Environmentally Friendly Polyvinyl Alcohol−Alginate/Bentonite Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods or Experimental
2.1. Materials
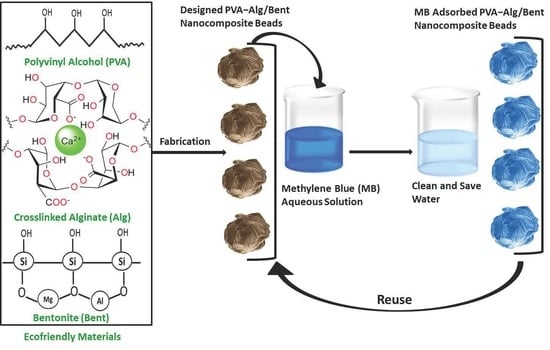
2.2. Preparation of Semi-IPN Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads
2.3. Characterization Methods
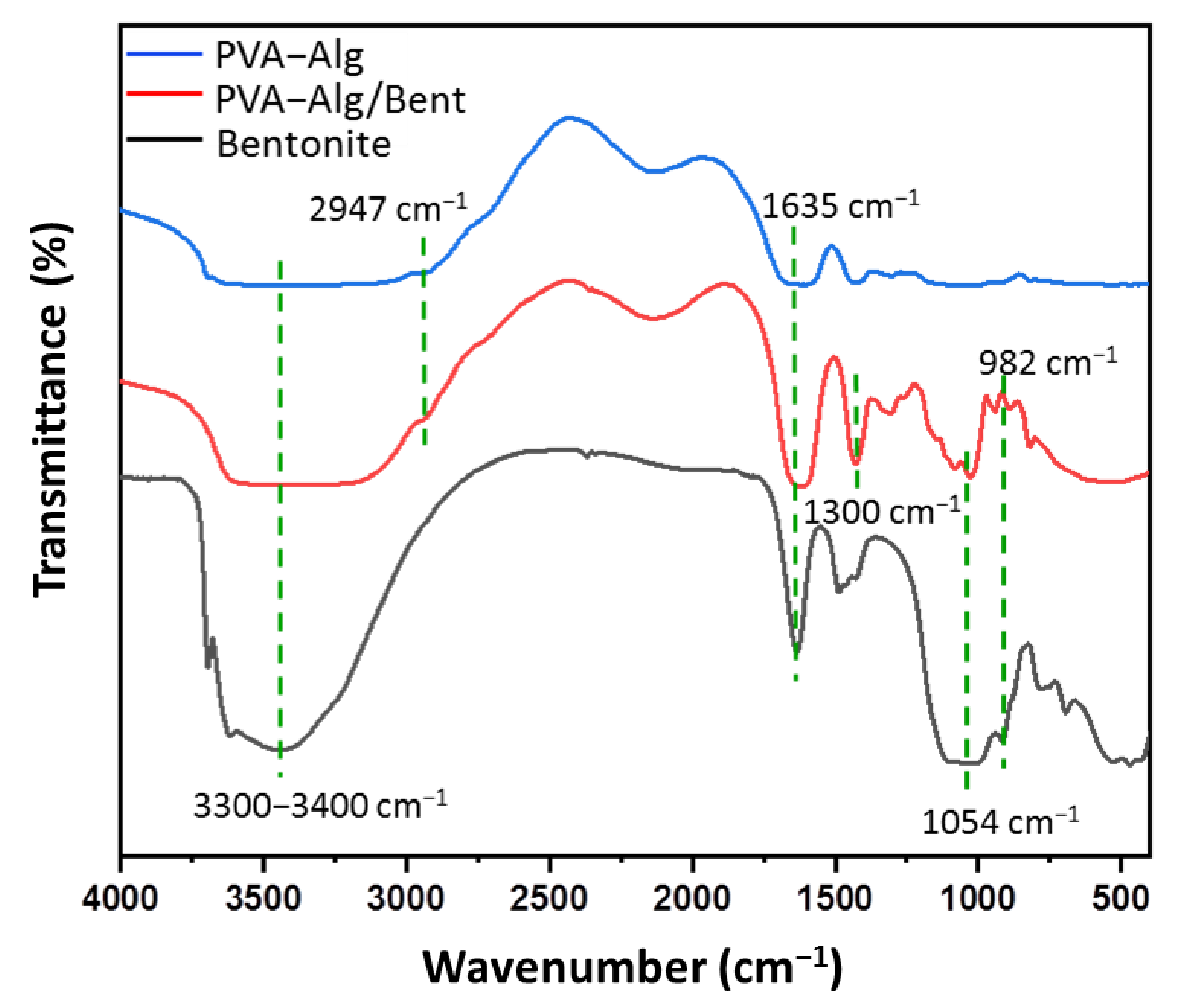
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
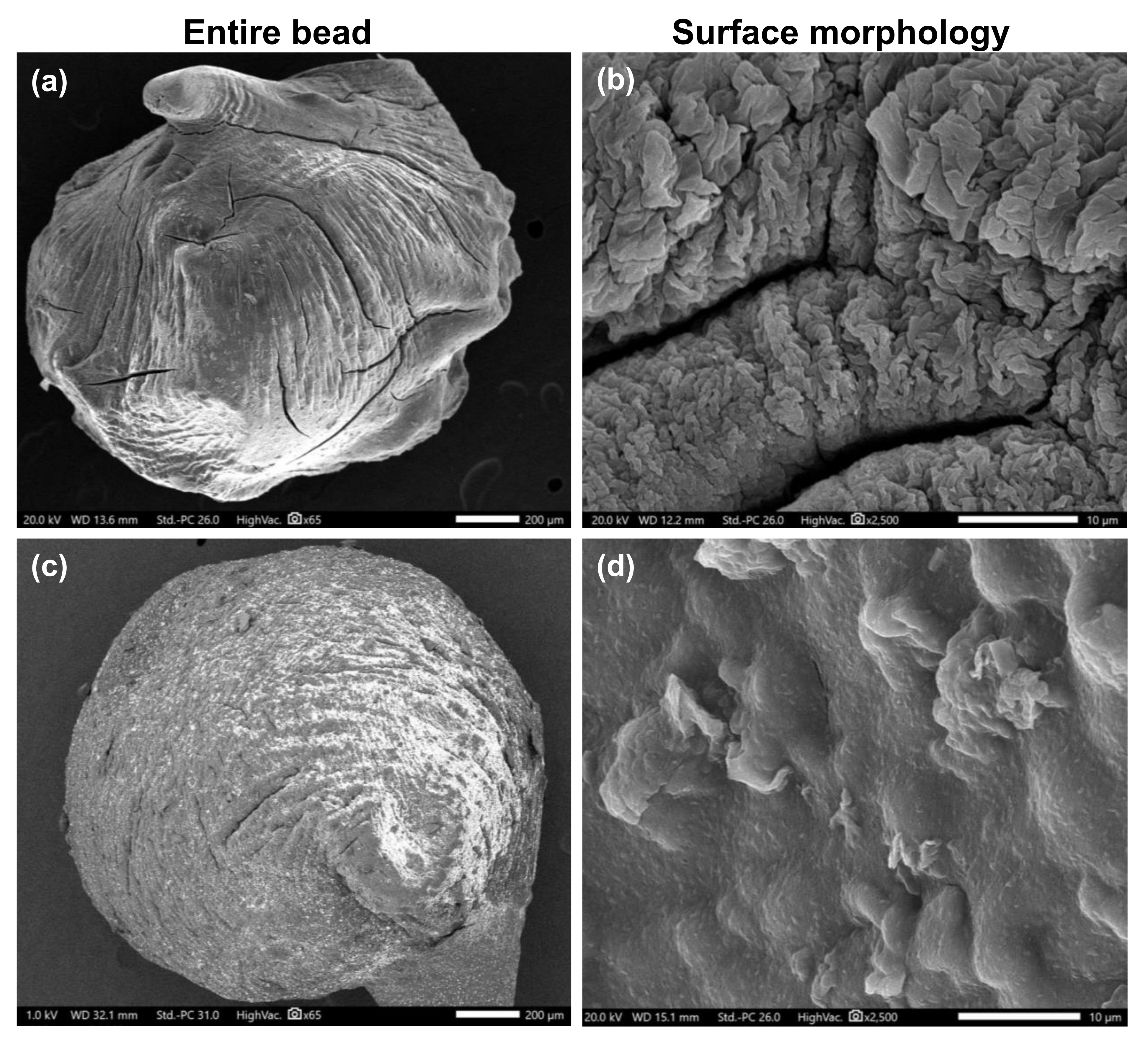
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
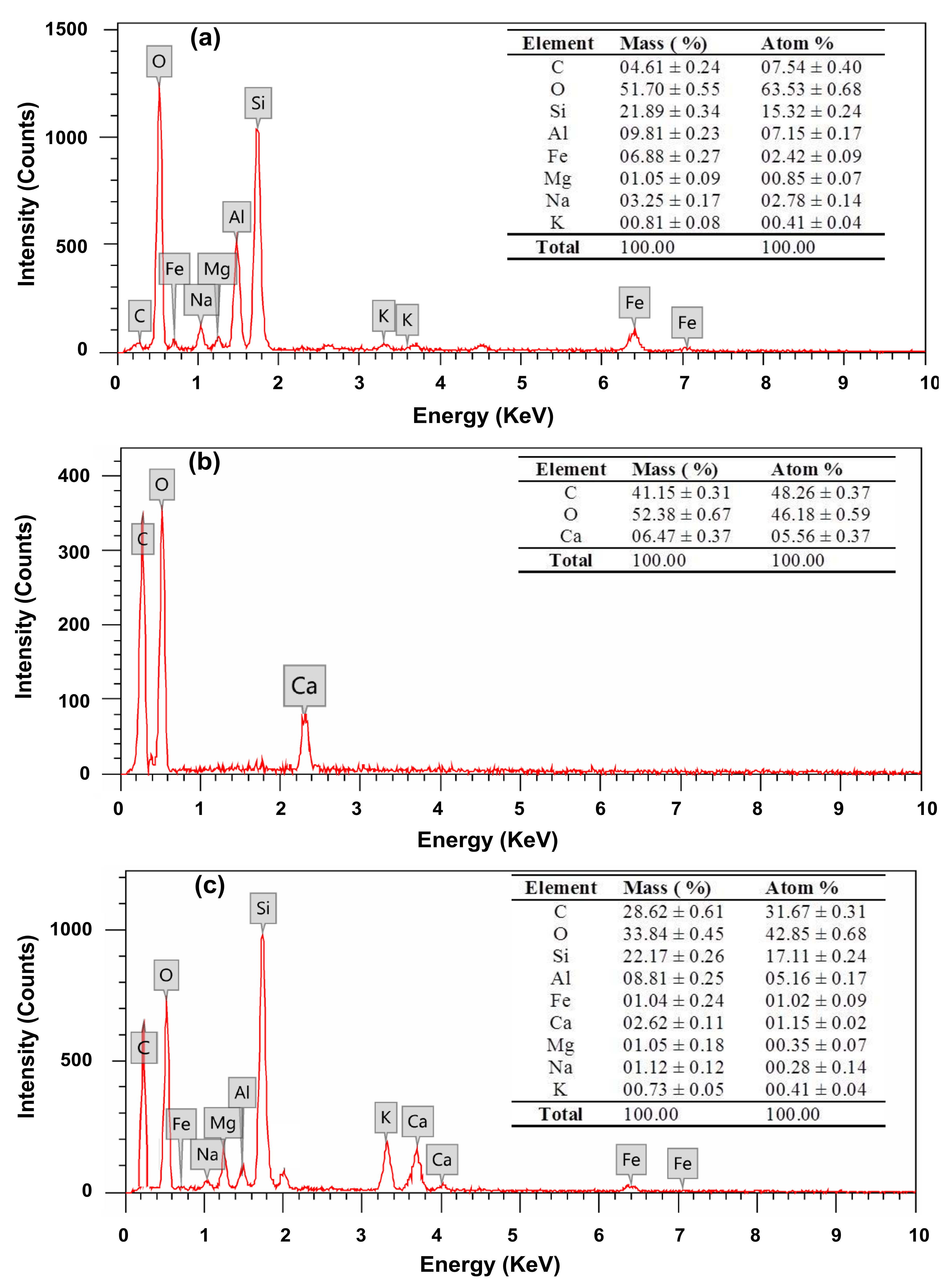
2.3.3. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
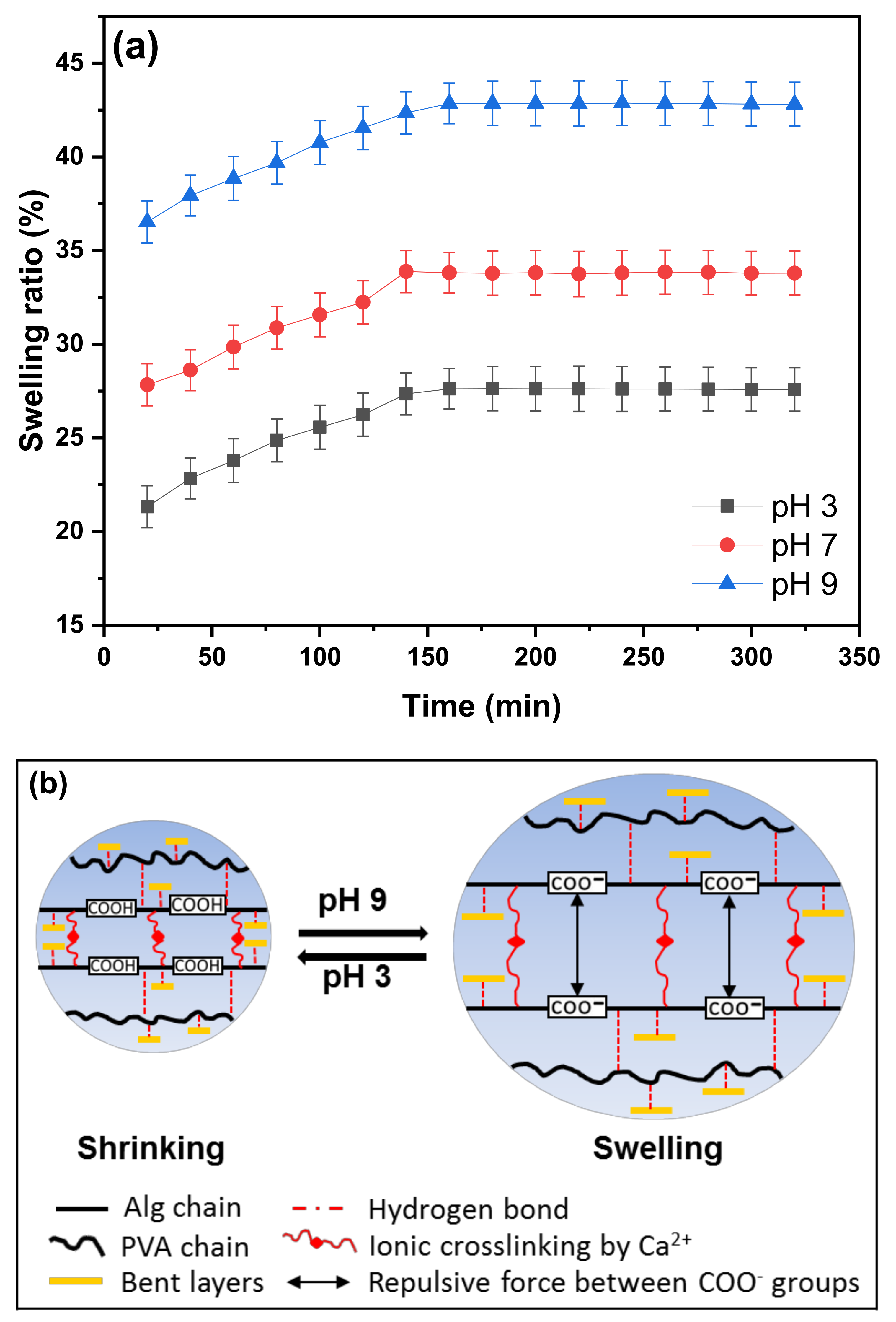
2.3.4. Swelling Behavior
2.4. MB Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Adsorbent Reusability Study
2.6. Adsorbent Isotherms
2.7. Adsorbent Kinetics
2.8. Adsorbent Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design Rationale of the Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads
3.2. Structure and Chemical Composition
3.3. Morphological Observation
3.4. Swelling Behavior
3.5. Adsorption Studies of MB
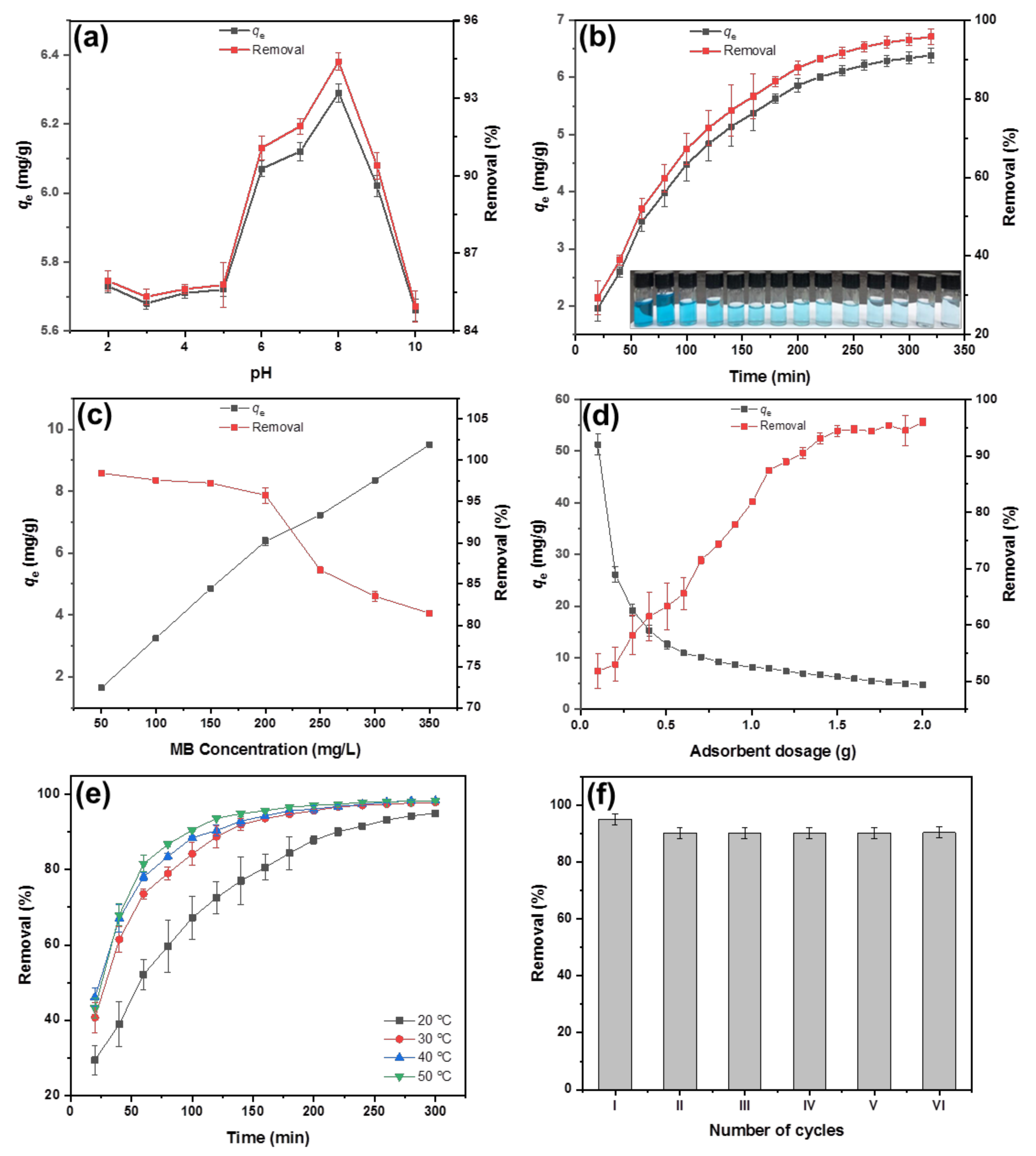
3.5.1. Effect of Solution pH
3.5.2. Effect of Contact Time
3.5.3. Effect of Initial MB Concentration
3.5.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.5.5. Effect of Temperature
3.5.6. Reusability of Adsorbent
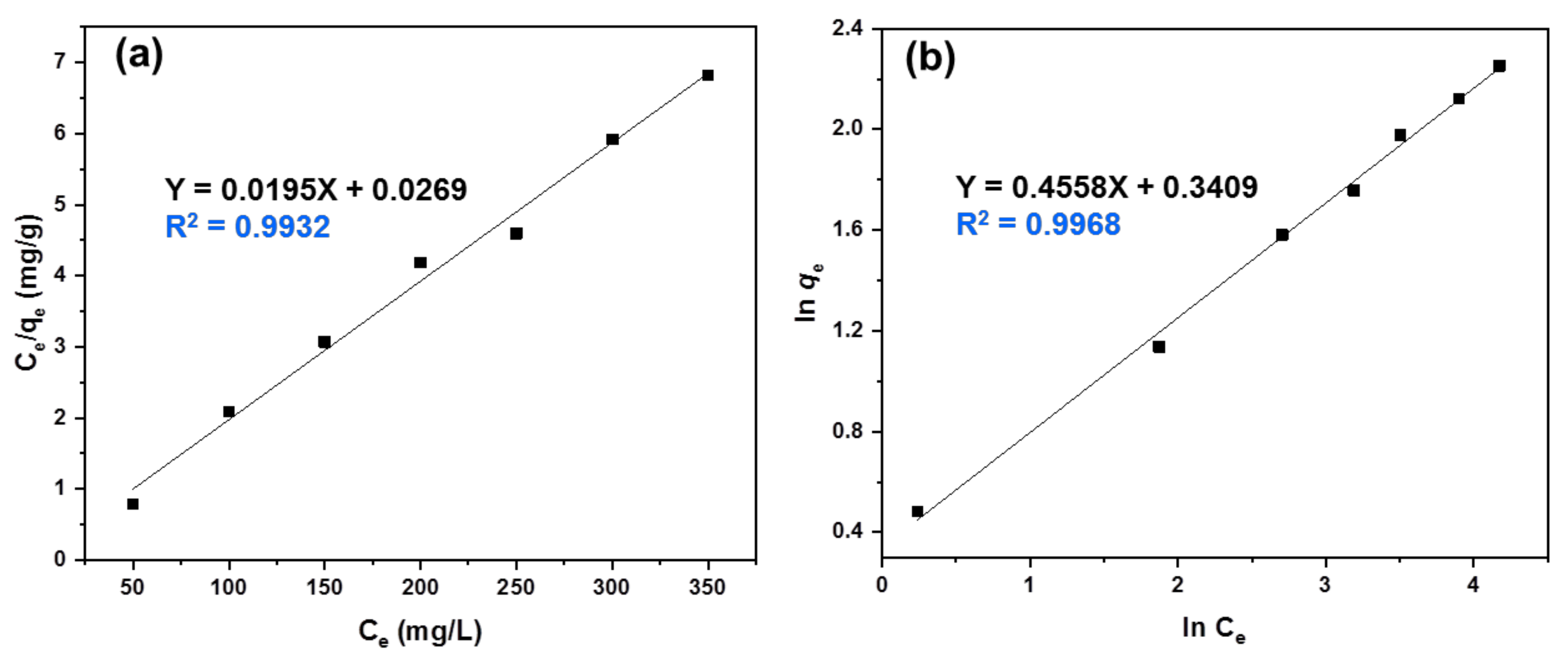
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm Study
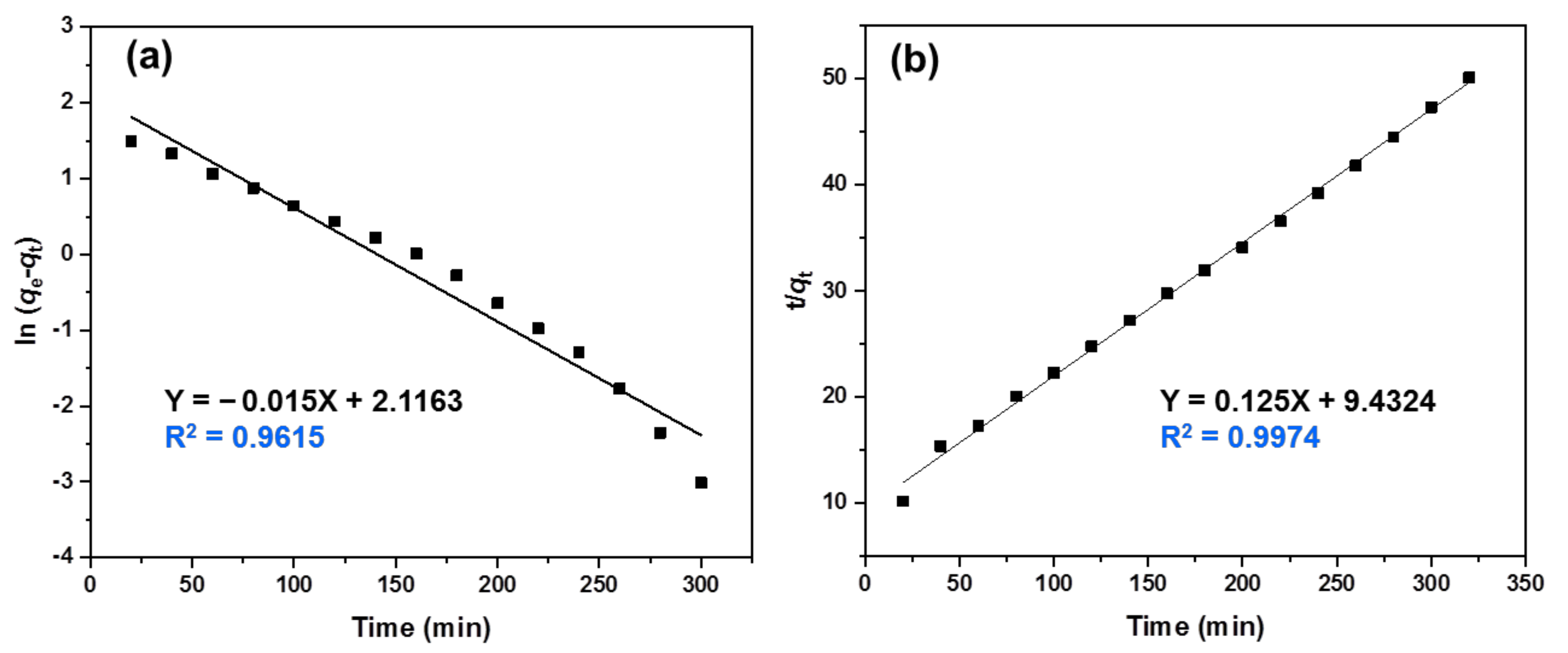
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics Study
3.8. Adsorption Mechanism of Cationic MB Dye
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Mamdouh, I.M.; El-Monaem, E.M.A.; El-Subruiti, G.M. Highly Efficient Removal for Methylene Blue and Cu2+ onto UiO-66 Metal–Organic Framework/Carboxylated Graphene Oxide-Incorporated Sodium Alginate Beads. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23528–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-J.; Li, M.-F.; Singh, S.K. Manganese-modified lignin biochar as adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusegun, S.J.; Freitas, E.T.F.; Lara, L.R.S.; Mohallem, N.D.S. Synergistic effect of a spinel ferrite on the adsorption capacity of nano bio-silica for the removal of methylene blue. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Ni, W.-X.; Li, B. Porous Organic Polymer Synthesized by Green Diazo-Coupling Reaction for Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, S.; Stefanello, N.; Sulkovski, A.A.; Foletto, E.L. Preparation of TiO2 supported on MDF biochar for simultaneous removal of methylene blue by adsorption and photocatalysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 95, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Jha, M.K.; Ghimire, J.; Koirala, A.R.; Shrestha, R.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Pant, B.; Park, M.; Pant, H.R. Decoration of Zinc Oxide Nanorods into the Surface of Activated Carbon Obtained from Agricultural Waste for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Materials 2020, 13, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, F.A.; Guevara, M.; Tene, T.; Angamarca, P.; Molina, R.; Valarezo, A.; Salguero, O.; Gomez, C.V.; Arias, M.; Caputi, L.S. The Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Eco-Friendly Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayl, A.A.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; El-Shanshory, A.A.; Soliman, H.M.A.; Akl, M.A.; Aly, H.F. A novel method for highly effective removal and determination of binary cationic dyes in aqueous media using a cotton–graphene oxide composite. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7791–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duhan, M.; Kaur, R. Nano-Structured Polyaniline as a Potential Adsorbent for Methylene Blue Dye Removal from Effluent. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, F.A.; Ali Alghamdi, A.; Alanazi, H.S.; Alsyahi, A.A.; Ahmad, N. Photocatalytic Degradation of the Light Sensitive Organic Dyes: Methylene Blue and Rose Bengal by Using Urea Derived g-C3N4/ZnO Nanocomposites. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, G.; Arputhalatha, A.; Kannan, K.; Lakkaboyana, S.; Hanafiah, M.; Kumar, V.; Marella, R. Current Trends in the Application of Nanomaterials for the Removal of Pollutants from Industrial Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Kasim, N.A.M.; Knight, V.F.; Misenan, M.S.M.; Janudin, N.; Shah, N.A.A.; Kasim, N.; Yusoff, W.Y.W.; Noor, S.A.M.; Jamal, S.H.; et al. Nanocellulose: A bioadsorbent for chemical contaminant remediation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 7347–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.; Bruno, R.; Ferrando-Soria, J.; Armentano, D.; Pardo, E. Metal–organic framework technologies for water remediation: Towards a sustainable ecosystem. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4912–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, P.; Bharti, M.K.; Chalia, S.; Dhar, R.; Ravelo, B.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A. Recent advances in synthesis, characterization, and applications of nanoparticles for contaminated water treatment—A review. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1526–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneez, M.; Hurel, C. A review on the potential uses of red mud as amendment for pollution control in environmental media. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22106–22125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ranjbari, S.; Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Orooji, Y.; Alizadeh, M.; Karimi, F.; Salmanpour, S.; Rouhi, J.; Sillanpää, M.; et al. Novel 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide impregnated chitosan hydrogel beads nanostructure as an efficient nanobio-adsorbent for cationic dye removal: Kinetic study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, M.A.; Shakeri, A.; Salehi, H.; Razavi, S.R.; Salari, N. The effect of nanosheets on polymer hydrogels performance in Rhodamine B dye removal by forward osmosis process. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 44, 102351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hao, R.; Xu, H.; Huang, C. Rapid adsorption and reductive degradation of Naphthol Green B from aqueous solution by Polypyrrole/Attapulgite composites supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, Z.N.; Zhou, W.; Lawan, I.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Z. An overview of chlorophenols as con-taminants and their removal from wastewater by adsorption: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Cui, F.; Xing, B. Theoretical insight into the adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Sheng, L. Preparation of straw activated carbon and its application in wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, G.; Hai, A.; Rambabu, K.; Savariraj, D.; Ibrahim, Y.; Banat, F. The fabrication of activated carbon and metal-carbide 2D framework-based asymmetric electrodes for the capacitive deionization of Cr (vi) ions toward industrial wastewater re-mediation. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouiya, M.; Bouazizi, A.; Abourriche, A.; Benhammou, A.; El Hafiane, Y.; Ouammou, M.; Abouliatim, Y.; Younssi, S.A.; Smith, A.; Hannache, H. Fabrication and characterization of a ceramic membrane from clay and banana peel powder: Application to industrial wastewater treatment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Salleh, N.M.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T.; Ali, M.H.; Puteh, M.H.; Ismail, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. The adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) in aqueous solution by novel natural zeolite based hollow fibre ceramic membrane. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, M.; Kakkar, R. Use of metal oxides for the adsorptive removal of toxic organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Torri, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Dye removal by biosorption using cross-linked chitosan-based hydrogels. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakdel, P.M.; Peighambardoust, S.J. Review on recent progress in chitosan-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Hydrogel applications for adsorption of contaminants in water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24569–24599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, P.C.; Perez, J.V.D.; Nadres, E.T.; Nannapaneni, R.G.; Krakowiak, K.J.; Rodrigues, D.F. Graphene oxide nanocom-posite hydrogel beads for removal of selenium in contaminated water. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, C.; Pospiech, D.; Allertz, P.J.; Müller, M.; Salchert, K.; Hommel, R. Chemical Design of Hydrogels with Immobilized Laccase for the Reduction of Persistent Trace Compounds in Wastewater. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.; Gupta, V.K.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sillanpää, M.; Megiel, E. The role of nanomaterials as effective adsorbents and their applications in wastewater treatment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalla, A.H.; Yaseen, Z.; Bhat, M.A.; Rangreez, T.A.; Maswal, M. Recent review for removal of metal ions by hydrogels. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, N.C. Water Uptake Kinetics and Control Release of Agrochemical Fertilizers from Nanoclay-Assisted Semi-interpenetrating Sodium Acrylate-Based Hydrogel. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Das, T.K.; Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; Bose, M.; Mondal, M.; Das, A.K.; Das, N.C. Acoustic cavitation assisted destratified clay tactoid reinforced in situ elastomer-mimetic semi-IPN hydrogel for catalytic and bactericidal application. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-M.; Yu, H.-Y.; Wang, D.-C.; Mao, Z.-H.; Yao, J.; Tam, K.C. Facile and Green Synthesis of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals as Efficient Adsorbents in Wastewater Treatments. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18067–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, M.; Javanbakht, V. Methylene Blue removal from aqueous solution by a biocomposite synthesized from sodium alginate and wastes of oil extraction from almond peanut. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Jacobs, N.V.; Luyt, A.S. Nanofibrous alginate membrane coated with cellulose nanowhiskers for water puri-fication. Cellulose 2018, 25, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, X.; Liao, P.; Rong, H.; Zhang, T.C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Meng, X. Phosphorus removal and recovery from water with macroporous bead adsorbent constituted of alginate-Zr4+ and PNIPAM-interpenetrated networks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.F.; Ching, Y.C.; Muhamad, F.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Hai, N.D.; Hassan, C.R.C. Adsorption of Dyes Using Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and PVA-Based Polymer Composite Adsorbents: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 775–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Lin, D.; Saroj, D.P.; Ali, M. Development and application of novel bio-magnetic membrane capsules for the removal of the cationic dye malachite green in wastewater treatment. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 3625–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Rozhina, E.; Konnova, S.; Kryuchkova, M.; Khaertdinov, N.; Fakhrullin, R. Organic-nanoclay composite materials as removal agents for environmental decontamination. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40553–40564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Daneshvar e Asl, S.; Vossoughi, M.; Simchi, A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Green Electrospun Membranes Based on Chi-tosan/Amino-Functionalized Nanoclay Composite Fibers for Cationic Dye Removal: Synthesis and Kinetic Studies. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 10816–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.V.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.D.A. Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite. Materials 2020, 13, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigorria, E.; Cano, L.A.; Sanchez, L.M.; Alvarez, V.A.; Ollier, R.P. Bentonite-composite polyvinyl alcohol/alginate hydrogel beads: Preparation, characterization and their use as arsenic removal devices. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvulunov, Y.; Radian, A. Alginate Composites Reinforced with Polyelectrolytes and Clay for Improved Adsorption and Bio-remediation of Formaldehyde from Water. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Fattah, A.; Mansour, A. Viscoelasticity, mechanical properties, and in vitro biodegradation of injectable chitosan-poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/nanohydroxyapatite composite hydrogel. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadi, S.; Eris, S.; Azizian, S. Alginate-Based Hydrogel Beads as a Biocompatible and Efficient Adsorbent for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15140–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.-B.; Yu, T.-J.; Lee, H.-C.; Ma, C.-M. Using Rice Bran Hydrogel Beads to Remove Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Susan, A.B.H. Cationic Dye Removal Using Novel Magnetic/Activated Charcoal/β-Cyclodextrin/Alginate Polymer Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravi; Pandey, L.M. Enhanced adsorption capacity of designed bentonite and alginate beads for the effective removal of methylene blue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wu, L.; Su, T.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. Polysaccharide-based cationic hydrogels for dye adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merakchi, A.; Bettayeb, S.; Drouiche, N.; Adour, L.; Lounici, H. Cross-linking and modification of sodium alginate biopolymer for dye removal in aqueous solution. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 3535–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, A.; Boukerroui, A. Alginate-bentonite beads for efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, T.; Ibarra-Galvan, V.; Song, S. Methylene blue removal from water using the hydrogel beads of poly(vinyl alcohol)-sodium alginate-chitosan-montmorillonite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Niu, F.; Lang, W.; Xia, M. Highly efficient flame-retardant and low-smoke-toxicity poly (vinyl alco-hol)/alginate/montmorillonite composite aerogels by two-step crosslinking strategy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.D.S.; de Moura, M.R.; Glenn, G.M.; Aouada, F.A. Thermal, microstructural, and spectroscopic analysis of Ca2+ alginate/clay nanocomposite hydrogel beads. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Dong, K.; Wei, G.; Yao, J. Facile preparation of tannic acid–poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hy-drogel beads for methylene blue removal from simulated solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7523–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Wang, R.; Wang, F.; Bai, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Jiao, T. Fabrication of Hydrogels via Host–Guest Polymers as Highly Efficient Organic Dye Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5470–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belhouchat, N.; Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Viseras, C. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Wu, L.; Pan, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, M.; Gao, R.; Qi, X.; Dong, W. Pullulan-derived nanocomposite hydrogels for wastewater remediation: Synthesis and characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 542, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Xu, J.-Y.; Yang, X.-L. MXene/sodium alginate gel beads for adsorption of methylene blue. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fu, K.; Yu, D.; Hristovski, K.D.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Review of advances in engineering nanomaterial ad-sorbents for metal removal and recovery from water: Synthesis and microstructure impacts. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 623–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yu, D.; Hristovski, K.D.; Fu, K.; Shen, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Critical Review of Advances in Engineering Nanomaterial Adsorbents for Metal Removal and Recovery from Water: Mechanism Identification and Engineering Design. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4287–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Ni, H. Surface functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyamide for efficient adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.; Mansur, A.A.; Mansur, H.S.; de Jesus, A.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; Chagas, P.; de Oliveira, L.C. Eco-friendly and biocompatible cross-linked Carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels as adsorbents for the removal of organic dye pollutants for en-vironmental applications. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2856–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Omer, A.; Ouyang, X. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellu-lose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.; Bui, L.T.; Dinh, T.T.; Le, D.H.; Huynh, C.D.; Trinh, A.X. Graphene oxide/Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite: A re-coverable and recyclable adsorbent for organic dyes removal. Application to methylene blue. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 35701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by a novel PVA/CMC/halloysite nanoclay bio composite: Characterization, kinetics, isotherm and antibacterial properties. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, B.; Cao, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of the novel hydrogel based on waste corn stalk for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wu, X.L.; Zhong, S.; Lin, H.; Chen, J.R. Biocompatible G-Fe3O4/CA nanocomposites for the removal of methylene blue. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrakchi, F.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-linked chitosan/sepiolite composite for the adsorption of meth-ylene blue and reactive orange 16. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Ollier, R.P.; Alvarez, V.A. Sorption behavior of polyvinyl alcohol/bentonite hydrogels for dyes removal. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Ray, J.; Mondal, B.; Tripathy, T. Efficient and selective removal of cationic organic dyes from their aqueous solutions by a nanocomposite hydrogel, katira gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid-co-N, N-dimethylacrylamide)@bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 173, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Adsorbent | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Activated charcoal/β-cyclodextrin/Alg hydrogel beads | 10.63 | [49] |
| PVA/cyclodextrin-modified poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel | 23.02 | [58] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)-based hydrogel | 25.00 | [65] |
| CMC/k-carrageenan/montmorillonite (MMT) beads | 12.50 | [66] |
| Graphene oxide (GO)/Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite | 30.10 | [67] |
| PVA/CMC/halloysite nanoclay membrane | 40.60 | [68] |
| Corn stalk/MMT composite hydrogel | 49.01 | [69] |
| GO/Fe3O4/Alg nanocomposite | 37.04 | [70] |
| Chitosan/sepiolite composite | 40.98 | [71] |
| PVA/Bent hydrogel | 27.90 | [72] |
| PVA–Alg/Bent nanocomposite hydrogel beads | 51.37 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljar, M.A.A.; Rashdan, S.; Abd El-Fattah, A. Environmentally Friendly Polyvinyl Alcohol−Alginate/Bentonite Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2021, 13, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13224000
Aljar MAA, Rashdan S, Abd El-Fattah A. Environmentally Friendly Polyvinyl Alcohol−Alginate/Bentonite Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Polymers. 2021; 13(22):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13224000
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljar, Mona A. Aziz, Suad Rashdan, and Ahmed Abd El-Fattah. 2021. "Environmentally Friendly Polyvinyl Alcohol−Alginate/Bentonite Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution" Polymers 13, no. 22: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13224000
APA StyleAljar, M. A. A., Rashdan, S., & Abd El-Fattah, A. (2021). Environmentally Friendly Polyvinyl Alcohol−Alginate/Bentonite Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Polymers, 13(22), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13224000