Hardness Modulated Thermoplastic Poly(ether ester) Elastomers for the Automobile Weather-Strip Application
Abstract
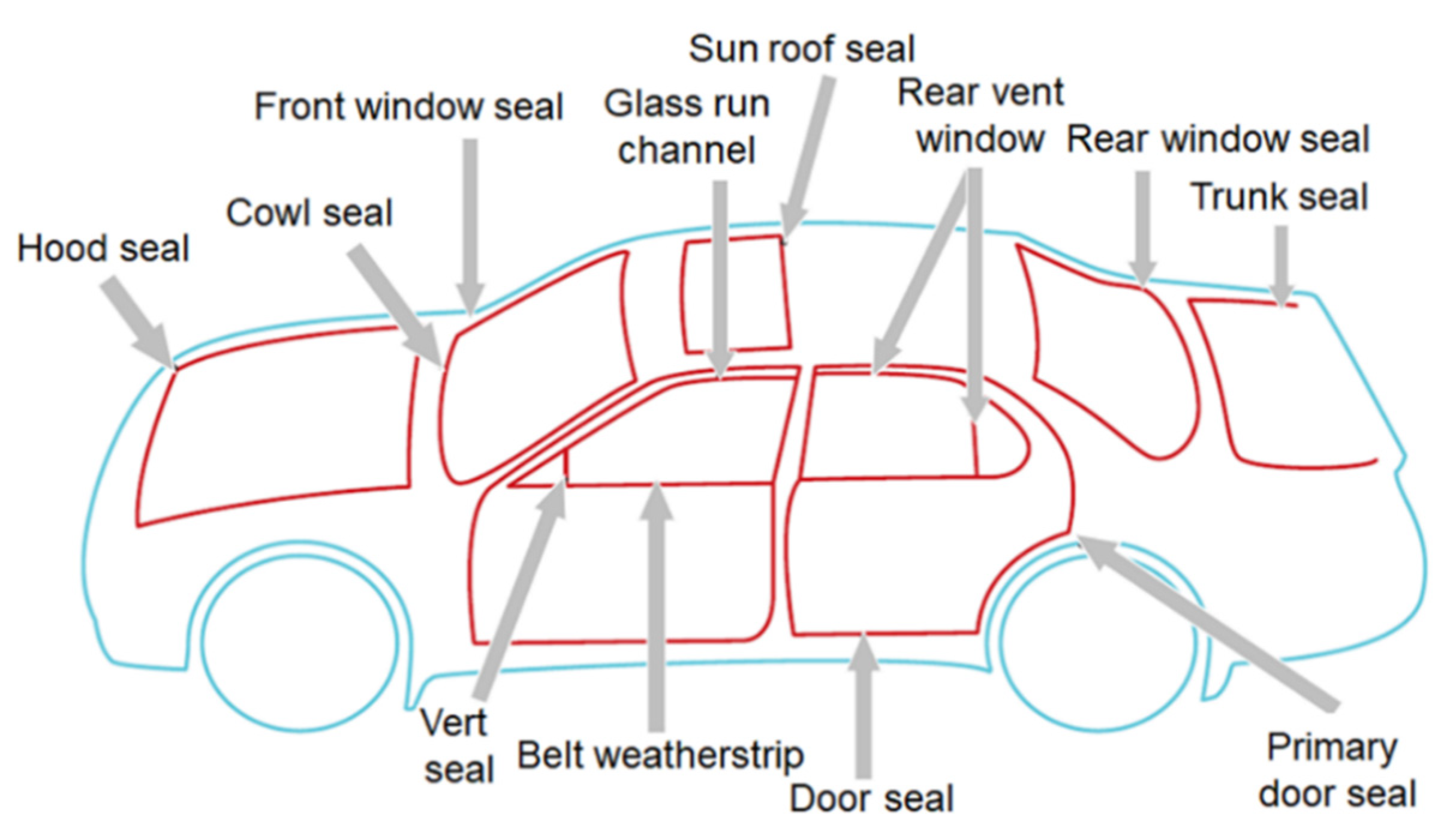
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of SOFA
2.3. Synthesis of TPEEs Using SOFA as CE
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Computer Simulations
3. Results
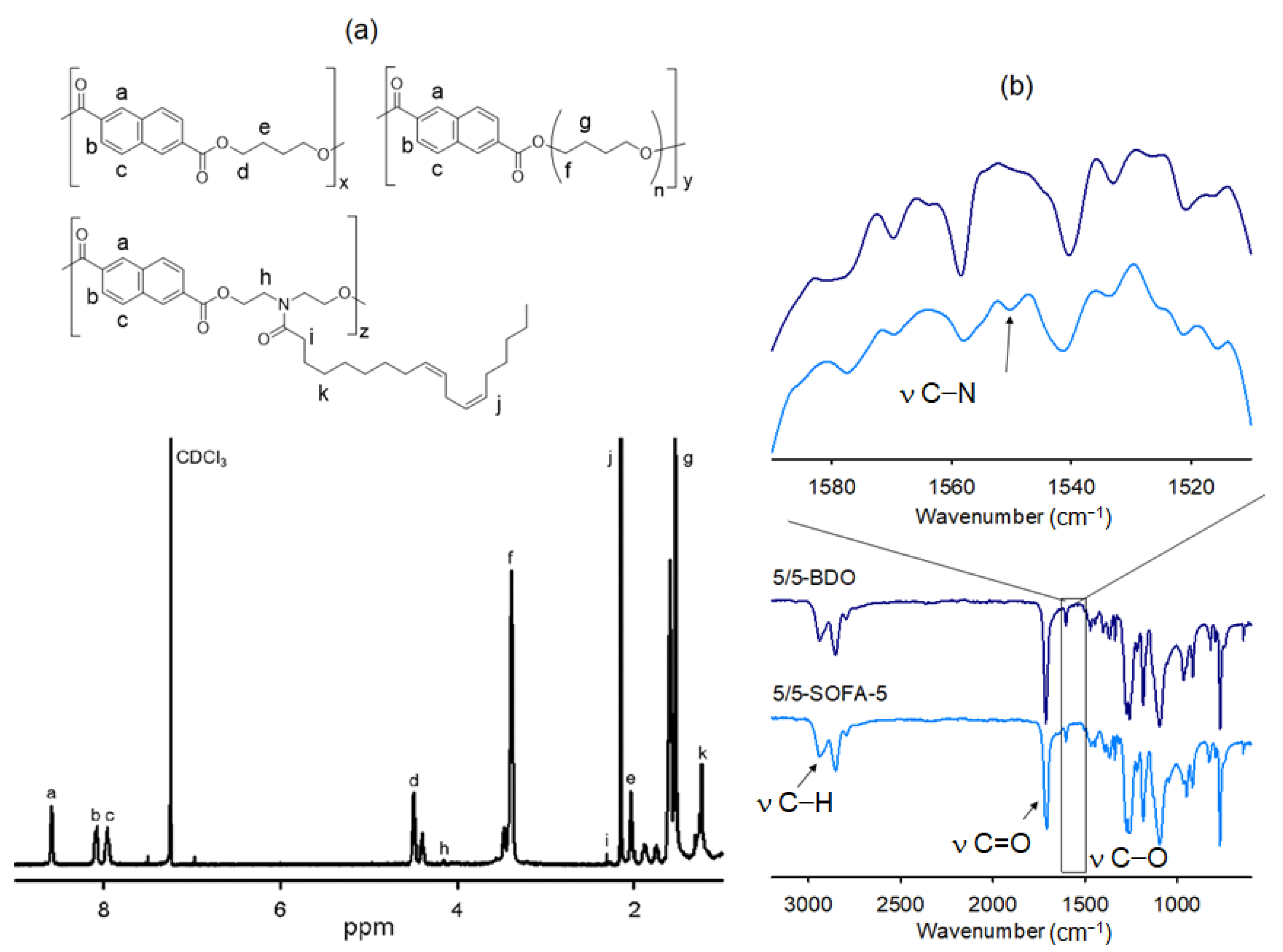
3.1. Characterization of TPEEs
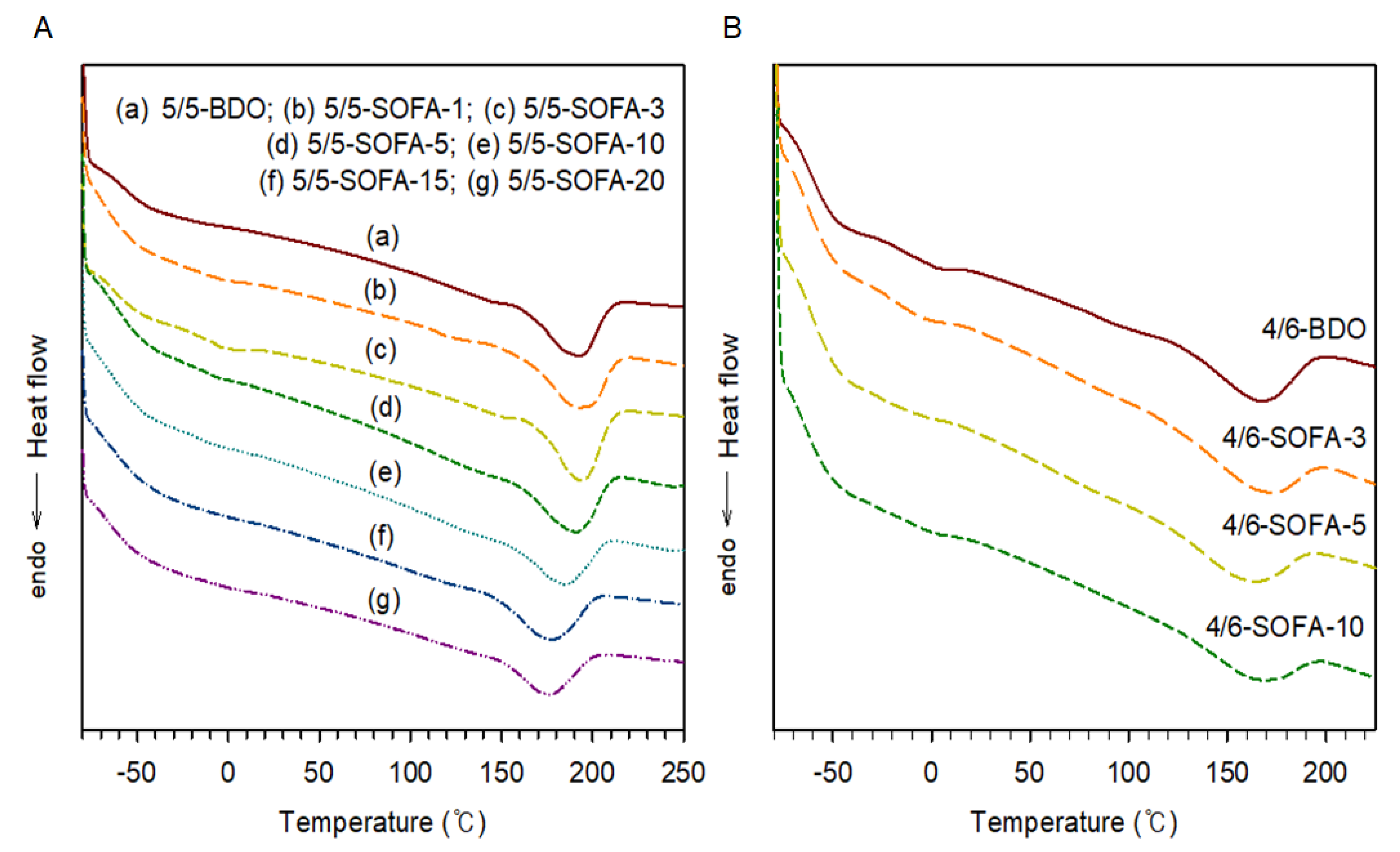
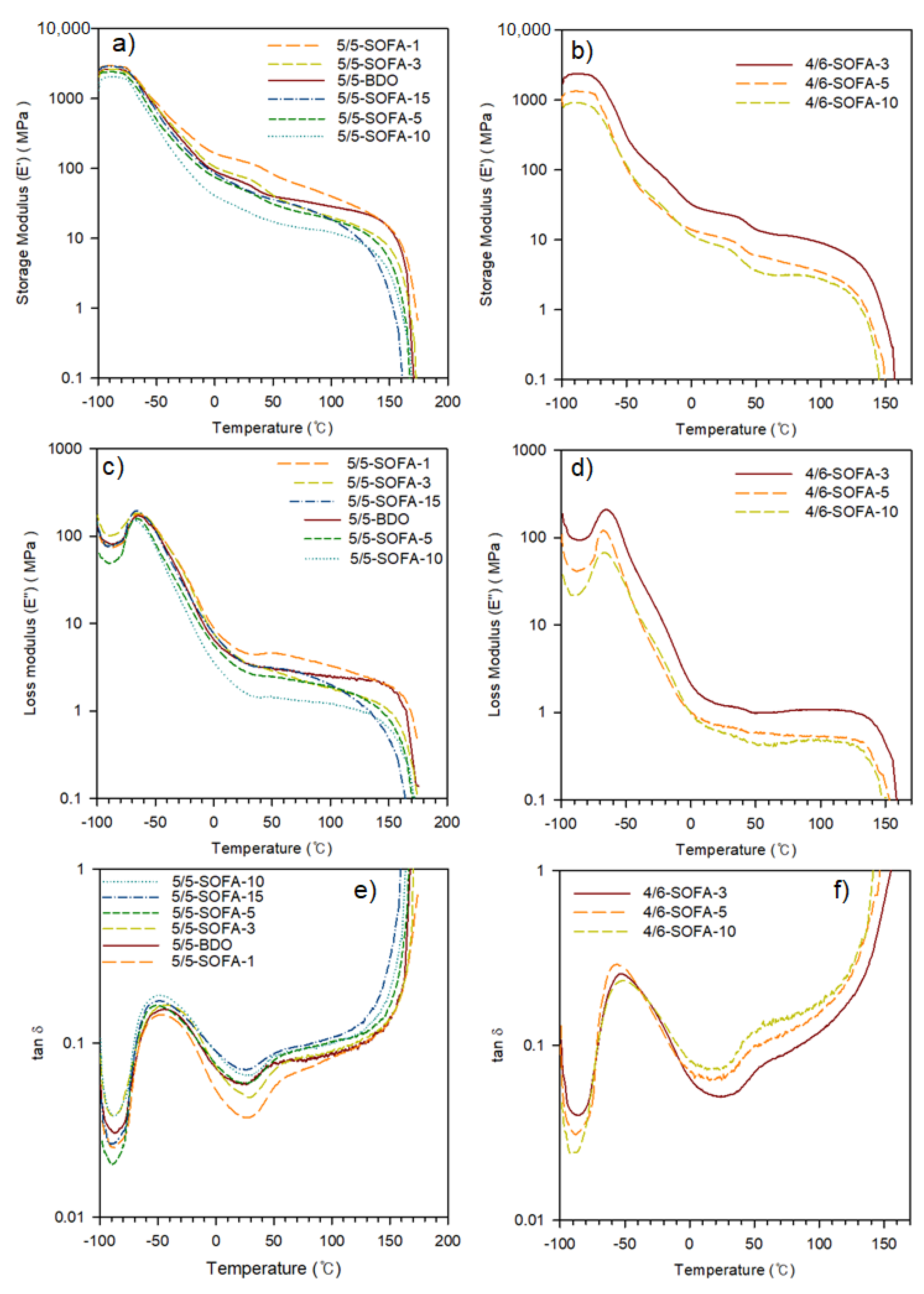
3.2. Thermal and Viscoelastic Analyses of TPEEs
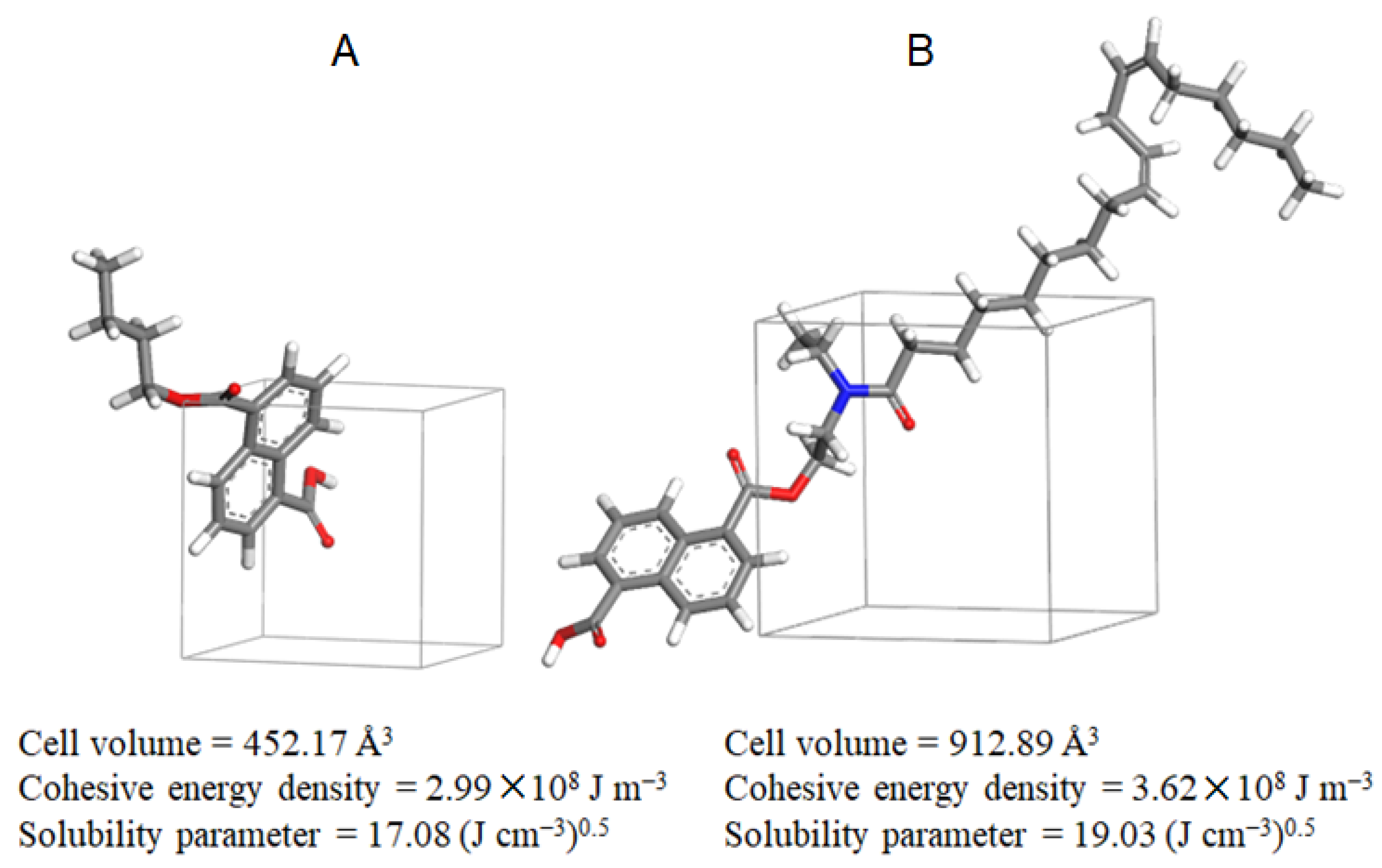
3.3. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
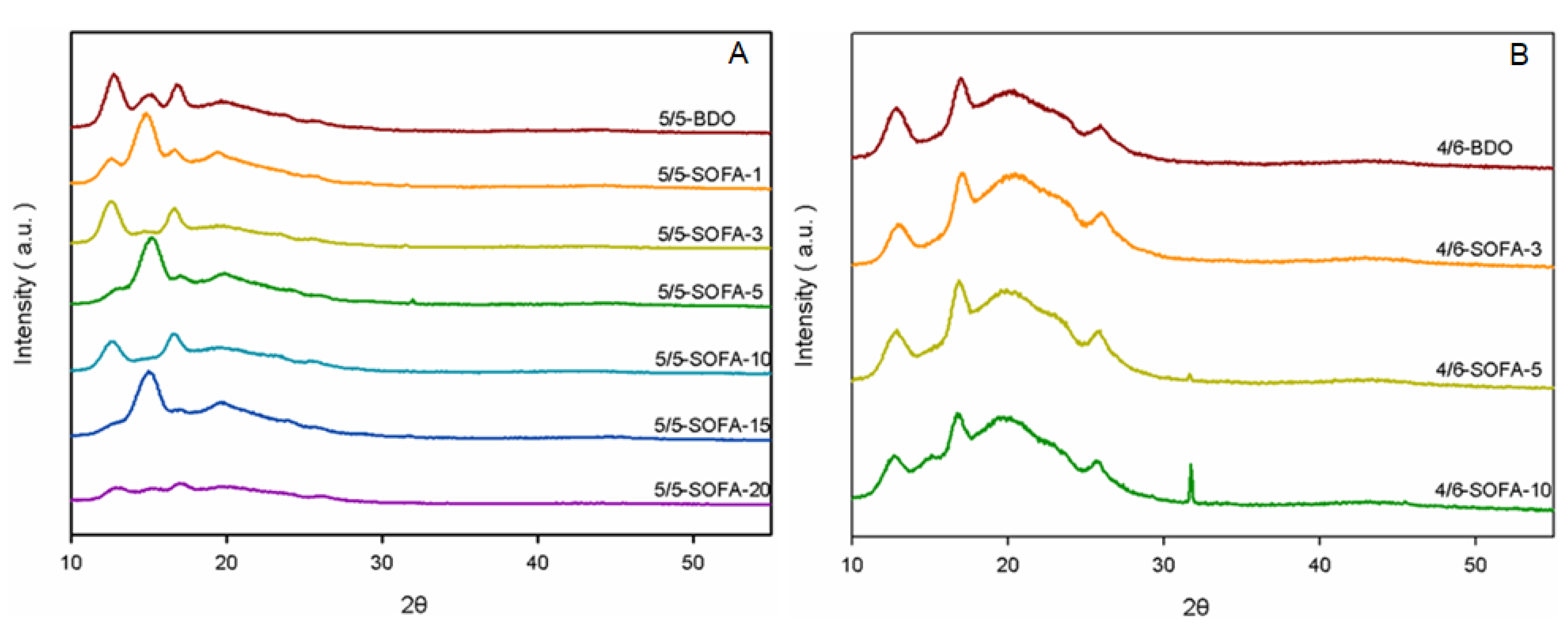
3.4. WAXD Analysis of TPEEs
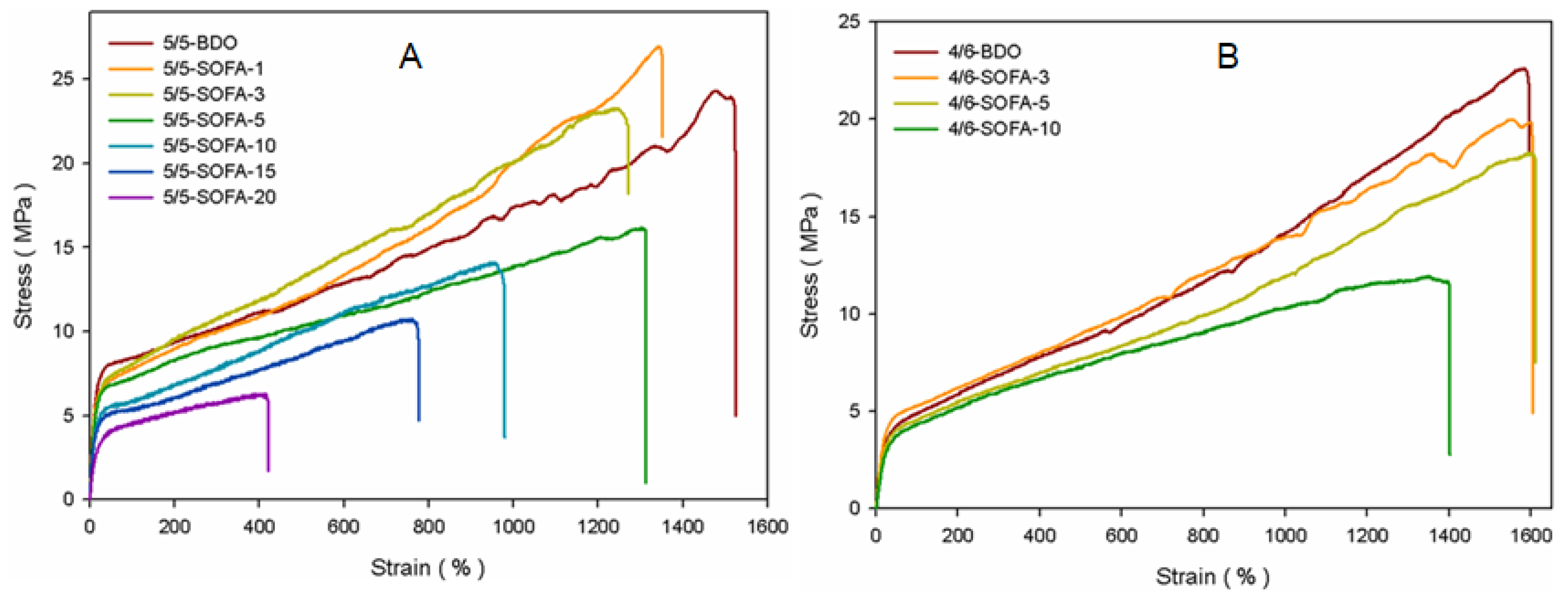
3.5. Mechanical Properties of TPEEs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maréchal, E. Creation and development of thermoplastic elastomers, and their position among organic materials. In Handbook of Condensation Thermoplastic Elastomers, 1st ed.; Fakirov, S., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A.B.; Chatterjee, T.; Naskar, K. Automotive applications of thermoplastic vulcanizates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrosoldi, S.; Soccio, M.; Gazzano, M.; Lotti, N.; Munari, A. Fully biobased, elastomeric and compostable random copolyesters of poly(butylene succinate) containing Pripol 1009 moieties: Structure-property relationship. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 178, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, S.I.; Gentekos, D.T.; Silberstein, M.N.; Fors, B.P. Tailor-made thermoplastic elastomers: Customisable materials via modulation of molecular weight distributions. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doerner, A.; Vetter, F.; Mijolovic, D. Thermoplastic elastomers for automotive applications: Keeping emission and odor under control. Rubber World 2019, 261, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.C.; Jo, M.Y.; Park, J.I.; Bae, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, I. Selection attributes and trends of thermoplastic elastomers for automobile parts. Elastomers Compos. 2017, 52, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Park, J.I.; Park, J.C.; Jo, M.Y.; Bae, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, I. Revisit of thermoplastic EPDM/PP dynamic vulcanizates. Elastomers Compos. 2017, 52, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, D. Block copolymers: Copolymerization of ethylene terephthalate and polyoxyethylene glycols. J. Polym. Sci. 1954, 14, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witsiepe, W.K. Segmented thermoplastic copolyester elastomers. U.S. Patent 3,651,014, 22 June 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.-L.; Wegner, G. The morphology of semicrystalline segmented poly (ether ester) thermoplastic elastomers. Die Makromolekulare Chemie 1981, 182, 3625–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, V.M.; Bertmer, M.; Gasper, L.; Demco, D.E.; Blümich, B. Phase composition of block copoly (ether ester) thermoplastic elastomers studied by solid-state NMR techniques. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7598–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, A.; Ouled-chikh, E.; Bouchouicha, B. Thermo-mechanical characterization of a thermoplastic copolyetherester (TPC): Experimental investigation. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.; Nébouy, M.; Baeza, G.P. Bimodal crystallization kinetics of PBT/PTHF segmented block copolymers: Impact of the chain rigidity. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, R.J. Morphology of segmented polyester thermoplastic elastomers. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Symp. 1973, 42, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilaonitkul, A.; Cooper, S.L. Properties of polyether-polyester thermoplastic elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1977, 50, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhou, C.; Dong, X.; Sauer, B.B.; Lai, Y.; Wang, D. The segmental responses to orientation and relaxation of thermoplastic poly (ether-ester) elastomer during cyclic deformation: An in-situ WAXD/SAXS study. Polymer 2020, 188, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriëlse, W.; Soliman, M.; Dijkstra, K. Microstructure and phase behavior of block copoly(ether ester) thermoplastic elastomers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Vlach, J.; Kavan, P. Improved mechanical properties of magneto rheological elastomeric composite with isotropic iron filler distribution. Ciência & Tecnologia dos Materiais 2016, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, S. Effect of shape and size of filler particle on the aggregation and sedimentation behavior of the polymer composite. Powder Technol. 2020, 366, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, D.A.; Mannari, V. N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) fatty amide as novel environmentally friendly crosslinking agent for acid functional acrylic copolymer resin. J. Coatings Technol. 1998, 70, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Linh, P.T.T.; Kang, J.; Kim, I. Phosphorus-containing thermoplastic poly(ether ester) elastomers showing intrinsic flame retardancy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Han, M.H. Preparation and properties of highly functional copolyetheresters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, H.H.; Lin-Vien, D.; Soni, U. Poly(trimethylene terephthalate) molecular weight and Mark-Houwink equation. Polymer 2001, 42, 7137–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accelrys Software Inc. Materials Studio Release Notes, Release 5.0; Accelrys Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, S.; Yang, S.; Lv, K.; Yuan, S. Mesoscale simulation on patterned core-shell nanosphere model for amphiphilic block copolymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, C.; Chen, W.-R.; Hong, K.; Smith, G.S. Equilibrium structure of a triblock copolymer system revealed by mesoscale simulation and neutron scattering. Physica B Condens. Matter 2013, 430, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; He, J. MesoDyn simulation study of phase behavior for dye-polyether derivatives in aqueous solutions. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1091, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S. Poly(ether ester) thermoplastic elatomers: Phase and deformation behavior on the nano- and microlevel. In Handbook of Condensation Thermoplastic Elastomers, 1st ed.; Fakirov, S., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 167–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y. Phase behavior of tri-block copolymers in solution: Mesoscopic simulation study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 322, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.G.; Jo, W.H.; Lee, S.C. Cocrystallization behavior of poly(butylene terephthalate-co-butylene 2,6-naphthalate) random copolymers. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9705–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HS/SS | Sample Code | XSOFA1 (%) in Feed | XSOFA1 (%) in Polymer | Tg12 (°C) | Tg22 (°C) | Tm3 (°C) | ΔHm3 (J/g) | η4 (dL/g) | Mv4 ×10−4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/50 | 5/5-BDO | 0 | 0 | −42 | 44 | 195 | 12.38 | 1.54 | 10.1 |
| 5/5-SOFA-1 | 1 | 1.3 | −47 | 43 | 195 | 10.21 | 1.65 | 11.2 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-3 | 3 | 3.8 | −46 | 43 | 194 | 11.85 | 1.87 | 13.5 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-5 | 5 | 5.0 | −47 | 44 | 188 | 11.20 | 2.01 | 15.0 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-10 | 10 | 9.2 | −48 | 46 | 185 | 10.38 | 2.06 | 15.6 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-15 | 15 | 11.7 | −49 | 42 | 180 | 9.26 | 1.97 | 14.5 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-20 | 20 | 14.5 | −49 | 40 | 176 | 9.19 | 1.93 | 14.1 | |
| 40/60 | 4/6-BDO | 0 | 0 | −51 | 41 | 166 | 10.98 | 1.89 | 13.7 |
| 4/6-SOFA-3 | 3 | 4.8 | −50 | 39 | 164 | 10.23 | 1.69 | 11.7 | |
| 4/6-SOFA-5 | 5 | 6.1 | −49 | 38 | 158 | 9.75 | 1.74 | 12.1 | |
| 4/6-SOFA-10 | 10 | 8.3 | −49 | 39 | 155 | 9.62 | 1.65 | 11.2 |
| SS1 | HS1 | HS2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS1 | 0 | 0.133 | 0.044 |
| HS1 | 0.183 | 0 | 0.183 |
| HS2 | 0.044 | 0.133 | 0 |
| HS/SS | Sample Code | Ultimate strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A | Shore D | ||||
| 50/50 | 5/5-BDO | 24.31 | 1490 | 96 | 45 |
| 5/5-SOFA-1 | 26.97 | 1318 | 96 | 45 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-3 | 23.26 | 1240 | 95 | 43 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-5 | 19.23 | 1312 | 94 | 42 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-10 | 14.09 | 955 | 93 | 41 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-15 | 10.71 | 754 | 91 | 39 | |
| 5/5-SOFA-20 | 7.62 | 412 | 89 | 36 | |
| 40/60 | 4/6-BDO | 22.01 | 1543 | 88 | 35 |
| 4/6-SOFA-3 | 19.97 | 1572 | 86 | 32 | |
| 4/6-SOFA-5 | 18.22 | 1577 | 85 | 30 | |
| 4/6-SOFA-10 | 11.93 | 1370 | 84 | 28 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, S.H.; Jeong, J.E.; Kim, S.; Jeon, S.; Choung, J.W.; Kim, I. Hardness Modulated Thermoplastic Poly(ether ester) Elastomers for the Automobile Weather-Strip Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040525
Jeon SH, Jeong JE, Kim S, Jeon S, Choung JW, Kim I. Hardness Modulated Thermoplastic Poly(ether ester) Elastomers for the Automobile Weather-Strip Application. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040525
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Su Hyeon, Jae Eon Jeong, Seongkyun Kim, Sungwan Jeon, Jin Woo Choung, and Il Kim. 2021. "Hardness Modulated Thermoplastic Poly(ether ester) Elastomers for the Automobile Weather-Strip Application" Polymers 13, no. 4: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040525
APA StyleJeon, S. H., Jeong, J. E., Kim, S., Jeon, S., Choung, J. W., & Kim, I. (2021). Hardness Modulated Thermoplastic Poly(ether ester) Elastomers for the Automobile Weather-Strip Application. Polymers, 13(4), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040525








