Novel, Environment-Friendly Cellulose-Based Derivatives for Tetraconazole Removal from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
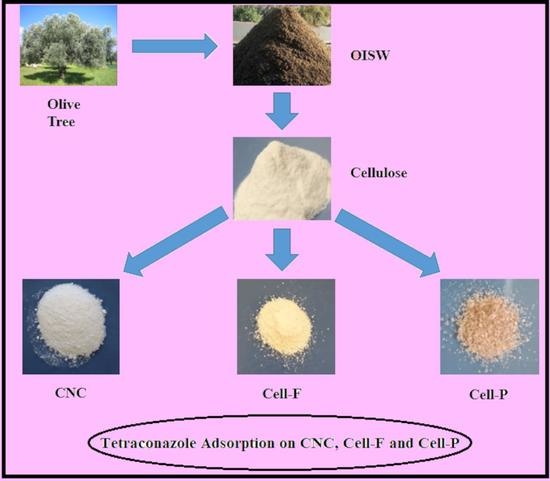
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystalline
2.4. Cellulose Dissolution
2.5. Cellulose Acylation with Furan-2-Carbonyl Chloride
2.6. Cellulose Crosslinking with Pyridine-2,6-Dicarbonyl Dichloride
2.7. Adsorption Study of Tetraconazole
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymer Analysis
3.1.1. InFrared Analysis
3.1.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analysis
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
SEM Characterization Was Obtained for the Adsorbents CNC, Cell-F and Cell-P
3.1.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.2. Adsorption Results
3.2.1. Effect of Contact Time
3.2.2. Effect of pH
3.2.3. Effect of Tetraconazole Concentration
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
3.2.5. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.3. Adsorption Analysis
3.3.1. Isotherm Models
Equilibrium Isotherm Models
Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetic Models
Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics
Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model
Intra-Particle-Diffusion Kinetic Adsorption Model
3.3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
Adsorbents’ Regeneration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Damalas, C.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Farmers’ exposure to pesticides: Toxicity types and ways of prevention. Toxics 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aktar, W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lafi, W.K.; Al-Qodah, Z. Combined advanced oxidation and biological treatment processes for the removal of pesticides from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, A.; Pizzolato, T.; Carissimi, É.; Schneider, I. Decolorizing dye wastewater from the agate industry with Fenton oxidation process. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, C. Degradation of organophosphorus pesticide induced by oxygen plasma: Effects of operating parameters and reaction mechanisms. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arami, M.; Limaee, N.Y.; Tabrizi, N.S. Decolorization and aromatic ring degradation kinetics of Direct Red 80 by UV oxidation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide utilizing TiO2 as a photocatalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 112, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Qin, Z.; Huang, W.; Cao, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J. Design and function of biomimetic multilayer water purification membranes. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Hsieh, Y.; Lai, P.; Li, C.; Kao, C. Photodegradation treatment of azo dye wastewater by UV/TiO2 process. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 68, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; El-Din, M.G. Aqueous pesticide degradation by ozonation and ozone-based advanced oxidation processes: A review (Part I). Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, S. Catalytic oxidation of the dye wastewater with hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2005, 44, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Han, Z.J.; Yu, S.F.; Pey, K.L.; Ostrikov, K.; Karnik, R. Carbon nanotube membranes with ultrahigh specific adsorption capacity for water desalination and purification. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.Z.; Ma, Y.Q.; Guan, W.B.; Wu, X.L.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Du, Y.L.; Pan, C.P. Preparation of cellulose/graphene composite and its applications for triazine pesticides adsorption from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Purkait, A.; Biswas, P.K.; Kole, R.K. Removal of pesticide residues by mesoporous alumina from water. IJCS 2019, 7, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Socorro, J.; Désert, M.; Quivet, E.; Gligorovski, S.; Wortham, H. Light induced heterogeneous ozone processing on the pesticides adsorbed on silica particles. AGUFM 2013, 2013, A51C-0033. [Google Scholar]
- Khalfallah, S.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Constantinidou, H.A. Dissipation study of the fungicide tetraconazole in greenhouse-grown cucumbers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Xanthopoulou, N.J.; Ioannidis, P.M. Dissipation of the fungicide tetraconazole from field-sprayed sugar beets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5342–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbar, N.; Bayram, A.; Filibeli, A.; Muezzinoglu, A.; Sengul, F.; Ozer, A. A review of waste management options in olive oil production. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 34, 209–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, O.A.; Foad, Y.; Hamed, E.M.; Al-Hajj, N. Cellulose Powder from Olive Industry Solid Waste. BioResources 2012, 7, 4190–4201. [Google Scholar]
- Salameh, Y. Methods for Extracting Cellulose Material from Olive Pulp. Master’s Thesis, An-Najah National University, Nablus, Palestine, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Buyuksari, U. Utilization of olive mill sludge in the manufacture of fiberboard. BioResources 2010, 5, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, L.A.; Morgado, D.L.; Gessner, F.; Frollini, E.; El Seoud, O.A. A physical organic chemistry approach to dissolution of cellulose: Effects of cellulose mercerization on its properties and on the kinetics of its decrystallization. Arkivoc 7 2011, 2011, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medronho, B.; Lindman, B. Competing forces during cellulose dissolution: From solvents to mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent trends in nanofibrous membranes and their suitability for air and water filtrations. Membranes 2011, 1, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banasiak, L.J.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Schäfer, A.I. Sorption of pesticide endosulfan by electrodialysis membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowsaka, K.; Okajima, K.; Kamide, K. Two-Dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of cellulose and cellulose triacetate. Polym. J. 1988, 20, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isogai, A. NMR analysis of cellulose dissolved in aqueous NaOH solutions. Cellulose 1997, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.; Hameed, B. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.-C.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zhang, Q.-X. Critical Review in Adsorption Kinetic Models. J. Zhejiang Univ. A 2009, 10, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejo, S.O. Proposing a new empirical adsorption isotherm known as Adejo-Ekwenchi isotherm. J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hong, S.; Zhang, L.; Gan, F.; Ho, Y.S. Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Rectorite. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 2651–2656. [Google Scholar]
- Sridev, D.; Rajendran, K.V. Synthesis and optical characteristics of ZnO nanocrystals. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Winnefeld, F.; Plank, J. Interaction of cement model systems with superplasticizers investigated by atomic force microscopy, zeta potential, and adsorption measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 347, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L. Comparison between linear and non-linear forms of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetic models for the removal of methylene blue by activated carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K. Kinetic and isotherm studies of cadmium adsorption on manganese nodule residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 137, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-H.; Wang, S.; Luan, Z.; Ding, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, D. Adsorption of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by surface oxidized carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2003, 41, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlu, M.; Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M. Comparison of textile dyeing effluent adsorption on commercial activated carbon and activated carbon prepared from olive stone by ZnCl2 activation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Hameed, B.; Ahmad, A. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on basic dye adsorption by oil palm fibre activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 127, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Polymer | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qo (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | KF (mg/g) | n (g/L) | |
| CNC | 6.481 | −3.547 | 8.955 | −4.796 |
| Cell-F | 7.604 | −6.779 | 8.956 | −7.225 |
| Cell-P | 6.935 | −4.697 | 8.904 | −5.650 |
| Polymer | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics | qexp (mg/g) | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics | Intra-Particle-Diffusion Kinetics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | K1 (mg·g−1·min−1) | qe (mg/g) | K2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | C (mg/g) | Kp (mg·g−1·min−0.5) | ||
| CNC | 17.179 | 7.139*10−3 | 7.112 | 7.380 | 0.0711 | 51.126 | 0.9449 |
| Cell-F | 17.95 | - | 7.619 | 7.716 | 0.238 | 52.046 | 0.0013 |
| Cell-P | 14.184 | - | 7.992 | 8.091 | 0.141 | 55.838 | −0.0091 |
| Polymer | ∆H (kJ) | ∆G° (kJ) | ∆S (J/K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC | −25.513 | −4.693 | −69.867 |
| Cell-F | −23.383 | −4.792 | −62.385 |
| Cell-P | −35.705 | −5.549 | −101.195 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalaf, B.; Hamed, O.; Jodeh, S.; Hanbali, G.; Bol, R.; Dagdag, O.; Samhan, S. Novel, Environment-Friendly Cellulose-Based Derivatives for Tetraconazole Removal from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2021, 13, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030450
Khalaf B, Hamed O, Jodeh S, Hanbali G, Bol R, Dagdag O, Samhan S. Novel, Environment-Friendly Cellulose-Based Derivatives for Tetraconazole Removal from Aqueous Solution. Polymers. 2021; 13(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030450
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalaf, Bayan, Othman Hamed, Shehdeh Jodeh, Ghadir Hanbali, Roland Bol, Omar Dagdag, and Subhi Samhan. 2021. "Novel, Environment-Friendly Cellulose-Based Derivatives for Tetraconazole Removal from Aqueous Solution" Polymers 13, no. 3: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030450
APA StyleKhalaf, B., Hamed, O., Jodeh, S., Hanbali, G., Bol, R., Dagdag, O., & Samhan, S. (2021). Novel, Environment-Friendly Cellulose-Based Derivatives for Tetraconazole Removal from Aqueous Solution. Polymers, 13(3), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030450