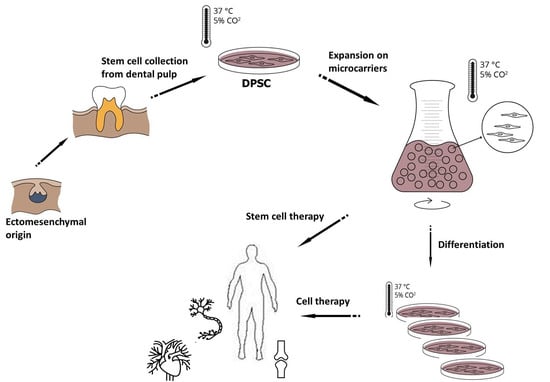
Culturing and Scaling up Stem Cells of Dental Pulp Origin Using Microcarriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Isolation for DPSC Cultures and Cultivation Procedures
2.2. Morphological Observations on DPSCs Cell Cultured on Plastic Culture Dishes
2.3. Immunocytochemical Characterization of DPSCs
2.4. Characterization of Osteogenic Differentiation of DPSCs
2.5. Characterization of Neurogenic Differentiation of DPSCs
2.6. DPSC Culture on Microcarriers under Static Conditions
2.7. Morphological Observations on DPSCs Cell on Microcarriers
2.8. Cell Viability Evaluation
2.9. Scaling-up Experiments under Dynamic Conditions
2.10. Glucose Consumption of DPSCs
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characterization of DPSCs
3.2. Stem Cell Marker Characteristics of DPSCs
3.3. Osteogenic and Neurogenic Differentiation Potential of DPSCs
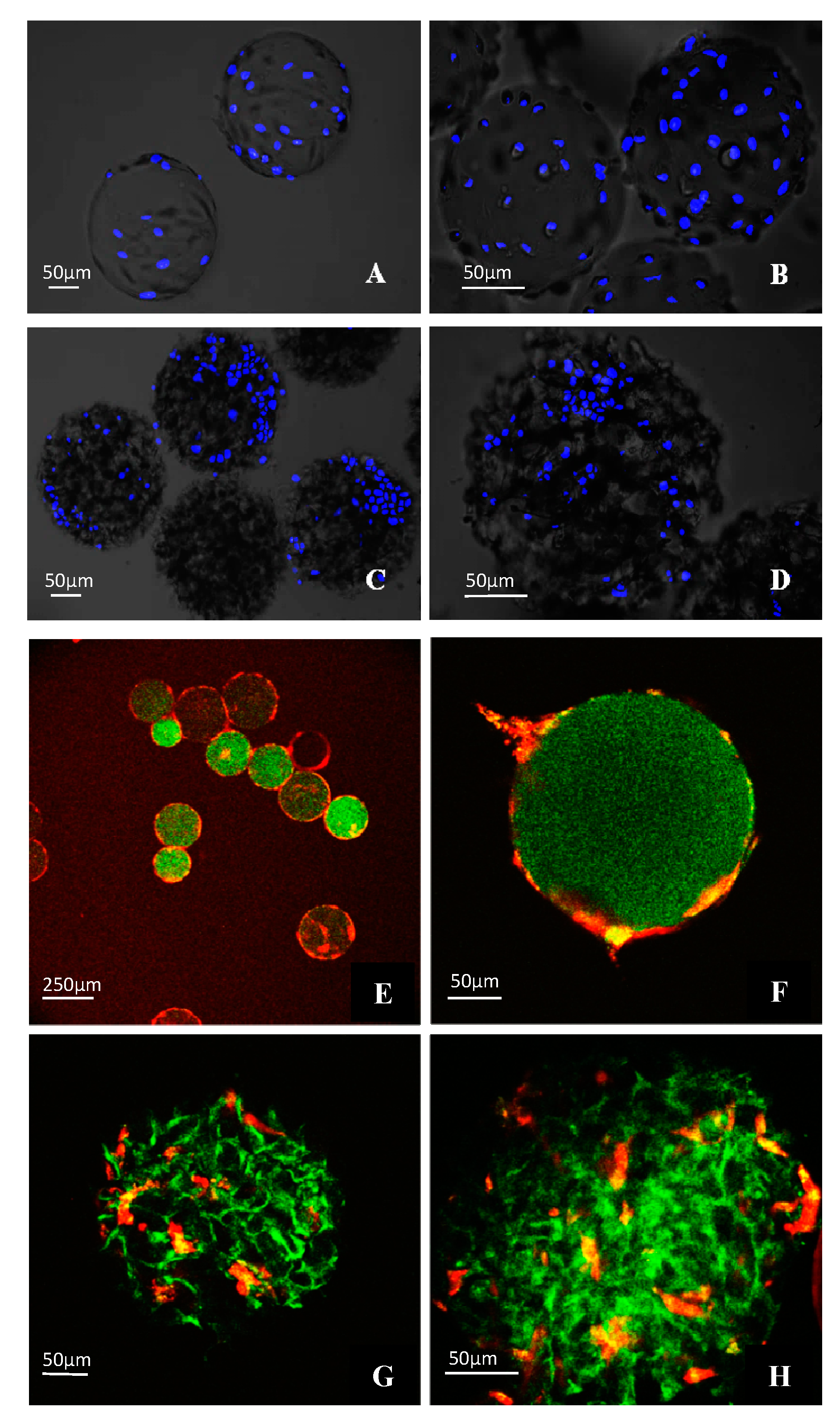
3.4. Morphological Observations on DPSCs Cultivated on Microcarriers
3.5. Viability of DPSCs Cultured under Static Conditions
3.6. Scaling-up Experiments under Dynamic Conditions
3.7. Glucose Consumption by Cultured Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalisserry, E.P.; Nam, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Anil, S. Therapeutic potential of dental stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. 2017, 8, 2041731417702531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, J.R.; Tomar, G.B. Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Applications in Tissue Engineering. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 429–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronthos, S.; Mankani, M.; Brahim, J.; Robey, P.G.; Shi, S. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13625–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, M.; Gronthos, S.; Zhao, M.; Lu, B.; Fisher, L.W.; Robey, P.G.; Shi, S. SHED: Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5807–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, B.M.; Miura, M.; Gronthos, S.; Bartold, P.M.; Batouli, S.; Brahim, J.; Young, M.; Robey, P.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Shi, S. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet 2004, 364, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsczeck, C.; Gotz, W.; Schierholz, J.; Zeilhofer, F.; Kuhn, U.; Mohl, C.; Sippel, C.; Hoffmann, K.H. Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoyama, W.; Liu, Y.; Fang, D.; Yamaza, T.; Seo, B.M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Gronthos, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.T.; Gronthos, S.; Shi, S. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: Their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Jia, L.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wen, Y.; Xu, X. An In Vitro Comparative Study of Multisource Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Dev. 2018, 27, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadar, K.; Kiraly, M.; Porcsalmy, B.; Molnar, B.; Racz, G.Z.; Blazsek, J.; Kallo, K.; Szabo, E.L.; Gera, I.; Gerber, G.; et al. Differentiation potential of stem cells from human dental origin-promise for tissue engineering. J. Physiol. Pharm. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2009, 60, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kiraly, M.; Porcsalmy, B.; Pataki, A.; Kadar, K.; Jelitai, M.; Molnar, B.; Hermann, P.; Gera, I.; Grimm, W.D.; Ganss, B.; et al. Simultaneous PKC and cAMP activation induces differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into functionally active neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perczel-Kovach, K.; Hegedus, O.; Foldes, A.; Sangngoen, T.; Kallo, K.; Steward, M.C.; Varga, G.; Nagy, K.S. STRO-1 positive cell expansion during osteogenic differentiation: A comparative study of three mesenchymal stem cell types of dental origin. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 122, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Pelaez, D.; Dominguez-Bendala, J.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Cheung, H.S. Plasticity of stem cells derived from adult periodontal ligament. Regen. Med. 2009, 4, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, M.F.H.; Zahari, W.; Hashim, S.N.M.; Osman, Z.F.; Chandra, H.; Kannan, T.P.; Noordin, K.; Azlina, A. Angiogenic and osteogenic potentials of dental stem cells in bone tissue engineering. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2018, 8, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Relano-Gines, A.; Lehmann, S.; Deville de Periere, D.; Hirtz, C. Dental stem cells as a promising source for cell therapies in neurological diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 56, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldes, A.; Kadar, K.; Keremi, B.; Zsembery, A.; Gyires, K.; Zoltan, S.Z.; Varga, G. Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Dental Origin-Their Potential for Antiinflammatory and Regenerative Actions in Brain and Gut Damage. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 914–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, S.J.; Byun, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.C.; Park, W.U.; Lee, J.H.; Rho, G.J.; Park, B.W. Immunomodulatory properties and in vivo osteogenesis of human dental stem cells from fresh and cryopreserved dental follicles. Differentiation 2015, 90, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, D.; Chung, W.O.; Johnson, J.D.; Paranjpe, A. Characterization of the Cellular Responses of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells to the Immune System. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiraly, M.; Kadar, K.; Horvathy, D.B.; Nardai, P.; Racz, G.Z.; Lacza, Z.; Varga, G.; Gerber, G. Integration of neuronally predifferentiated human dental pulp stem cells into rat brain in vivo. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G.; Gerber, G. Mesenchymal stem cells of dental origin as promising tools for neuroregeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva Couto, P.; Rotondi, M.C.; Bersenev, A.; Hewitt, C.J.; Nienow, A.W.; Verter, F.; Rafiq, Q.A. Expansion of human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (hMSCs) in bioreactors using microcarriers: Lessons learnt and what the future holds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosh, T.J.; Ylostalo, J.H.; Mohammadipoor, A.; Bazhanov, N.; Coble, K.; Claypool, K.; Lee, R.H.; Choi, H.; Prockop, D.J. Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13724–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Itaka, K.; Ohba, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Chung, U.I.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. 3D spheroid culture system on micropatterned substrates for improved differentiation efficiency of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, I.N.; Boura, J.S.; dos Santos, F.; Andrade, P.Z.; Cardoso, C.M.; Gimble, J.M.; da Silva, C.L.; Cabral, J.M. Human mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord matrix: Successful isolation and ex vivo expansion using serum-/xeno-free culture media. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.K.; Ogando, C.R.; Wang See, C.; Chang, T.Y.; Barabino, G.A. Changes in phenotype and differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells aging in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Eglen, R.M. Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures in Drug Discovery and Development. Slas Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R D 2017, 22, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapalczynska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyla, W.; Zajaczkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Blizniak, R.; Luczewski, L.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures—A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.K.; Chew, Y.K.; Tan, H.Y.; Reuveny, S.; Weng Oh, S.K. Increasing efficiency of human mesenchymal stromal cell culture by optimization of microcarrier concentration and design of medium feed. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, D.S.; Bhuvan, T.; Meagher, L.; Heng, T.S.P. Biological Considerations in Scaling Up Therapeutic Cell Manufacturing. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.T.; Li, J.; Toh, J.P.; Sim, E.J.; Chen, A.K.; Chan, J.K.; Choolani, M.; Reuveny, S.; Birch, W.R.; Oh, S.K. Biodegradable poly-epsilon-caprolactone microcarriers for efficient production of human mesenchymal stromal cells and secreted cytokines in batch and fed-batch bioreactors. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Tomokiyo, A.; Hasegawa, D.; Hamano, S.; Sugii, H.; Maeda, H. Insight into the Role of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Biology 2020, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, B.; Logan, A.; Berry, M.; Leadbeater, W.; Scheven, B.A. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szepesi, A.; Matula, Z.; Szigeti, A.; Varady, G.; Szalma, J.; Szabo, G.; Uher, F.; Sarkadi, B.; Nemet, K. In Vitro Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Different Tissues with a Potential to Promote Complex Bone Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3595941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Midha, S.; Jain, K.G.; Bhaskar, N.; Kaur, A.; Rawat, S.; Giri, S.; Basu, B.; Mohanty, S. Tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cell-dependent osteogenesis in highly porous chitosan-based bone analogs. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsali, A.K.; Pontikoglou, C.; Koutroulakis, D.; Pavlaki, K.I.; Damianaki, A.; Mavroudi, I.; Alpantaki, K.; Kouvidi, E.; Kontakis, G.; Papadaki, H.A. Differential expression of cell cycle and WNT pathway-related genes accounts for differences in the growth and differentiation potential of Wharton’s jelly and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calcat, I.C.S.; Sanz-Nogues, C.; O’Brien, T. When Origin Matters: Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells From Different Sources for Clinical Translation in Kidney Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 728496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuptani, R.S.; Patravale, V.B. Porous microscaffolds for 3D culture of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Z.; Kim, H.W. Porous microcarrier-enabled three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes for cartilage engineering: A feasibility study. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 13, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, S.; Ni, L.; Ma, P.X. Nanofibrous spongy microspheres for the delivery of hypoxia-primed human dental pulp stem cells to regenerate vascularized dental pulp. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, C.; Olmos, E.; Balandras, F.; Tran, N.; Chevalot, I.; Guedon, E.; Marc, A. Investigation of growth conditions for the expansion of porcine mesenchymal stem cells on microcarriers in stirred cultures. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemoun, P.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S.; Rue, J.; Farges, J.C.; Gennero, I.; Conte-Auriol, F.; Briand-Mesange, F.; Gadelorge, M.; Arzate, H.; Narayanan, A.S.; et al. Human dental follicle cells acquire cementoblast features under stimulation by BMP-2/-7 and enamel matrix derivatives (EMD) in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 329, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Matsubara, K.; Sakai, K.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K.; Ueda, M.; Yamamoto, A. Dopaminergic differentiation of stem cells from human deciduous teeth and their therapeutic benefits for Parkinsonian rats. Brain Res. 2015, 1613, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Lin, S.Z.; Li, Y.S.; Harn, H.J.; Chiou, T.W. Functional cells cultured on microcarriers for use in regenerative medicine research. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Bartold, P.M.; Miura, M.; Seo, B.M.; Robey, P.G.; Gronthos, S. The efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells to regenerate and repair dental structures. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2005, 8, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakopoulou, A.; Leyhausen, G.; Yolk, J.; Tsiftsoglou, A.; Garefis, P.; Koidis, P.; Geurtsen, W. Comparative analysis of in vitro osteo/odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and stem cells from the apical papilla (SCAP). Arch. Oral Biol. 2011, 56, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroos, B.; Maenpaa, K.; Ylikomi, T.; Oja, H.; Suuronen, R.; Miettinen, S. Characterisation of human dental stem cells and buccal mucosa fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.V.; Passos, S.T.; Campos, T.M.; Bernardi, L.; Vilas-Boas, D.S.; Nor, J.E.; Telles, P.D.; Nascimento, I.L. The dental pulp stem cell niche based on aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winning, L.; El Karim, I.A.; Lundy, F.T. A Comparative Analysis of the Osteogenic Potential of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, S.R.; Orellana, M.D.; Mizukami, A.; Fernandes, T.R.; Fontes, A.M.; Suazo, C.A.; Oliveira, V.C.; Covas, D.T.; Swiech, K. Growth and functional harvesting of human mesenchymal stromal cells cultured on a microcarrier-based system. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, C.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, X. A review of protein adsorption on bioceramics. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, F.; Smith, J.R.; Leber, J.; Salzig, D.; Czermak, P.; Weiss, M.L. Manufacturing of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Microcarriers in a Dynamic System for Clinical Use. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4834616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.K.; Reuveny, S.; Oh, S.K. Application of human mesenchymal and pluripotent stem cell microcarrier cultures in cellular therapy: Achievements and future direction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafiq, Q.A.; Coopman, K.; Hewitt, C.J. Scale-up of human mesenchymal stem cell culture: Current technologies and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubiere, C.; Sion, C.; De Isla, N.; Reppel, L.; Guedon, E.; Chevalot, I.; Olmos, E. Impact of the type of microcarrier and agitation modes on the expansion performances of mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.F.Y.; Choolani, M.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Reuveny, S.; Oh, S.K.W. Critical attributes of human early mesenchymal stromal cell-laden microcarrier constructs for improved chondrogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chui, C.Y.; Odeleye, A.; Nguyen, L.; Kasoju, N.; Soliman, E.; Ye, H. Electrosprayed genipin cross-linked alginate-chitosan microcarriers for ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellor, L.F.; Baker, T.L.; Brown, R.J.; Catlin, L.W.; Oxford, J.T. Optimal 3D culture of primary articular chondrocytes for use in the rotating wall vessel bioreactor. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2014, 85, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Mei, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, W.S. Fabrication of viable centimeter-sized 3D tissue constructs with microchannel conduits for improved tissue properties through assembly of cell-laden microbeads. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 8, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Niu, Y. Silencing integrin alpha6 enhances the pluripotency-differentiation transition in human dental pulp stem cells. Oral Dis. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Z.; Kim, H.W. Co-culture of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Endothelial Cells Using Porous Biopolymer Microcarriers: A Feasibility Study for Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 14, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, S.; Kang, N.Y.; Subramanian, S.; Nandi, T.; Sudhagar, S.; Xing, Q.; Tong, G.J.; Chen, A.K.; Srijaya, T.C.; Tan, P.; et al. Novel live cell fluorescent probe for human-induced pluripotent stem cells highlights early reprogramming population. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurashina, Y.; Imashiro, C.; Hirano, M.; Kuribara, T.; Totani, K.; Ohnuma, K.; Friend, J.; Takemura, K. Enzyme-free release of adhered cells from standard culture dishes using intermittent ultrasonic traveling waves. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnar, K.; Voniatis, C.; Feher, D.; Szabo, G.; Varga, R.; Reiniger, L.; Juriga, D.; Kiss, Z.; Krisch, E.; Weber, G.; et al. Poly(amino acid) based fibrous membranes with tuneable in vivo biodegradation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, K.; Varga, R.; Jozsa, B.; Barczikai, D.; Krisch, E.; Nagy, K.S.; Varga, G.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A.; Puskas, J.E. Investigation of the Cytotoxicity of Electrospun Polysuccinimide-Based Fiber Mats. Polymers 2020, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juriga, D.; Sipos, E.; Hegedus, O.; Varga, G.; Zrinyi, M.; Nagy, K.S.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A. Fully amino acid-based hydrogel as potential scaffold for cell culturing and drug delivery. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, O.; Juriga, D.; Sipos, E.; Voniatis, C.; Juhasz, A.; Idrissi, A.; Zrinyi, M.; Varga, G.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A.; Nagy, K.S. Free thiol groups on poly(aspartamide) based hydrogels facilitate tooth-derived progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juriga, D.; Nagy, K.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A.; Perczel-Kovach, K.; Chen, Y.M.; Varga, G.; Zrinyi, M. Biodegradation and Osteosarcoma Cell Cultivation on Poly(aspartic acid) Based Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23463–23476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Földes, A.; Reider, H.; Varga, A.; Nagy, K.S.; Perczel-Kovach, K.; Kis-Petik, K.; DenBesten, P.; Ballagi, A.; Varga, G. Culturing and Scaling up Stem Cells of Dental Pulp Origin Using Microcarriers. Polymers 2021, 13, 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223951
Földes A, Reider H, Varga A, Nagy KS, Perczel-Kovach K, Kis-Petik K, DenBesten P, Ballagi A, Varga G. Culturing and Scaling up Stem Cells of Dental Pulp Origin Using Microcarriers. Polymers. 2021; 13(22):3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223951
Chicago/Turabian StyleFöldes, Anna, Hajnalka Reider, Anita Varga, Krisztina S. Nagy, Katalin Perczel-Kovach, Katalin Kis-Petik, Pamela DenBesten, András Ballagi, and Gábor Varga. 2021. "Culturing and Scaling up Stem Cells of Dental Pulp Origin Using Microcarriers" Polymers 13, no. 22: 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223951
APA StyleFöldes, A., Reider, H., Varga, A., Nagy, K. S., Perczel-Kovach, K., Kis-Petik, K., DenBesten, P., Ballagi, A., & Varga, G. (2021). Culturing and Scaling up Stem Cells of Dental Pulp Origin Using Microcarriers. Polymers, 13(22), 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223951