Evaluation of the Performance and Ductility Index of Concrete Structures Using Advanced Composite Material Strengthening Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
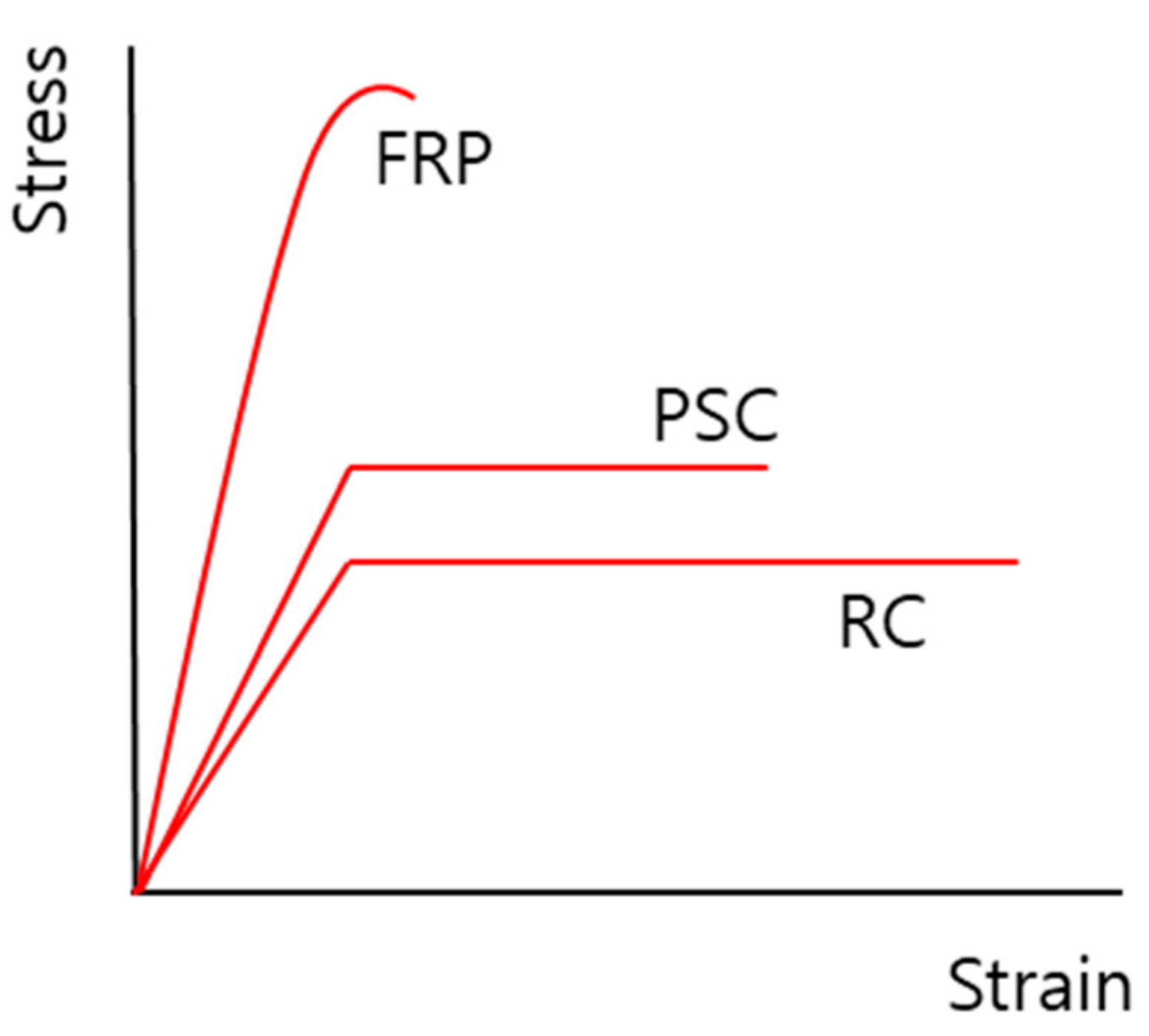
2.1. Advanced Composite Materials
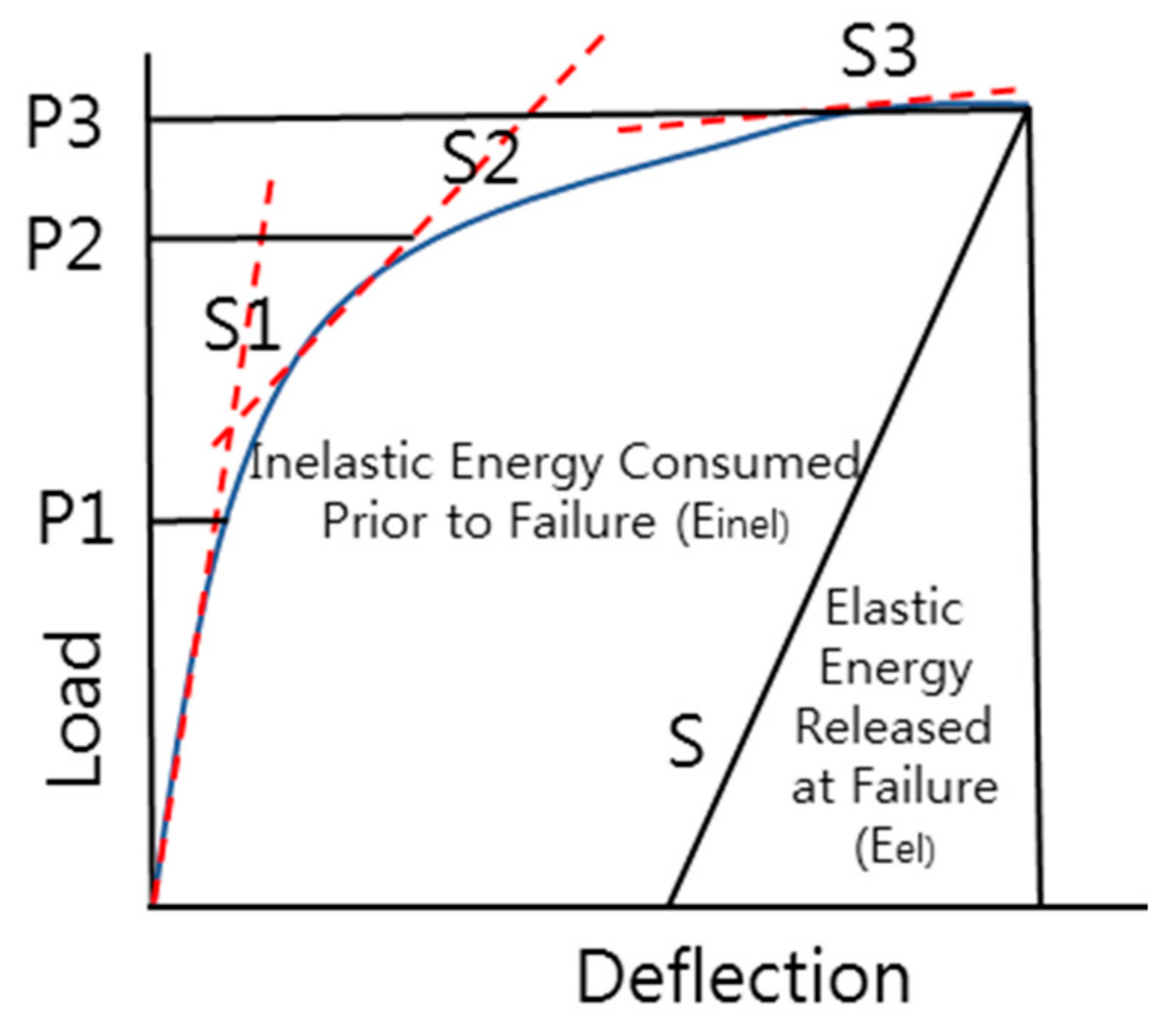
2.2. Ductility Index Theory
3. Ductility Index Evaluation
3.1. Prestressed Concrete (PSC) Structure
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Ductility Index Change Rates of PSC and RC Structures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, H.M.; Lee, J.H. Reinforced Concrete, 11th ed.; Dong Myeong: Paju City, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.M. Prestressed Concrete, 10th ed.; Dong Myeong: Paju City, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, P.K.; Paulo, J.M.M. Concrete (Microstructure, Properties, and Materials), 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sidney, M.; Francis, Y.; David, D. Concrete, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bakis, C.E.; Bank, L.C.; Brown, V.; Cosenza, E.; Davalos, J.F.; Lesko, J.J.; Triantafillou, T.C. Fiber-reinforced polymer composites for construction—State-of-the-art review. J. Compos. Constr. 2002, 6, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Pham, T.M.; Sichembe, H.; Chen, L.; Hao, H. Experimental study of flexural behaviour of RC beams strengthened by longitudinal and U-shaped basalt FRP sheet. Compos. B Eng. 2018, 134, 114–126. [Google Scholar]
- Toutanji, H.; Ortiz, G. The effect of surface preparation on the bond interface between FRP sheets and concrete members. Compos. Struct. 2001, 53, 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, L.; Fang, Q.; Wang, T. Blast resistance of externally prestressed RC Beam: A theoretical approach. Eng. Struct. 2019, 179, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Singh, J. A Review on external prestressing in concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil, R.; Manisekar, R. Ultimate flexural behaviour of externally prestressed new beams and distressed beams. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 461–484. [Google Scholar]
- Pisani, M.A. Behaviour under long-term loading of externally prestressed concrete beams. Eng. Struct. 2018, 160, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.K.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.H.J.; Chu, Y.S.; Yu, E. Performance based evaluation of carbonation resistance of concrete according to various curing conditions from climate change effect. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2017, 11, 687–700. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Jung, W.T.; Chung, W. Post-tension near-surface mounted strengthening system for reinforced concrete beams with changes in concrete condition. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2019, 161, 514–529. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, M.R.; Sena-Cruz, J.M.; Neves, L.A. A review on the bond behavior of FRP NSM systems in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Bilotta, A.; Ceroni, F.; Nigro, E.; Pecce, M. Efficiency of CFRP NSM strips and EBR plates for flexural strengthening of RC beams and loading pattern influence. Compos. Struct. 2015, 124, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, N.H.; Lee, S.W.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.H.J. Performance evaluations of PSC panel from impact-induced fire loading. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Fantilli, A.P.; Chiaia, B.; Gorino, A. Fiber volume fraction and ductility index of concrete beams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Abbass, A.; Abid, S.; Özakça, M. Experimental investigation on the effect of steel fibers on the flexural behavior and ductility of high-strength concrete hollow beams. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8390345. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I.H.; Joh, C.; Kim, K.C. A comparative experimental study on the flexural behavior of high-strength fiber-reinforced concrete and high-strength concrete beams. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7390798. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Yang, K.H.; Kwak, M.K. Evaluation on the Effectiveness of Supplementary V-ties on Flexural Ductility of Reinforced Concrete Columns. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2017, 29, 345–351. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.H.; Mun, J.H.; Lee, K.H. Evaluation of Ductility of Lightweight Aggregate Concrete T-beam Arranged with Maximum Longitudinal Reinforcement Ratio. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2020, 32, 11–18. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Yang, K.Y.; Zeng, J.J.; Quach, W.M.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhang, L. Compressive behavior of FRP-confined ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) in circular columns. Eng. Struct. 2021, 249, 113246. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.J.; Ye, Y.Y.; Quach, W.M.; Lin, G.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhou, J.K. Compressive and transverse shear behaviour of novel FRP-UHPC hybrid bars. Compos. Struct. 2021, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.K.; Lin, W.K.; Guo, S.X.; Zeng, J.J.; Bai, Y.L. Behavior of FRP-confined FRP spiral reinforced concrete square columns (FCFRCs) under axial compression. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103452. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Zeng, J.J.; Bai, Y.L.; Zhang, L. Bond Behavior between GFRP Bars and High Strength and Ultra-High Strength Fiber Reinforced Seawater Sea-sand Concrete (SSC) under Pullout Loading. Compos. Struct. 2021, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, A.R.; Klyuev, S.; Marvila, M.T.; Vatin, N.; Alfimova, N.; de Lima, T.E.; Olisov, A. Investigation of the potential use of curauá fiber for reinforcing mortars. Fibers 2020, 8, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Zou, S.; Ding, T.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Q. Fiber-reinforced mortar with 100% recycled fine aggregates: A cleaner perspective on 3D printing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128720. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Geng, H.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Synergistic Bond Properties of Different Deformed Steel Fibers Embedded in Mortars Wet-Sieved from Self-Compacting SFRC. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10144. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, Y.M. Behavior of Prestressed Concrete Beams with CFRP Strands. Master’s Thesis, Portland State University, Portland, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.M. Evaluation of Ductility in Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Fiber Reinforced Plastic Tendons. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.B. Experimental Evaluation of PSC Structures from FRP with a Prestressing Strengthening Method. Materials 2021, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, N.F.; Soliman, A.K.; Abdel-Sayed, G.; Saleh, K.R. Behavior and Ductility of Simple and Continuous FRP Reinforced Beams. J. Compos. Constr. 1998, 2, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.K.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, W.T. Structural Behavior Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete Using the Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Strengthening Method. Polymers 2021, 13, 780. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Specimens | Ductility Index (D) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load (kN) | Disp. (mm) | Load (kN) | Disp. (mm) | Load (kN) | Disp. (mm) | |||
| 1 | PH4C | 94.5 | 5.90 | 218.8 | 28.14 | 237.6 | 79.35 | 2.82 |
| 2 | PL4C | 63.7 | 3.14 | 185.5 | 28.98 | 239.3 | 98.10 | 3.39 |
| 3 | PH2C | 83.3 | 5.58 | 219.6 | 33.29 | 233.3 | 63.03 | 1.89 |
| 4 | PL2C | 50.6 | 3.57 | 180.4 | 30.17 | 227.3 | 71.76 | 2.38 |
| 5 | PH4NP | 125.6 | 6.60 | 273.3 | 28.89 | 312.8 | 79.80 | 2.76 |
| 6 | PL4NP | 90.2 | 4.29 | 232.0 | 27.01 | 300.0 | 63.48 | 2.35 |
| 7 | PL2NN(H) | 46.2 | 3.36 | 198.1 | 32.32 | 271.4 | 82.64 | 2.56 |
| 8 | PL2NN(S) | 42.6 | 2.64 | 188.8 | 31.75 | 248.7 | 72.12 | 2.27 |
| 9 | PH4EP | 141.7 | 5.62 | 323.9 | 33.30 | 356.4 | 56.49 | 1.70 |
| 10 | PL4EP | 132.1 | 4.95 | 311.3 | 31.72 | 336.8 | 47.43 | 1.50 |
| 11 | PH2EP | 98.6 | 6.04 | 285.9 | 37.16 | 317.0 | 57.66 | 1.55 |
| 12 | PL2EP | 108.4 | 5.81 | 275.8 | 36.91 | 335.3 | 56.70 | 1.54 |
| No. | Specimens | Energy | Analysis | Ductility Index(E) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Elastic | Inelastic | Rate | ||||
| 1 | PH4C | 15,448.79 | 3027.56 | 12,421.23 | 80.40 | D | 3.05 |
| 2 | PL4C | 18,000.76 | 3590.56 | 14,410.20 | 80.05 | D | 3.01 |
| 3 | PH2C | 11,163.71 | 3306.37 | 7857.34 | 70.38 | SD | 2.19 |
| 4 | PL2C | 11,640.74 | 4183.77 | 7456.97 | 64.06 | B | 1.89 |
| 5 | PH4NP | 19,779.40 | 4501.40 | 15,277.99 | 77.24 | D | 2.70 |
| 6 | PL4NP | 13,554.69 | 4641.88 | 8912.81 | 65.75 | B | 1.96 |
| 7 | PL2NN(H) | 15,427.70 | 6495.72 | 8931.98 | 57.90 | B | 1.69 |
| 8 | PL2NN(S) | 12,255.20 | 5091.69 | 7163.51 | 58.45 | B | 1.70 |
| 9 | PH4EP | 14,730.16 | 4698.41 | 10,031.75 | 68.10 | B | 2.07 |
| 10 | PL4EP | 11,352.68 | 4007.79 | 7344.89 | 64.70 | B | 1.92 |
| 11 | PH2EP | 12,460.32 | 5720.95 | 6739.37 | 54.09 | B | 1.59 |
| 12 | PL2EP | 12,336.05 | 6075.34 | 6260.71 | 50.75 | B | 1.52 |
| No. | RC Specimens | RC Ductility Index | PSC Specimens | PSC Ductility | PSC Specimens | PSC Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R4C | 4.39 | PH4C | 2.82 | PL4C | 3.39 |
| 2 | R2C | 7.32 | PH2C | 1.89 | PL2C | 2.38 |
| 3 | R4NSP | 5.58 | PH4NP | 2.76 | PL4NP | 2.35 |
| 4 | R2NSP | 3.87 | - | - | ||
| 5 | R2NSN(H) | 2.02 | - | PL2NN(H) | 2.56 | |
| 6 | R2NSN(S) | 3.98 | - | PL2NN(S) | 2.27 | |
| 7 | R4EPP | 1.60 | PH4EP | 1.70 | PL4EP | 1.50 |
| 8 | R2EPP | 1.79 | PH2EP | 1.55 | PL2EP | 1.54 |
| 9 | R4EBN | 1.82 | - | - | ||
| 10 | R2EBN | 1.92 | - | - | ||
| No. | RC | PSC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimens | Energy Rate | Analysis | Specimens | Energy Rate | Analysis | Specimens | Energy Rate | Analysis | |
| 1 | R4C | 93.47(D) | 8.16 | PH4C | 80.40(D) | 3.05 | PL4C | 80.05(D) | 3.01 |
| 2 | R2C | 93.51(D) | 8.20 | PH2C | 70.38(SD) | 2.19 | PL2C | 64.06(B) | 1.89 |
| 3 | R4NSP | 89.60(D) | 5.31 | PH4NP | 77.24(D) | 2.70 | PL4NP | 65.75(B) | 1.96 |
| 4 | R2NSP | 84.69(D) | 3.77 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | R2NSN(H) | 62.11(B) | 1.82 | PL2NN(H) | 57.90(B) | 1.69 | |||
| 6 | R4NSN(S) | 73.12(SD) | 2.36 | PL2NN(S) | 58.45(B) | 1.70 | |||
| 7 | R4EPP | 74.86(SD) | 2.49 | PH4EP | 68.10(B) | 2.07 | PL4EP | 64.70(B) | 1.92 |
| 8 | R2EPP | 72.40(SD) | 2.31 | PH2EP | 54.09(B) | 1.59 | PL2EP | 50.75(B) | 1.52 |
| 9 | R4EBN | 76.38(D) | 2.62 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | R2EBN | 49.77(B) | 1.50 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.-K.; Park, J.-S. Evaluation of the Performance and Ductility Index of Concrete Structures Using Advanced Composite Material Strengthening Methods. Polymers 2021, 13, 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234239
Kim T-K, Park J-S. Evaluation of the Performance and Ductility Index of Concrete Structures Using Advanced Composite Material Strengthening Methods. Polymers. 2021; 13(23):4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234239
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae-Kyun, and Jong-Sup Park. 2021. "Evaluation of the Performance and Ductility Index of Concrete Structures Using Advanced Composite Material Strengthening Methods" Polymers 13, no. 23: 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234239
APA StyleKim, T.-K., & Park, J.-S. (2021). Evaluation of the Performance and Ductility Index of Concrete Structures Using Advanced Composite Material Strengthening Methods. Polymers, 13(23), 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234239






