Morphology-Mechanical Performance Relationship at the Micrometrical Level within Molded Polypropylene Obtained with Non-Symmetric Mold Temperature Conditioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Optical Microscopy
2.2. Micro-Indentation
2.3. AFM Analysis
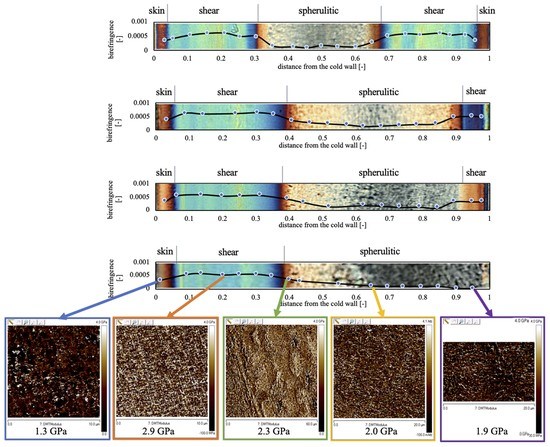
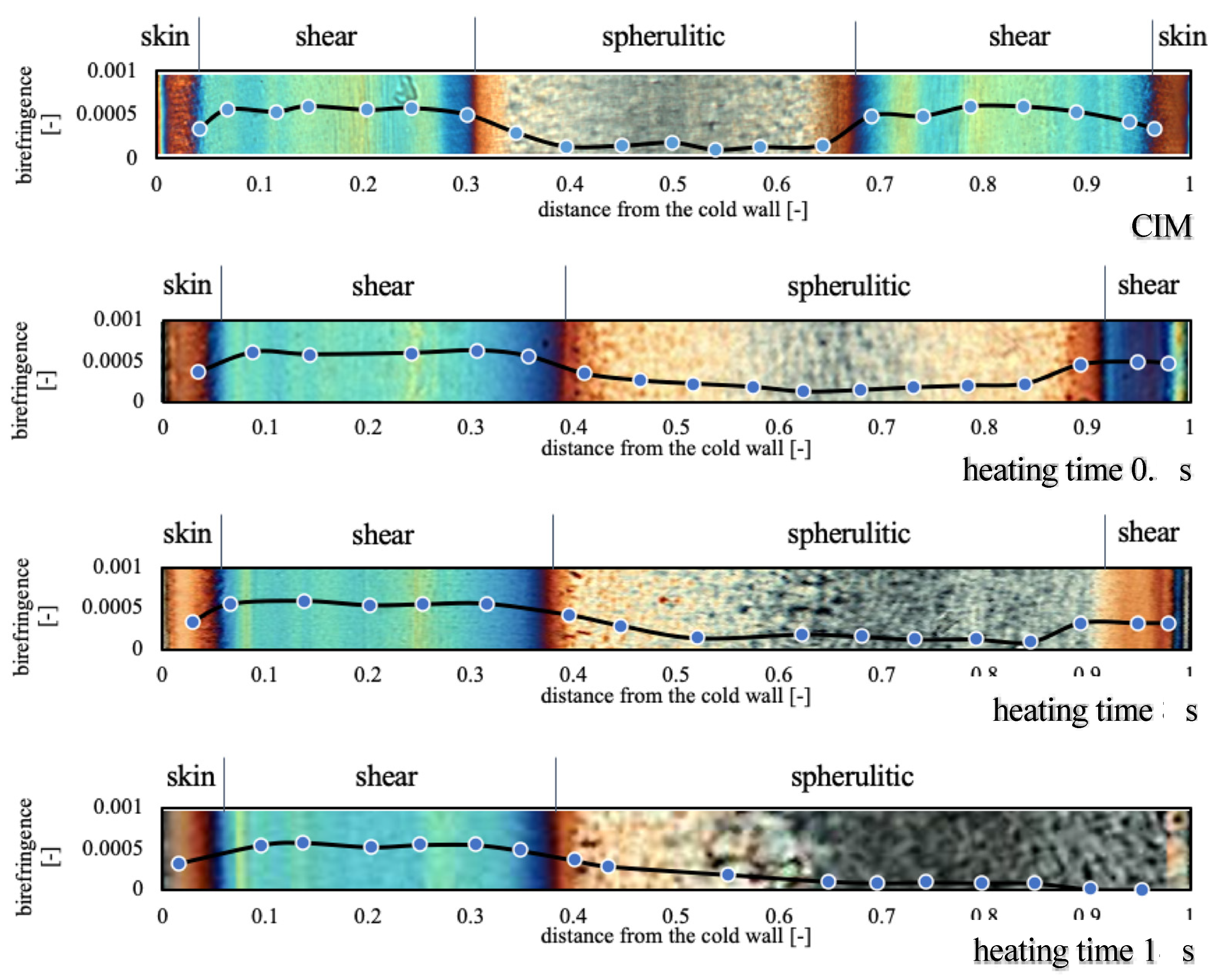
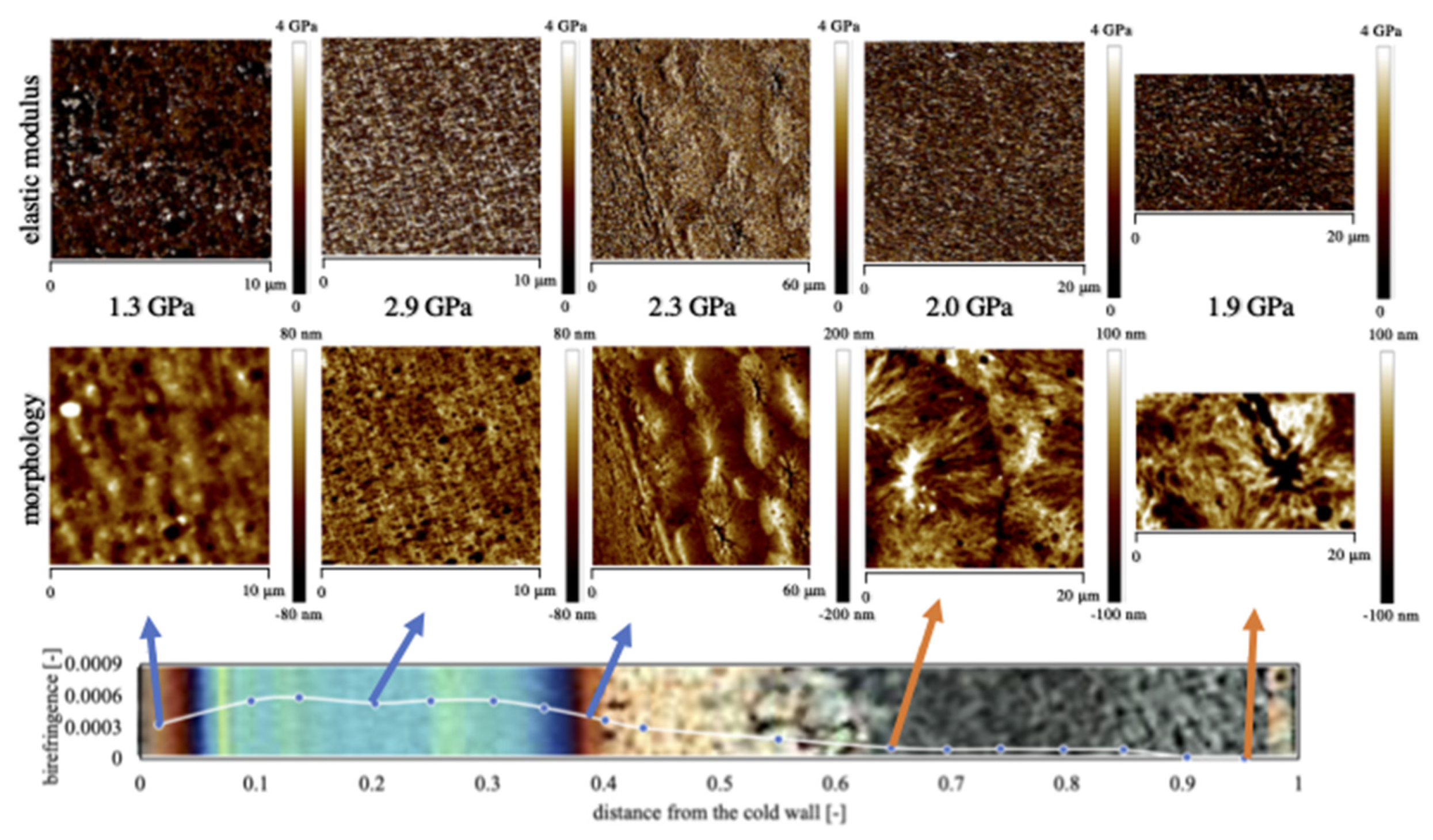
3. Results
3.1. Optical Morphology
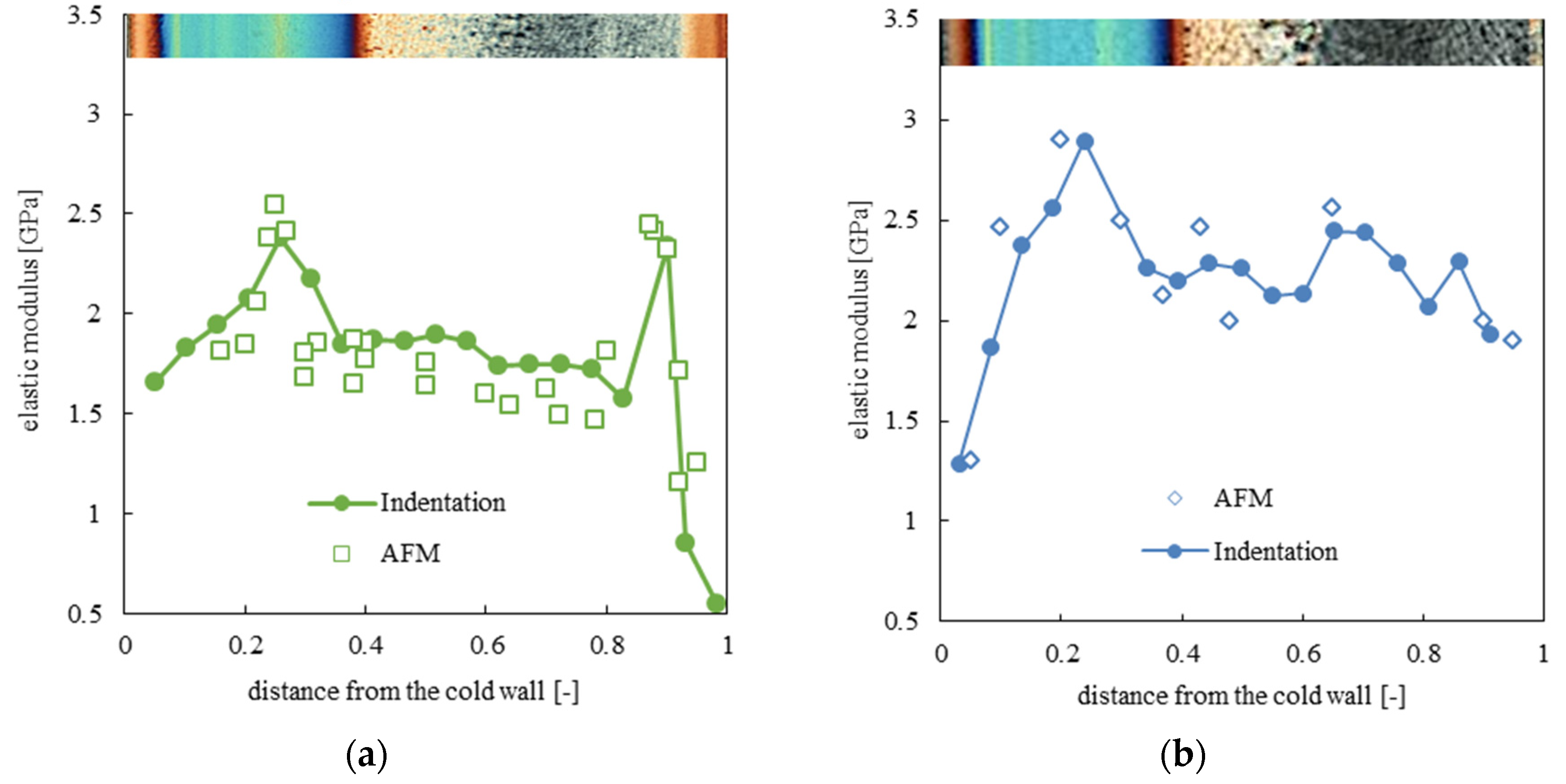
3.2. Elastic Modulus Distribution
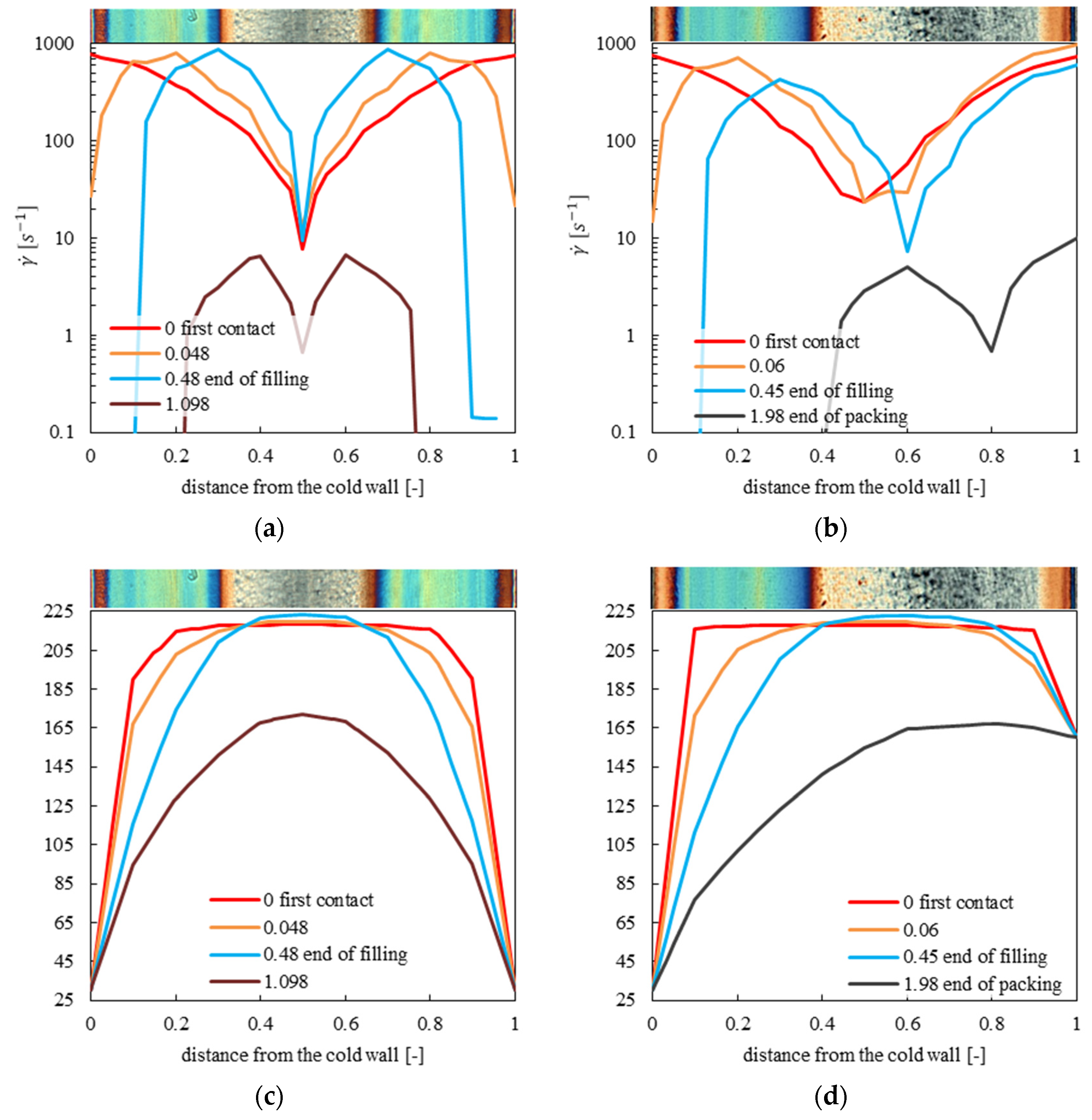
3.3. Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Olah, A.; Baer, E. Micro- and nano-layered processing of new polymeric systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 102, 101210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.; Te Nijenhuis, K. Mechanical Properties of Solid Polymers. Prop. Polym. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Ania, F.; Baltá-Calleja, F.J. From the glassy state to ordered polymer structures: A microhardness study. Polymer 2009, 50, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, I.M.; Sweeney, J. An introduction to the mechanical properties of solid polymers. Choice Rev. Online 2004, 42, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giró-Paloma, J.; Roa, J.J.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Rayón, E.; Flores, A.; Martínez, M.; Chimenosa, J.M.; Fernándeza, A.I. Depth-sensing indentation applied to polymers: A comparison between standard methods of analysis in relation to the nature of the materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 4047–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pharr, G.M.; Oliver, W.C.; Brotzen, F.R. On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, Y.M.; Kotova, S.L.; Timashev, P.S. Viscoelasticity in simple indentation-cycle experiments: A computational study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelto, J.; Heino, V.; Karttunen, M.; Rytöluoto, I.; Ronkainen, H. Tribological performance of high density polyethylene (HDPE) composites with low nanofiller loading. Wear 2020, 460–461, 203451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liparoti, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Speranza, V.; Titomanlio, G. Multiscale mechanical characterization of iPP injection molded samples. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 90, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.P.; Liu, J. Nanoindentation Techniques. Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 5908–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. A review of recent research on nanoindentation of polymer composites and their constituents. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Beyond Indentation Hardness and Modulus: Recent Advances in Nanoindentation Techniques: Part II. JOM 2018, 70, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahin, O.; Magonov, S.; Su, C.; Quate, C.F.; Solgaard, O. An atomic force microscope tip designed to measure time-varying nanomechanical forces. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, C.J.; Garcia, R. Determination and simulation of nanoscale energy dissipation processes in amplitude modulation AFM. Ultramicroscopy 2010, 110, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokukin, M.E.; Sokolov, I. Quantitative Mapping of the Elastic Modulus of Soft Materials with HarmoniX and PeakForce QNM AFM Modes. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16060–16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emri, I.; Gergesova, M. Time-Dependent Behavior of Solid Polymers. In Rheology; Eolss Publishers Co Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.; Sinn, G.; Schwendtner, K.; Lichtenegger, H.C.; Wan-Wendner, R. Time-dependent changes of mechanical properties of polymer-based composite materials for adhesive anchor systems. Compos. Struct. 2018, 196, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojzewski, H.; Imre, B.; Check, C.; Chartoff, R.; Vancso, J. Mechanical mapping and morphology across the length scales unveil structure-property relationships in polycaprolactone based polyurethanes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Troisi, E.M.; Jaensson, N.O.; Peters, G.W.M.; Anderson, P.D. Modelling flow induced crystallization of IPP: Multiple crystal phases and morphologies. Polymer 2019, 182, 121806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caelers, H.J.M.; Parodi, E.; Cavallo, D.; Peters, G.W.M.; Govaert, L.E. Deformation and failure kinetics of iPP polymorphs. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huda Shaik, N.; GReifenberger, R.; Raman, A. Nanomechanical mapping in air or vacuum using multi-harmonic signals in tapping mode atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 455502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, S.E.; Pruitt, L.A. Nanomechanical analysis of medical grade PEEK and carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK composites. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 111, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Hernández, B.; Soccio, M.; Castrillo, I.; Guidotti, G.; Lotti, N.; Alegría, Á.; Martínez-Tong, D.E. Poly(alkylene 2,5-furanoate)s thin films: Morphology, crystallinity and nanomechanical properties. Polymer 2020, 204, 122825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liparoti, S.; Speranza, V.; Sorrentino, A.; Titomanlio, G. Mechanical Properties Distribution within Polypropylene Injection Molded Samples: Effect of Mold Temperature under Uneven Thermal Conditions. Polymers 2017, 9, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speranza, V.; Liparoti, S.; Pantani, R.; Titomanlio, G. Hierarchical Structure of iPP During Injection Molding Process with Fast Mold Temperature Evolution. Materials 2019, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nofar, M.; Ozgen, E.; Girginer, B. Injection-molded PP composites reinforced with talc and nanoclay for automotive applications. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020, 33, 1478–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, X.; Cai, X.; Shao, J.; Zou, F.; Song, W.; Qiao, J.; Wu, C. The orientation of the dispersed phase and crystals in an injection-molded impact polypropylene copolymer. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, G.H. Effect of mold temperature on the structures and mechanical properties of micro-injection molded polypropylene. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, G.; Guan, Y.; Wu, X.; Hui, Y. Effect of rapid heating cycle injection mold temperature on crystal structures, morphology of polypropylene and surface quality of plastic parts. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, C.; Kahve, C.; Schmitz, M. Development of a novel control strategy for a highly segmented injection mold tempering for inline part warpage control. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divekar, M.; Gaval, V.R.; Wonisch, A. Improvement of warpage prediction through integrative simulation approach for thermoplastic material. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, İ. An effect of mold surface temperature on final product properties in the injection molding of high-density polyethylene materials. Polym. Bull. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, A.; Fiala, T.; Manas, M.; Stoklásek, P.; Ovsik, M. Influence of Injection Moulding Process Parameters on High-Density Polyethylene Surface Hardness. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2020, 994, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liparoti, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Speranza, V. Micromechanical Characterization of Complex Polypropylene Morphologies by HarmoniX AFM. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.M.; Bassett, D.C. On Row Structures, Secondary Nucleation and Continuity in Alpha- Polypropylene. Polymer 1998, 39, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.R.; Isayev, A.I.; Liu, S.-J. Injection molding: Technology and fundamentals. In Progress Polymer Processing; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munich, Germany, 2009; p. 737. [Google Scholar]
- Mavridis, H.; Hrymak, A.N.; Vlachopoulos, J. Finite element simulation of fountain flow in injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1986, 26, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, P.G.; Kamal, M.R. A structure-oriented computer simulation of the injection molding of viscoelastic crystalline polymers part I: Model with fountain flow, packing, solidification. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1986, 26, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Zhao, Z. Warpage prediction of the injection-molded strip-like plastic parts. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labour, T.; Vigier, G.; Séguéla, R.; Gauthier, C.; Orange, G.; Bomal, Y. Influence of the β-crystalline phase on the mechanical properties of unfilled and calcium carbonate-filled polypropylene: Ductile cracking and impact behavior. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.V.B.; Muller, V.M.V.; Toporov, Y.P. Effect of contact deformations on the adhesion of particles. J. Colloid Interface 1975, 53, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liparoti, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Guzman, G.; Cakmak, M.; Titomanlio, G. Fast mold surface temperature evolution: Relevance of asymmetric surface heating for morphology of iPP molded samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36434–36448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liparoti, S.; Speranza, V.; Titomanlio, G.; Pantani, R. Effect of Rapid Mold Heating on the Structure and Performance of Injection-Molded Polypropylene. Polymers 2020, 12, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pantani, R.; Speranza, V.; Titomanlio, G. Effect of flow-induced crystallization on the distribution of spherulite dimensions along cross section of injection molded parts. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantani, R.; Speranza, V.; Titomanlio, G. Thirty years of modeling of injection molding. A brief review of the contribution of UNISA code to the field. Int. Polym. Process. 2016, 31, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, V.; Liparoti, S.; Volpe, V.; Titomanlio, G.; Pantani, R. Modelling of morphology development towards spherulites and shish–kebabs: Application to isothermal flow-induced crystallization experiments on isotactic polypropylene. Polymer 2020, 196, 122459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantani, R.; Speranza, V.; Titomanlio, G. Simultaneous morphological and rheological measurements on polypropylene: Effect of crystallinity on viscoelastic parameters. J. Rheol. 2015, 59, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.-P.; Wang, J.-H.; Yang, B.; Yang, M.-B.; Feng, J.-M. Effects of annealing on the hierarchical crystalline structures and mechanical properties of injection-molded bars of high-density polyethylene. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Macromolecular Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kindi, M.; Schreiber, H.P. Morphological responses in thermally conditioned linear low density polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1992, 32, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
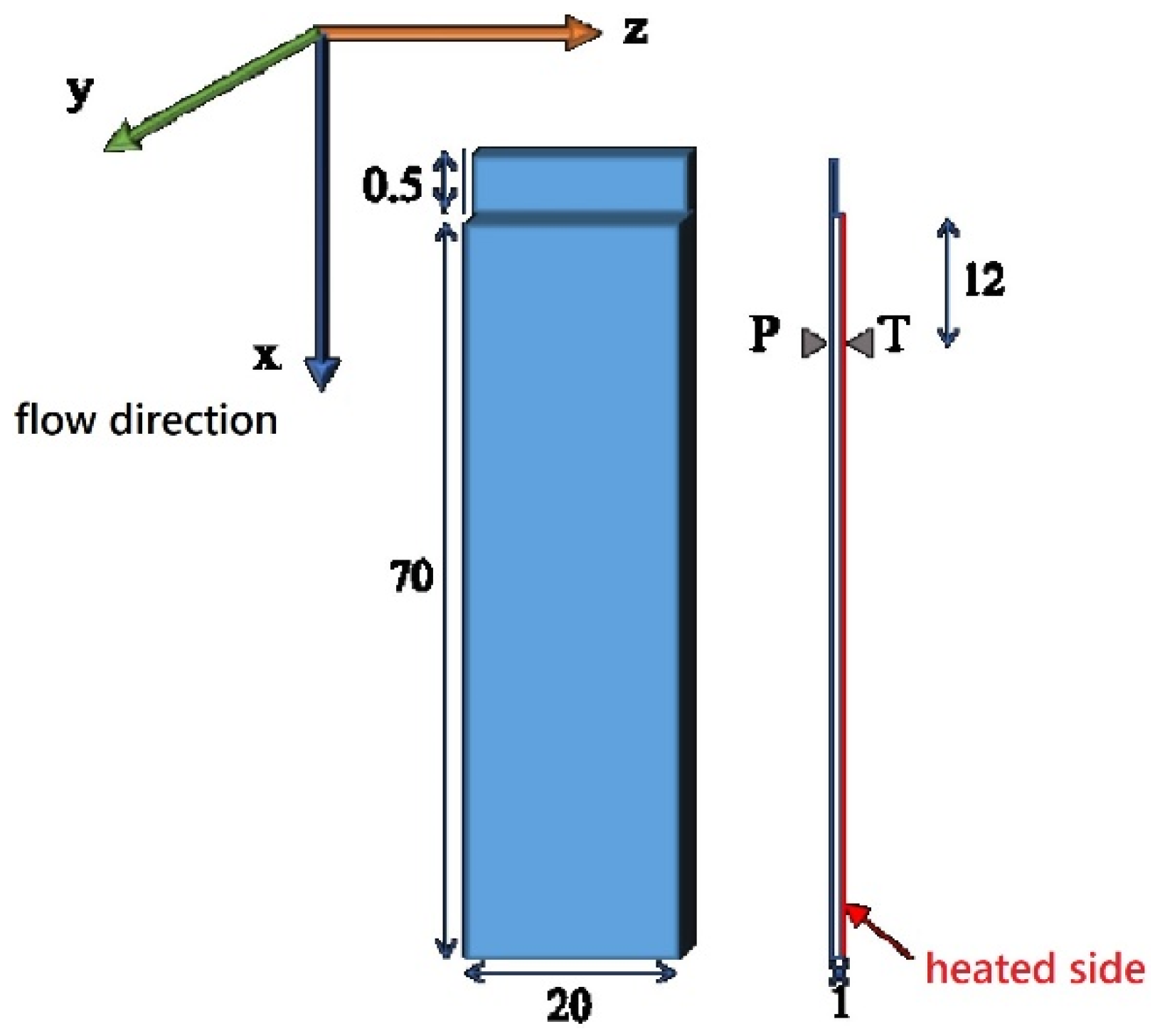


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| injection temperature | 220 °C |
| injection time | 3 s |
| flow rate | 4 cm3 s–1 |
| packing pressure | 300 bar |
| packing time | 2 s |
| cavity temperature, cold side | 25 °C |
| cavity temperature, hot side | 25 °C (CIM), 140 °C, 160 °C |
| heating time, th | 0 (CIM), 0.5, 8 and 18 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liparoti, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Speranza, V. Morphology-Mechanical Performance Relationship at the Micrometrical Level within Molded Polypropylene Obtained with Non-Symmetric Mold Temperature Conditioning. Polymers 2021, 13, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030462
Liparoti S, Sorrentino A, Speranza V. Morphology-Mechanical Performance Relationship at the Micrometrical Level within Molded Polypropylene Obtained with Non-Symmetric Mold Temperature Conditioning. Polymers. 2021; 13(3):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030462
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiparoti, Sara, Andrea Sorrentino, and Vito Speranza. 2021. "Morphology-Mechanical Performance Relationship at the Micrometrical Level within Molded Polypropylene Obtained with Non-Symmetric Mold Temperature Conditioning" Polymers 13, no. 3: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030462
APA StyleLiparoti, S., Sorrentino, A., & Speranza, V. (2021). Morphology-Mechanical Performance Relationship at the Micrometrical Level within Molded Polypropylene Obtained with Non-Symmetric Mold Temperature Conditioning. Polymers, 13(3), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030462