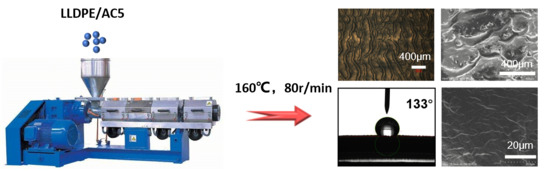
Utilization of Melt Fracture Phenomenon for the Preparation of Shark Skin Structured Hydrophobic Film
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
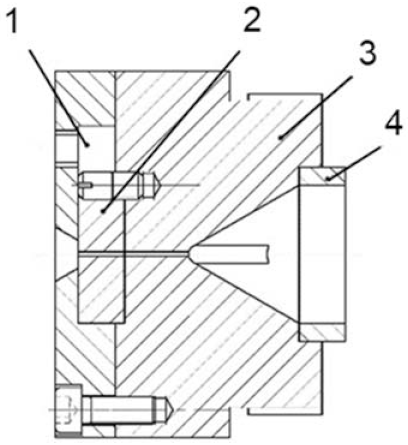
2.2. Preparation of the Hydrophobic Surface of Shark Skin
2.3. Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Different Additives on Surface Morphology
3.2. The Influence of Die Temperature on Surface Morphology
3.3. The Influence of the Screw Speed on the Surface Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.-I.; Kim, S.; Kang, J.-K.; Choi, W. Graphene oxide embedded into TiO2 nanofiber: Effective hybrid photocatalyst for solar conversion. J. Catal. 2014, 309, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gose, J.W.; Golovin, K.; Boban, M.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A.; Perlin, M.; Ceccio, S.L. Characterization of superhydrophobic surfaces for drag reduction in turbulent flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 845, 560–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Shen, X.; Min, Y.; Xu, Q. The research on preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces of pure copper by hydrothermal method and its corrosion resistance. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 270, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhou, T.; Song, L. Fabricating Microstructures on Glass for Microfluidic Chips by Glass Molding Process. Micromachines 2018, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Qian, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Liao, B.; Niu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, P.; Li, P.; Cao, L.; et al. The microstructure and property of W/Ti multilayer composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 79, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S. Superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings by electrochemical anodic oxidation and plasma electrolytic oxidation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 283, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Q.; Hokkanen, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, F.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, S.-P.; Zhou, T.; Chang, Q.; He, B.; et al. Design of robust superhydrophobic surfaces. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 582, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Ge, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, H.; Xing, G.; Lai, Y.; et al. Constructing Mechanochemical Durable and Self-Healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Dai, H.; Liu, H.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. High-Performance Solar Steam Generator Based on Polypyrrole-Coated Fabric via 3D Macro- and Microstructure Design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40664–40672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, D. Robust Micro-Nanostructured Superhydrophobic Surfaces for Long-Term Dropwise Condensation. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 9824–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bruse, M.; Hage, W. Experiments with three-dimensional riblets as an idealized model of shark skin. Exp. Fluids 2000, 28, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, M. Fabrication of biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces inspired by lotus leaf and silver ragwort leaf. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Choo, S.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, K.-I.; Lee, H. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Oleophobic Surfaces with Overhang Structure by Reverse Nanoimprint Lithography. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24354–24359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. A designable surface via the micro-molding process. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2018, 4, 17099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raayai-Ardakani, S.; McKinley, G.H. Geometric optimization of riblet-textured surfaces for drag reduction in laminar boundary layer flows. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 053601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ao, M.; Wang, M.; Zhu, F. Investigation of the Turbulent Drag Reduction Mechanism of a Kind of Microstructure on Riblet Surface. Micromachines 2021, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.; Dimov, S.; Bigot, S.; Ivanov, A.; Popov, K. Micro-EDM—recent developments and research issues. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 149, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, R. Long-term wettability of titanium surfaces by combined femtosecond laser micro/nano structuring and chemical treatments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lai, L.; Li, Y. Preparation of Microneedle Array Mold Based on MEMS Lithography Technology. Micromachines 2020, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chu, J.P.; Jang, J.S.C.; Hsieh, C.W.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.L.; Jeng, J.Y.; Chen, Y.M. Replication of nano/micro-scale features using bulk metallic glass mold prepared by femtosecond laser and imprint processes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 035030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Z.; Wang, H.; Leow, W.R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wei, J.; Huo, F.; Chen, X. Microstructured Graphene Arrays for Highly Sensitive Flexible Tactile Sensors. Small 2014, 10, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Zuo, F.; Guo, Z. Fabrication of a Metal Micro Mold by Using Pulse Micro Electroforming. Micromachines 2018, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ritchie, R.O. Architecture of high-strength aluminum–matrix composites processed by a novel microcasting technique. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Coates, P.; Gao, X. Compression-induced electrical percolation and enhanced mechanical properties of polydimethylsiloxane-based nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 10611–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-I.; Kim, P.K.; Ha, T.-G. Fabrication of hybrid fine metal mask through micro/nano-photolithography and electroforming. Microelectron. Eng. 2021, 247, 111598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingyao, S.; Daming, W.; Ying, L.; Zhenzhou, Y.; Pengsheng, G. Rapid fabrication of micro structure on polypropylene by plate to plate isothermal hot embossing method. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Jiang, C. Numerical simulation and experimental study of filling process of micro prism by isothermal hot embossing in solid-like state. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; Gou, P. Rapid Fabrication of Microstructure on PMMA Substrate by the Plate to Plate Transition-Spanning Isothermal Hot Embossing Method Nearby Glass Transition Temperature. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Jazrawi, B.; Mehrkhodavandi, P.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Wall slip and melt fracture of poly(lactides). Rheol. Acta 2011, 51, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzigiannakis, E.; Ebrahimi, M.; Wagner, M.H.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Melt fracture of polyisobutylenes. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Tomković, T.; Liu, G.; Doufas, A.A.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Melt fracture of linear low-density polyethylenes: Die geometry and molecular weight characteristics. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 053103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Derakhshandeh, M.; Doufas, A.A.; Tomkovic, T.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. The role of microstructure on melt fracture of linear low density polyethylenes. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Inn, Y.W.; Sukhadia, A.M.; DesLauriers, P.J.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Melt fracture of HDPEs: Metallocene versus Ziegler–Natta and broad MWD effects. Polymer 2012, 53, 4195–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochard, F.; De Gennes, P.G. Shear-dependent slippage at a polymer/solid interface. Langmuir 1992, 8, 3033–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Q.; Drda, P.A. Superfluid-Like Stick− Slip Transition in Capillary Flow of Linear Polyethylene Melts. 1. General Features. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, R.; Mackley, M. The correlation of experimental surface extrusion instabilities with numerically predicted exit surface stress concentrations and melt strength for linear low density polyethylene. J. Rheol. 2000, 44, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Happel, J.; Brenner, H. Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics: With Special Applications to Particulate Media; Springer Science & Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Weill, A. About the origin of sharkskin. Rheol. Acta 1980, 19, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Drda, P.A.; Inn, Y. Exploring molecular origins of sharkskin, partial slip, and slope change in flow curves of linear low density polyethylene. J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 875–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, V.; Cai, X.; Stroh, A.; Bernard, R.; Kriegseis, J.; Frohnapfel, B.; Marschall, H.; Wörner, M. Drop bouncing by micro-grooves. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 70, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Chen, H. High-precision bio-replication of synthetic drag reduction shark skin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Ting, Y.-S.; Chen, B.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Liu, T.-Y. Bionic shark skin replica and zwitterionic polymer brushes functionalized PDMS membrane for anti-fouling and wound dressing applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 391, 125663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Jia, Z.-H.; He, J.-C.; Cai, T.-M.; Wang, G. Vibration-induced Wenzel-Cassie wetting transition on microstructured hydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 181601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Hierarchical roughness optimization for biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces. Ultramicroscopy 2007, 107, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Koch, K.; Jung, Y.C. Biomimetic hierarchical structure for self-cleaning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 93101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, D. Simple and Affordable Way to Achieve Polymeric Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Biomimetic Hierarchical Roughness. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2750–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvi, J.T.; Pakkanen, T.A. Enhanced Hydrophobicity of Rough Polymer Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3336–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Material | Microstructure Width (μm) | Microstructure Shape | Number of Microstructures in the Area (1 mm × 1.2 mm) | Water Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLDPE | 243 ± 23 | Wavy | 4 | 93 ± 3 |
| LLDPE/AC3 (9:1) | 208 ± 19 | Wavy | 5 | 102 ± 1 |
| LLDPE/AC5 (9:1) | 150 ± 20 | Lumpy | 6 | 90 ± 2 |
| LLDPE/AC15 (9:1) | 163 ± 17 | Lumpy | 10 | 118 ± 4 |
| LLDPE/180 (9:1) | 214 ± 24 | Lumpy | 5 | 98 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, B.; Yue, Y.; Gai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, J.; Wu, D. Utilization of Melt Fracture Phenomenon for the Preparation of Shark Skin Structured Hydrophobic Film. Polymers 2021, 13, 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244299
Tang B, Yue Y, Gai Z, Huang Y, Liu Y, Gao X, Sun J, Wu D. Utilization of Melt Fracture Phenomenon for the Preparation of Shark Skin Structured Hydrophobic Film. Polymers. 2021; 13(24):4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244299
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Bin, Yaoyu Yue, Zipeng Gai, Yao Huang, Ying Liu, Xiaolong Gao, Jingyao Sun, and Daming Wu. 2021. "Utilization of Melt Fracture Phenomenon for the Preparation of Shark Skin Structured Hydrophobic Film" Polymers 13, no. 24: 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244299
APA StyleTang, B., Yue, Y., Gai, Z., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Gao, X., Sun, J., & Wu, D. (2021). Utilization of Melt Fracture Phenomenon for the Preparation of Shark Skin Structured Hydrophobic Film. Polymers, 13(24), 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244299