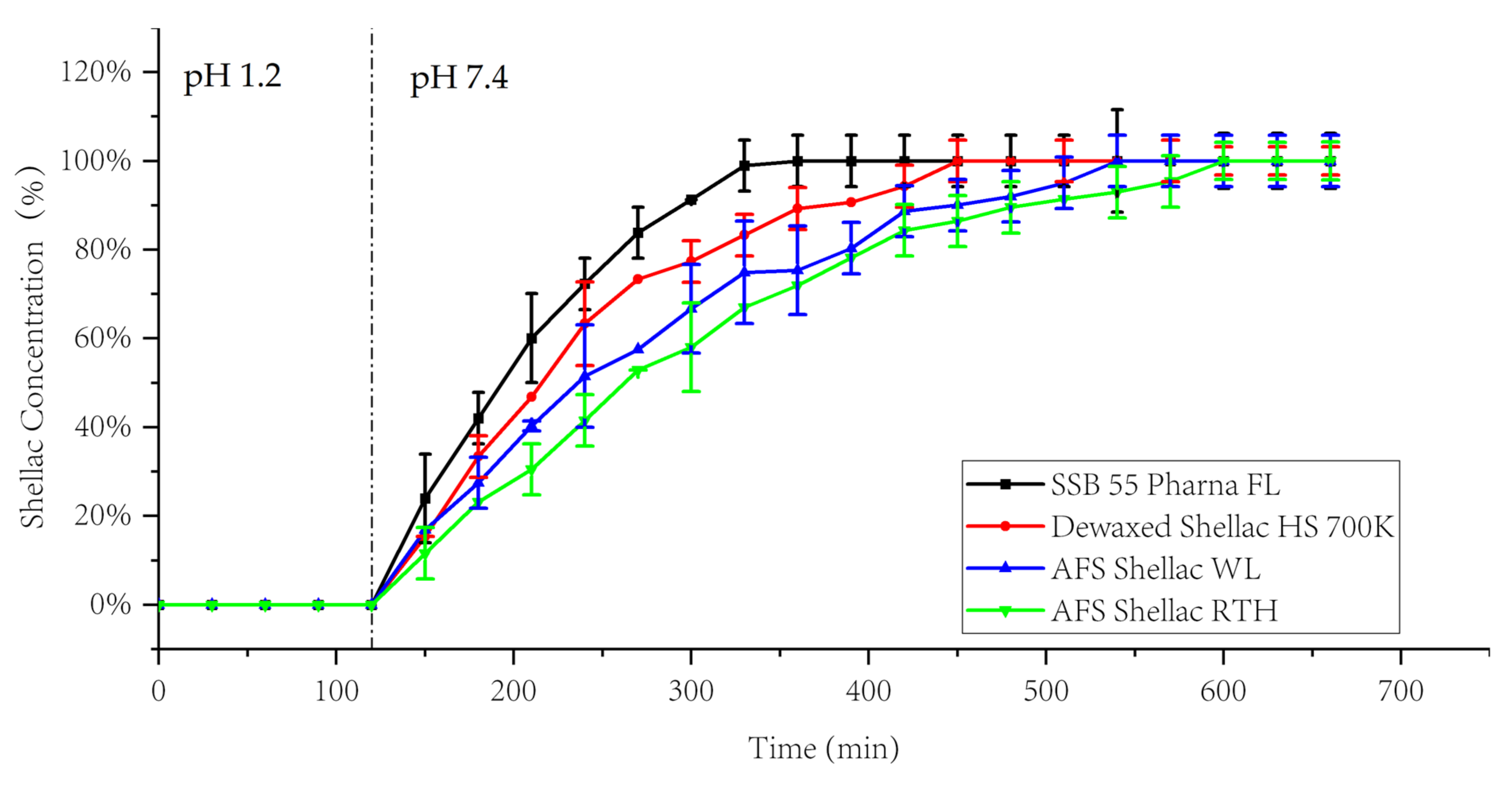
3.5. Dissolution
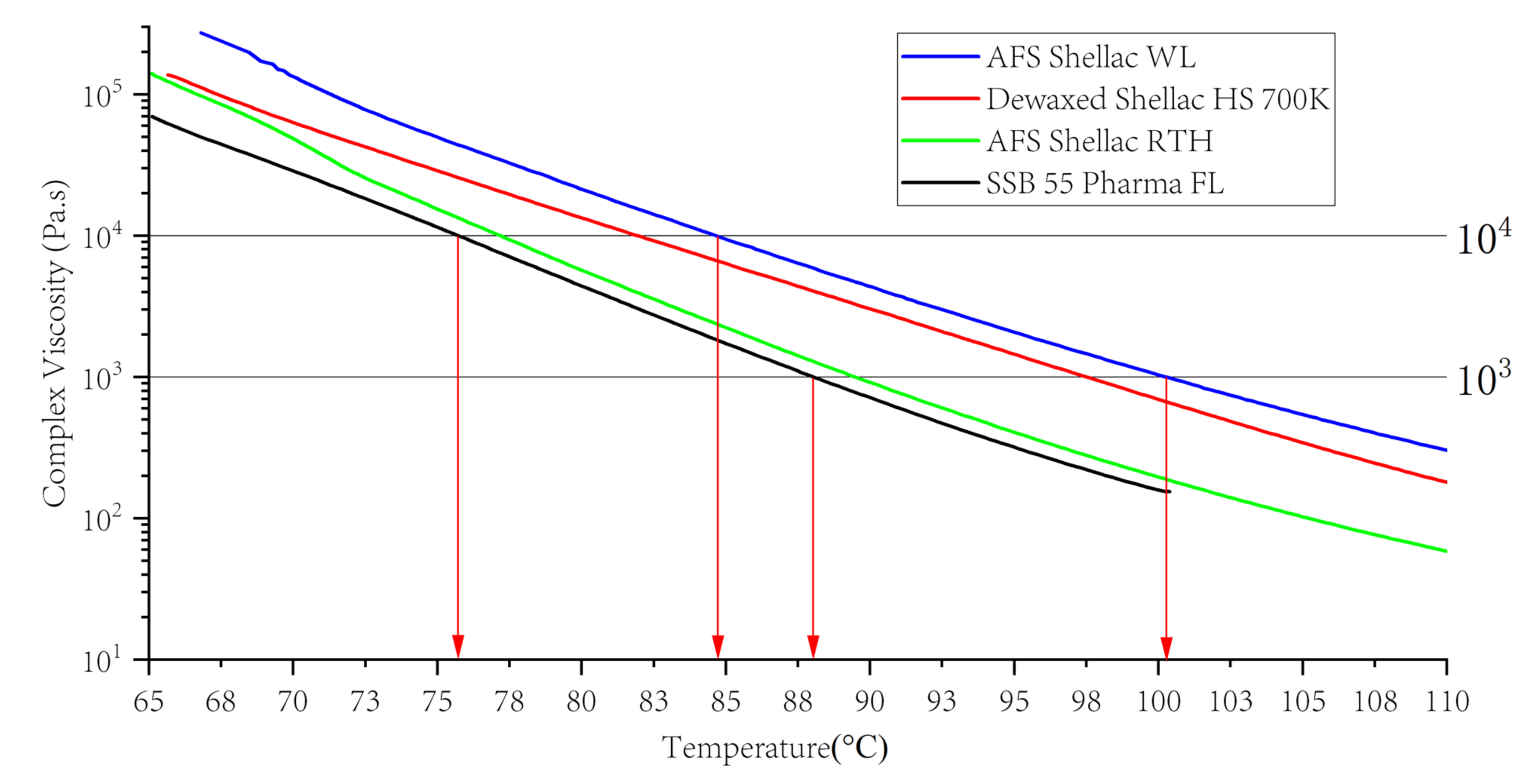
3.6. Suggestion for Hot Melt Extrusion Process Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.; Jacob, S.E. Shellac. Dermatitis 2011, 22, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, V.S.; Ram, N.S.; Subramanian, G.B.V.; Singh, H. Chromatographic separation of the alkaline hydrolysis products of shellac. J. Chromatogr. A 1973, 84, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ishida, Y.; Ohtani, H.; Tsuge, S.; Nakayama, T. Characterization of natural resin shellac by reactive pyrolysis-gas chromatography in the presence of organic alkali. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, K.; Penning, M.; Wchtersbach, E.; Maskos, M.; Langguth, P. Investigation of various shellac grades: Additional analysis for identity. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Y.; Leopold, C.S. Physicochemical properties of various shellac types. Dissolution Technol. 2009, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, E.W.; Fadeyev, V.; Haber, C.; Jin, J.; Nordmeyer, R.; Golden, M. Using optical metrology to reconstruct sound recordings. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2007, 579, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiavari, G.; Fabbri, D.; Prati, S. Characterisation of Natural Resins by Pyrolysis—Silylation. Chromatographia 2002, 55, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, G.; Fabbri, D.; Mazzeo, R.; Bocchini, P.; Galletti, G.C. Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of natural resins used for artistic objects. Chromatographia 1995, 41, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Jin, X. Present research on the composition and application of lac. For. Stud. China 2006, 8, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearnchob, N.; Dashevsky, A.; Bodmeier, R. Improvement in the disintegration of shellac-coated soft gelatin capsules in simulated intestinal fluid. J. Control Release 2004, 94, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, C.; Paris, C.; Le Hô, A.S.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Échard, J.P. A joint use of Raman and infrared spectroscopies for the identification ofnatural organic media used in ancient varnishes. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, G.; Hogan, J.; Holton, M. Pharmaceutical Coating Technology; Taylor & Francis: Singapore, 1995; ISBN 978-0136628910. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, Y.; Leopold, C.S. Development of shellac-coated sustained release pellet formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuschagne, P.W.; Naicker, B.; Kalombo, L. Micronization, characterization and in-vitro dissolution of shellac from PGSS supercritical CO2 technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.P.; Müller, R.H. Production of aqueous shellac dispersions by high pressure homogenisation. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 223, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, H.; Bedir, Y.; Al-Hayani, A. Efficacy of shellac, a natural product, for the prevention of wet gangrene. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchapornpon, D.; Limmatvapirat, C.; Luangtana-Anan, M.; Nunthanid, J.; Sriamornsak, P.; Limmatvapirat, S. Fabrication of thermally stabilized shellac through solid state reaction with phthalic anhydride. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnautov, A.; Korhov, V.; Faitelson, F. Physicomechanical Properties of Shellac Films. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2013, 49, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soradech, S.; Limatvapirat, S.; Luangtana-anan, M. Stability enhancement of shellac by formation of composite film: Effect of gelatin and plasticizers. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearnchob, N.; Siepmann, J.; Bodmeier, R. Pharmaceutical applications of shellac: Moisture-protective and taste-masking coatings and extended-release matrix tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.F.; Sarkhel, G.; Goswami, D.N.; Baboo, B. Effect of temperature on coating properties of shellac-novolac blends. Pigment Resin Technol. 2013, 42, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.P.; Tulini, F.L.; Ribas, M.M.; Penning, M.; Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; Poncelet, D. Microcapsules loaded with the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei BGP-1 produced by co-extrusion technology using alginate/shellac as wall material: Characterization and evaluation of drying processes. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limmatvapirat, S.; Limmatvapirat, C.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Luangtana-anan, M.; Sriamornsak, P. Modulation of drug release kinetics of shellac-based matrix tablets by in-situ polymerization through annealing process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gately, N.M.; Kennedy, J.E. The development of a melt-extruded shellac carrier for the targeted delivery of probiotics to the colon. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwendaal, C. Polymer Extrusion, 5th ed.; Hanser: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781569905166. [Google Scholar]
- Chokshi, R.; Zia, H. Hot-Melt Extrusion technique: A Review. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2004, 3, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Repka, M.A.; Battu, S.K.; Upadhye, S.B.; Thumma, S.; Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Martin, C.; McGinity, J.W. Pharmaceutical Applications of Hot-Melt Extrusion: Part II. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Pang, H.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Application of Hot Melt Extrusion for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs: Limitations, Advances and Future Prospects. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on Absorption of Eutectic Mixture. I. A Comparison of the Behavior of Eutectic Mixture of Sulfathiazole and that of Ordinary Sulfathiazole in Man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beneš, M.; Pekárek, T.; Beránek, J.; Havlíček, J.; Krejčík, L.; Šimek, M.; Tkadlecová, M.; Doležal, P. Methods for the preparation of amorphous solid dispersions—A comparative study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, J.; Boetker, J.P.; Baldursdottir, S.; Rantanen, J. Rheology as a tool for evaluation of melt processability of innovative dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Üstüner, E.E.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Predicting melt rheology for hot-melt extrusion by means of a simple Tg-measurement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Parikh, T.; Meena, A.K.; Mahajan, N.; Vitez, I.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Effect of carbamazepine on viscoelastic properties and hot melt extrudability of Soluplus®. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, S.M.; De Matas, M.; Kelly, A.; Paradkar, A. Characterization of thermal and rheological properties of zidovidine, lamivudine and plasticizer blends with ethyl cellulose to assess their suitability for hot melt extrusion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Suwardie, H.; Wang, P.; Gogos, C.G. Miscibility Studies of Indomethacin and Eudragit® E PO by Thermal, Rheological, and Spectroscopic Analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellac-Wax-Containing Flakes. Available online: https://www.afsuter.com/product/wax-containing-shellac-flakes/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Shellac-Dewaxed Flakes—Food and Pharma Grade. Available online: https://www.afsuter.com/product/dewaxed-shellac-flakes-food-pharma/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Plastics—Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)—Part 2: Determination of Glass Transition Temperature and Step Height. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/77310.html (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Brian, C.S. Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781420069303. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; He, Y. Preparation of environmental friendly coatings based on natural shellac modified by diamine and its applications for copper protection. Prog. Org. Coatings 2008, 62, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlic, C.A.; Strouse, J. Problems in NMR and IR Spectroscopy NMR Links of Interest. Available online: https://webspectra.chem.ucla.edu// (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Tripathi, S.N.; Saini, P.; Gupta, D.; Choudhary, V. Electrical and mechanical properties of PMMA/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites prepared via in situ polymerization. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6223–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.H. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; Ando, D.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Sydney, Australia, 2004; ISBN 0470854278. [Google Scholar]
- Derry, J. Investigating Shellac: Documenting the Process, Defining the Product; University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pramono, E.; Utomo, S.B.; Wulandari, V.; Zahrotul, W.A.A.; Clegg, F. The effect of polyethylene glycol on shellac stability. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 107, 12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombini, M.P.; Bonaduce, I.; Gautier, G. Molecular Pattern Recognition of Fresh and Aged Shellac. Chromatographia 2003, 58, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, E.K.; Gately, N.M.; Killion, J.A.; Devine, D.M.; Higginbotham, C.L.; Geever, L.M. Melt Extruded Bioresorbable Polymer Composites for Potential Regenerative Medicine Applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1238-10. Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion Plastometer; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, S.D.C.; João, I.M.; Pimentel Real, L.E. Evaluation of the influence of testing parameters on the melt flow index of thermoplastics. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rides, M.; Allen, C.; Omloo, H.; Nakayama, K.; Cancelli, G. Interlaboratory comparison of melt flow rate testing of moisture sensitive plastics. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 572–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.P. Plastics materials. Polym. Test. 1988, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TA Instruments Analytical Rheology. Appl. Notes TA Instrum. 2003, 1–4. Available online: https://www.tainstruments.com/applications-library-search/ (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Cao, Z.; Daly, M.; Geever, L.M.; Major, I.; Higginbotham, C.L.; Devine, D.M. Synthesis and characterization of high density polyethylene/peat ash composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 94, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangam, R.; Majumdar, S.; Upadhye, S.B.; Kumar Battu, S.; Repka, M.A.; Majumdar, S.; Kumar Battu, S.; Srirangam, R.; Upadhye, S.B. Applications of hot-melt extrusion for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 1357–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Services, P.S.D.D. Technical Brief Volume 3: Hot-Melt Extrusion. Tech. Br. 2011, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Suwardie, H.; Wang, P.; Todd, D.B.; Panchal, V.; Yang, M.; Gogos, C.G. Rheological study of the mixture of acetaminophen and polyethylene oxide for hot-melt extrusion application. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D′Este, M.; Alini, M.; Eglin, D. Single step synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive hyaluronan hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Solanki, N.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Investigation of Thermal and Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers Relevant to Hot Melt Extrusion, IV: AffinisolTM HPMC HME Polymers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyon, D.M.; Aktaş, S. Factors Affecting the Rheology and Processability of Highly Filled Suspensions. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liptak, B.G. Instrument Engineers’ Handbook, Volume One: Process Measurement and Analysis; Instrument Engineers’ Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 9781420064025. [Google Scholar]
- Kaboorani, A.; Blanchet, P. Determining the linear viscoelastic region of sugar maple wood by dynamic mechanical analysis. BioResources 2014, 9, 4392–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, K.P. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis: A Practical Introduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781420049183. [Google Scholar]
- Douroumis, D. Hot-Melt Extrusion: Pharmaceutical Applications; Douroumis, D., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2012; ISBN 9780470711187. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, N.; Gupta, S.S.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Rheological analysis of itraconazole-polymer mixtures to determine optimal melt extrusion temperature for development of amorphous solid dispersion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Nanabala, R.; Ménager, M.; Commereuc, S.; Verney, V. Molecular changes during natural biopolymer ageing—The case of shellac. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Meena, A.; Parikh, T.; Serajuddin, A. Investigation of thermal and viscoelastic properties of polymers relevant to hot melt extrusion-I: Polyvinylpyrrolidone and related polymers. Simerdeep. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2014, 5, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteyne, T.; Heeze, L.; Oldörp, K.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; De Beer, T. Vibrational spectroscopy to support the link between rheology and continuous twin-screw melt granulation on molecular level: A case study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, A.; Parikh, T.; Gupta, S.S.; Serajuddin, A. Investigation of thermal and viscoelastic properties of polymers relevant to hot melt extrusion-II: Cellulosic polymers. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2014, 5, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Austen Angell, C.; Sivarajan, S. Glass Transition. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128035818. [Google Scholar]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiry, J.; Lebrun, P.; Vinassa, C.; Adam, M.; Netchacovitch, L.; Ziemons, E.; Hubert, P.; Krier, F.; Evrard, B. Continuous production of itraconazole-based solid dispersions by hot melt extrusion: Preformulation, optimization and design space determination. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duflot, A.V.; Kitaeva, N.K.; Duflot, V.R. Radiation-chemical preparation of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 107, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gousous, J.; Penning, M.; Langguth, P. Molecular insights into shellac film coats from different aqueous shellac salt solutions and effect on disintegration of enteric-coated soft gelatin capsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, W. Thermal analysis of four insect waxes based on differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Procedia Eng. 2011, 18, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Batch Name | Type | Seedlac | Refining Process | Bleaching Process | Wax Containing | Manufacture Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dewaxed Shellac AFS HS 700K | Dewaxed shellac | Kushmi | Solvent extraction | Activated carbon | Less than 0.2% | 16 February 2017 |
| SSB 55 Pharma FL | Dewaxed shellac | Kushmi | Solvent extraction | Activated carbon | Less than 0.2% | August 2017 |
| AFS Shellac WL | Wax containing shellac | Kushmi | Melting process | N/A | 4.5% | 05 June 2017 |
| AFS Shellac RTH | Wax containing shellac | Kushmi | Melting process | N/A | 3.6% | 13 December 2017 |
| Name | AFS Shellac RTH | AFS Shellac WL | Dewaxed Shellac HS 700K | SSB 55 Pharma FL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance at 720 cm−1 | 0.026 | 0.03 | 0.021 | 0.02 |
| Temperature | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||
| AFS Shellac WL | N/A | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 30.8 ± 0.8 | 78.9 ± 0.4 | |
| Dewaxed Shellac AFS HS 700K | N/A | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 33.7 ± 0.6 | 82.6 ± 1.0 | |
| Shellac SSB 55 Pharma FL | N/A | 0.1 ± 0.004 | 64.2 ± 1.6 | 85.5 ± 1.0 | |
| AFS Shellac RTH | N/A | 15.3 ± 0.3 | 51.0 ± 0.2 | 68.4 ± 0.8 | |
| Material | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Shellac SSB 55 Pharma F | 41.7 ± 0.1 | - |
| Dewaxed Shellac HS 700K | 44.6 ± 0.1 | - |
| AFS Shellac RTH | 46.4 ± 0.1 | 76.5 ± 0.3 |
| AFS shellac WL | 48.2 ± 0.2 | 77.5 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, G.; Cao, Z.; Devine, D.; Penning, M.; Gately, N.M. Physical Properties of Shellac Material Used for Hot Melt Extrusion with Potential Application in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Polymers 2021, 13, 3723. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213723
Yan G, Cao Z, Devine D, Penning M, Gately NM. Physical Properties of Shellac Material Used for Hot Melt Extrusion with Potential Application in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3723. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213723
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Guangming, Zhi Cao, Declan Devine, Manfred Penning, and Noel M. Gately. 2021. "Physical Properties of Shellac Material Used for Hot Melt Extrusion with Potential Application in the Pharmaceutical Industry" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3723. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213723
APA StyleYan, G., Cao, Z., Devine, D., Penning, M., & Gately, N. M. (2021). Physical Properties of Shellac Material Used for Hot Melt Extrusion with Potential Application in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Polymers, 13(21), 3723. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213723







