Enhanced Thermal Insulation of the Hollow Glass Microsphere/Glass Fiber Fabric Textile Composite Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
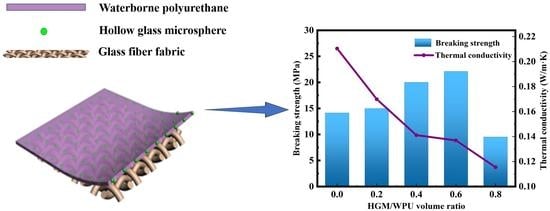
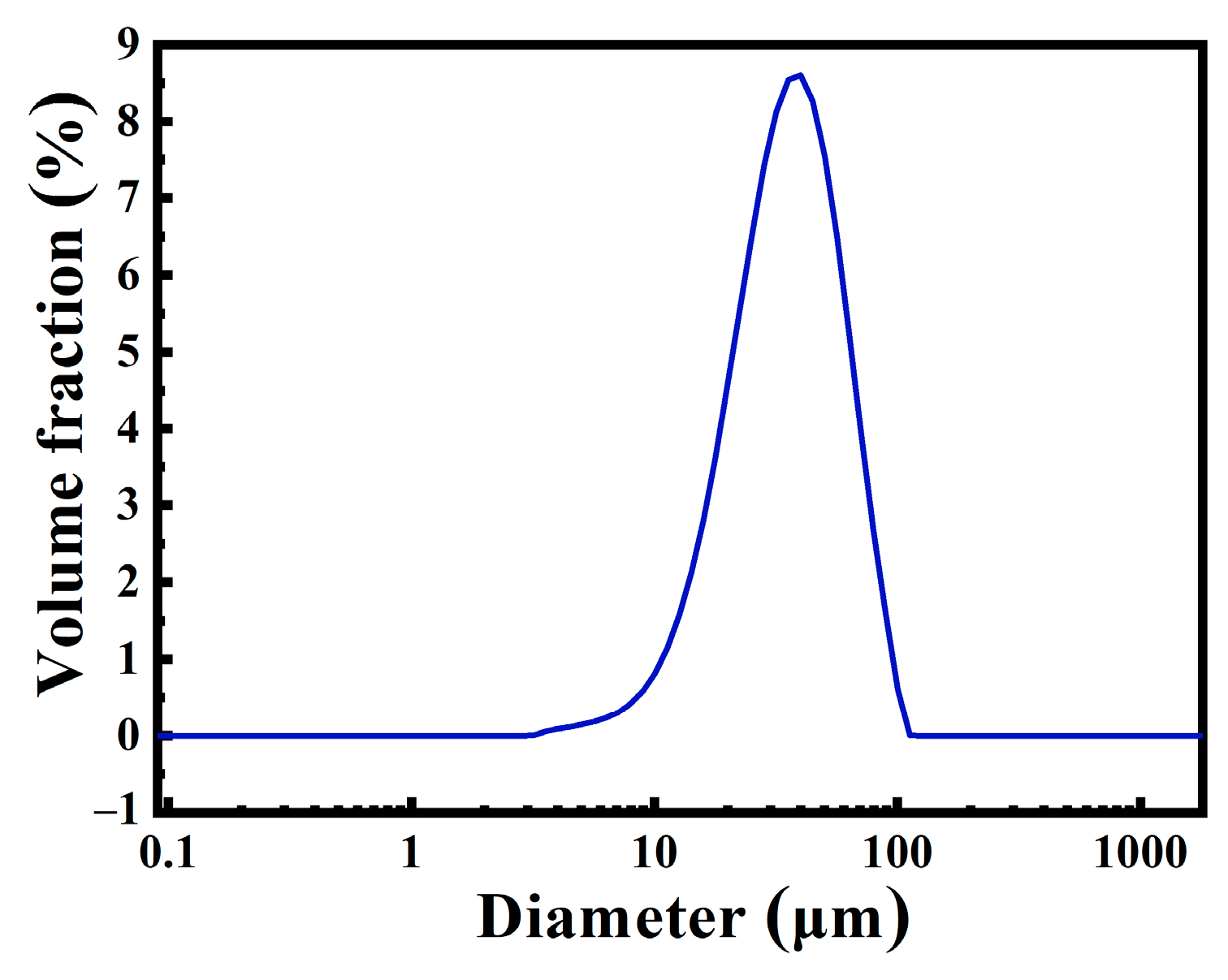
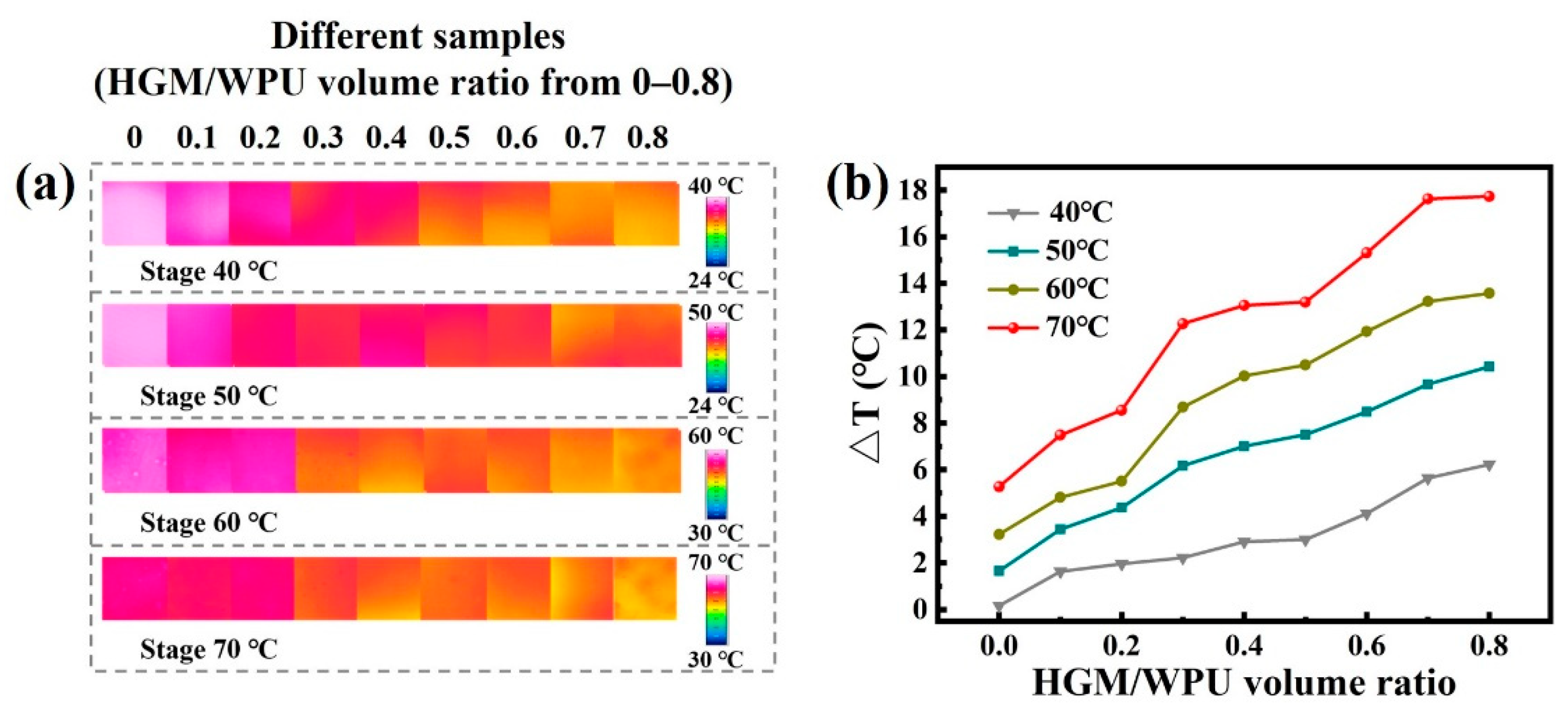
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biros, C.; Rossi, C.; Talbot, A. Translating the International Panel on climate change reports: Standardisation of terminology in synthesis reports from 1990 to 2014. Perspect. Stud. Transl. 2020, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.; Hammer, S.; Mehrotra, S. Cities lead the way in climate-change action. Nature 2010, 467, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.; McGuire, A.; Schadel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J.; Hayes, D.; Hugelius, G.; Koven, C.; Kuhry, P.; Lawrence, D.; et al. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature 2015, 520, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaje, I. Renewable energy for sustainable development in Africa: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2006, 10, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Ni, Q.; Fu, Y.; Fu, S. Super-low thermal conductivity fibrous nanocomposite membrane of hollow silica/polyacrylonitrile. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Mao, X.; Zheng, H.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Silica nanofibrous membranes with ultra-softness and enhanced tensile strength for thermal insulation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dylewski, R.; Adamczyk, J. Study on ecological cost-effectiveness for the thermal insulation of building external vertical walls in Poland. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liao, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Highly flame retardant expanded polystyrene foams from phosphorus-nitrogen-silicon synergistic adhesives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 4649–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Sun, H. Expanded polystyrene foams containing ammonium polyphosphate and nano-zirconia with improved flame retardancy and mechanical properties. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, A.; Tapia, J.; Neitzert, T.; Clifton, G. Effects of expanded polystyrene (EPS) particles on fire resistance, thermal conductivity and compressive strength of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Yu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, R. Aluminum hypophosphite in combination with expandable graphite as a novel flame retardant system for rigid polyurethane foams. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Phosphorus and nitrogen-containing polyols: Synergistic effect on the thermal property and flame retardancy of rigid polyurethane foam composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 10813–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranska, M.; Cabulis, U.; Auguscik, M.; Prociak, A.; Ryszkowska, J.; Kirpluks, M. Bio-based polyurethane-polyisocyanurate composites with an intumescent flame retardant. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 127, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, B.; Han, X.; Ma, B.; Li, J. Synthesis and characterization of flame retardant rigid polyurethane foam based on a reactive flame retardant containing phosphazene and cyclophosphonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 144, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Thermal conductivity of powder silica hollow spheres. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 526, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Huo, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y. Study on thermal insulating behavior of silica glass fiber/aluminum phosphate composite. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 512–515, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, E.; Fan, F. Study of the thermal insulation properties of the glass fiberboard used for interior building envelope. Energy Build. 2015, 107, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Rahaman, A.; Pal, S. Carbon nano-materials coating over hollow glass microspheres and its composite foam. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Chen, X. Fire hazard reduction of hollow glass microspheres in thermoplastic polyurethane composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Ramirez, L.; Cano, M.; Villoria, R. Low thermal and high electrical conductivity in hollow glass microspheres covered with carbon nanofiber polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 151, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mireja, S.; Khandelwal, V.; Arun, B.; Manik, G. Light-weight high-strength hollow glass microspheres and bamboo fiber based hybrid polypropylene composite: A strength analysis and morphological study. Compos. Part B 2017, 109, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, G.; Bauer, J.; Eder, A.; Eisenmenger-Sittner, C. A hybrid hydrolytic hydrogen storage system based on catalyst-coated hollow glass microspheres. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, S.; Savithri, V.; Shrivastava, P.; Sivam, S.; Sharma, P. Fabrication of zinc-loaded hollow glass microspheres (HGMs) for hydrogen storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Park, B.; Lee, W.; Hwang, D. Hybrid nanostructure formation on hollow glass microparticles as thermally insulating composite elements. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2017, 9, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, K.; Zhu, B.; Yue, T.; Xie, C. Preparation and properties of hollow glass microsphere-filled epoxy-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, F. Measurement of thermal conductivity of hollow glass-bead-filled polypropylene composites. Polym. Test. 2006, 25, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, A.; Ren, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, S. Fabrication of heat-resistant syntactic foams through binding hollow glass microspheres with phosphate adhesive. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ye, F.; Gao, Y. Preparation and characterization of hollow glass microsphere ceramics and silica aerogel/hollow glass microsphere ceramics having low density and low thermal conductivity. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 154737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtrus, M.; Oras, S.; Antsov, M.; Reedo, V.; Maeorg, U.; Lohmus, A.; Saal, K.; Lohmus, R. Mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy composite thermal insulators filled with silica aerogel and hollow glass microspheres. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2017, 66, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yuan, J.; An, Z.; Zhang, J. Effect of microstructure and physical parameters of hollow glass microsphere on insulation performance. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1992–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lu, X.; Qu, J.; Yuan, T. Synergistic effect of hollow glass beads and intumescent flame retardant on improving the fire safety of biodegradable poly (lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 164, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumbia, A.S.; Bourmaud, A.; Jouannet, D.; Falher, T.; Orange, F.; Retoux, R.; Le Pluart, L.; Cauret, L. Hollow microspheres-poly-(propylene) blends: Relationship between microspheres degradation and composite properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 114, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, D. Thermal, dielectric and compressive properties of hollow glass microsphere filled epoxy-matrix composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkutlu, M.; Dilek, C.; Bayram, G. Effects of hollow glass microsphere density and surface modification on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) syntactic foams. Compos. Struct. 2018, 202, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, E.; Naebe, M.; Kashi, S.; Cai, Z.; Xie, W.; Yuen, A.; Montazer, M.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Functional cotton fabric using hollow glass microspheres: Focus on thermal insulation, flame retardancy, UV-protection and acoustic performance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 141, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, A.; Narula, A. Fabrication of thermoplastic composites using fly-ash a coal and hollow glass beads to study their mechanical, thermal, rheological, morphological and flame retradency properties. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J. Estimation of thermal conductivity for polypropylene/hollow glass bead composites. Compos. Part B 2014, 56, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, O.; Beril, B.; Taşdemir, M. Thermal, structural and dynamical mechanical properties of hollow glass sphere-reinforced polypropylene composites. Polym. Bull. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, D.; Wan, C.; Pan, H.; Jiang, S. Mechanical, thermal and fire performance of an inorganic-organic insulation material composed of hollow glass microspheres and phenolic resin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, I.; Ariful, R.; Soumen, P. Effect of Low Concentration Hollow Glass Microspheres on Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties of Epoxy Composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 3493–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Mei, R.; An, Z.; Zhang, J. Silicon rubber/hollow glass microsphere composites: Influence of broken hollow glass microsphere on mechanical and thermal insulation property. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 79, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.; Kranov, Y. Hollow glass microsphere HDPE composites for low energy sustainability. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ke, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, C.; Li, Z. Investigation of the Thermal Conductivity of Resin-Based Lightweight Composites Filled with Hollow Glass Microspheres. Polymers 2020, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Li, F. Heat transfer in polymer composites filled with inorganic hollow micro-spheres: A theoretical model. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J. Thermal insulating epoxy composite coatings containing sepiolite/hollow glass microspheres as binary fillers: Morphology, simulation and application. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, A.; Zang, W.; Geng, H.; Tao, X.; Du, H. Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of a temperature resistance hollow glass microspheres/borosilicate glass buoyance material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Model | Density (g/cm3) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS5500 | 0.38 | 37.9 | 0.127 | white |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Cai, F.; Tao, D.; Ni, Q.; Fu, Y. Enhanced Thermal Insulation of the Hollow Glass Microsphere/Glass Fiber Fabric Textile Composite Material. Polymers 2021, 13, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040505
Sun J, Cai F, Tao D, Ni Q, Fu Y. Enhanced Thermal Insulation of the Hollow Glass Microsphere/Glass Fiber Fabric Textile Composite Material. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040505
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jintao, Fei Cai, Dongzhi Tao, Qingqing Ni, and Yaqin Fu. 2021. "Enhanced Thermal Insulation of the Hollow Glass Microsphere/Glass Fiber Fabric Textile Composite Material" Polymers 13, no. 4: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040505
APA StyleSun, J., Cai, F., Tao, D., Ni, Q., & Fu, Y. (2021). Enhanced Thermal Insulation of the Hollow Glass Microsphere/Glass Fiber Fabric Textile Composite Material. Polymers, 13(4), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040505